Professional Documents
Culture Documents
00020
Uploaded by
Christian JaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
00020
Uploaded by
Christian JaraCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1
Internal Medicine
Questions
Questions 1 through 4 A 45-year-old male comes to your office for his first annual checkup in the last 10 years. On first impression, he appears overweight but is otherwise healthy and has no specific complaints. He has a brother with diabetes and a sister with high blood pressure. Both of his parents are deceased and his father died of a stroke at age 73. He is a long-standing heavy smoker and only drinks alcohol on special occasions. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 166/90 in the left arm and 164/88 in the right arm. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. He is concerned about his health and does not want to end up on medication, like his siblings. 1. Regarding your initial recommendations, which of the following would be most appropriate? (A) You should take no action and ask him to return to the clinic in 1 year for a repeat blood pressure check. (B) You should immediately start him on an oral antihypertensive medication and ask him to return to the clinic in 1 week. (C) You should advise him to stop smoking, start a strict diet and exercise routine with the goal of losing weight, and return to the clinic in 6 months. (D) You should consider starting a workup for potential causes of secondary hypertension. (E) You should screen him for diabetes and evaluate him for other cardiovascular risk factors before proceeding any further. 2. In the initial evaluation of a patient such as this, which of the following should be routinely recommended? (A) (B) (C) (D) a urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio an echocardiogram thyroid function tests renal function tests (serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen [BUN]) (E) an exercise stress test
3. Which of the following describes the patients blood pressure status? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) normal blood pressure prehypertension stage 1 hypertension stage 2 hypertension stage 3 hypertension
4. Your patient returns to clinic a few weeks later for a follow-up appointment. Despite having lost 3 lbs and increasing his activity to walking 2 mi three times per week, his blood pressure remains elevated at 162/92. His initial evaluation revealed a fasting blood sugar of 156 and a hemoglobin (Hgb) A1C of 7.5. Along with starting hypoglycemic medications to control his diabetes, you recommend that he take an antihypertensive medication. At this point, you decide to start the patient on hypoglycemic medications to control his diabetes. What other intervention is appropriate at this time? (A) allow more time for the patient to practice lifestyle modifications (B) start treatment with an angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor only (C) start treatment with a thiazide diuretic only (D) start treatment with a beta-blocker only (E) start treatment with a two-drug combination
1
Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Click here for terms of use.
You might also like
- The Chronic Disease of Obesity: How Sponge Syndrome Causes Repeated Weight GainFrom EverandThe Chronic Disease of Obesity: How Sponge Syndrome Causes Repeated Weight GainNo ratings yet
- At the Precipice: My Three-Year Journey from Stroke to Good Health with Type 2 DiabetesFrom EverandAt the Precipice: My Three-Year Journey from Stroke to Good Health with Type 2 DiabetesNo ratings yet
- Panduan Hipertensi JNC 8Document24 pagesPanduan Hipertensi JNC 8Joko RinantoNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Hipertensi + PTO HT +HL 02Document39 pagesContoh Soal Hipertensi + PTO HT +HL 02Arif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Hypertension PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Hypertension PDFFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- GPHC Question Style ReviewDocument33 pagesGPHC Question Style ReviewJonathan BaileyNo ratings yet
- WwhypertensionDocument42 pagesWwhypertensionarif razaNo ratings yet
- 1 QE Competency 1 Therapeutic MOCK Test 1 QA May 2013Document54 pages1 QE Competency 1 Therapeutic MOCK Test 1 QA May 2013Yathrika YathrikaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 QuesDocument12 pagesCH 2 Queslomax13100% (1)
- Hopkins Medicine Review Cardiology SectionDocument54 pagesHopkins Medicine Review Cardiology SectiondrsalilsidhqueNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Managing GG Hypertension: Defining The Barriers To ControlDocument37 pagesCase Studies in Managing GG Hypertension: Defining The Barriers To Controlkirubel deribNo ratings yet
- 1st Case Session ToT CPG HPTDocument124 pages1st Case Session ToT CPG HPThakimahsNo ratings yet
- JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines For The Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsDocument40 pagesJNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines For The Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsArum Nadia HafifiNo ratings yet
- Cardio QuestionsDocument16 pagesCardio QuestionspogichannyNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Complications & Management of Hypertension Questions For StudentsDocument14 pagesDiagnosis, Complications & Management of Hypertension Questions For StudentsJiaYee GoNo ratings yet
- JNC 8Document40 pagesJNC 8Nadira Wulandari100% (1)
- HTN NewDocument22 pagesHTN NewsirishayadavalliNo ratings yet
- CPS2 MED20 Scenario 1Document7 pagesCPS2 MED20 Scenario 1mNo ratings yet
- Section 3Document30 pagesSection 3Nacf NafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Endocrine, Metabolic, and Nutritional Disorders: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChapter 14: Endocrine, Metabolic, and Nutritional Disorders: Multiple ChoiceJamieNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionheadseNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Case StudyDocument8 pagesDiabetic Case Studyrenana12100% (1)
- Studi Kasus HipertensiDocument1 pageStudi Kasus HipertensidaryasanindyaNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet For CandidatesDocument3 pagesInformation Sheet For Candidatesfire_n_iceNo ratings yet
- Make 130 The New 140: Allen N. Miguel, MDDocument49 pagesMake 130 The New 140: Allen N. Miguel, MDMercy Juliana JacqualineNo ratings yet
- NEW Case of Farter-1Document5 pagesNEW Case of Farter-1RahmaNo ratings yet
- All CasesDocument32 pagesAll CasesMona NasrNo ratings yet
- Hypertension - Resident Case FileDocument6 pagesHypertension - Resident Case FileTala MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Week 1 HTN Resident FinalDocument4 pagesWeek 1 HTN Resident Finalbudreaux79No ratings yet
- Section 11. Endocrine and Metabolic ProblemsDocument9 pagesSection 11. Endocrine and Metabolic ProblemsAliNo ratings yet
- Hypertension NCLEX Quiz Questions: A. I Will Make Sure I Consume Foods High in PotassiumDocument5 pagesHypertension NCLEX Quiz Questions: A. I Will Make Sure I Consume Foods High in PotassiumMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of HypertensionDocument2 pagesCase Study of HypertensionRirin RamdhaniNo ratings yet
- 1210 DIASTOLIC HypertensionDocument44 pages1210 DIASTOLIC HypertensionBoysz TheBestNo ratings yet
- M3 TutorialDocument10 pagesM3 TutorialmisswongNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Metabolic Syndrome MOCK Test: Pharmacy PREPDocument26 pagesCardiovascular and Metabolic Syndrome MOCK Test: Pharmacy PREPNOORNo ratings yet
- Quality Improvement Acticity-HypertensionDocument45 pagesQuality Improvement Acticity-HypertensionAicy Joy LarracocheaNo ratings yet
- Exit ExamDocument6 pagesExit ExamKai SibayanNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care Plan IIIDocument20 pagesPharmaceutical Care Plan IIIAdemilola AdekoyaNo ratings yet
- (Clinical Cases Uncovered) - CARDIOLOGY - (2010) - Halaman-202-207Document6 pages(Clinical Cases Uncovered) - CARDIOLOGY - (2010) - Halaman-202-207zizaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 1Document14 pagesMed Surg 1Wendera T. S CooperNo ratings yet
- Med 250Document26 pagesMed 250TrisNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten RhymesDocument15 pagesKindergarten RhymesAkshit R Shah100% (1)
- Hypertension - Student HandoutDocument4 pagesHypertension - Student HandoutEliesther RiveraNo ratings yet
- Pharma Past PaperDocument11 pagesPharma Past PaperMasood MughalNo ratings yet
- Endo QuizDocument3 pagesEndo Quizمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document6 pagesCase Study 1rajambal_ayyasamy0% (1)
- Nbme 5.1Document54 pagesNbme 5.1Hafsa SafdarNo ratings yet
- l01.Htn .CaseDocument29 pagesl01.Htn .CaseFaith Castillo100% (2)
- Makalah HypertensionDocument6 pagesMakalah HypertensionFatin ZafirahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HypertensionDocument6 pagesChapter 32 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HypertensionMichael BoadoNo ratings yet
- JNC 7 &8Document3 pagesJNC 7 &8Calm NewgateNo ratings yet
- Pharm DDocument9 pagesPharm DHesham IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Monitoring The Metabolic Side-Effects of Atypical AntipsychoticsDocument6 pagesMonitoring The Metabolic Side-Effects of Atypical AntipsychoticsAdina OlteanuNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Case ConferenceDocument6 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal Case ConferenceGhazal KangoNo ratings yet
- Jurding KardioDocument40 pagesJurding KardioDesra AufarNo ratings yet
- Universal Prescription in DiabetesDocument4 pagesUniversal Prescription in DiabetesIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Journal EBMDocument12 pagesJournal EBMmairahimadhaniNo ratings yet
- Pebc CVS QuestionnaireDocument53 pagesPebc CVS QuestionnaireNOORNo ratings yet
- INTERNAL MEDICINE - Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesINTERNAL MEDICINE - Cardiovascular SystemAiswaryaNo ratings yet
- How I reversed Type 2 Diabetes, healed from severe neuropathy and lost 41 lbs in six months naturallyFrom EverandHow I reversed Type 2 Diabetes, healed from severe neuropathy and lost 41 lbs in six months naturallyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tiki Taka CK CardiologyDocument46 pagesTiki Taka CK CardiologyChristian Jara100% (2)
- Respiratory Emergencies: Eileen Humphreys PA-C, EMT-IDocument71 pagesRespiratory Emergencies: Eileen Humphreys PA-C, EMT-IChristian JaraNo ratings yet
- Tiki Taka CK CardiologyDocument46 pagesTiki Taka CK CardiologyChristian Jara100% (2)
- Question of The Week # 433: Archer Red 11:25 AM Links To This PostDocument34 pagesQuestion of The Week # 433: Archer Red 11:25 AM Links To This PostChristian JaraNo ratings yet
- Step3 Áß¿äÁ ®Document111 pagesStep3 Áß¿äÁ ®Christian JaraNo ratings yet
- Stress Test1Document13 pagesStress Test1Christian JaraNo ratings yet
- Urology MCQDocument16 pagesUrology MCQChristian Jara80% (5)
- Introduction To Ophthalmology: by DR - Bakhtiar Q. JafDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Ophthalmology: by DR - Bakhtiar Q. JafChristian JaraNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1Christian JaraNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Balance: Daily RequirementsChristian JaraNo ratings yet
- DM Guidelines CCPDocument53 pagesDM Guidelines CCPChristian JaraNo ratings yet
- 100 Test Aarogya 2.0:: Mrs - Nisha KatouriaDocument18 pages100 Test Aarogya 2.0:: Mrs - Nisha KatouriaNisha KathuriaNo ratings yet
- Fire Evacuation Routine and Record Book 2015Document81 pagesFire Evacuation Routine and Record Book 2015Muhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Priorities in Critical Care Nursing 7th Edition Urden Test BankDocument35 pagesPriorities in Critical Care Nursing 7th Edition Urden Test Banklief.tanrec.culjd100% (26)
- GLOBAL MIN-MET - EMS-L2-004 r00 Procedure On Compliance ObligationDocument3 pagesGLOBAL MIN-MET - EMS-L2-004 r00 Procedure On Compliance Obligationjalefaye abapoNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Teach Your Baby Math - Glenn DomanDocument200 pages(PDF) Teach Your Baby Math - Glenn Domansugapovex0% (1)
- Sentinel Node Biopsy For CA BreastDocument7 pagesSentinel Node Biopsy For CA Breastwasima1956No ratings yet
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: Zithromax, Zmax, Z-PakDocument2 pagesNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: Zithromax, Zmax, Z-PakJanet Sheldon50% (2)
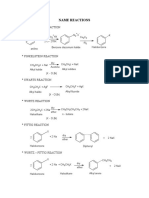
- Name Reactions: Sandmeyer'S ReactionDocument9 pagesName Reactions: Sandmeyer'S ReactionSai Krishnan100% (1)
- Activity Sheet 3 in Science ViDocument4 pagesActivity Sheet 3 in Science ViJohn Cyrel MondejarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document33 pagesChapter 11Niraj DevalNo ratings yet
- Apply Health, Safety and Security Procedures in The WorkplaceDocument9 pagesApply Health, Safety and Security Procedures in The WorkplaceRene EspenocillaNo ratings yet
- Leica LS10 LS15 User ManualDocument106 pagesLeica LS10 LS15 User Manualabdelghafour adjNo ratings yet
- Bollard MarkDocument1 pageBollard MarkAnonymous JZFSB3DNo ratings yet
- People Vs DulinDocument3 pagesPeople Vs DulinRia Evita Revita100% (1)
- Handouts First Aid in MasonryDocument5 pagesHandouts First Aid in MasonryIvyNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Cost AllocationDocument14 pagesChapter4 Cost AllocationNetsanet BelayNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument386 pagesUntitledG PalaNo ratings yet
- RFOC Learner's Guide Page 1-212Document240 pagesRFOC Learner's Guide Page 1-212Travel GnrOneNo ratings yet
- Pigment Overview 26-5-2015Document36 pagesPigment Overview 26-5-2015Phạm Nguyên Phương ChiNo ratings yet
- Plant ClassificationDocument105 pagesPlant ClassificationsjoerjenNo ratings yet
- Fujiwara2011 New Molten Salt Systems For High Temperature Molten Salt Batteries Ternary and QuaternaryDocument7 pagesFujiwara2011 New Molten Salt Systems For High Temperature Molten Salt Batteries Ternary and QuaternaryThirupathi ThippaniNo ratings yet
- LUMBERPUNCTURDocument14 pagesLUMBERPUNCTURRahul VasavaNo ratings yet
- Ka TurayDocument6 pagesKa TurayNizelCalmerinBaesNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia in Lateral Medullary Syndrome ObjavljenDocument10 pagesDysphagia in Lateral Medullary Syndrome ObjavljenMala MirnaNo ratings yet
- Pile Hammer Delmag d12-42Document1 pagePile Hammer Delmag d12-42Jorge Rosero QuevedoNo ratings yet
- Letter To The GuardianDocument3 pagesLetter To The GuardianBelle Princess DuraNo ratings yet
- Sabah Malaysian Borneo Buletin August 2007Document28 pagesSabah Malaysian Borneo Buletin August 2007Sabah Tourism Board100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument6 pagesCranial Nervesvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- 1HDH 118 041 en - Rev. IDocument53 pages1HDH 118 041 en - Rev. IKhắc Đồng Trần100% (1)
- Guidance ProgramDocument4 pagesGuidance ProgramShainajoy BoterNo ratings yet