Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 3 Magnetic Induction PDF
Uploaded by
Reddyvari VenugopalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04 3 Magnetic Induction PDF
Uploaded by
Reddyvari VenugopalCopyright:
Available Formats
www.sakshieducation.
com
MAGNETISM
3.MAGNETIC INDUCTION
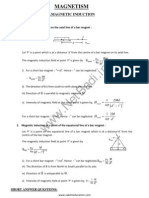
POINTS TO REMEMBER 1. Magnetic induction at a point on the axial line of a bar magnet :
o l
d P Baxial
Let P is a point which is at a distance d from the centre of a bar magnet on its axial line. The magnetic induction field at point P is given by
B axial = 0 2Md 4 d 2 l 2
i) For a short bar magnet l 2<<d2. Hence l 2 can be neglected. B axial =
0 2M 4 d3
ii) The direction of B is from south to north along the axial line. iii) Direction of B is parallel to magnetic moment M . v) Intensity of magnetic field at the same point is given by, H axial =
r r
1 2Md 2 4 ( d 2 l 2 )
1 2M 4 d 3
For a short bar magnet l 2<<d2. Hence l 2 can be neglected. H axial =
2. Magnetic induction at a point of the equatorial line of a bar magnet : Let P is a point on the equatorial line of a bar magnet which is at a distanced from the centre of the bar magnet. The magnetic induction field at point P is given by
Beqi = 0 M 4 d2 + l 2
Bequi P d
S
3/2
c) For a short bar magnet l 2<<d2. Hence l 2 can be neglected, Beqi = iii) The direction of B is from North to South parallel to its axis. iv) Direction of B is antiparallel to M . v) Intensity of magnetic field at point P is given by, H =
1 M 4 d3
0 M 4 d3
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
1. Ans:
Derive an expression for the magnetic induction on the equatorial line of a bar magnet?
Consider a bar magnet of length 2l and pole strength m. Consider a point P on the axial line of the bar magnet at a distance d from the centre O of the bar magnet. Let a unit north is placed at a point P. It experiences a repulsive force FN due to the North Pole and an attractive pole FS due to the South Pole.
FN =
0 m l 4 ( d l )2
Along NP
uuu r
And
FS =
0 m l 4 ( d + l )2
Along PS
uuu r
The resultant force on unit North Pole is given by Fnet = FN FS =
0 m m 0 2 4 ( d l ) 4 ( d + l )2
2 2
0 m 1 1 0 m ( d + l ) ( d l ) 2 2 = 2 2 4 d l d l + ( ) ( ) 4 (d l ) (d + l )
4dl F = 0 m 4 ( d 2 l 2 )2
But M = 2lm is called the magnetic moment .Net force ( or) magnetic induction (B) is given by
F =
0 2Md 4 ( d 2 l 2 )2
For a short bar magnet (i.e. if l is very much less than d, l < < < d then
0 2 M 1 2M or H = 3 4 d 4 d 3
uuu r
The direction of magnetic induction is from South Pole SN along the axis.
2.
Derive an expression for the magnetic induction at a point on the equatorial line of a bar magnet.?
Equatorial line of a magnet is the perpendicular bisector of the axis of the Ans: magnet. Let us Consider a bar magnet of length 2l and pole strength m. Consider a
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com point P on the equatorial line of the bar magnet at a distance d form the centre O of the bar magnet. Let a unit North Pole is placed at the point P. It experience a repulsive force FN due to the north and attractive force FS due to the south pole of the bar magnet.
FN =
0 m 1 m 1 and FS = 0 2 2 2 2 4 ( d + l ) 4 ( d + l )
The resultant force acting on the unit North Pole can be determined by drawing a parallelogram with FN and FS as adjacent sides as shown. The diagonal PC represents the resultant force. In the diagram PAC and PNS are similar triangles.
PC PA = NS PN
(or)
PC =
PA NS PN
PC =
Or PC =
FN 2l d 2 + l2
(or)
0 m 2l 2 2 4 ( d + l ) d 2 + l 2 1 2 ( )
But M = 2lm = magnetic moment. The magnetic induction on the equatorial line is given by
B=
0 M 4 d 2 + l 2 3 2 ( )
For a short bar magnet i.e. if l << d; then
0 M 4 d 3
(or)
H=
1 M 4 d 3
The direction of magnetic induction on the equatorial line is from north to south uuu r NS parallel to the axis www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Very Short Answer Questions: 1. Give the expressions for the magnetic induction due to a bar magnet on (i) the axial line and (ii) equatorial line.? ( March 2010) Ans: If the length is 2land pole strength is m for a bar magnet, the magnetic induction at
a point on the axial line at a distance d from the centre of the magnet is given by,
Barial =
0 2Md . 2 2 2 4 (d l )
For a short magnet, Barial =
0 2 M . 4 d 3
0 . 4
M (d 2 + l 2 ) 2
3
On the equatorial line of the bar magnet, Bequatorial =
For a short magnet, Bequatorial =
2.
0 M . . 4 d 3
Where do you find the null points in the combined field due to a bar magnet and the earth, when (i) the N-pole of the magnet is kept towards the north of the earth, (ii) the S-Pole of the magnet is kept towards the north of the earth?
Ans: (i)When the N-pole of the magnet is kept towards the north pole of earth, the null points in the combined field due to the bar magnet and the earth are obtained on the equatorial line of the magnet on either side at equal distance from the centre of the magnet.. ii) When the S-pole of the magnet is kept towards the north pole of earth, the null points in the combined field due to the bar magnet the bar magnet and the earth are obtained on the axial line of the magnet on either side at equal distance from the centre of the magnet. SOLVED PROBLEMS 1. Find the magnetic induction at a distance of 20cm on the equatorial line of a short bar magnet with a magnetic moment 60 Am2
Sol:
The magnetic induction on the equatorial line of a short bar magnet, BE =
0 M 4 d 3
BE =
2.
4 107 60 4 (20 102 )3
The magnetic moment of a bar magnetic is 45 Am2 and its length is 10cm. Calculate the magnetic field induction at a point 10cm away from the centre of the magnet on the axial line.?
Sol: Magnetic field induction on the axial line B =
0 2 Md 4 (d 2 l 2 ) 2
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
B = 10
2 45 10 102
2 2 2 2 (10 10 ) (5 10 ) 2
= 16 103 T
3.
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 1.2 Am 2 is placed in the magnetic meridian with its south pole pointing the north. If a neutral point is found at a distance of 20cm from the centre of the magnet, what is the value of the horizontal component of the earths magnetic field? BH =
Sol:
4.
0 2M 4 107 2 1.2 = = 30 106 T 3 4 d 4 (20 102 )3
Two short bar magnets having magnetic moments in the ratio 27 : 8 are placed on opposite arms of a deflection magnetometer. Find the distance of stronger magnet if the weaker magnet is at a distance of 10cm from the centre of the magnetometer for null deflection.?
M 1 : M 2 = 27 : 8 and d1 = ? and d 2 = 10cm = 0.1 m
Sol:
M1 d13 = 3 M 2 d2
d1 =
5.
27 (0.1)3 33 (0.1)3 d13 27 3 d1 = = = 8 23 8 (0.1)3
3 0.1 = 0.15 m = 15cm 2
The ratio of magnetic moments of two bar magnets is 4:5. If the deflection due to first bar magnet in the deflection magnetometer is 450, then what is the deflection due to second bar magnet?
M 1 tan 1 and = M 2 tan 2
M1 : M 2 = 4 : 5
Sol:
4 Tan 450 1 5 = = Tan 2 = = 1.25 2 = tan 1 (1.25) = 51.340 5 Tan 2 Tan 2 4
Unsolved Problem 1. A short bar magnet produces magnetic fields of equal induction at two points one on the axial line and the other on the equatorial line. What is the ratio of their distances?
Asn:
Ba = Be
2 M 0 M 0 = 3 4 d13 4 d 2
2.
d 1 = 2 d2
d1 = 21/ 3 d1 : d 2 = 21/ 3 :1 d2
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 0.4 Am2 is placed in the magnetic meridian with its north pole pointing north. A neutral point is obtained at a distance of 10cm from the centre of the magnet. If the length of the magnet is
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
also 10 cm what is the value of horizontal component of earths field at the place? Ans:
M = 0.4 Am2 ; 2l = 10cm = 101 m l =
101 m ; d = 10cm = 101 m 2
Since North Pole is pointing north, null point is obtained on equatorial line of the bar magnet. Hence at null point,
BH =
0 M 107 0.4 = 3/2 4 (d 2 + l 2 )3/2 2 102
10 + 4
BH = 2.86 105 T .
ASSESS YOURSELF: 1. Ans: What do you infer from the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet which are closed loops?
Isolated poles do not exist.
www.sakshieducation.com
You might also like
- Deflection Magneto MeterDocument11 pagesDeflection Magneto MeterYugandhar Veeramachaneni79% (14)
- MagnetismDocument6 pagesMagnetismMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Magnetic Feild 2016 ReviewedDocument160 pagesChapter 4 Magnetic Feild 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CE Transistor CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesCE Transistor CharacteristicsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic InductionDocument6 pagesMagnetic InductionYugandhar Veeramachaneni0% (1)
- Coulombs Law - MagnetismDocument5 pagesCoulombs Law - MagnetismYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (5)
- B Along Axial and Equitorial LineDocument2 pagesB Along Axial and Equitorial Linesurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument42 pagesMagnetismAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Permanent MagnetDocument15 pagesPermanent MagnetthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Physics Mapping Magnetic Field Lines of A Bar MagnetDocument18 pagesPhysics Mapping Magnetic Field Lines of A Bar Magnet7H VENOM TMNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of Material PDFDocument19 pagesMagnetic Properties of Material PDFavi taylorNo ratings yet
- 04 4 Deflection Magneto Meter PDFDocument11 pages04 4 Deflection Magneto Meter PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- PHY13 Lesson 1 MagnetismDocument48 pagesPHY13 Lesson 1 MagnetismAmante Rivera JrNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument33 pagesPhysics XIPavithra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Mapping The Magnetic FieldDocument26 pagesPhysics Project - Mapping The Magnetic Fieldmohammadumair2006No ratings yet
- SDASDASDSADocument17 pagesSDASDASDSAAkash BidhuriNo ratings yet
- 3 2 Formulae MagnetismDocument4 pages3 2 Formulae MagnetismNathanianNo ratings yet
- IITJEE 2014-Physics-School Handout-Magnetism and MatterDocument10 pagesIITJEE 2014-Physics-School Handout-Magnetism and MatterDikshant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Vibration Magneto MeterDocument5 pagesVibration Magneto MeterYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (3)
- 04 5 Vibration Magneto Meter PDFDocument5 pages04 5 Vibration Magneto Meter PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument4 pagesMagnetism and MatterShaurya SinghNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Document24 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Bharati PatilNo ratings yet
- SR Set-1 Phy C.R.D - 05.02.07 - 2Document4 pagesSR Set-1 Phy C.R.D - 05.02.07 - 2Sesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument21 pagesMagnetism and MatterDeept azaadNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument16 pagesMagnetism and Matterarghyabhai685No ratings yet
- 6 - Magnetism - Solved Exam. Module-4Document5 pages6 - Magnetism - Solved Exam. Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Chapter 5 - Magnetism Matter Saju HssliveDocument10 pagesXII Physics Chapter 5 - Magnetism Matter Saju HssliveVikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetism & MatterDocument12 pagesJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetism & MattervarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument16 pagesElectricity and MagnetismHazel Riyenzi100% (1)
- Magnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Document22 pagesMagnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Chandradeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Magnetism MatterDocument18 pagesMagnetism MatterSri D0% (1)
- Deflection Magnetometer ExperimentDocument8 pagesDeflection Magnetometer ExperimentNurul Haseena100% (1)
- 01 Magnetism TheoryDocument13 pages01 Magnetism TheoryAnonymous Ob697T5oBlNo ratings yet
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Viii (Magnetism and Matter)Document6 pagesSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Viii (Magnetism and Matter)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument19 pagesMagnetismAkash Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 17 MagnetostaticsDocument29 pages17 MagnetostaticsChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- 4 MagnetismDocument17 pages4 MagnetismThinkershub11No ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument12 pagesMagnetism and MatterAditya DasksgNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Determining The Value of Horizontal Magnetic Field of Earth by MagnetometersDocument39 pagesA Seminar On Determining The Value of Horizontal Magnetic Field of Earth by MagnetometersKamaljit RajkumarNo ratings yet
- BKM - MagnetismDocument26 pagesBKM - Magnetismdny001No ratings yet
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocument21 pagesCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreAnaya SajilalNo ratings yet
- Prhysic Report Magnetic FieldDocument4 pagesPrhysic Report Magnetic FieldSot MeowNo ratings yet
- Fichen4 Chapitre4-EnDocument1 pageFichen4 Chapitre4-EnDimitri Valdes TchuindjangNo ratings yet
- WWW - Magnetostatic AskiitiansDocument12 pagesWWW - Magnetostatic Askiitiansthiripura sundariNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Document17 pagesLab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Sitaramaraju VengalarajuNo ratings yet
- Magnetism & MatterDocument17 pagesMagnetism & Matterkartiksingh46648No ratings yet
- Astons Mass Spectrograph by Sonu RaniDeptt. of PhysicsDocument4 pagesAstons Mass Spectrograph by Sonu RaniDeptt. of PhysicsDNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Text DocumentTanuja MagarNo ratings yet
- Alternative Method To Calculate The Magnetic Field of Permanent Magnets With Azimuthal Symmetry PDFDocument10 pagesAlternative Method To Calculate The Magnetic Field of Permanent Magnets With Azimuthal Symmetry PDFjames<XIIINo ratings yet
- Biot Savart LawDocument7 pagesBiot Savart LawTornadoNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument3 pagesMagnetismalvin talaveraNo ratings yet
- CoupleDocument4 pagesCoupleYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (2)
- Current Carrying ConductorsDocument12 pagesCurrent Carrying ConductorsYugandhar Veeramachaneni33% (3)
- Magnetic DipolesDocument10 pagesMagnetic DipolesMarina RukavinaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Formulas DownlaodDocument17 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Formulas Downlaodksdb50% (2)
- 10 Iind Year MagnetismDocument2 pages10 Iind Year MagnetismmohamedNo ratings yet
- Indah Permata Sari - Resume Medan MagnetDocument13 pagesIndah Permata Sari - Resume Medan MagnetIndah Permata sariNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 EamcetDocument103 pagesMagnetism and Matter Class 12 Eamcetsai mukeshNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Y Y Y Y Y Y Y YDocument1 pageÈí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Èí©'°Æ Ƒyk! Y Y Y Y Y Y Y YReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Important Keller BoxDocument10 pagesImportant Keller BoxReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- How Much Insurance Do I NeedDocument6 pagesHow Much Insurance Do I NeedReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Colleges ListDocument35 pagesAutonomous Colleges ListReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexDocument28 pagesPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Lab ExperimentDocument7 pagesLab ExperimentBryan Owen Salcedo SantosNo ratings yet
- D.C. Power Supply: Experiment ADocument5 pagesD.C. Power Supply: Experiment AReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Attenuation in OFCDocument4 pagesAttenuation in OFCReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Charging and Discharging of A CapacitorDocument6 pagesCharging and Discharging of A CapacitorReddyvari Venugopal33% (3)
- Solid State Physics: Unit IVDocument20 pagesSolid State Physics: Unit IVReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 06 5 Potentiometer PDFDocument6 pages06 5 Potentiometer PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Sakshi: V. X, X, X, X .... X W, W, W, W .... WDocument3 pagesSakshi: V. X, X, X, X .... X W, W, W, W .... WReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 09 4 Compton Effect PDFDocument6 pages09 4 Compton Effect PDFReddyvari Venugopal100% (1)
- Açúõ Ûª°Æ¤P©'! Îáê°P-¢√∞¡Ÿx ™‰Éπ..Document1 pageAçúõ Ûª°Æ¤P©'! Îáê°P-¢√∞¡Ÿx ™‰Éπ..Reddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 07 Thermo Electricity PDFDocument16 pages07 Thermo Electricity PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 10 3 Nuclear Fission PDFDocument14 pages10 3 Nuclear Fission PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 11 3 Logic Gates PDFDocument7 pages11 3 Logic Gates PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Problems of The Week: VisualDocument27 pagesProblems of The Week: VisualRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Community ServiceDocument2 pagesReflection On Community Serviceapi-594729139No ratings yet
- SequencesDocument13 pagesSequencesSai Swetha KVNo ratings yet
- Workbook in Matlh FourthDocument68 pagesWorkbook in Matlh FourthKaren Kichelle Navarro EviaNo ratings yet
- First Grade Mathematics TestDocument34 pagesFirst Grade Mathematics TestLucille Gacutan AramburoNo ratings yet
- Birthday Speech OutlineDocument3 pagesBirthday Speech OutlineSARAH NAJWA BINTI ZAINUDDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Basic 2d Shapes and Their Properties CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources - 95467Document37 pagesBasic 2d Shapes and Their Properties CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources - 95467Desy KamajayaNo ratings yet
- An Elegant Proof of The Pythagoras Theorem PDFDocument7 pagesAn Elegant Proof of The Pythagoras Theorem PDFRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- 'Persistently Dangerous Schools' in New YorkDocument2 pages'Persistently Dangerous Schools' in New YorkQuiana KingNo ratings yet
- Procedure in The Ranking of Honor PupilsDocument15 pagesProcedure in The Ranking of Honor PupilsNormandy MiraflorNo ratings yet
- Geometry BasicsDocument136 pagesGeometry Basicsmrs raamNo ratings yet
- S Puiching01 f3Document7 pagesS Puiching01 f3Llosemi LsNo ratings yet
- Lauda Jerusalem - Vespro - Monteverdi PDFDocument13 pagesLauda Jerusalem - Vespro - Monteverdi PDFJavier Martos CarreteroNo ratings yet
- Setting and ContextDocument11 pagesSetting and Contextapi-237496570No ratings yet
- Christina Hakell Resume 2Document2 pagesChristina Hakell Resume 2api-220398145No ratings yet
- 1st Year Math 1st Test SeriesDocument16 pages1st Year Math 1st Test SeriesSindhu JattNo ratings yet
- 2022 KMT CadetDocument7 pages2022 KMT CadetjeeshikaNo ratings yet
- Nsejs Geometry Sa4Document7 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa4gobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- Personal ProfileDocument8 pagesPersonal Profileapi-323627571No ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument44 pagesFourier SeriesSilverblack ManNo ratings yet
- 21 Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations With Constant CoefficientsDocument24 pages21 Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations With Constant CoefficientsRL EstonaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Algebra 1 Simplifying Exponential Expressions WS2Document4 pagesKeystone Algebra 1 Simplifying Exponential Expressions WS2Jesus PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Missouri Learning Standards For Math 2017Document3 pagesMissouri Learning Standards For Math 2017Cheryl Townsend DickNo ratings yet
- Individual Ranking Sheet For MT IDocument2 pagesIndividual Ranking Sheet For MT IRusty Rjerusalem0% (1)
- CBSE Board Class X Maths Standard Question Paper Solutions 2023Document37 pagesCBSE Board Class X Maths Standard Question Paper Solutions 2023Siddharth SainiNo ratings yet
- Fernanda Sandoval ResumeDocument2 pagesFernanda Sandoval Resumeapi-354338267No ratings yet
- The Learner's Development and Environment: Learning Episode 3Document9 pagesThe Learner's Development and Environment: Learning Episode 3Jovinson LozanoNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis and Post Mortem TemplateDocument11 pagesItem Analysis and Post Mortem TemplateKamahabzanizam Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- Application For Selection As A Deck Cadet & TmeDocument8 pagesApplication For Selection As A Deck Cadet & TmeRajat BasnetNo ratings yet
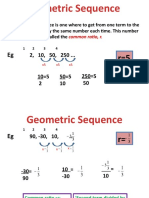
- Grade 12 Geometric Sequence Intro L2Document17 pagesGrade 12 Geometric Sequence Intro L2Sri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet