Professional Documents
Culture Documents
File Motor Brushless English.
Uploaded by
Eli AiradaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
File Motor Brushless English.
Uploaded by
Eli AiradaCopyright:
Available Formats
BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR (BLDC) FUNTAMENTAL FEATURES
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are one type of motors that have won more popularity in recent years. Today, BLDC motors are used in industries such as: Automobile, Aerospace, Consumer, Medical, and automation equipment and instrumentation. BLDC motors have the characteristic that they do not use brush to transfer energy; in this case the commutation is done electronically. This feature eliminates the major problem with the conventional DC brushed motors, which produce friction and decrease performance, emit heat, are noisy, periodic maintenance. BLDC motors have many advantages compared with brushed DC motors some of them are: Higher speed with rated load Higher dynamic response Higher efficiency Longer life Less noise BLDC motors produce more out-put power per frame size than brushed DC motors making them ideal for limited access areas. By the other hand BLDC have two disadvantages: 1.- They have higher cost 2.- The control is complex and expensive Despite the complexity of the control, MASTER INGENIEROS has over 10 year of BLDC motors experience. BLDC Motor Electronic commutation based on Hall position sensors Less required due to absence of brushes Longer Flat Enables operation at all speeds with rated load. High No voltage drop across brushes. High Reduced size due to superior thermal characteristics. Because BLDC has the windings on the stator, which is connected to the case, the heat dissipation is better. Low, because it has permanent magnets on the rotor. This improves the dynamic response. Higher No mechanical limitation imposed by brushes/commutator. Low. Higher Since it has permanent magnets, building costs are higher. Complex and expensive. A controller is always required to keep the motor running. The same controller can be used for variable speed control. Brushed DC Motor Brushed commutation Periodic maintenance is required Shorter Moderately flat At higher speeds, brush friction increases, thus reducing useful torque. Moderate. Moderate/Low The heat produced by the armature is dissipated in the air gap, thus increasing the temperature in the air gap and limiting specs on the output power/frame size Higher rotor inertia which limits the dynamic characteristics. Lower Mechanical limitations by the brushes. Arcs in the brushes will generate noise causing EMI in the equipment nearby. Low. Simple and inexpensive. No controller is required for fixed speed; a controller is required only if variable speed is desired.
Conmutation Maintenance Life Speed/Torque Characteristics Efficiency Output Power/ Frame Size
Rotor Inertia Speed Range Electric Noise Generation Cost of Building Control Control Requirements
This document has been created with the next bibliography: AN885. Brushless DC Motor Fundamentals Microchip Technology Inc. Informe sobre motores D.S.I.E. Department of UPCT University (Universidad Politcnica de Cartagena).
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
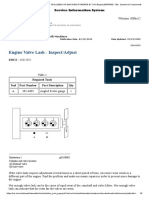
- BGDservice ManualDocument107 pagesBGDservice ManualDaniel Wellner100% (2)
- BOMAG Roller BW161 203AD 4 ST ENDocument178 pagesBOMAG Roller BW161 203AD 4 ST ENLieLiec CriStianto100% (3)
- CATMX1601Document1,234 pagesCATMX1601renatoNo ratings yet
- Turbo ChargerDocument6 pagesTurbo ChargerSk.Abdul NaveedNo ratings yet
- Catalogo XTREET II 200Document33 pagesCatalogo XTREET II 200Claudio D. PaschieroNo ratings yet
- cm142 1 0Document122 pagescm142 1 0dudleydoright100% (1)
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument18 pagesHydraulic Turbinesmech100% (1)
- Fuel Metering SystemDocument3 pagesFuel Metering Systemmellon3duwenNo ratings yet
- 01.section 01Document16 pages01.section 01kaushik.pooja12No ratings yet
- 643 e 4 FDB 381008794Document103 pages643 e 4 FDB 381008794Cao HieuNo ratings yet
- MERCEDES W123 Serv Manual Engine 617 - 95 - TDDocument532 pagesMERCEDES W123 Serv Manual Engine 617 - 95 - TDriomaior94% (32)
- Nissan hr16 Taller PDFDocument237 pagesNissan hr16 Taller PDFJhon Sanchez Lopez100% (2)
- 3.1524 3.152 Range: Diesel Engine - ElectropakDocument2 pages3.1524 3.152 Range: Diesel Engine - ElectropakRoberto RomeroNo ratings yet
- PZ 8 PDFDocument2 pagesPZ 8 PDFgustavo animasNo ratings yet
- Project Specification - ComplianceDocument1 pageProject Specification - ComplianceMohameduwais Badurdeen Haqqiyul QadiriNo ratings yet
- C11 Troubleshooting High Coolant Temperature PDFDocument3 pagesC11 Troubleshooting High Coolant Temperature PDFmanu luvungaNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi - Commercial Spec Sheets - Industrial Engine - Variable Speed - L3E-Z564SPHDocument1 pageMitsubishi - Commercial Spec Sheets - Industrial Engine - Variable Speed - L3E-Z564SPHTECNOLOGO LOGISTICO PAPAMIJA SALGADONo ratings yet
- Dhillon BrosDocument24 pagesDhillon Brosjohn.trans121No ratings yet
- Gps Waukesha 7042 BrochureDocument2 pagesGps Waukesha 7042 BrochureAlan SantosNo ratings yet
- B3.3-65 (CPR451)Document2 pagesB3.3-65 (CPR451)Dennis K ThomasNo ratings yet
- 6 Nef Engine Tier 3 PDF FreeDocument74 pages6 Nef Engine Tier 3 PDF FreeIbnu MalkanNo ratings yet
- Calibracion de MotorDocument5 pagesCalibracion de MotorAbel CondoriNo ratings yet
- Corolla Matrix Turbo Kit InstallationDocument23 pagesCorolla Matrix Turbo Kit InstallationSolymar CardonaNo ratings yet
- Black Bandit Jeep Wrangler EcoDieselDocument1 pageBlack Bandit Jeep Wrangler EcoDieseljoedeobaldNo ratings yet
- Catálogo de Peças: Parts ListDocument21 pagesCatálogo de Peças: Parts ListNicolau FerreiraNo ratings yet
- d6r Parts ManualDocument1,073 pagesd6r Parts ManualSandeep Nikhil100% (1)
- Variable Turbine GeometryDocument2 pagesVariable Turbine GeometryRowan CorneliusNo ratings yet
- Pt6a Engine Training OverwiewDocument20 pagesPt6a Engine Training OverwiewRafael Alves Dos Santos100% (1)
- Mygale m14-f4 Parts Catalogue Renault Engine v1.0 2017Document32 pagesMygale m14-f4 Parts Catalogue Renault Engine v1.0 2017Jose PalomoNo ratings yet
- 320 & 365 Kva PDFDocument156 pages320 & 365 Kva PDFManish AgarwalNo ratings yet