Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lenses Virtual Lab Using Phet Geometric Optics Materials: Objectives
Uploaded by
Cecilia ObregónOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lenses Virtual Lab Using Phet Geometric Optics Materials: Objectives
Uploaded by
Cecilia ObregónCopyright:
Available Formats
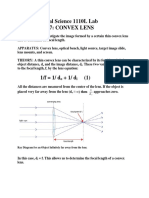
Lenses Virtual Lab using PhET Geometric Optics Name____________________________ Materials: Computer, Internet connection, and ruler Hour
______ Objectives: To demonstrate the formation of images from convex and concave lenses. To identify the type of image formed by convex and concave lenses. To confirm the lens equations. Procedure: Convex Lens . !o to PhET imulations to Pla! "ith ims to Ph!sics to Light and #adiation to Geometric Optics to Run Now! ". Ta#e some time to play $ith the simulation to get familiar $ith ho$ it $or#s. %. &aximi'e your screen. $arning: (or the measurements ta#en in this lab, the ruler in the )h*T program $ill not $or#. Therefore, $e $ill use a standard ruler measuring from the computer monitor. The scale used to ma#e these measurements $ill change from computer to computer so once you start, you must finish. +. In this lab, you $ill be moving the ob,ect to analy'e ho$ images are formed. -hen you are ready to get started be sure that your settings are as follo$s.
Change object to yellow arrow
/. 0sing the ruler, measure the distance from x to the center line of lens. 1ecord in 2ata Table as f. 2ouble this value and record as "f. 3. &easure the height of ob,ect 4ho5 and record. 6. )lace the yello$ arro$ beyond "f. 7. In 2ata Table ", record do, di, hi and your observations of the image. 8. &ove the yello$ arro$ to "f. 1ecord in 2ata Table " 9our measurements for do, di, hi and your observations of the image. :. &ove the yello$ arro$ to bet$een "f and f. 1ecord in 2ata Table " 9our measurements for do, di, hi and your observations of the image. . )lace the yello$ arro$ at f. 1ecord your observations. 4Having trouble locating image, chec# your ray diagram sheet5 1ecord your observations in Table ". ". &ove the yello$ arro$ to a position that is half$ay bet$een f and the lens. If you can;t locate the image, chec# the box next to <irtual Image. 1ecord your observations in Table ". %ata: Table & (ocal length, f "f Height of ob,ect, ho
Position o( Object do
)e!ond '( *cm+
,t '( *cm+
Table ' )et"een '( and ( *cm+
,t ( *cm+
)et"een ( and lens *cm+
di
hi
Type of image. real, none, or virtual 2irection of image. inverted or upright Concave Lens: . !o to the follo$ing $eb address. http.==,anggeng.com=convex>lens>and>concave>lens= ". Choose the concave lens. %. 1ecord f, do 4s5, di 4s;5, & and your observations of the image into 2ata Table %. +. 0se the slider to change the focal length and record your ne$ data into Table %. Table Trial & f 4cm5 do4cm5 di4cm5 & Type of image. real, none, or virtual 2irection of image. inverted or upright Trial '
.uestions and Conclusions:
. (or each of the real images you observed, calculate the focal length of the convex lens, using the lens=mirror equation. 2o your values agree $ith each other?
". @verage the values for f found in question 3 and calculate the percent error bet$een this average and the value for f from 2ata Table .
%. -hen does a convex lens act li#e a magnifying glass?
+. 2escribe the conditions for forming a virtual image $ith lenses.
/. Ho$ does the image of a concave lens al$ays appear? -here is it located $ith respect the lens and the ob,ect?
3. 1esearch the t$o basic types of vision problems, farsightedness and nearsightedness, and describe the lens prescription for each. 0se diagrams of the eye to sho$ the light paths before and after remediation.
You might also like
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNo ratings yet
- Zahid Final Thesis PDFDocument52 pagesZahid Final Thesis PDFM.ZahidNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Report 1 - NaclDocument3 pagesChem Lab Report 1 - Naclapi-305320920No ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: Lecture - 1Document40 pagesProperties of Fluids: Lecture - 1Nawaz441No ratings yet
- Proposal Defiance Gelatin ExtractionDocument26 pagesProposal Defiance Gelatin ExtractionSiti Amirah100% (2)
- AP Physics Unit 10 FluidsDocument57 pagesAP Physics Unit 10 FluidsDylan DanovNo ratings yet
- 3.36 Fluid Flow and Bernoulli's Equation PDFDocument27 pages3.36 Fluid Flow and Bernoulli's Equation PDFLeah Ann Mari BongcoNo ratings yet
- Redox - (Oxidation Reduction) PDFDocument18 pagesRedox - (Oxidation Reduction) PDFAlia RastogiNo ratings yet
- Sodium Chloride SlideDocument39 pagesSodium Chloride Slideummi surayaNo ratings yet
- Cheese Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCheese Lab Reportapi-359551163No ratings yet
- Activity 2Document3 pagesActivity 2Carat OneNo ratings yet
- Classification of FluidDocument29 pagesClassification of FluidAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 350992444-Optics NMAT ReviewerDocument11 pages350992444-Optics NMAT ReviewerKorra SamiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - Sound IntensityDocument1 pageProblem Set - Sound IntensityStef BacalangcoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Action Research (Car)Document12 pagesClassroom Action Research (Car)CINDY FATIKANo ratings yet
- Themicroscope HowtouseDocument3 pagesThemicroscope Howtouseapi-262958395No ratings yet
- Chapter 03-A - 20111108094508Document29 pagesChapter 03-A - 20111108094508Heri YantiNo ratings yet
- Unit1Soil PollutionDocument19 pagesUnit1Soil PollutionsomeshNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Q2 REVIEWER Google DocsDocument7 pagesSCIENCE Q2 REVIEWER Google DocsShyra Khaye NapalaNo ratings yet
- Factos Affecting Enzymatic Activity Notes PDFDocument7 pagesFactos Affecting Enzymatic Activity Notes PDFmohdsabirNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument8 pagesFluid MechanicsFearless HeroNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument74 pagesModern PhysicsLàXsun ShrèsthàNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Part 2: Scientific NotationDocument12 pagesLesson 8 - Part 2: Scientific NotationmisterreidNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Experiential ActivitiesDocument47 pagesEffectiveness of Experiential ActivitiesKevn KvenNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction: General ChemistryDocument13 pagesOxidation-Reduction: General ChemistryBeatrice AgustinNo ratings yet
- SSSWWW Agency and PartnershipDocument2 pagesSSSWWW Agency and PartnershipTrick San AntonioNo ratings yet
- The Phase Rule and Phase Diagrams-T and CDocument31 pagesThe Phase Rule and Phase Diagrams-T and CKunwarPawanSinghBhatiNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Pascal's PrincipleDocument19 pages3.4 Pascal's Principlekhodijahamin100% (1)
- Final Research - Group6Document68 pagesFinal Research - Group6Kent MoriNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1Document4 pagesLab Exercise 1Alessandra WyNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & HealthDocument37 pagesGlobal Warming & HealthFaheem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem Solving Chapter 14Document13 pagesChemfile Mini-Guide To Problem Solving Chapter 14MANDARAW100% (1)
- Applications of ColloidsDocument3 pagesApplications of ColloidsKevin ChapleyNo ratings yet
- Cheese Lab ReportDocument8 pagesCheese Lab Reportapi-341090482No ratings yet
- Modern Physics Notes 2020 PDFDocument16 pagesModern Physics Notes 2020 PDFNorthrop B2spiritNo ratings yet
- Electricity MagnestismDocument51 pagesElectricity MagnestismMiranti UrbaningrumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ThermodynamicDocument56 pagesChapter 7 ThermodynamicshahrulNo ratings yet
- Britton High School Chapter 7 Gases: ChemistryDocument89 pagesBritton High School Chapter 7 Gases: ChemistryMatthew GraceNo ratings yet
- Acorus Calamus, Cucurbita Maxima, Azadirachta Indica) ThroughDocument73 pagesAcorus Calamus, Cucurbita Maxima, Azadirachta Indica) ThroughAhmad KhalilNo ratings yet
- Microbial Ecology - Part IDocument8 pagesMicrobial Ecology - Part Isomide kayodeNo ratings yet
- Some Important Point: Modern PhysicsDocument5 pagesSome Important Point: Modern PhysicsBhanuNo ratings yet
- Test PaperDocument4 pagesTest PaperAnonymous doCtd0IJDNNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 1 Differences Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds and Tests For Elements Found in Organic CompoundsDocument8 pagesLab Activity 1 Differences Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds and Tests For Elements Found in Organic CompoundsANGELA CLAIRE MELICANONo ratings yet
- Water Flow in Pipes: The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument111 pagesWater Flow in Pipes: The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentZami FurqonNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas LawDocument25 pagesIdeal Gas LawAndreea Ella100% (1)
- Colligative Property of SolutionDocument9 pagesColligative Property of SolutionissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument13 pagesSound WavesAndrewKiNo ratings yet
- Concentrations of SolutionsDocument2 pagesConcentrations of Solutionsarjun2014No ratings yet
- Population EcologyDocument43 pagesPopulation EcologyKhairy IestNo ratings yet
- Ob Refresher Part 1 Normals Nov 2023 Pnle For Davao BabiesDocument12 pagesOb Refresher Part 1 Normals Nov 2023 Pnle For Davao BabiesKristine QuindozaNo ratings yet
- Me 27 Ef - Fluid Mechanics/Hydraulics: W V m γ= mg ρg mDocument67 pagesMe 27 Ef - Fluid Mechanics/Hydraulics: W V m γ= mg ρg mJoseph NjugunaNo ratings yet
- 1.-Intro ORGCHEMDocument17 pages1.-Intro ORGCHEMEy — deeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Water QualityDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Water QualityLogarithemNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of AlkenesDocument2 pagesHydrogenation of AlkenesNur FarahinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 18: Mirrors and Lenses: BjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment 18: Mirrors and Lenses: BjectiveCely Marie VillarazaNo ratings yet
- OEK-02-Real Images and Thin Lens EquationDocument11 pagesOEK-02-Real Images and Thin Lens EquationNitty MeYaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Project CompleteDocument10 pagesModule 2 Project CompleteNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab: The Letter "E": PurposeDocument4 pagesMicroscope Lab: The Letter "E": PurposeAntonio aNo ratings yet
- General Science 1110L Lab Lab 7: Convex Lens: Ray Diagram For An Object Infinitely Far Away From The LensDocument9 pagesGeneral Science 1110L Lab Lab 7: Convex Lens: Ray Diagram For An Object Infinitely Far Away From The LensMuhammad AzrinNo ratings yet
- Lenses - Virtual LabPhET Geometric OpticsDocument3 pagesLenses - Virtual LabPhET Geometric OpticsEMMABOICUNo ratings yet
- Prepare For GDPR Today With Microsoft 365Document16 pagesPrepare For GDPR Today With Microsoft 365Imperial ArnelNo ratings yet
- Input Output ModelsDocument4 pagesInput Output ModelsMaheen KhanNo ratings yet
- ELSTER Energy Meter-Kar KeyDocument52 pagesELSTER Energy Meter-Kar KeyIrfan Ullah67% (3)
- WCP Faceplates PIDCtrl enDocument106 pagesWCP Faceplates PIDCtrl enchupoNo ratings yet
- Related Learning Experience Journal: Lipa City, BatangasDocument7 pagesRelated Learning Experience Journal: Lipa City, BatangasushenNo ratings yet
- TPS 6X SetupDocument3 pagesTPS 6X SetupleonsmaltoNo ratings yet
- (3T) 3R - Ilvjhi:-: 150 QV Pitd Y Ynffe 1 Y Y Os Yy #TT, Try Y JyrfeDocument11 pages(3T) 3R - Ilvjhi:-: 150 QV Pitd Y Ynffe 1 Y Y Os Yy #TT, Try Y JyrfesonalofficewscworkfileNo ratings yet
- Microservice Spring BootDocument707 pagesMicroservice Spring BootOliver Raileanu100% (1)
- Limesurvey Manual For Instructors EDocument24 pagesLimesurvey Manual For Instructors EramiusNo ratings yet
- I Love U GajDocument8 pagesI Love U GajEmiray KarunariNo ratings yet
- en Piston Pump Unit - Product Series KFGDocument20 pagesen Piston Pump Unit - Product Series KFGJurun_BidanshiNo ratings yet
- V Mahogany Mphss ResultDocument13 pagesV Mahogany Mphss ResultJohn Paul CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Analog - TransmissionDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Analog - TransmissionMd Saidur Rahman Kohinoor92% (86)
- Health Care Data Privacy and Compliance: Navigating Regulatory LandscapeDocument13 pagesHealth Care Data Privacy and Compliance: Navigating Regulatory LandscapeCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- MiCOM P220 TechnicalGuide enDocument412 pagesMiCOM P220 TechnicalGuide enajeez8650% (2)
- Sr650 Setup GuideDocument230 pagesSr650 Setup GuideDebojit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Nueva Vizcaya State University: Bayombong CampusDocument1 pageNueva Vizcaya State University: Bayombong CampusJenny TubaranNo ratings yet
- NTT Docomo Inc. - Group 9 - EOS BDocument9 pagesNTT Docomo Inc. - Group 9 - EOS BManas DasNo ratings yet
- Adjusted AU7505 CW Pump-Screening (Harbin)Document2 pagesAdjusted AU7505 CW Pump-Screening (Harbin)waqas_a_shaikh4348No ratings yet
- Sample IEEE Article Ready FormatDocument5 pagesSample IEEE Article Ready FormatSandra WendamNo ratings yet
- Hidden Secret Codes For Google Android Mobile Phones - AskVGDocument5 pagesHidden Secret Codes For Google Android Mobile Phones - AskVGTrungVũNguyễnNo ratings yet
- Anna University SyllabusDocument112 pagesAnna University SyllabusChitra KaruppiahNo ratings yet
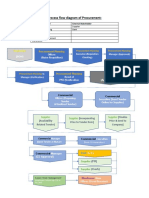
- Process Flow Diagram of Procurement:: ProductionDocument2 pagesProcess Flow Diagram of Procurement:: ProductionShah AlamNo ratings yet
- Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Build Applications With Adf IIDocument4 pagesOracle Fusion Middleware 11g Build Applications With Adf IIMohamedNo ratings yet
- COMP4660-8420 Assignment2Document3 pagesCOMP4660-8420 Assignment2390942959No ratings yet
- Lex Yacc TutorialDocument38 pagesLex Yacc TutorialAbhijit DasNo ratings yet
- Network Strategy Whitepaper enDocument21 pagesNetwork Strategy Whitepaper ensamsedNo ratings yet
- Dispute FormDocument1 pageDispute Formadarsh2dayNo ratings yet
- Mihai Nicusor: Curriculum Vitae Replace With First Name(s) Surname(s)Document2 pagesMihai Nicusor: Curriculum Vitae Replace With First Name(s) Surname(s)Nicusor MihaiNo ratings yet
- Upgrep Repository Merge Upgphys ( ) Prepare The Application DataDocument11 pagesUpgrep Repository Merge Upgphys ( ) Prepare The Application DataKhang DươngNo ratings yet
- The Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYFrom EverandThe Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Energy Codes: The 7-Step System to Awaken Your Spirit, Heal Your Body, and Live Your Best LifeFrom EverandThe Energy Codes: The 7-Step System to Awaken Your Spirit, Heal Your Body, and Live Your Best LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (159)
- Follow your interests: This will make you feel better about yourself and what you can do.: inspiration and wisdom for achieving a fulfilling life.From EverandFollow your interests: This will make you feel better about yourself and what you can do.: inspiration and wisdom for achieving a fulfilling life.No ratings yet
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1462)
- Neville Goddard Master Course to Manifest Your Desires Into Reality Using The Law of Attraction: Learn the Secret to Overcoming Your Current Problems and Limitations, Attaining Your Goals, and Achieving Health, Wealth, Happiness and Success!From EverandNeville Goddard Master Course to Manifest Your Desires Into Reality Using The Law of Attraction: Learn the Secret to Overcoming Your Current Problems and Limitations, Attaining Your Goals, and Achieving Health, Wealth, Happiness and Success!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (285)
- The Basics of a Course in MiraclesFrom EverandThe Basics of a Course in MiraclesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (226)
- Leveraging the Universe and Engaging the MagicFrom EverandLeveraging the Universe and Engaging the MagicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (37)
- Notes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendFrom EverandNotes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)
- No Mud, No Lotus: The Art of Transforming SufferingFrom EverandNo Mud, No Lotus: The Art of Transforming SufferingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (176)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)From EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- The Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthFrom EverandThe Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (179)
- Breaking the Habit of Being Yourself by Joe Dispenza - Book Summary: How to Lose Your Mind and Create a New OneFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being Yourself by Joe Dispenza - Book Summary: How to Lose Your Mind and Create a New OneRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (123)
- The Beginner's Guide to the Akashic Records: The Understanding of Your Soul's History and How to Read ItFrom EverandThe Beginner's Guide to the Akashic Records: The Understanding of Your Soul's History and How to Read ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Secret of the Golden Flower: A Chinese Book Of LifeFrom EverandThe Secret of the Golden Flower: A Chinese Book Of LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Energy Medicine: The Science and Mystery of HealingFrom EverandEnergy Medicine: The Science and Mystery of HealingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Expand the Power of Your Subconscious MindFrom EverandExpand the Power of Your Subconscious MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- The Light of Egypt; Or, the Science of the Soul and the Stars [Two Volumes in One]From EverandThe Light of Egypt; Or, the Science of the Soul and the Stars [Two Volumes in One]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Deep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!From EverandDeep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Money Magic: Clearing Your Path to Money, Time and HappinessFrom EverandMoney Magic: Clearing Your Path to Money, Time and HappinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- The Creation Frequency: Tune In to the Power of the Universe to Manifest the Life of Your DreamsFrom EverandThe Creation Frequency: Tune In to the Power of the Universe to Manifest the Life of Your DreamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (552)
- The Subconscious Mind Superpower: How to Unlock the Powerful Force of Your Subconscious MindFrom EverandThe Subconscious Mind Superpower: How to Unlock the Powerful Force of Your Subconscious MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (127)
- The Gospel of Love and Peace: Essene Books I - IVFrom EverandThe Gospel of Love and Peace: Essene Books I - IVRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Life and Teachings of Thoth Hermes TrismegistusFrom EverandThe Life and Teachings of Thoth Hermes TrismegistusRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (75)
- 369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESFrom Everand369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (50)










































































































![The Light of Egypt; Or, the Science of the Soul and the Stars [Two Volumes in One]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/711585154/198x198/1c6f6943ad/1712060545?v=1)








