Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Postpartum Care Plan
Uploaded by
Becky KiplingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Postpartum Care Plan
Uploaded by
Becky KiplingCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
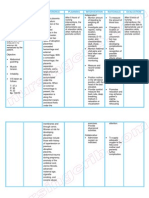
Nursing Care Plan Assessment Objective: -Pt vaginally delivered a live female -Pt has a perineal tear Nursing Diagnosis Acute Pain r/t childbearing, including perineal tear AEB clients verbalizations of pain Expected outcomes 1. Client will report no pain, or that pain management regimen reduces pain to a functional level before she is discharged. Interventions 1. a) Assess pain level in a client using a valid and reliable selfreport pain tool, such as the 0-10 numerical pain rating scale (0=no pain, 10= most pain possible). Rationale 1. a) Singledimension pain ratings are valid and reliable as measures of pain intensity level (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 601). Subjective: -Pt states they are experiencing pain 1. b) Assess the client for pain presence routinely at frequent intervals, at the same time as vitals are taken. 1. b) Pain assessment is as important as physiological vital signs and pain is considered the fifth vital sign (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 602). 1. c) Administer an opioid analgesic if indicated for moderate 1. c) Opioids are indicated for the Evaluation -Pt will report no pain or pain at a functional level during stay in hospital
NURSING CARE PLAN to severe pain as per doctors orders treatment of moderate to severe pain (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 603) 2. Client will express understanding of pain and pain management, including nonpharmacological methods of analgesia, and adverse effects of analgesics. 2. a) Manage acute pain using a multimodal approach 2. a) The advantage of a multimodal approach is that the lowest effective dose of each drug can be administered, resulting in fewer or less severe adverse effects (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 603). 2. b) Avoid giving pain medication intramuscularly (IM) when possible. 2. b) IM injections are painful, result on unreliable absorption, and lead to variable blood levels of the
-Client will articulate understanding of pain management before leaving the hospital
NURSING CARE PLAN administered medication (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 603). 2. c) Administer opioids orally or intravenously (IV). 2. c) IM injections are painful, result on unreliable absorption, and lead to variable blood levels of the administered medication (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 603). Deficient Knowledge r/t primipara status AEB client history 1. Client will state confidence in her ability to manage situation and remain in control of life before she is discharged. 1. a) Assess the client/family learning needs, information needs, and current level of knowledge. 1. a) Caregivers express a need for having their informational needs met (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 520).
Objective: -G1P0 Subjective: -Pt states that she is nervous that this is all really
-Client will feel confident in her ability to leave the hospital and care for the new baby
NURSING CARE PLAN happening now 1. b) Consider the clients ability and readiness to learn (e.g., mental acuity, ability to see and hear, existing pain, emotional readiness, motivation, and previous knowledge) when teaching clients. 1. b) Each client is unique, and client motivation, beliefs, and expectations will influence learning (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 518). 1. c) Engage clients as a partner in the educational process. 1. c) A nursing approach that is collaborative and that uses encouragement and support to increase self-efficacy resulted in client satisfaction, empowerment, and confidence (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 518).
NURSING CARE PLAN 2.Client will list resources that can be used for more information and support after discharge, before she is discharged. 2. a) Engage clients as a partner in the educational process. 2. a) A nursing approach that is collaborative and that uses encouragement and support to increase self-efficacy resulted in client satisfaction, empowerment, and confidence (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 518). 2. b) Use individualized approaches that support client priorities, preferences, and choice. 2. b) Individualized educational interventions have a positive effect on client outcomes (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 518). 3. c) Consider coordinated, multifaceted methods of 2. c) Coordinated efforts using a -Client will
articulate/show resources she can use to support her through life changes before she is discharged.
NURSING CARE PLAN disbursing information. combination of written and verbal information have proven beneficial for self-care behavioral change (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 518). Risk for Bleeding r/t childbearing AEB risk statistics 1.Pt will maintain stable vital signs with minimal blood loss both before and after her discharge. 1. a) Check vital signs at frequent intervals, according to AHS policy on 3A. 1. a) Watch for changes associated with bleeding including increased heart rate, respiratory rate, and eventually decreased blood pressure. (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 170). 1. b) Assess for clinical signs and symptoms of blood loss, such as 1. b). Blood loss is frequently
-Pts vital signs will remain stable -Pt will have minimal blood loss
NURSING CARE PLAN dizziness, fatigue, tachycardia, and hypotension. underestimated (500mL for vaginal delivery). (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 171). 1. c)Assess fundus and lochia amount regularly, according to AHS policy on 3A. 1. c)Vigorous massage and downward pressure should be avoided (Ackley & Ladwig, 2011, p. 171).
Ackley, B. J. & Ladwig, J. B. (2011). Nursing diagnosis handbook. An evidence based guide to planning care (9th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum DepressionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Postpartum DepressionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- Postpartum Care PlanDocument6 pagesPostpartum Care Planallie-jones-6489100% (27)
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageLei Ortega95% (21)
- Acute Pain, Post Partum CareDocument1 pageAcute Pain, Post Partum Carekbernil83% (18)
- Newborn Nursing CareplanDocument7 pagesNewborn Nursing CareplanSamantha MillerNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Redo For NeonateDocument2 pagesCare Plan Redo For NeonateIris Lopez100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Concept MapDocument4 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage Concept MapGCNo ratings yet
- Pain - Post Partum MotherDocument2 pagesPain - Post Partum Motherulrikov91% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan - Delivery RoomDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Delivery RoomMarivic Misola100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan-OBDocument20 pagesNursing Care Plan-OBPriscilla Paula Benavidez100% (3)
- NCP - Post PartumDocument10 pagesNCP - Post PartumSa Dei91% (22)
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- NCP NewbornDocument2 pagesNCP Newbornsonylynne94% (17)
- Newborn Nursing Care Plan With ReferncesDocument6 pagesNewborn Nursing Care Plan With Referncesneuronurse92% (63)
- NCP NewbornDocument8 pagesNCP Newbornsupacalifragirlistic67% (9)
- NCP (Post-Partum Pain)Document1 pageNCP (Post-Partum Pain)allure*2083% (6)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanDaniel Marcos80% (10)
- Prioritize NCPDocument19 pagesPrioritize NCPzey young94% (34)
- Newborn Careplan 9-15-2011Document17 pagesNewborn Careplan 9-15-2011Brittany Wood100% (1)
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocument8 pagesFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshNo ratings yet
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocument7 pagesPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care Planrockerespi1283No ratings yet
- First TrimesterDocument18 pagesFirst Trimesternursereview100% (9)
- NB Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNB Nursing Diagnosisnursingmvd92% (13)
- Obstetric Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesObstetric Nursing Care Planlilchristina0178% (9)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPNichole Audrey Saavedra100% (1)
- Preeclampsia Care MapDocument3 pagesPreeclampsia Care Mapapi-38011595475% (4)
- NCP Ineffective Breast Feeding R/T Flat NippleDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breast Feeding R/T Flat NippleLafayette Kirsi Noel100% (5)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis82% (33)
- Care Plan PostpartumDocument2 pagesCare Plan PostpartumSiwei Yang100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan of Labor PainDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan of Labor PainKenneth Cole80% (61)
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseDocument9 pagesNCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseJavieNo ratings yet
- Clinical Simulation Day 1 Care Plan ms3 Chest Pain SHDocument3 pagesClinical Simulation Day 1 Care Plan ms3 Chest Pain SHapi-575469761No ratings yet
- Client Care Plan ADocument12 pagesClient Care Plan AArithmajikNo ratings yet
- s1 Chest Pain Care PlanDocument2 pagess1 Chest Pain Care Planapi-638320935No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Fundamental Nursing Skills and Concepts Tenth EditionDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Fundamental Nursing Skills and Concepts Tenth EditionMonica Degan100% (39)
- Nursing Assessment For PainDocument9 pagesNursing Assessment For PainNDJNo ratings yet
- ShaylaDocument3 pagesShaylaapi-530728661No ratings yet
- NCM 101Document8 pagesNCM 101Anna LaritaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Care PlanDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Care PlanKim Biro Turner86% (37)
- Cholecystitis Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Nursing Care PlanMDCITY83% (6)
- NANDA NursingDocument159 pagesNANDA NursingAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- Managing PostoperativeDocument9 pagesManaging PostoperativeWardah Fauziah El SofwanNo ratings yet
- NCP For Pain - NephrolithiasisDocument3 pagesNCP For Pain - NephrolithiasisDepia Leah NgislawanNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument7 pagesNCP FinalRuss RussNo ratings yet
- NCP - PCGHDocument9 pagesNCP - PCGHLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: The ABCDEF Bundle in Critical CareDocument23 pagesHHS Public Access: The ABCDEF Bundle in Critical CareRodrigoSachiFreitasNo ratings yet
- SLN Tutorial - Session 3Document53 pagesSLN Tutorial - Session 3ataraxialliNo ratings yet
- SCR 270 L & D Care PlanDocument5 pagesSCR 270 L & D Care PlanRenzo MarcosNo ratings yet
- Nursing ResumeDocument5 pagesNursing Resumechindy KusumadiraNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Clinical Reasoning in Patient Care 6th Edition Lemone Test BankDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Clinical Reasoning in Patient Care 6th Edition Lemone Test BankLindaMoodyrqdp100% (45)
- Nursing Process DiagnosingDocument49 pagesNursing Process DiagnosingAnuchithra100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Medical Diagnoses: Acute PainDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Medical Diagnoses: Acute PainRosaNo ratings yet
- 11-16-2023 Care Plan ICU PT No Name IncludedDocument5 pages11-16-2023 Care Plan ICU PT No Name IncludedRJ ManierNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Health Assessment QuestionsDocument3 pagesComprehensive Health Assessment Questionsaznknight323No ratings yet
- Application Project - Team 11Document30 pagesApplication Project - Team 11api-601587526No ratings yet
- PlateletDocument16 pagesPlateletArgene Rose MilletNo ratings yet
- W Epdw Ukltiw M B0C08ADBDocument6 pagesW Epdw Ukltiw M B0C08ADBVanessa Mueller100% (1)
- Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromsDocument4 pagesNephrotic Nephritic SyndromsKimiwari100% (2)
- How To Mix InsulinDocument2 pagesHow To Mix InsulinchareneadamsNo ratings yet
- Cba Ospe RevisedDocument11 pagesCba Ospe RevisedSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- General ObjectivesDocument13 pagesGeneral ObjectiveskevinNo ratings yet
- 1803ict Gary Monday4pm Scanlan Jordan s5054901 MajorassignmentDocument8 pages1803ict Gary Monday4pm Scanlan Jordan s5054901 Majorassignmentapi-319771684No ratings yet
- Recovery of Glycerine From Spent Palm Kernel Soap and Palm Oil Soap LyeDocument8 pagesRecovery of Glycerine From Spent Palm Kernel Soap and Palm Oil Soap LyeNadya Larasati KrdNo ratings yet
- Mastering MRCP Vol2Document348 pagesMastering MRCP Vol2mostachek88% (8)
- Tooth Discoloration and HomoeopathyDocument12 pagesTooth Discoloration and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- 5 Ways To Discipline An Autistic ChildDocument4 pages5 Ways To Discipline An Autistic ChildHaryati Mustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopy 2021Document23 pagesLaparoscopy 2021Аташ КочкоровNo ratings yet
- NHS Acdf ConsentDocument15 pagesNHS Acdf ConsentHamish JugrooNo ratings yet
- Ishikawa 2007Document9 pagesIshikawa 2007Anggi RefinandaNo ratings yet
- FDA Approved Drug Products 29th Edition Cumulative Supplement 02Document44 pagesFDA Approved Drug Products 29th Edition Cumulative Supplement 02Narottam ShindeNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Respiratory CompensationDocument3 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis and Respiratory CompensationcpccoderNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocument36 pagesThyroid Disease in Pregnancypeni_dwiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Quality ControlDocument42 pagesLaboratory Quality ControlKuzhandai Velu93% (43)
- GrummonsDocument24 pagesGrummonsAmelia ChristabelNo ratings yet
- B. Braun Water TreatmentDocument48 pagesB. Braun Water TreatmentMedical TechniciansNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Press CatalogueDocument50 pagesPharmaceutical Press CataloguePharmaceuticalPress50% (2)
- Abruptio Placentae: B.HemanathDocument18 pagesAbruptio Placentae: B.HemanathDewina Dyani Rosari IINo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy: N. Julian Holland and Jonathan M. BernsteinDocument21 pagesBell's Palsy: N. Julian Holland and Jonathan M. BernsteinEeqNo ratings yet
- Katz Adl Lawton IadlDocument4 pagesKatz Adl Lawton IadlAmbaejo96No ratings yet
- Twelve TissueDocument432 pagesTwelve TissueRohanKanhai100% (2)
- My Health, I Manage!: Paida (Patting, Slapping) TheoryDocument1 pageMy Health, I Manage!: Paida (Patting, Slapping) TheorydalbogondesNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Parents Medication GuideDocument20 pagesAnxiety Parents Medication GuideCatalina Walker Alvarez Medico Psiquiatra CSJDMNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Cough From AngiotensinDocument1 pageMechanisms of Cough From AngiotensinironNo ratings yet
- ICH Guidelines IndexDocument5 pagesICH Guidelines Indexyashpandya01No ratings yet
- First Aid 10Document16 pagesFirst Aid 10Oswaldo TorresNo ratings yet
- Data Dictionary: NO Label Operational Scale of Measurem ENT 1Document6 pagesData Dictionary: NO Label Operational Scale of Measurem ENT 1nik nur nisa azlinNo ratings yet
- 2.trends of Psychiatric NursingDocument24 pages2.trends of Psychiatric NursingAMAN THAWKARNo ratings yet