Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0910sem1 Me3162 PDF
Uploaded by
Chun Ping OngOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
0910sem1 Me3162 PDF
Uploaded by
Chun Ping OngCopyright:
Available Formats
ME3162/ME3162E
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE
ME3162/ME3162E MANUFACTURING PROCESSES (Semester I : AY2009/2010) Time Allowed : 2 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
1.
This examination paper contains ELEVEN (11) questions and comprises TEN (10) printed pages.
2.
Answer ALL questions.
3.
This is an OPEN-BOOK EXAMINATION.
PAGE 2
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 1
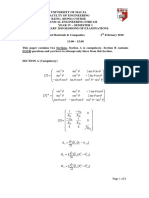
Figure 1 The food container shown on the right in Figure 1 is produced by deep drawing from 1 mm stainless steel sheet. Its diameter is 145 mm and its height is 64 mm. Calculate the smallest number of drawing operations required to produce it. Assume the cup corner radii are relatively sharp (d/r >> 20) and there is no ironing. Neglect friction, and progressively use Cranes constants of 40%, 25%, 15% and 10%, respectively. (6 marks) If the yield strength of the material is 250 MPa, what is the force needed for the first draw? (3 marks) Calculate the punch and die sizes required to produce the blank (taking the allowance as 50 microns and clearance as 10% of thickness). (4 marks) On the left of the picture is the carrier, made of the same material of thickness 1 mm and width 20 mm. How is it produced and joined? Ignore the latch on top. (8 marks)
PAGE 3
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 2
Figure 2 (i) The base of an electric steam iron (Figure 2) is simply a 2 mm aluminium plate with 3 mm holes for the steam to pass through. If the holes have to be dimensionally accurate, which one of these processes would you use? (a) Drilling (b) EDM (c) Piercing with a punch (d) Die cast the plate with the holes in situ (3 marks) If the holes do not need dimensional accuracy, which one of these processes would you use? (a) Drilling (b) EDM (c) Piercing with a punch (d) Die cast the plate with the holes in situ (3 marks) If the holes are only 0.1 mm diameter, which one of these processes would you use? (a) Drilling (b) Piercing with a punch (c) EDM (d) Die cast the plate with the holes in situ (3 marks) If the iron is just an ordinary iron with no holes for steam to pass through, which one of these processes would you use to manufacture the aluminium plates? (a) Rolling and stamping out the shapes (b) Die casting (c) Machining from a sheet (d) Investment casting (3 marks)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
PAGE 4
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 3
Figure 3 Which of the following is the reason why Gillette stainless steel razor blades (shown in Figure 3) must be attached by laser spot welding and not other methods? (a) (b) (c) (d) The blades are too small for joining by other processes Stainless steel is a very good conductor of electricity High accuracy is needed for the weld positions The blades are disposable, so the weld joints need not last long (3 marks) QUESTION 4
Figure 4 The dental equipment shown in Figure 4 is made of low carbon stainless steel. Which one of the following is the most likely process for manufacturing them? (a) (b) (c) (d) Heat the metal, extrude through a hexagonal die, bend to shape Heat the metal, forge to shape using progressive forging dies, trim flash Cold draw the extruded bar through progressive dies, heat the material to above recrystallisation temperature, bend to shape while hot Cold draw the extruded bar through progressive dies, bend to shape at room temperature (3 marks)
PAGE 5
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 5
Figure 5 (i) Each panel of the cast iron filigree decorative structure of this food centre at Lau Pa Sat (shown in Figure 5) is cast in one piece and not joined from several smaller cast iron components. Which are the main reasons? (a) Joining is too time consuming and the melting point of cast iron is too high (b) Cast iron cannot be welded properly and the melting point of cast iron is too high (c) Joining is too time consuming and cast iron cannot be welded properly (d) Joining is too time consuming and the dimensional tolerances are not important (3 marks) (ii) Why is it not made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride)? (5 marks)
PAGE 6
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 6
Figure 6 Figure 6 shows a lectern used for giving speeches. It is made of acrylic, a transparent thermoplastic. Which methods of joining the acrylic plates are suitable? (a) (b) (c) (d) By heat seal or by adhesive By solvent or by friction welding By heat seal or by friction welding By solvent or by adhesive (3 marks)
PAGE 7
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 7
Figure 7 (i) The dustpan shown in Figure 7 is made of polypropylene. What is the most suitable method for manufacturing it is bulk? (2 marks) How would you manufacture the vertical handle if it were hollow PVC (polyvinyl chloride)? (2 marks) How would you manufacture the vertical handle if it were hollow aluminium? (2 marks) How would you manufacture the vertical handle if it were hollow mild steel? (4 marks)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
PAGE 8
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 8
Figure 8 Figure 8 shows a piston from an engine cylinder. It is made of aluminium. Compare its properties if it were produced by forging and by casting. (4 marks)
QUESTION 9 210 mm diameter and 300 mm long steel shafts are to be machined from bars stocks of 225 mm diameter and 400 mm length using a lathe of 100 KW motor running at an efficiency of 50%. The machining time for both roughing and finishing operations should be completed in 12 min. The specific cutting energy ps, for the work material is 2.73 GJ/m3, and the time taken to load and unload a workpiece is 1min. Select proper cutting speeds, feed rates, depth of cuts, tool materials and type of rake angles for both roughing and finishing operations. (14 marks)
PAGE 9
ME3162/ME3162E
QUESTION 10 In a particular turning operation, the cost of the labour and machine time in resetting a cutting edge is $10.00, the cost of each throw-away insert having eight cutting edges is $12.00, and the cost of the insert holder is $800 and it can be used for 1000 inserts. The initial cost of the lathe was $100,000.00 which is amortized for 6 years. Machine running costs including labour and overheads but neglecting depreciation are estimated at $8.00/hr. The Taylor tool-life equation for this turning process is as follows: vt0.25 = 25 where v is the cutting speed (m/s), and t is the tool life (s). Calculate, for minimum cost conditions, the tool life, in seconds and cutting speed in metres per second, if the machine is to be used on a (a) single-shift, 40 h/wk basis, and (b) double-shift, 80 h/wk basis. Assume 50 working weeks per year. (14 marks)
QUESTION 11 (CHOOSE THE RIGHT ANSWER) (i) If aluminium is to be machined in small quantity which of the following tool materials should be economical? (a) (b) (c) (d) Ceramic Tungsten carbide High speed steel Diamond (2 marks) (ii) Which of the following rake angles will should be used to machine hard materials? (a) (b) (c) (d) 15 degrees 5 degrees + 15 degrees + 5 degrees (2 marks) (iii) Which of the following statement is correct? (a) (b) (c) (d) Tool life increases with the increase of cutting speed Tool life decreases with the increase of cutting speed Cutting speed has no influence on tool life None of the above (2 marks)
PAGE 10
ME3162/ME3162E
(v)
Which of the following statement is correct? (a) (b) (c) (d) Tool life is shorter in intermittent/discontinuous machining Tool life is shorter in continuous machining Tool life is not dependent on type of machining None of the above (2 marks)
- END OF PAPER -
You might also like
- Final-Term Examination - First Semester 2018/2019Document3 pagesFinal-Term Examination - First Semester 2018/2019Hossam MohamedNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: (Semester I: AY2012/2013)Document10 pagesNational University of Singapore: (Semester I: AY2012/2013)Haridas SridharanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Exam QuestionsDocument7 pagesManufacturing Processes Exam QuestionsHaridas SridharanNo ratings yet
- EPP201 Pass Paper Revision Questions 1Document9 pagesEPP201 Pass Paper Revision Questions 1Boey Keen HuangNo ratings yet
- 1314sem1-Me3162 Me3162eDocument6 pages1314sem1-Me3162 Me3162eZheng YongjiaNo ratings yet
- Bda 30502 Sem 2 1213Document5 pagesBda 30502 Sem 2 1213Iskandar BellNo ratings yet
- Answer BDA30502 - FINAL 012015Document11 pagesAnswer BDA30502 - FINAL 012015SmithNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Final Exam GuideDocument17 pagesManufacturing Final Exam GuideShah MalikNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesAdvanced Materials Exam QuestionsBernice JohnsonNo ratings yet
- University of Mauritius: Faculty of Engineering Mechanical & Production Engineering DepartmentDocument1 pageUniversity of Mauritius: Faculty of Engineering Mechanical & Production Engineering DepartmentlokiNo ratings yet
- PRDT01C04 Final Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesPRDT01C04 Final Exam QuestionsSherif El-soudyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Tool Design PDFDocument4 pagesAdvanced Tool Design PDFgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Final Examination SEMESTER I, SESSION2014/2015Document13 pagesFinal Examination SEMESTER I, SESSION2014/2015Mohamad Yusuf HelmiNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksDocument3 pagesTime: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- HW 8 Non Traditional Machining Ch26Document2 pagesHW 8 Non Traditional Machining Ch26BobNo ratings yet
- Mech3002y 3 2010 2 PDFDocument5 pagesMech3002y 3 2010 2 PDFKeshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- UTA026Document7 pagesUTA026Panshul SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Me 5 PT 2021Document3 pagesMe 5 PT 2021SameerNo ratings yet
- ME204Document2 pagesME204raja93satNo ratings yet
- Mech3002y 3 2007 2 PDFDocument6 pagesMech3002y 3 2007 2 PDFKeshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- TIE 3213 Assignment 2 (2020) PDFDocument2 pagesTIE 3213 Assignment 2 (2020) PDFphillip chirongwe0% (1)
- BTME 2nd Year AssignmentDocument15 pagesBTME 2nd Year AssignmentshishunalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3M Shahrul IzuanNo ratings yet
- Interim Semester Take HomeDocument7 pagesInterim Semester Take HomeLhekha RaviendranNo ratings yet
- Production Question Set 2 2Document70 pagesProduction Question Set 2 2KBSMANIT89% (19)
- Question Bank (PPII)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (PPII)Udaiyar BarathadhithyaNo ratings yet
- Production Question Set 2Document70 pagesProduction Question Set 2ErKRGautamNo ratings yet
- Adv - Design of Weldments Seme1 2004Document4 pagesAdv - Design of Weldments Seme1 2004mukesh3021No ratings yet
- Final Exam MCT3214 Nov09Document6 pagesFinal Exam MCT3214 Nov09Deerah Aziz100% (1)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Priyadharshan RNo ratings yet
- Tool Life Wear Mach Inability Q A For StudentsDocument13 pagesTool Life Wear Mach Inability Q A For StudentsRavinder Antil100% (4)
- r05322001 Tool DesignDocument8 pagesr05322001 Tool DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Question Bank Set - 2 PDFDocument69 pagesQuestion Bank Set - 2 PDFsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Singapore Polytechnic: Engineering Materials IDocument8 pagesSingapore Polytechnic: Engineering Materials IsubipuruNo ratings yet
- MF 441 ProcessPlanning and Cost Estimation Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesMF 441 ProcessPlanning and Cost Estimation Exam QuestionsMohan MKNo ratings yet
- End Sem PyqDocument5 pagesEnd Sem PyqJaspreet veeraNo ratings yet
- CAD Modelling and Structural Anaysis of A DieDocument21 pagesCAD Modelling and Structural Anaysis of A DieWaseem ShameerNo ratings yet
- Mech3002y 3 2015 2Document7 pagesMech3002y 3 2015 2Keshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- Core Classification Materials CoresDocument26 pagesCore Classification Materials CoresThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- 114 DM 052017Document2 pages114 DM 052017Ravindra JeeviNo ratings yet
- MEC330Document2 pagesMEC330gowthamNo ratings yet
- Production Technology March 2021Document8 pagesProduction Technology March 2021LuckyNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes ExplainedDocument7 pagesMetal Forming Processes ExplainedAida Syauqina Ibrahim 7BNo ratings yet
- Model Answer - Sheet (1&2)Document17 pagesModel Answer - Sheet (1&2)YSMHXSTS SYTMXSNo ratings yet
- 2022-Dec ME-312 53Document2 pages2022-Dec ME-312 53Aakash TiwariNo ratings yet
- TYPE A - Real Time Quiz End Semester Examination - ME331Document7 pagesTYPE A - Real Time Quiz End Semester Examination - ME331Selvi RNo ratings yet
- Mee 210-Ipe 210.Document2 pagesMee 210-Ipe 210.dreamivory29No ratings yet
- MP Assignment-VIDocument1 pageMP Assignment-VIRaja HarisNo ratings yet
- Slip TestDocument3 pagesSlip TestSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering-Estimating and Costing MAR-APRIL 2021Document4 pagesIndustrial Engineering-Estimating and Costing MAR-APRIL 2021Sai Radha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- NUST Manufacturing Engineering AssignmentsDocument4 pagesNUST Manufacturing Engineering AssignmentsNativity MabasaNo ratings yet
- Test Project Sheet MetalDocument10 pagesTest Project Sheet MetalSyed Idrus Syed OmarNo ratings yet
- Guide to Eyelet Drawing ProcessDocument49 pagesGuide to Eyelet Drawing ProcessPra Vee33% (3)
- PRODUCTIONTECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesPRODUCTIONTECHNOLOGYSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Time: 1:30 Hrs Max. Marks: 20: B. Tech. (PE) Fourth Semester Class Test-2 (March - 2021) Me-262 Machine Design - IDocument2 pagesTime: 1:30 Hrs Max. Marks: 20: B. Tech. (PE) Fourth Semester Class Test-2 (March - 2021) Me-262 Machine Design - Ionline onlineNo ratings yet
- Master Glenium SKY 8108: High Range Water Reducing AdmixtureDocument2 pagesMaster Glenium SKY 8108: High Range Water Reducing Admixturedana setiawanNo ratings yet
- HHD-S Cavity anchor installation guideDocument2 pagesHHD-S Cavity anchor installation guideIngeniero Miguel VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Bulk Sampling of Liquid Uranium Hexafluoride: Standard Practice ForDocument4 pagesBulk Sampling of Liquid Uranium Hexafluoride: Standard Practice Formohammed ;arasnehNo ratings yet
- Mahaa One RMC: Er - Nanthakumar Boomi Textile MillsDocument19 pagesMahaa One RMC: Er - Nanthakumar Boomi Textile MillsMAHAA ONE RMC RAMASAMY MNo ratings yet
- Bayer Process Diagram ExplainedDocument6 pagesBayer Process Diagram ExplainednatsmdNo ratings yet
- Application of Permeable Pavements in Highways ForDocument15 pagesApplication of Permeable Pavements in Highways ForYEGAR SAHADUTA HEBZIBAH K 08211942000015No ratings yet
- PCC Technova Series CPL Cylindrical ValvesDocument5 pagesPCC Technova Series CPL Cylindrical ValvesAnju VijayanNo ratings yet
- Rheological Properties of Some Oil Based Muds Used in Reservoirs in The Niger Delta, NigeriaDocument6 pagesRheological Properties of Some Oil Based Muds Used in Reservoirs in The Niger Delta, NigeriaNurfatini CheNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Dioxide PDFDocument4 pagesChlorine Dioxide PDFSudhakar Rao100% (1)
- Applied Thermodynamics For Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument19 pagesApplied Thermodynamics For Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- Gyproc Plasters: Product CatalogueDocument24 pagesGyproc Plasters: Product CatalogueFariz AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Duct Tape and Insulation Tape GuideDocument2 pagesDuct Tape and Insulation Tape GuideDhanish AhsenNo ratings yet
- Development of An Electrochemical Metal-Ion Biosensor Using Self-Assembled Peptide NanofibrilsDocument7 pagesDevelopment of An Electrochemical Metal-Ion Biosensor Using Self-Assembled Peptide NanofibrilsRenan Guilherme de Oliveira GuihNo ratings yet
- Aashto M288Document29 pagesAashto M288jong_hao_su5167% (3)
- Aci 318-14 RC-BM-001Document7 pagesAci 318-14 RC-BM-001Bunkun15No ratings yet
- Figure 1: Basic Design of Fluidized-Bed ReactorDocument3 pagesFigure 1: Basic Design of Fluidized-Bed ReactorElany Whishaw0% (1)
- Physico-chemical characteristics of corrosion scales in old iron pipesDocument9 pagesPhysico-chemical characteristics of corrosion scales in old iron pipesGustavo Alejandro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Evalene LF20185Document2 pagesEvalene LF20185Oscar Tan IIINo ratings yet
- BS en Iso 9712 Standard CodeDocument17 pagesBS en Iso 9712 Standard CodeVilam Ndt100% (1)
- Why nanocrystals get softer with decreasing grain sizeDocument8 pagesWhy nanocrystals get softer with decreasing grain sizeSaadFarooqNo ratings yet
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocument25 pagesThe Particle Nature of MatterMaria bonny aquinoNo ratings yet
- Angora Wool: Ultra-Soft Fiber From RabbitsDocument2 pagesAngora Wool: Ultra-Soft Fiber From RabbitsYogen Garbiyal100% (1)
- Hapter: Occurrence of Noble GasesDocument10 pagesHapter: Occurrence of Noble GasesSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Exp. 4 LipidsDocument6 pagesExp. 4 LipidsAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Slon Magnetic Separators Applied in TheDocument8 pagesSlon Magnetic Separators Applied in TheMulti DELLNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2015 1Document1 pageAssignment 2015 1manishNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2, WK 6 - Module 6Document41 pagesScience: Quarter 2, WK 6 - Module 6Ericha Solomon73% (11)
- CLP Regulation (EC) No. 1272-2008 On The Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures PDFDocument1 pageCLP Regulation (EC) No. 1272-2008 On The Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures PDFCan YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet for Penguard HB - Comp. ADocument5 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Penguard HB - Comp. ABalasubramanian AnanthNo ratings yet
- CPVC - Cat VIKING Conexiones UL FM BlazemasterDocument28 pagesCPVC - Cat VIKING Conexiones UL FM BlazemasterpvaldezmtzNo ratings yet