Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Rain and Fuel Gas Desulfurization
Uploaded by
Ana TopaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Rain and Fuel Gas Desulfurization
Uploaded by
Ana TopaCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid rain is a rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it possesses elevated levels
of hydrogen ions (low pH). What is it caused by? Acid rain is mainly caused by the substances that are being released into the air: Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide is released by burning coal, oil, and natural gas. If you inhale carbon dioxide, then since it is toxic, it can cause you to have to breathe more than usual, unconsciousness, and other serious health problems. CO2 + Carbon monoxide: Carbon monoxide is released by burning gasoline, oil, and wood. When carbon monoxide enters your body, it goes into the bloodstream. When this happens, it will slow down the delivery of oxygen to the rest of the body, causing dizziness, headaches, and fatigue. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): CFCs are the chemicals that are used in industry, refrigeration, air conditioning systems, and consumer products. Whenever CFCs are released into the air, they reduce the stratospheric ozone layer. The stratospheric ozone layer protects Earths surface from the harmful rays of the sun. Hazardous air pollutants (HAPS): HAPS are released into the air by sources such as chemical plants, dry cleaners, printing plants, and motor vehicles (cars, trucks, buses, and planes). HAPS can cause serious health problems like cancer, birth defects, nervous system problems, and deaths that are all due to people accidentally letting them go into the air. Lead: Lead is released by house and car paint as well as the manufacturing of lead batteries, fishing lures, certain parts of bullets, some ceramic ware, water pipes, and fixtures. In young children, lead can cause nervous system damage and learning problems. Nitrogen oxides: Nitrogen Oxides are released into the air by burning fuels such as gasoline and coal. When nitrogen oxides combine with VOCs, they can cause breathing difficulty in people who have asthma, coughs in children, and general illness in your respiratory system. Ozone: Ozone is released by motor vehicles, industries, burning coal, gasoline, and other fossil fuels, and in the chemicals that are in hairspray and paints. When ozone is close to the ground (ground level ozone) it can cause chest pain, irritated respiratory tract, or persistent cough, can make you unable to take deep breaths, and can make you more likely to get lung infections. Particulate matter (PM): PM, little particles of pollution, is released by cars, trucks, and buses that are burning diesel fuel, fertilizers, pesticides, road construction, steel
making, mining, and turning on fire places and wood stoves. When PMs mix with air particles and get breathed in by something, they get stuck in the lung tissue. There they can cause increased respiratory disease and lung damage. Sulphur dioxides: Sulphur dioxides are released by burning coal, paper production, and melting metal. Sulphur dioxide can harm vegetation, harm metals, and cause lung problems, which include breathing problems and permanent lung damage. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): VOCs are released into the air by burning gasoline, wood, coal, or natural gas, solvents, paints, glues, and other products that are used at work or at home. Good research but what about the equations?
How does it affect the environment? Acid rain is very harmful to the environment. Acid rain damages everything over a period of time because it makes the living things in the environment die. Acid rain makes waters acidic and causes them to absorb the aluminum that makes its way from soil into lakes and streams. This combination makes waters toxic to crayfish, clams, fish, and other aquatic animals. Some species can tolerate acidic waters better than others. However, in an interconnected ecosystem, what impacts some species eventually impacts many more throughout the food chainincluding non-aquatic species such as birds. Acid rain also damages forests, especially those at higher elevations. It robs the soil of essential nutrients and releases aluminum in the soil, which makes it hard for trees to take up water. Trees' leaves and needles are also harmed by acids. The effects of acid rain, combined with other environmental stressors, leave trees and plants less able to withstand cold temperatures, insects, and disease. The pollutants may also inhibit trees' ability to reproduce. Some soils are better able to neutralize acids than others. In areas where the soil's "buffering capacity" is low, the harmful effects of acid rain are much greater. How can we stop it? The only way to fight acid rain is by curbing the release of the pollutants that cause it. This means burning fewer fossil fuels. Many governments have tried to curb emissions by cleaning up industry smokestacks and promoting alternative fuel sources. These efforts have met with mixed results. But even if acid rain could be stopped today, it would still take many years for its harmful effects to disappear. Individuals can also help prevent acid rain by conserving energy. The less electricity people use in their homes, the fewer chemicals power plants will emit. Vehicles are also major fossil
fuel users, so drivers can reduce emissions by using public transportation, carpooling, biking, or simply walking wherever possible.
Flue gas desulfurization is a set of technologies used to remove sulfur dioxide (SO2) from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants, and from the emissions of other sulfur oxide emitting processes. Most FGD systems employ two stages: one for fly ash removal and the other for SO2 removal. Attempts have been made to remove both the fly ash and SO2 in one scrubbing vessel. However, these systems experienced severe maintenance problems and low removal efficiency. In wet scrubbing systems, the flue gas normally passes first through a fly ash removal device, either an electrostatic precipitator or a wet scrubber, and then into the SO2-absorber. However, in dry injection or spray drying operations, the SO2 is first reacted with the sorbent, and then the flue gas passes through a particulate control device. Equations? Another important design consideration associated with wet FGD systems is that the flue gas exiting the absorber is saturated with water and still contains some SO2. These gases are highly corrosive to any downstream equipment such as fans, ducts, and stacks. Two methods that can minimize corrosion are: (1) reheating the gases to above their dew point, or (2) choosing construction materials and design conditions that allow equipment to withstand the corrosive conditions. Both alternatives are expensive, and engineers designing the system determine which method to use on a site-by-site basis.
Benefits for the environment Sulphur dioxide is a colourless gas produced when fossil fuels like coal and oil are burnt. Flue gas desulphurization drastically removes sulphur dioxide from chimney emissions. We know that sulphur dioxide is extremely harmful to the environment and one of the main chemicals that can cause acid rain. Sulphur dioxide is harmful to plants and can damage trees. With the use of technologies such as flue gas desulphurisation we will strive one-step closer to a clean environment. I like the detail you have gone into, but you are likely to be asked the equations associated with the theory. 7/10.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Pull Test Procedure - Chile Cabildo & Villa Seca 3MW-SkyLineDocument7 pagesPull Test Procedure - Chile Cabildo & Villa Seca 3MW-SkyLinecnuneza4No ratings yet
- Usn LM2500 Asme Paper GT2010-22811 61410 JalDocument7 pagesUsn LM2500 Asme Paper GT2010-22811 61410 Jalferrerick0% (1)
- CED 426 Quiz # 2 SolutionsDocument26 pagesCED 426 Quiz # 2 SolutionsMary Joanne AninonNo ratings yet
- MIMO Channel CapacityDocument9 pagesMIMO Channel CapacityGendyNo ratings yet
- 13 - Principles of Flight - QuestionsDocument80 pages13 - Principles of Flight - QuestionsEdgar Muñoz Fernández50% (4)
- SW-TS40T Sub-Miniature Toggle SwitchesDocument4 pagesSW-TS40T Sub-Miniature Toggle SwitchesVALTERNo ratings yet
- Linear Slot DiffuserDocument15 pagesLinear Slot DiffuserhyderabadNo ratings yet
- Stressman Engineering - Brochure Norway 2018-6Document8 pagesStressman Engineering - Brochure Norway 2018-6FelipeNo ratings yet
- 03.job Specification Instrumentaton PDFDocument27 pages03.job Specification Instrumentaton PDFshareyhouNo ratings yet
- FAA Significant Regulatory DifferencesDocument3 pagesFAA Significant Regulatory DifferencesOpteron K.No ratings yet
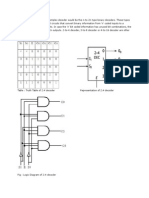
- 2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesDocument6 pages2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesPavithraRamNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Syngas Bypass Line Rupture inDocument11 pagesFailure Analysis of Syngas Bypass Line Rupture inshahgardezNo ratings yet
- New Schedule For Sunset Limited Benefits Passengers and Improves Financial PerformanceDocument3 pagesNew Schedule For Sunset Limited Benefits Passengers and Improves Financial Performanceapi-26433240No ratings yet
- Dacnewppt p4Document21 pagesDacnewppt p4vmspraneethNo ratings yet
- Struts by Kamalakar DanduDocument237 pagesStruts by Kamalakar DanduKamalakar DanduNo ratings yet
- Essential safety tips for using a pressure cookerDocument18 pagesEssential safety tips for using a pressure cookerCarlotaNo ratings yet
- Batch Profile - 2017Document57 pagesBatch Profile - 2017Praneet TNo ratings yet
- Communication System (LC-ECE204G) LAB ManualDocument54 pagesCommunication System (LC-ECE204G) LAB ManualBindia HandaNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Conbextra EP10: Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesFosroc Conbextra EP10: Constructive SolutionsVincent JavateNo ratings yet
- Using Electricity SafelyDocument1 pageUsing Electricity SafelymariaNo ratings yet
- End All Red Overdrive: Controls and FeaturesDocument6 pagesEnd All Red Overdrive: Controls and FeaturesBepe uptp5aNo ratings yet
- Airflex 728 Vinyl Acetate-Ethylene Copolymer Modified With Vinyl ChlorideDocument2 pagesAirflex 728 Vinyl Acetate-Ethylene Copolymer Modified With Vinyl ChlorideNissim Hazar CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Quotation 615-4078 BabulalDocument14 pagesQuotation 615-4078 Babulaldevrajan631No ratings yet
- Minor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument40 pagesMinor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantArpit Garg100% (1)
- Assign4 RANSDocument2 pagesAssign4 RANSankitsaneetNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements LabDocument40 pagesElectrical Measurements Labmdayyub100% (4)
- Motores SumergiblesDocument68 pagesMotores SumergiblescyberespiaNo ratings yet
- Parts List 09 636 02 02: AC Brake Motors BMG05-BMG1 Additional List: BrakeDocument2 pagesParts List 09 636 02 02: AC Brake Motors BMG05-BMG1 Additional List: Brakeali morisyNo ratings yet
- ESAB Welding HandbookDocument31 pagesESAB Welding Handbookhooky1100% (4)
- Vehicle Air Conditioning (VAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesVehicle Air Conditioning (VAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleVarun RaizadaNo ratings yet