Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shakrganj Mills Internship Report by Imitaz
Uploaded by
Imtiaz AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shakrganj Mills Internship Report by Imitaz
Uploaded by
Imtiaz AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Shakarganj Mills Private limited
Imtiaz Ali 1 Najeeb ur Rehman
Imtiaz Ali
2010-Ch-71
Najeeb Ur Rehman 2010-CH-95
U.E.T Lahore U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 2 Najeeb ur Rehman
Letter of Transmittal
Mr. Imtiaz Ali, Mr. Najeeb ur Rehman, University of Engineering and Technology Lahore.
HOD production House, Shakarganj Mills Jhang
Respected Sir, Here is the report on Production department Of Shakarganj sugar mill you asked to submit on 30th July 2012.As you will see in the report, we have discussed about the understanding of the flow of Juice, some, how juice is extracted from sugarcane, steam production and power production plant. We have put our best in this report to make it effective and understandable. We hope our report will be according to your demands from us. If you need any assistance in interpreting this report please contact us.
Yours sincerely, Signature: Dated: 30th July 2012
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 3 Najeeb ur Rehman
Executive Summary:
First of all the cane is generally weighted on large platform scale in the transport unit. Then the sugarcane is carried to the mill house for the extraction of juice from it. After extraction juice is sent to the heaters and clarifiers for purification. When larger impurities like mud are removed then juice is carried to the evaporators where water is removed and Syrup is transported to the Pan station where crystallization occurs. Then for further clarification of the liquor it is sent to the Telo station. At the end clarified liquor is Refined at the Refined Pan station. Refined sugar is dried and packed for commercial use.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 4 Najeeb ur Rehman
Acknowledgements:
My gratitude is for the well-esteemed organization Shakarganj for giving me an opportunity to enhance my practical knowledge in the field of Sugar Manufacturing. This internship report could not have been completed without the help of capable and concerned individuals. First and foremost, I would like to thank Engr. Shahzad and Engr. Zeshan, of Production Department of Shakarganj under the kind Supervision of whom I have completed this report. Special thanks to Mr. Ammar Hanif and Engr. Nouman for helping us in every sort of quarries during the period of our internship. I would also like to thank the Engineers, Supervisors and In-charges of Boiler House, Power House, Mill House and Process House who very generously let me enhance my knowledge and also made me familiar with the professional attitude, manner and skills as well.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 5 Najeeb ur Rehman
Contents Introduction: ........................................................................................................................................... 7 Cane Unloaders ..................................................................................................................................... 7 Mill house tandem No.1 .................................................................................................................... 8
Dumping Carrier ........................................................................................................................................ 8 Main Carrier .............................................................................................................................................. 8 Levelers ..................................................................................................................................................... 9 Pusher Drum ............................................................................................................................................. 9 Fabirizer .................................................................................................................................................... 9 Magnetic Iron Separator ........................................................................................................................... 9
Mill house Tandem No. 2 ................................................................................................................ 10
Cutters..................................................................................................................................................... 10 Cane Shredder......................................................................................................................................... 10 Rotary Mills ................................................................................................................................................. 11 Mill House Output................................................................................................................................... 11
Boiler House.......................................................................................................................................... 12
Types of Boilers ....................................................................................................................................... 12 Boiler Fans............................................................................................................................................... 14 ID Fan (Induced Draught Fan): ............................................................................................................ 14 FD Fan (Forced Draught Fan): ............................................................................................................. 14 SD Fan (Secondary Fan): ..................................................................................................................... 14 Super heater ........................................................................................................................................... 14 Air Pre-heater.......................................................................................................................................... 15 Key Factors For Boiler Efficiency Calculations ........................................................................................ 15
Boiler Water treatment Plant ....................................................................................................... 15
Why we need Water Treatment?......................................................................................................... 15 Reverse Osmosis Plant ........................................................................................................................... 16 Demineralization plant: ......................................................................................................................... 17 Deaerator ................................................................................................................................................ 17
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 6 Najeeb ur Rehman
Power House..................................................................................................................................... 18
Back Pressure Turbine............................................................................................................................. 18 Condensed Turbines ............................................................................................................................... 18
Production House ............................................................................................................................... 19
Primary Heaters ...................................................................................................................................... 19 Defication tanks ...................................................................................................................................... 20 Lime Dozer .............................................................................................................................................. 20 Retention Tanks ...................................................................................................................................... 20 Defecation Tanks: ................................................................................................................................... 21 Secondary heaters .................................................................................................................................. 21 Flash Tank ............................................................................................................................................... 21 Clarifiers .................................................................................................................................................. 21 Mud Level in Clarifiers ............................................................................................................................ 22 Mud Boot ................................................................................................................................................ 22 BD (begasse dust) Mixer ......................................................................................................................... 22 Vacuum Filter .......................................................................................................................................... 22 Preheaters: ............................................................................................................................................. 23
Evaporators ........................................................................................................................................... 23
Syrup storage tank .................................................................................................................................. 26
Raw crystallization ............................................................................................................................. 26 Sugar Refining ...................................................................................................................................... 30
Reaction tank .......................................................................................................................................... 31 Telo Clarifiers .......................................................................................................................................... 32 Pressure filters ........................................................................................................................................ 33 Deep Bed Filters ...................................................................................................................................... 34
Refine crystallization and centrifugation ................................................................................ 35 Packaging and storing of refined granulated sugar ........................................................... 35
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 7 Najeeb ur Rehman
Introduction:
Steps involved in sugar manufacturing:
Cane Preparation Milling/Juice Extraction Juice Purification Evaporation Raw Sugar Crystallization Liquor Clarification Refinery Sugar Crystallization Drying and Packing
Cane Weighing:
Cane is Brought from cane yard to Sugar Factories on the Trucks and Trawlers .Cane weighing is take place with the help of Three Weigh Bridges. These Weigh Bridges are Avery England Design .02 Weigh Bridges are for Gross Weight and 01 Weigh Bridges is for Tare Weight..Capacity of the Weigh Bridges is 50 Tons. Mill House: After weighing of the cane, sugarcane is moved to the mill station for the extraction of the juice. There are two mills working for the extraction of the juice named as: Mill house Tandem No. 1 Mill house Tandem No. 2
Cane Unloaders:
There are two types of Unloaders Mechanical type cane unloader Hydraulic type cane unloader
The function of cane unloader is to pick the cane from the tractor and put in to the carrier. Cane Unloading is done with the help of Electric Hoists. Three Electric Hoist are attached to Mill Tandem .The Function of these Electric Hoists is to Lift the Cane loaded Truck and throw it to Dumping Carrier. It can lift 40-50 ton at a time. Lifting Speed 13-20 ft/ min Lifting Height 20 m
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 8 Najeeb ur Rehman
Mill house tandem No.1:
Dumping Carrier:
There are three dumping carrier in each mill tandom. In Which sliding plates are attached which carry the cane to the Main Carrier. Idler Pulleys are used to support the chain on which sliding plates move. These idler pulleys are coated with some material so that to stop wear and friction. V-Belt drive used to transmit power from motor driven shaft to gear system and from there with the chain sprocket mechanism it drives the Dumping. Dumping Carrier Length Dumping Carrier Angle 42 ft 18deg
When high torque load is to be transmitted. We use chain sprocket mechanism. By the Formula of power as torque is very high and speed is low then slippage takes place. So belt could not be used there and chain sprocket mechanism is the better choice.
Main Carrier:
After passing out through the Dumping cane carriers, sugarcane moves into the Main cane carrier. Mill Tandem no. 1 has main cane carriers of different lengths. Main cane carrier in Tandem no. 2 has three cutters while main carriers of Tandom no. 1 have two levelers on it to move the cane in an organized way.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 9 Najeeb ur Rehman
Levelers:
As the name implies it function is to provide evenly feed to cutters. Mill Tandem No. 1 has two Levelers. These are rotated by the motors. As they rotate they level the sugarcane passing through the levelers. Leveling the cane not only increases the capacity of the Tandem but also it makes the juice extraction easy. Leveler 1 Leveler 2 No. Of arms No of arms 26 24
Pusher Drum:
The function of the pusher drum is to push the compact sugar cane to the Fabiriser. Dia of Drum Length of the Drum 2250 mm 7200 mm
Fabirizer:
Fabirizer does the same function in Tandom #1 as Shredder in Tandom #2.In Fabirizer it takes input feed from the top and pushes it to the bottom. It has anvil plate on the top. Then it has feed rake bar and rake bar under carrier. It is Turbine Driven.
Magnetic Iron Separator:
Iron or other harmful metals may attach to the sugar during harvesting or transporting. These particles must be removed otherwise they may harm the mills. The purpose of magnetic iron separator is to separate the iron particles attached to the sugarcane. Power 17.7 kW
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 10 Najeeb ur Rehman
Mill house Tandem No. 2:
Cutters:
The purpose of cutters here is to cut the cane in small pieces so that they are easily shredded and juice cane be extracted more efficiently. Ther are Three cutters for Mill House Tandem No. 2. Cutter #01 Cutter # 02 Cutter # 03 No. of knives No. of knives No. of knives 70 70 52
Cane Shredder:
The main function of the shredder is to rapture the structure in order to open the cells of the cane .It is driven by Backpressure Impulse Turbine. This Shredder is covered by anvil plate .It is below the Shredder. It has very low spacing in mm with
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 11 Najeeb ur Rehman
hammers . Shredder has Stainless steel hammers with beadings. Shredder gets feed from below and takes it above .that is why its anvil plate is below.
Rotary Mills:
This is the area where juice is extracted from the cane and is separated from the Baggasse.Numbers of mills for Mill House Tendem No.1 and Tandem No. 2 is different. Rotary Mills are run by th turbines which provide sufficient Mechanical Energy to rotae the mills. Cane passes through these rotary mills and juice is extracted from the cane by rotary motion of the mills leaving Baggasse behind. No. of mills For Tandem No. 1 No. of Mills for Tandem no. 2 5 6
Mill House Output:
Screened cane juice and bagass is the output of the mill house.
The manager needs to process the cane as soon as possible if sugar losses are to be avoided yet needs to have a sufficient supply in storage for times when cutting and transport are stopped, whether deliberately or not. Typically, cane is processed within 24 hours of cutting;
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 12 Najeeb ur Rehman
Cane preparation is critical to good sugar extraction, particularly with diffusion extraction. This is achieved with rotating knives and sometimes hammer mills called "shredders". However shredding requires extra energy and more equipment;
Imbibitions:
The extraction is actually conducted as a counter-current process using fresh hot water at one end being pumped in the opposite direction to the cane. The more water that is used, the more sugar is extracted but the more dilute the mixed juice is and hence the more energy that is required to evaporate the juice;
Compositions:
A typical mixed juice from extraction will contain perhaps 15% sugar and the residual fiber, called bagass, will contain 1 to 2% sugar, about 50% moisture and some of the sand and grit from the field as "ash". A typical cane might contain 12 to 14% fibre which, at 50% moisture content gives about 25 to 30 tons of bagass per 100 tons of cane or 10 tons of sugar
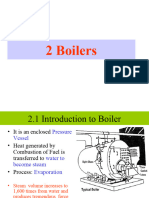
Boiler House:
A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated
Types of Boilers:
1. Water Tube Boiler:
In water tube Boiler a number of water tubes are arranged in and around the furnace.Water circulates in the tubes and outside is the fire. This type generally gives high steam production rates, but less storage capacity. water tube boilers are also capable of high efficiencies and can generate saturated or superheated steam
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 13 Najeeb ur Rehman
2. Fire Tube Boiler:
In fire Tube Boiler There is a fire in the tubes and water is present outside the tubes in the big vessel or cylinderical drum. Fire-tube boilers usually have a comparatively low rate of steam production, but high steam storage capacity
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 14 Najeeb ur Rehman
The type of boiler in use in Shakrganj mill is the water tube boiler. The number of boilers are 3. These boilers use Baggasse or SUI gas as their fuel. In off season, SUI gas gas is use for the production of the steam because no availability of the baggase. The baggase fed to boilers is that coming from the Mill House Teandem o.1 and 2 and it contains 50% moisture. The working conditions of these Boilers are as followed: Steam Temperature Working Pressure 325-350 C 23-24 kg/ g.cm2
Boiler Fans:
ID Fan (Induced Draught Fan):
Induced draught fan draw gases out of the boiler. The gas has already passed through the air heaters and precipitators before it has reached these fans.
FD Fan (Forced Draught Fan):
It takes air from atmosphere and passes it through the air pre-heater tubes, which is then blown into the furnace from its base through dumping gate. This warm air helps in combustion and spreading bagasse. Each unit has forced draught fan. The fan draws warm air from the top of the boiler house through large air heaters becoming the primary and secondary air used for the boiler combustion process. The air heater warms the incoming air by transferring heat energy from the outgoing flue gases.
SD Fan (Secondary Fan):
Secondary Fan is also admitted turbulently to complete the combustion. This fan supplies air to the furnace from the bottom surface to ensure complete combustion. This fan is only used when Bagasse is used as fuel otherwise it is kept off.
Super heater:
A super heater is a device in a boiler that heats the steam generated by the boiler again, increasing its thermal energy and decreasing the likelihood that it will condense inside the header.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 15 Najeeb ur Rehman
Super heaters increase the efficiency of the boiler, and were widely adopted. Steam which has been superheated is logically known as super heated steam.
Air Pre-heater:
This air pre-heater is used to heat the air inducted to the boiler by the hot flue gases. Thus raising the temperature of inlet air up to 110 C. Economizer: Flue gases from large boilers are typically 450 - 650F.Economizers recover some of this heat for pre-heating water. The water is most often used for boiler makeup water or some other need that coincides with boiler operation. Economizers should be considered as an efficiency measure when large amounts of make-up water are used
Key Factors For Boiler Efficiency Calculations:
Flue gas temperature (Stack temperature) Fuel specification Excess air Ambient air temperature Radiation and convection losses.
Boiler Water treatment Plant:
There are two plants for treatment of water that is fed to the boiler. Reverse osmosis plant Demineralization plant
Why we need Water Treatment?
Impure water may cause many problems in the boiler so it must be pured someway to avoid problems in the boiler. The most common problems caused by the impure water are as followed: Scaling: Total hardness in the water if not properly removed will cause in scale formation. A layer of scale on the metal surface of the boiler will acts as an insulator and reduce the rate of heat transfer from hot zone to water. Scaling results in
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 16 Najeeb ur Rehman
More fuel will be used to maintain boiler output at acceptable level Since heat transfer is retarded the metal become hotter to a point where it deforms and even rapture with disastrous results
Corrosion:
The most common source of corrosion in boiler systems is dissolved gas: oxygen, carbon dioxide and ammonia. Of these, oxygen is the most aggressive. The importance of eliminating oxygen as a source of pitting and iron deposition cannot be overemphasized. Even small concentrations of this gas can cause serious corrosion problems
Sludge formation:
The impurities which are floating on the surface in the form of light fluffy mass are called sludges .These are insoluble impurities that float at the su rface of water at high temperature. Treatment is as follows: The impurities of Na , Ca , Mg ,react with ant scaling agent and form their sulphates and phosphates which are easily removed. However due to sludge formation the rate of water evaporation is decreased .The sludge formation starts at 40oc and maximum sludge is produced at 80oc, at this temperature it is automatically drained off.
Reverse Osmosis Plant:
Reverse osmosis plants have at their heart a membrane that if damaged reduces output, increases costs and gives poor water quality so it is important to keep it clean and operating efficiently. Most reverse osmosis membranes are formed from hollow fibre or thin film composite sheets with the membrane allowing passage of pure water and rejecting the dissolved solids contained in the water. As water passes along the membrane surface the solids concentration increases and some sparingly soluble salts start to exceed their solubility and precipitate. When precipitated onto the membrane surface this causes fouling that may reduce output and increase product water conductivity. The worst of these solids being calcium carbonate and calcium sulphate and so the prevention of their precipitation is vital if the membrane is to function efficiently.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 17 Najeeb ur Rehman
Demineralization plant:
A Demineralisation Plant consists of two pressure vessels containing cation and anion exchange resins. Various types of ion exchange resins can be used for both the cation and the anion process, depending on the type of impurities in the water and what the final water is used for. Typically, the cation resin operates in the hydrogen cycle. The cat ions in the water (i.e. calcium, magnesium and sodium) pass through the cation exchange resin where they are chemically exchanged for hydrogen ions. The water then passes through the anion exchange resin where the anions (i.e. chloride, sulphate, nitrate and bicarbonate) are chemically exchanged for hydroxide ions. The final water from this process consists essentially of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions, which is the chemical composition of pure water. Simple demineralisation plant consist of Composite resin vessels with charge of strong cation and anion resin; control-panel encompassing a conductivity measurement and alarms, etc; acid and caustic injection facility from bulk, semi-bulk or carboy containers.
Deaerator:
purposes of deaeration are: To remove oxygen, carbon dioxide and other non-condensable Gases from feed water. To heat the incoming makeup water and return condensate to an optimum temperature for: i. Minimizing solubility of the undesirable gases ii. Providing the highest temperature water for injection to the boiler
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 18 Najeeb ur Rehman
Power House:
Power house use s steam produced by the boiler house to generate electric power.In power house first heat energy of steam is converted in mechanical energy by turbines and then mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by the help of generators. In Shakarganj mills two different types of turbines are used for the creation of mechanical energy: Back pressure Turbines Condensing Turbines
Back Pressure Turbine:
First three Turbines in the powerhouse are backpressure Impulse Turbines. Backpressure means that the exhaust of these turbines is not also steam of pressure above than atmospheric pressure. Noncondensing or backpressure turbines are most widely used for process steam applications. The exhaust pressure is controlled by a regulating valve to suit the needs of the process steam pressure. These are commonly found at refineries, district heating units, pulp and paper plants, and desalination facilities where large amounts of low pressure process steam is available. Advantages of Back pressure Turbines: 1234Process Heat For various Operating loads can be provided. Electrical power to meet the own and for Feeding into the Public grid is available. Balancing of operational Fluctuations between Power and steam requirement. Avoidance of exceeding the maximum Demand limits for power imported from the Public grid.
Condensed Turbines:
Condensing turbines are most commonly found in electrical power plants. These turbines exhaust steam in a partially condensed state, typically of a quality near 90%, at a pressure well below atmospheric to a condenser.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 19 Najeeb ur Rehman
Production House
Juice that is coming from milling house has following properties; Acidic Opaque Greenish color Brix (thickness) 10 15 Soluble impurities
Insoluble impurities like proteins, waxes, gums etc. Physical and chemical processes are required for the production of sugar. These operations carried out in process house. Main units in process house are:
Primary Heaters:
Juice which is coming from Tandem 1 and Tandem 2 is pumped to primary heaters, there are three primary heaters for tandem 1 and tandem 2, two set for each tandem. Heaters used for heating juice coming from tandem 1 is called primary heaters set no.1 and that is used for heating juice of tandem 2 is called primary heater set no. 2. These are shell and tube heaters, heating are done by vapors coming from evaporators, juice moves in tube side and vapors in shell side, duplex valves are used for the transfer of juice in heaters. Heating is done for proper reaction with lime in reaction tank. Juice heating temperature 60-770C
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 20 Najeeb ur Rehman
Defication tanks:
Defecation is process of removal of impurities by the action of lime and heating. Defication is carried out in following equipments
Lime Dozer:
Juice coming from primary heater set no. 1 and primary heater set no. 2 enters in lime dozer from top. Here we add lime {Ca (OH)2} to it. CaO + H2O Ca (OH) 2
Lime is used to combine impurities that is present in juice because juice is acidic in nature and when lime is added which is basic in nature then pH is maintained at 7.8 to 8.2.
Retention Tanks:
In retention tanks juice enters from the bottom. The object of these tanks is to mix juice with lime and to give the reaction to lime and juice and reaction time is provided. There are four retention tanks in SML. In retention tanks plates are arranged in manner that one plate is below and other is above, this arrangement is done for proper mixing and mixing is done by agitation.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 21 Najeeb ur Rehman
Defecation Tanks:
There are two defecation tanks in SML. Juice coming from retention tanks enters in defecation tanks separately. From defecation tanks juice is pumped to the secondary heaters.Two centrifugal pumps are attached to each tank pumping the juice to the secondary heaters.
Secondary heaters:
Neutralized juice coming from defecation tank no.1 and defecation tank no.2 is heated in secondary heaters set no. 1 and secondary heaters set no.2 respectively. These are total eight (8) in numbers and four (4) for each set. Heating media in first three secondary heaters is vapors that is coming from evaporators and in forth one heating is done by exhaust stream (stream that is exhausted from turbine). Exhaust stream is used because we require high temperature to clarifier the juice and vapors cant do this job. Juice heating temperature 100 - 1050C
Flash Tank:
Juice that is heated in secondary heaters set no.1 and secondary heater set no. 2 is now brought to flash tank with the help of duplex valves (to bypass the juice).Flash tank is simply a conical tank where juice is entered from the side of conical section. There are four(4) flash tanks one for each clarifier. It helps in removing vapors and to avoid bubbling of heated juice in Clarifier. The purpose of flash tank is to remove non condensable gases and air from juice. Now juice is transferred to next equipment from bottom of flash tank.
Clarifiers:
There are four (4) clarifiers. Clarifiers are used for the clarification of juice. Bagasse and mud are removed here.Poly electrolyte (poly acryl amide) solution is added in clarifier from coagulation tank (tank where solution is prepared) . The stock solution of polyelectrolyte is prepared in one tank and then diluted in two tanks. The dose of polyelectrolyte is in ppm. The stock solution of polyelectrolyte is prepared before 8-10 hours. There are two coagulation tanks in SML one is sufficient for two clarifiers. Overflow Juice from clarifier is collected in juice tank at the side of clarifier then it is passed through 80- mesh screen where particles present in juice are removed then it sent to clear juice tank.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 22 Najeeb ur Rehman
In sugar industry, clarifiers are the complicated and more sensitive point. These clarifiers are actually responsible to run an industry or shut down. It is the process where the juice is clarified.
Mud Level in Clarifiers:
The mud level in the clarifiers is determined by dipping iron rod with thread. When it touches the mud, the length of the thread is measured and we came to know the level of the mud in clarifiers. Then the clear juice is passed through 60 to 80mesh plate into the clear tank. This juice must be clear. If juice is not clear, then it increases many problems Suspended and dissolved particles decrease brix in evaporators due to scale formation. More energy is required to get same level of brix of syrup. The sugar produced contains fibrous material as foreign matter
Mud Boot:
Impurities which are settle down in clarifier are collected in tank known as mud boot placed at the bottom of the clarifier. There are four mud boots, one for each clarifier.
BD (begasse dust) Mixer:
Mud from mud boot is pumped to BD mixer and baggasse from mill house is added with the help of conveyer. It is simply a vessel and baggasse is added just to increase pore size of mud so that we can easily separate juice from mud
Vacuum Filter:
Mixture of mud and baggasse is brought to vacuum filter. There are ten (10) vacuum filters in SGL.Here vacuum pressure about 30-35 cm Hg is applied by the vacuum pumps.Vacuum filters are use to remove sweetness from mud. This drum rotates at a very slow speed i.e. 0.5 rpm. When it is rotated, mud become attached with the walls and at the same time mud is treated with hot water from the top. Sweetness of input juice = 75%
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 23 Najeeb ur Rehman
Sweetness in output juice = 2-2.5%
Clear juice goes to turbid juice tank and then to reaction tank for further clarification.Mud is sent to bio-composting plant where after composting with stillage (waste of distillery) bio-compost is prepared.
Preheaters:
Clear juice after screening goes to preheaters where juice is heated up to 105 C.There are two(2) prheaters in SML.Juice is preheated before evaporation.
0
Juice heating temperature
100 - 1050C
Evaporators:
The clarified juice (85% water) in clear juice tank is pumped to evaporators where it is concentrated to a heavy clear syrup. Evaporation is done in multiple effect evaporators to achieve maximum steam economy .Each effect is arranged in series and operated so that each succeeding one operates under high vacuum (low pressure). This arrangement allows the juice to be drawn from one vessel to the next and permits it to boil at low temperature. Evaporation is done in two stages. The first in an evaporator station to concentrate the solution and second in a vacuum pan is to crystallize the sugar from solution. First step is done generally in multiple effect evaporators for improved thermal
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 24 Najeeb ur Rehman
economy; and second is performed in single effect vessels e.g vacuum pans to control the batch crystallization. The evaporator station in raw sugar manufacture typically removes 90% of the water from the clarified juice from about 15 brix to about 65-70 brix. There are different terms, which are used here in factory for evaporators, bodies and quads are more common. When four bodies are combined then it is called quad.The triple, quintuple-effect evaporators are also used but quadruple-effect type is more common. In this one pound of steam evaporates four pounds of water.
Juice from clarifiers goes to the vapor cell. Vapor cell is used before each quad for steam economy . There are three vapors cells. The exhaust Steam is applied on vapor cell and temperature is raised to about 110oC.Then juice goes to evaporator No.1. Its temperature is kept at 110o C. The Vapors of 1st body are used in 2nd body as heating media and hence there is no use of steam in body No.2. The temperature of 3rd and 4th body is 85oC and 60o C respectively. Creating vacuum of 60-65 mm Hg decreases the temperature of 4th body. The 4th evaporator is attached with condenser, which removes condensable gases through jet and condenses the vapors by spraying the cold water. Syrup of 60 to 65 brix is obtained from the 4th evaporator. Then this syrup is sent to syrup tanks called syrup storage tank. The cleaning of evaporator is necessary to maintain the brix. After 12-15 days every evaporator has to be cleaned.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 25 Najeeb ur Rehman
Juice
Clear juice Vapour cell Evaporator 1 Evaporator 2 Evaporator 3 Evaporator 4
Temperature
890C 1040C 1030C 930C 89 0C 580C
Brix
15 22 35 38 41 65
Pressure
1 kg / cm2 0.33 kg / cm2 0.29 kg / cm2 0.11 kg / cm2 -28.13 kg / cm2 -53.63 kg / cm2
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 26 Najeeb ur Rehman
Syrup storage tank:
Syrup from syrup storage tanks is sent to syrup storage tank,from there it is sent to raw crystallization pans.
Raw crystallization:
Syrup from evaporators is pumped to a vacuum pan in which it is evaporated to supersaturation in order to cause sugar to crystallize .This is done in pans which may be either Batch pan or Continuous vacuum pans The function pan is to produce satisfactory sugar crystals from syrup. The concentration of feed used in pans is usually 60-65 brix and may reach to 74 here. These pans are specified for different boiling of different massecuite and seeds. Batch Pan # 1,2 Seed for A massecuite, Continuous Pan # 1,2 for A-massecuite ,Batch Pan # 3 seed for c-massecuite, Continuous pan # 3 for c- massecuite and Batch Pan # 4,5,6,7,8 for B-massecuite Massecuite = molasses + crystals Crystallization is done through following pans that work mutually. A pan B pan C pan
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 27 Najeeb ur Rehman
A pan:
Syrup from syrup storage tank is taken into A pan. Through vacuum boiling brix level is increased to 70, where crystals start to form. Vacuum boiling (pressure 76 mm Hg) is done at 60C. Now A massecuite is done by the addition of B seed( added up to 1/4 or 1/8 of total tank volume). Here A grain (brix 90-95) is formed that is further transfer to continuous vacuum pans continuous vacuum pans consists of 12 parts where syrup and A grain is brought in contact to each other in tubes and steam is applied as heating media.
The product from continous pans is A massecuite and that is dropped into A crystallizer by vacuum breakage. Sugar is formed within three to four hours. This material is further transferred to A centrifugals where high. In centrifugals speed is applied separate grain of sugar and molasses comes out. These machines work mechanically, centrifugal force works when basket of the centrifugal rotates with high speed i.e. 1600 rpm.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 28 Najeeb ur Rehman
There are 10 Nos. of A-centrifugals, 9 Nos. of B centrifugals, 8 Nos. of C centrifugals. From the centrifugation of massecuite A , A melt, A heavy and A wash are obtained. Raw melt is sent for clarification while A heavy and A wash are brought into B pans for preparation of massecuite B.
B Pan:
There are five nos. of B pans in SML. Physical parameters are same as that is pan A. Here B massecuite is formed which is dropped into B crystallizer. Centrifugation of massecuite gives B seed and B heavy.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 29 Najeeb ur Rehman
First of all B seed that is used for A massecuite is prepared by slurry ( crystals + isopropyl alcohol) and syrup. Isopropyl alcohol is added for proper size of grains.
C Pan:
There is a single C pan in SML. Here C massecuite is prepared from B heavy taken from B pans and slurry. Here C grains are formed that are than dropped to C continuous pan where syrup is added and product is than sent to vertical crystallizers( two in numbers) then it is sent to cassettes (four in numbers)where temperature is dropped to 40C which is best temp. For crystallization.
Then it is sent to re-heaters (four in numbers) The purpose of re-heaters is to increase the temp. of massecuite to such a level suitable for centrifugation. Centrifugation (single curing centrifuges) of massecuite C gives C seed along with final molasses. This final molasses is sent to distillery for production of alcohol. C seed is sent to double curing centrifuges from where we get C Light (purity 56 to 58) and C seed that is used for preparation of soft sugar.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 30 Najeeb ur Rehman
Sugar Refining:
The raw sugar produced in industry as described in preceding section is LIGHT BROWN in color and contains 98% sucrose .In order for it to be competitive for marketplace, it is necessary to bring about level of sucrose to 99.9% to make it white. There are four routes for production of white sugar from sugar cane or raw cane sugar. (1): traditional plantation white , obtained directly from sugar juice with settling clarification and sulfitation. (2): improved plantation white with carbonation and sulfitation. (3): refined white, from a white end refinery attached to raw sugar factory, involving remelting raw sugar and refinery classification and decolorizing process; and (4) refined white, refinery not incorporated into raw sugar factory.
Phosphitation Process:
A-melt which is the final product of the raw process is further transferred for melt clarification. The process involves following steps:
Buffer tank:
Raw melt goes into buffer tank. Its purpose is to store the raw melt. The capacity of buffer tank is 65 cubic meter.
Supply tank:
Raw melt from buffer tank comes into supply tank situated at ground flour.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 31 Najeeb ur Rehman
Liquor Heaters:
Liquor from supply tank is sent to liquor heaters for heating up to 80 to 85 C that is suitable for purification. Melt is heated so that it may be reacted efficiently and to get optimum Condition. Juice heating temperature 80 - 850C
Reaction tank:
After heating the product is taken into reaction tank. In reaction tank following chemicals are added: Phosphoric acid (300-400 ppm) Talofloc : It is used as decolorizing agent Talofloat: It is used to float the ppt. sludge, colloidal solution so that it can easily removed from the upper surface. Lime Socrates: To maintain the pH of the raw melt.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 32 Najeeb ur Rehman
Telo Clarifiers:
From reaction tank the liquor comes in telo clarifiers. Due to the addition of low molecular weight coagulants (Taloflot), the mud floats on the surface of liquor. Here mud is collected with the help of scrappers and sent to vacuum filters. Liquor is collected into liquor tank and sent for sulphitation.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 33 Najeeb ur Rehman
Sulfitation/sulfur tank:
Sulphitation is an eminent process done to decolorize the liquor. For this purpose liquor is taken in a tank and SO 2 is passed from the bottom of this tank. SO2 is removed from top of tower. Sulphur dioxide is passed through clear liquor to give brightness to liquor After sulphitation liquor is collected into smear tank and then passes through pressure filters with the help of pumps.
Filtration:
The liquor from phosphatation/ carbonation/ sulphitation clarifiers contain small amount of finely dispersed particulate matter that require filtration for removal . This process is done in the pressure filters.
Pressure filters:
There are eight pressure filters in SML, four are big and four are small. Small press. Filters have 48 plates and 24 out let and large press. Filters have 36 plates and 24 out
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 34 Najeeb ur Rehman
let. Here small dust particles are removed and clear liquor is obtained. Pressure upto 12 kg / cm2.
Deep Bed Filters:
Liquor from vacuum filters is sent to deep bed filters where layers of different sizes of stones are applied for further filtration. Fine liquor is dropped from top and moves towards bottom. There are 4 large containers for this purpose and each contain three different layers of different materials. i. Carbon ii. Sand iii. Small stones All these three materials are so stable that even concentrated acids and base have No effect on them. It is used to remove the dust particles as well as other small particles In the liquor. There are layers of different sized small stones of 3mm, 6mm, 12mm and 18mm.
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 35 Najeeb ur Rehman
Decolourization:
The filtered clarified liquor is a clear, dark brown liquid having solid contents b/w 55 to 65 Brix, a pH of 6.7 to 7.2 and temperature b/w 65-----85oc. At this stage certain decolorizing agents are added to remove colour such as charcoal ,bone char , ion exchange resins etc and this send for refine crystallization and centrifugation in the refine pans and centrifugals which are discussed as next topic .
Refine crystallization and centrifugation:
Clear liquor obtained after melt clarification is brought into refinery pans for final crystallization. There are nine nos. refinery pans in SML. First of all massecuite is drawn from refinery crystallizer at 200 rpm. Then this massecuite is washed with hot water coming from nozzles. Water comes out for few seconds. The purpose of washing is to wash the sugar and to make it white. When hot water stops, then steam comes from the same nozzle for few seconds. The purpose of this steaming is to dry the sugar. Centrifugal rotates with high speed almost to 1600 rpm. Then machine starts to stop with low speed. It rotates with 50rpm. Then centrifugal is discharged by dropping the sugar into the hopper. In refinery centrifugal we can refine 1500 kg sugar at once.
Packaging and storing of refined granulated sugar:
In recent decades, there have been significant changes in the methods of handling refined sugar as it leaves the dryer. Bulk delivery of refined granulated sugar to customers has made it necessary for the refiner to store finished products in bulk rather than in bags .Granulated sugar remains free flowing for a long period of time if it is CONDITIONED as conditioning reduces the handling , packaging and storing problems resulting from caking.Conditioning involves following factors , including control of moisture contents , the temperature ,and grain size , as well as good inventory management .
U.E.T Lahore
Imtiaz Ali 36 Najeeb ur Rehman
References:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cane_sugar_mill www.essortment.com/process-making-sugar-419 kiranpalwasha.blogspot.com/.../some-videos-from-sugar-mill-process.. www.sugaraustralia.com.au/Industry.aspx?content=MillingBusiness www05.abb.com/global/scot/...nsf/.../a-n-sugar_ph_sulfitation_a.pd www.clarencetourism.com/media/docs/sugarcane.pdf - Australia
http://www.acfa.com.au/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=100&Itemid=135 http://www.rudolphresearch.com/refractometers/how-to-choose/sugar.php http://www.citehr.com/research-sugar-mill-process-page1.html?status=closed ://ethanolfacts.com.au/sugarprocess
U.E.T Lahore
You might also like
- Descriptive Pamphlet of the Richmond Mill Furnishing WorksFrom EverandDescriptive Pamphlet of the Richmond Mill Furnishing WorksNo ratings yet
- Amare Amare 2121212123232323Document44 pagesAmare Amare 2121212123232323aderaj getinetNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report: Perera P.O. EN11ME2049Document82 pagesIndustrial Training Report: Perera P.O. EN11ME2049Oshani PereraNo ratings yet
- Lakeland Terrier Guide Lakeland Terrier Guide Includes: Lakeland Terrier Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, and MoreFrom EverandLakeland Terrier Guide Lakeland Terrier Guide Includes: Lakeland Terrier Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Dedicated to Our ParentsDocument74 pagesDedicated to Our ParentsHassan Bin AliNo ratings yet
- Standard Poodle Guide Standard Poodle Guide Includes: Standard Poodle Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, Breeding and MoreFrom EverandStandard Poodle Guide Standard Poodle Guide Includes: Standard Poodle Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, Breeding and MoreNo ratings yet
- Internship Report: DG Khan CementDocument30 pagesInternship Report: DG Khan CementArfa Sarwar Arfa SarwarNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument41 pagesInternship ReportShafi UddinNo ratings yet
- Proposed 45KLPD Distillery Unit in Cuddalore DistrictDocument15 pagesProposed 45KLPD Distillery Unit in Cuddalore DistrictVasanth Kumar100% (1)
- Coton de Tulear Guide Coton de Tulear Guide Includes: Coton de Tulear Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, and MoreFrom EverandCoton de Tulear Guide Coton de Tulear Guide Includes: Coton de Tulear Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit Report of Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument17 pagesIndustrial Visit Report of Department of Mechanical EngineeringEternalNo ratings yet
- Rhodesian Ridgeback Guide Rhodesian Ridgeback Guide Includes: Rhodesian Ridgeback Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, and MoreFrom EverandRhodesian Ridgeback Guide Rhodesian Ridgeback Guide Includes: Rhodesian Ridgeback Training, Diet, Socializing, Care, Grooming, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Intership ReportDocument65 pagesIntership Reportali bestNo ratings yet
- Agegnehu Kebede Final Intrnship Report GMFDocument31 pagesAgegnehu Kebede Final Intrnship Report GMFNakachew Aschalew100% (2)
- Internship report on nitro phosphate plant operations and projectDocument38 pagesInternship report on nitro phosphate plant operations and projectKalimullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Denzong FinalDocument27 pagesDenzong Finalj4jhnyNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL REFINERY LIMITED 2Document21 pagesNATIONAL REFINERY LIMITED 2mjunaidNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Final 21jan09Document132 pagesMSC Thesis Final 21jan09David Cruz ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Desalter PDFDocument132 pagesDesalter PDFAlzahraa Alhaj AliNo ratings yet
- IndustrialvisitreportDocument17 pagesIndustrialvisitreportEternalNo ratings yet
- Final Report EndDocument59 pagesFinal Report Endtesfayebulti33No ratings yet
- Name of Intern: Id Number: Emebet Chalachew R/1219/10 Getenesh Debeb R/1520/10 Rahel Shiferaw R/2887/10 Name of Mentor: Mr. KumlachewDocument61 pagesName of Intern: Id Number: Emebet Chalachew R/1219/10 Getenesh Debeb R/1520/10 Rahel Shiferaw R/2887/10 Name of Mentor: Mr. KumlachewDegsew MesafintNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Internship Report at Noon Sugar Mills LTD DistilleryDocument59 pagesChemical Engineering Internship Report at Noon Sugar Mills LTD DistilleryAhmAd GhAzi100% (1)
- Final Abdu ProjectDocument47 pagesFinal Abdu Projecttazeb Abebe100% (1)
- Internship Report On MTM (Masood Textile Mills Limited)Document55 pagesInternship Report On MTM (Masood Textile Mills Limited)Does it Matter?83% (6)
- Arihant Sugar FactoryDocument9 pagesArihant Sugar FactoryNikhil HallurNo ratings yet
- Rolo Cdm512d Cdm514dDocument67 pagesRolo Cdm512d Cdm514dLuzioNeto50% (2)
- Denim WashingDocument141 pagesDenim WashingAamir Shabbir78% (9)
- Sadiq Oil Extraction (Final Report)Document36 pagesSadiq Oil Extraction (Final Report)Muhammad Nasir ShabbirNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument63 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentetayhailu67% (3)
- Production of Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether Using Snamprogetti ProcessDocument103 pagesProduction of Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether Using Snamprogetti ProcessMuntazer QasimNo ratings yet
- LP7000 / 40-11 User Manual - Complete Guide to Rowenta Steampod Flat IronDocument17 pagesLP7000 / 40-11 User Manual - Complete Guide to Rowenta Steampod Flat IronAnonymous smNKM7gBNo ratings yet
- Declaration: Name Signature DateDocument65 pagesDeclaration: Name Signature DateArgaw DagneNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument17 pagesProposalJimmy ReeceNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Line BrochureDocument21 pagesVegetable Line BrochureAndrea HernandezNo ratings yet
- Utilities of Nishat Mills LimitedDocument33 pagesUtilities of Nishat Mills LimitedossumyaqoobNo ratings yet
- Assela Malt ApparentDocument41 pagesAssela Malt ApparentAbdulkudus Abdulshukur100% (4)
- Industrial Attachment Report: Langat KevinDocument44 pagesIndustrial Attachment Report: Langat KevinPAUL KIBET90% (10)
- Sugar 2Document54 pagesSugar 2Kirà ÀàãNo ratings yet
- Tata Surgical PVT LimitedDocument41 pagesTata Surgical PVT Limitedrushda asmatNo ratings yet
- SFML ReportDocument82 pagesSFML ReportMukarram Ali Khan100% (1)
- Working CapitalDocument62 pagesWorking CapitalSahil SethiNo ratings yet
- DECLARATIONDocument39 pagesDECLARATIONAlex MekoNo ratings yet
- Coceptual of Design Transmission For Small Tractor PDFDocument55 pagesCoceptual of Design Transmission For Small Tractor PDFRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Mirpurkhas Sugar Mills Internship ReportDocument31 pagesMirpurkhas Sugar Mills Internship ReportSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Manufacturing of SugarDocument33 pagesTraining Report On Manufacturing of SugarShivam Mittal50% (6)
- Internship Report at Agritech LimitedDocument37 pagesInternship Report at Agritech LimitedEngineer TalhaNo ratings yet
- Submit 2Document110 pagesSubmit 2Nahom AbebeNo ratings yet
- Sugar Mill Report: Chemical Engineering Training at Bajaj HindusthanDocument20 pagesSugar Mill Report: Chemical Engineering Training at Bajaj HindusthanSatwik SinghNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: Master of Buisness ApplicationDocument28 pagesTerm Paper: Master of Buisness Applicationashishsuman50% (2)
- Final ReportDocument59 pagesFinal Reporttesfayebulti33No ratings yet
- Project Report: Toyota Islamabad Motors: Submitted ToDocument21 pagesProject Report: Toyota Islamabad Motors: Submitted Tohassan0% (1)
- HashaamDocument48 pagesHashaamRana HashaamNo ratings yet
- Sheikh Technical Veterinary School (STVS)Document39 pagesSheikh Technical Veterinary School (STVS)haashi94No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Project ReportDocument51 pagesCooling Tower Project ReportOsama Hasan97% (31)
- Varsha GoyalDocument36 pagesVarsha Goyalajay sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cement Factory ReportDocument19 pagesCement Factory ReportUzair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reptiles List BkanaDocument9 pagesReptiles List BkanaImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Scintillators-Interest: William Crookes Zns Spinthariscope CurranDocument5 pagesScintillators-Interest: William Crookes Zns Spinthariscope CurranImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- CooltwrsDocument4 pagesCooltwrsJoseNo ratings yet
- Pat Us 4227018Document4 pagesPat Us 4227018Imtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Adobe After Effects CS5 TutorialsDocument26 pagesAdobe After Effects CS5 TutorialsImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Accounting Principles and Concepts PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Accounting Principles and Concepts PDFkhurmeji50% (2)
- 4-Nonelementary Reaction KineticsDocument23 pages4-Nonelementary Reaction KineticsFajri AmrullahNo ratings yet
- AcetyleneDocument13 pagesAcetyleneImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- API - Solid Bed Adsorbers PDFDocument70 pagesAPI - Solid Bed Adsorbers PDFImtiaz Ali100% (1)
- Christianity and The Nazi Movement ResponseDocument27 pagesChristianity and The Nazi Movement ResponseImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Adobe After Effects CS5 TutorialsDocument26 pagesAdobe After Effects CS5 TutorialsImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet TemplateDocument4 pagesBalance Sheet TemplateSardar A A KhanNo ratings yet
- API - Behavoiur of Hydrocarbons PDFDocument53 pagesAPI - Behavoiur of Hydrocarbons PDFImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- API - Instrumentation For Operators - Unit 1 Measuring Instruments (Section 1,2,3,4,5) PDFDocument153 pagesAPI - Instrumentation For Operators - Unit 1 Measuring Instruments (Section 1,2,3,4,5) PDFImtiaz Ali100% (1)
- API - Gas Measurement (Unit 1,2) PDFDocument88 pagesAPI - Gas Measurement (Unit 1,2) PDFImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- API - Hydrate Inhibition PDFDocument47 pagesAPI - Hydrate Inhibition PDFImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument30 pagesFluid DynamicsImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- API - Cooling Tower (Section 1) PDFDocument44 pagesAPI - Cooling Tower (Section 1) PDFImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Selection of GasketsDocument53 pagesSelection of GasketsImtiaz Ali100% (2)
- API - Centrifugal Pump (Section 1,2,3) PDFDocument128 pagesAPI - Centrifugal Pump (Section 1,2,3) PDFImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Gaskets PDFDocument7 pagesGaskets PDFImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Methods of Firing Steam BoilerDocument22 pagesMethods of Firing Steam BoilerAnonymous mRBbdopMKf100% (2)
- CI Spare ListDocument1 pageCI Spare ListআতীকNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 PT PFTDocument22 pagesSec 1 PT PFTDenny NataliaNo ratings yet
- Past ME BoardDocument105 pagesPast ME BoardHerson Fronda BucadNo ratings yet
- Water Tube Boiler Advantages: High Efficiency, Flexibility, Rapid StartupDocument1 pageWater Tube Boiler Advantages: High Efficiency, Flexibility, Rapid StartupJogesh.S.NandaNo ratings yet
- ME421 Steam Generation FundamentalsDocument69 pagesME421 Steam Generation FundamentalsKhairulNo ratings yet
- Herz Industrial Brochure - Rural EnergyDocument12 pagesHerz Industrial Brochure - Rural EnergysigitgunaNo ratings yet
- Power Generation - Week 3Document62 pagesPower Generation - Week 3Tayyab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assistant Professor Mechanical Department, Vasad: Presented byDocument24 pagesAssistant Professor Mechanical Department, Vasad: Presented byshivani sutharNo ratings yet
- Lab Name: Demonstration and Operation of 5KW Steam Power PlantDocument14 pagesLab Name: Demonstration and Operation of 5KW Steam Power PlantFarhan EdwinNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background of The Project 1.2 Problem Statement 1.3 Objectives of The Project 1.4 Project ScopeDocument21 pages1.1 Background of The Project 1.2 Problem Statement 1.3 Objectives of The Project 1.4 Project ScopeAbdi samad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hydronic Heating SystemDocument50 pagesHydronic Heating Systema_salehiNo ratings yet
- An Investigation On Tube Temperature Distribution in A Water Tube BoilerDocument6 pagesAn Investigation On Tube Temperature Distribution in A Water Tube BoilerKelvinWongNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 - Steam Generating UnitDocument121 pagesTOPIC 1 - Steam Generating UnitCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- W4000Document28 pagesW4000Alfredo CubaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 4 PDFMuhammed Bn JihadNo ratings yet
- Boilers TypesDocument7 pagesBoilers TypesNazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized 40-Character Title for STEAM GENERATORS DocumentDocument11 pagesSEO-Optimized 40-Character Title for STEAM GENERATORS DocumentGokulAgNo ratings yet
- 006Document12 pages006grimdorlfNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual of Thermal Engg - Updated 1Document54 pagesLab Mannual of Thermal Engg - Updated 1Ritesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and Accessories PDFDocument4 pagesBoiler Mountings and Accessories PDFShankar JhaNo ratings yet
- File by VivekDocument14 pagesFile by VivekVîvëk JoshiNo ratings yet
- Basic Presentation On CombipacDocument15 pagesBasic Presentation On CombipacTashmeet Singh100% (1)
- Boiler FundamentalsDocument73 pagesBoiler Fundamentalsmasoodism100% (1)
- TBL 31 E QH EH01 CP 001 en 0 Startup and Commissioning Procedures Auxiliary BoilerDocument128 pagesTBL 31 E QH EH01 CP 001 en 0 Startup and Commissioning Procedures Auxiliary Boileryazid manurungNo ratings yet
- VTG Firetube Condensing Boilers Technical DataDocument6 pagesVTG Firetube Condensing Boilers Technical DatajrodNo ratings yet
- Boilers - Powerpoint PresentationDocument45 pagesBoilers - Powerpoint PresentationDuggineni RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Introduction To Thermal Engineering: Strength of Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesUnit II - Introduction To Thermal Engineering: Strength of Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsMahesh DhopeNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit IVDocument116 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit IVA.R. Pradeep Kumar100% (4)
- The Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionFrom EverandThe Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Other People's Dirt: A Housecleaner's Curious AdventuresFrom EverandOther People's Dirt: A Housecleaner's Curious AdventuresRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (104)
- The Asshole Survival Guide: How to Deal with People Who Treat You Like DirtFrom EverandThe Asshole Survival Guide: How to Deal with People Who Treat You Like DirtRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (60)
- Welcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticFrom EverandWelcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- You Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherFrom EverandYou Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherNo ratings yet
- The House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedFrom EverandThe House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Sexual Bloopers: An Outrageous, Uncensored Collection of People's Most Embarrassing X-Rated FumblesFrom EverandSexual Bloopers: An Outrageous, Uncensored Collection of People's Most Embarrassing X-Rated FumblesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Lessons from Tara: Life Advice from the World's Most Brilliant DogFrom EverandLessons from Tara: Life Advice from the World's Most Brilliant DogRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]From EverandThe Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Smartest Book in the World: A Lexicon of Literacy, A Rancorous Reportage, A Concise Curriculum of CoolFrom EverandThe Smartest Book in the World: A Lexicon of Literacy, A Rancorous Reportage, A Concise Curriculum of CoolRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- My Man, Jeeves, The Inimitable Jeeves and Right Ho, Jeeves - THREE P.G. Wodehouse Classics! - UnabridgedFrom EverandMy Man, Jeeves, The Inimitable Jeeves and Right Ho, Jeeves - THREE P.G. Wodehouse Classics! - UnabridgedNo ratings yet
- Spoiler Alert: You're Gonna Die: Unveiling Death One Question at a TimeFrom EverandSpoiler Alert: You're Gonna Die: Unveiling Death One Question at a TimeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (56)
- Humorous American Short Stories: Selections from Mark Twain, O. Henry, James Thurber, Kurt Vonnegut, Jr. and moreFrom EverandHumorous American Short Stories: Selections from Mark Twain, O. Henry, James Thurber, Kurt Vonnegut, Jr. and moreNo ratings yet
- The Comedians in Cars Getting Coffee BookFrom EverandThe Comedians in Cars Getting Coffee BookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)




























































































































![The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/711420909/198x198/ba98be6b93/1712018618?v=1)










