Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QP Firstyear Supply Nov09 Classical Mechanics PDF
Uploaded by
kalirajgurusamyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QP Firstyear Supply Nov09 Classical Mechanics PDF
Uploaded by
kalirajgurusamyCopyright:
Available Formats
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 1
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. A rod AB shown in Figure 1 is held by a ball and socket joint at A and supports a mass C weighing 1200 N at end B. The rod is in x-y plane and is inclined to y axis at an angle of 150 . The rod is 10 m long and has negligible weight. Find the forces in the cables DF and EB. [16]
Figure 1 2. Five strings are tied at a point and are pulled in all directions, equally spaced, from one another. If the magnitude of the pulls on three consecutive strings is 70 N, 40 N and 55 N respectively, nd graphically the magnitude of the pulls on two other strings, if the system is in equilibrium. [16] 3. Determine the volume of the body shown in gure 3 using Pappus-Guldinus theorem. [16]
1 to of remove 3 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 1
Figure 3 4. Find the product of inertia about X and Y axes of the area as shown in gure 4.
Figure 4 5. (a) Write down the assumptions made while nding out the forces in various members of a framed structure. (b) Find the forces in all the members of a structure shown in gure 5b. [6+10]
2 to of remove 3 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 1
Figure 5b 6. A helicopter is descending vertically downward with a uniform velocity. At a certain instant, a food packet is dropped from it which takes 6 secs to reach the ground. As this packet strikes the ground, another food packet is dropped from it, which takes 5 secs to reach he ground. Find the velocity with which the helicopter is descending and its height, when second packet is dropped. Also nd the distance traveled by the helicopter during the interval of dropping the packets. [16] 7. A bullet is red straight up from the surface of the moon with an initial velocity 620 m/s. Determine the mass elevation reached by the bullet. (a) Assuming a uniform gravitational eld with g = 1.782 m/s2 (b) using Newtons law of gravitation. (Radius of moon = 1750 km). [16]
8. The central deection of a simply supported beam with a central point load is given by S = PL3 / 48EI. Where L = 5 M, E = 2 105 N/mm2 , I = 1.73 105 m4 . The beam is of uniform cross section with a static load P. Determine (a) equivalent spring constant of the beam (b) the frequency of vibration of a 60kg block attached to the centre of the beam. Neglect the mass of the beam and assume that the load remaining in contact with the beam. [16]
3 to of remove 3 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 2
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. Determine and locate the resultant R of the forces and one couple acting on the beam as shown in gure 1. [16]
Figure 1 2. A force F with a magnitude of 150 N is applied at the origin O of the axes x, y and z as shown in Figure 2. The line of action of F passes through a point A whose co-ordinates are 2 m, 4 m and 6 m. Determine (a) the x, y, and z scalar components of F (b) the projection of F on x-y plane, and (c) the projection of F along the line OB. [16]
Figure 2 1 to of remove 3 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 2
3. (a) Find the centroid of the L section shown in gure 3a.
Figure 3a (b) Determine the Co-ordinates of the centroid of the shaped area OAB shown in gure 3b. [8+8]
Figure 3b 4. Calculate the moment of inertia of the L section shown in gure 4 with respect the controidal x-axis and y axis. [16]
Figure 4 5. Find the axial forces in all the members of a truss shown in gure 5. [16]
2 to of remove 3 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 2
Figure 5 6. (a) Dene curvilinear linear motion of a particle. (b) Show that the system of the eective forces for a rigid slab in plane motion reduces to a single vector, and express the distance from the mass center G of the slab to the line of action of this vector in terms of the centroidal radius of gyration k of the slab, the magnitude a of the acceleration of G, and the angular acceleration . [4+12] 7. (a) A 500kg communications satellite is in a circular geosynchronous orbit and complete one revolution about the earth in 23 hrs and 58min at an attitude of 35800 km above the surface of the earth. The radius of the earth is 6510km. Determine the Kinetic energy of the satellite. (b) Express the acceleration of gravity g at an altitude h above the surface of the earth in terms of the acceleration of gravity go . at the surface the earth, the altitude h, and the radius R of the earth. [8+8] 8. The central deection of a simply supported beam with a central point load is given by S = PL3 / 48EI. Where L = 5 M, E = 2 105 N/mm2 , I = 1.73 105 m4 . The beam is of uniform cross section with a static load P. Determine (a) equivalent spring constant of the beam (b) the frequency of vibration of a 60kg block attached to the centre of the beam. Neglect the mass of the beam and assume that the load remaining in contact with the beam. [16]
3 to of remove 3 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 3
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
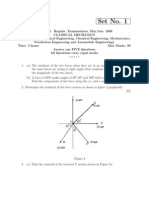
1. (a) Four parallel forces of magnitudes 25 N, 50 N, 75 N and 100 N are shown in Figure 1a. Determine the magnitude of the resultant and also the distance of the resultant from point A.
Figure 1a (b) Two forces of 2kN and 5kN with an included angle of 300 between the lines of action act at a point A. Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant. [8+8] 2. A force F with a magnitude of 150 N is applied at the origin O of the axes x, y and z as shown in Figure 2. The line of action of F passes through a point A whose co-ordinates are 2 m, 4 m and 6 m. Determine (a) the x, y, and z scalar components of F (b) the projection of F on x-y plane, and (c) the projection of F along the line OB. [16]
1 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 3
Figure 2 3. Find the centroid of the area shown gure 3. [16]
Figure 3 4. Find the moment of inertia of the plane area shown in gure 4 about X and Y axes through its centroid. [16]
2 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 3
Figure 4 5. A pin jointed frame is supported at A and B and loaded as shown in gure 5. Find the forces in all the members of the frame and state in each case, whether the force is tensile or compressive. [16]
Figure 5 6. (a) What is the relation between initial velocity, nal velocity and displacement of a particle under the action of a constant force? (b) A particle is projected to move along a parabola y2 = 4x. At a certain instant, when passing through a point P (4, 4) its speed is 5 m/S and the rate of increase of its speed is 3 m/S2 along the path. Express the velocity and acceleration of the particle in terms of rectangular coordinately. [6+10] 7. A block rests on a horizontal surface as shown in gure 7 It is acted on by an applied force P. (a) If the block is initially at rest, nd the velocity of the block when t = 6s (b) Verify the result in part (a) by direct use of Newtons second law. [16]
3 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 3
Figure 7 8. The central deection of a simply supported beam with a central point load is given by S = PL3 / 48EI. Where L = 5 M, E = 2 105 N/mm2 , I = 1.73 105 m4 . The beam is of uniform cross section with a static load P. Determine (a) equivalent spring constant of the beam (b) the frequency of vibration of a 60kg block attached to the centre of the beam. Neglect the mass of the beam and assume that the load remaining in contact with the beam. [16]
4 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 4
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. A rod AB shown in Figure 1 is held by a ball and socket joint at A and supports a mass C weighing 1200 N at end B. The rod is in x-y plane and is inclined to y axis at an angle of 150 . The rod is 10 m long and has negligible weight. Find the forces in the cables DF and EB. [16]
Figure 1 2. A force F with a magnitude of 150 N is applied at the origin O of the axes x, y and z as shown in Figure 2. The line of action of F passes through a point A whose co-ordinates are 2 m, 4 m and 6 m. Determine (a) the x, y, and z scalar components of F (b) the projection of F on x-y plane, and (c) the projection of F along the line OB. [16]
1 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 4
Figure 2 3. Find the centroid of the area shown gure 3. [16]
Figure 3 4. Find the moment of inertia of the plane area shown in gure 4 about X and Y axes through its centroid. [16]
2 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 4
Figure 4 5. Find the axial forces in all the members of a truss shown in gure 5. [16]
Figure 5 6. (a) The motion of a particle is given by the relation x = t2 - (t - 3)2 where x and t are expressed in metres and records, respectively. Determine: i. When the acceleration is zero ii. The position and velocity of the particle at that time. (b) The motion of a particle is dened by the relation x = t2 - (t - 1)3 when x and t are expressed is m and sec, respectively. Determine i. the two positions at which the velocity is zero 3 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
Code No: Z0321/R07
Set No. 4
[8+8]
ii. the total distance traveled by the particle from t = 0 to t = 2s.
7. (a) A particle which moves in rectilinear translation is acted upon by a resultant force R. i. ii. iii. iv. Give the form of the impulse-momentum equation for the particle What is the linear momentum of the particle? What are the units of linear momentum? What is the graphical interpretation of an impulse?
(b) Give the equation for the conservation of linear momentum of two particles which move in rectilinear translation. What is signicant limitation of the equation. [8+8] 8. The central deection of a simply supported beam with a central point load is given by S = PL3 / 48EI. Where L = 5 M, E = 2 105 N/mm2 , I = 1.73 105 m4 . The beam is of uniform cross section with a static load P. Determine (a) equivalent spring constant of the beam (b) the frequency of vibration of a 60kg block attached to the centre of the beam. Neglect the mass of the beam and assume that the load remaining in contact with the beam. [16]
4 to of remove 4 Please purchase PDF Split-Merge on www.verypdf.com this watermark.
You might also like
- Engineering MechanicsqpDocument14 pagesEngineering MechanicsqpKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics March 2014r13Document14 pagesEngineering Mechanics March 2014r13api-248483124No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics EquationsDocument16 pagesEngineering Mechanics Equationsgovind4ever5No ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument18 pagesEngineering MechanicsSiva ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- QB-em-1 - Mem202Document19 pagesQB-em-1 - Mem202rahuljaiswal1931No ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Document6 pagesStructural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Michael BlairNo ratings yet
- April 2011 2008Document7 pagesApril 2011 2008Piyush BhandariNo ratings yet
- TSM101 (SS2019) - Set ADocument9 pagesTSM101 (SS2019) - Set ANgeedup DhojeeNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument15 pagesEngineering Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics AME1103Document4 pagesEngineering Mechanics AME1103Ravi Kiran GotetiNo ratings yet
- Second Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. TechDocument7 pagesSecond Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. Techlatendra kumar srivastavNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument37 pagesEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- 152AH052019Document4 pages152AH052019చిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిNo ratings yet
- rr10105 Applied MechanicsDocument13 pagesrr10105 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 7W 11bt11202022 PDFDocument22 pages7W 11bt11202022 PDFNagarjuna KonduruNo ratings yet
- WWW Manaresults Co inDocument3 pagesWWW Manaresults Co inravi maskeNo ratings yet
- Ge 131 - Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument3 pagesGe 131 - Engineering Mechanics Question BankAnonymous RJfsy8PtNo ratings yet
- 1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsDocument11 pages1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsSaivenkat PenuguduruNo ratings yet
- Module1 - Set 1aDocument2 pagesModule1 - Set 1aindhubalab200413chNo ratings yet
- Be First Year Fe Engineering Semester 1 2019 November Engineering Mechanics Pattern 2019Document6 pagesBe First Year Fe Engineering Semester 1 2019 November Engineering Mechanics Pattern 2019Bhairavi MoreNo ratings yet
- nov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂Document14 pagesnov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂badboy_rockssNo ratings yet
- Me2151 QBDocument18 pagesMe2151 QBDhinakaran VeemanNo ratings yet
- r/10 V/MS: 82 AL/Structural Question/PDocument7 pagesr/10 V/MS: 82 AL/Structural Question/P林柄洲No ratings yet
- Structure Analysis I Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesStructure Analysis I Exam QuestionsSreNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Question - Paper JntukDocument3 pagesMechanics Question - Paper JntukVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Dec 2013Document11 pagesEngineering Mechanics Dec 2013api-248483124No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Subject Code: R161111/R16 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Nov. - 2016 Set No - 1Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Subject Code: R161111/R16 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Nov. - 2016 Set No - 1nagarama kotaiahNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics July 2021Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics July 2021DANDEM SAIRAMNo ratings yet
- R13 Engineering Mechanics TitleDocument3 pagesR13 Engineering Mechanics TitlePrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS MODEL QUESTION PAPERDocument7 pagesSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS MODEL QUESTION PAPERreynanbelendhran23No ratings yet
- 121ac - Engineering MechanicsDocument3 pages121ac - Engineering MechanicsSayyadh Rahamath BabaNo ratings yet
- INPHO Solved Paper 2013Document31 pagesINPHO Solved Paper 2013Pankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics Assign MentsDocument11 pagesEngg Mechanics Assign Mentsdayanand moreNo ratings yet
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDocument9 pagesPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertNo ratings yet
- PU Exam Paper KME 402Document2 pagesPU Exam Paper KME 402daso khagoNo ratings yet
- Applied MechanicsDocument13 pagesApplied Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- Serial No. A-Gse-P-Hqb: Please Read Each o F The Following Instructions Carefully Before Attempting QuestionsDocument8 pagesSerial No. A-Gse-P-Hqb: Please Read Each o F The Following Instructions Carefully Before Attempting QuestionsShyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument8 pagesEngineering MechanicsUgender SingarapuNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis (SA)Document7 pagesStructural Analysis (SA)Richa SinghNo ratings yet
- Forces in members of a trussed structureDocument8 pagesForces in members of a trussed structureSrikrishna JanaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1011 (Nov)Document10 pagesEngineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1011 (Nov)Amirul AizatNo ratings yet
- BIT MESRA RANCHI DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MECHANICS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SHEET 1Document34 pagesBIT MESRA RANCHI DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MECHANICS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SHEET 1monumunduriNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodsDocument12 pagesFinite Element Methodspraneeth4a100% (1)
- R05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™Document12 pagesR05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™badboy_rockssNo ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument14 pagesClassical MechanicsinaylakNo ratings yet
- FE6Document109 pagesFE6Jyoti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- From Microstructure Investigations to Multiscale Modeling: Bridging the GapFrom EverandFrom Microstructure Investigations to Multiscale Modeling: Bridging the GapDelphine BrancherieNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualFrom EverandPressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- The Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandThe Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Awakening Article 4Document4 pagesAwakening Article 4kalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Mechanical EngineeringDocument16 pagesA A A A A: Mechanical Engineeringmanikantar15No ratings yet
- Awakening Article 3Document4 pagesAwakening Article 3kalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Mday December 10 2012 PDFDocument1 pageMday December 10 2012 PDFkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Newspaper Article XVDocument12 pagesNewspaper Article XVkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- The High Performance EntrepreneurDocument29 pagesThe High Performance Entrepreneurkalirajgurusamy100% (1)
- Qeme PDFDocument33 pagesQeme PDFmeetbalakumarNo ratings yet
- Apr 15Document118 pagesApr 15kalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- My Philosophies of LifeDocument11 pagesMy Philosophies of LifekalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- A.E. (Mechanical Engineering I) 2007Document24 pagesA.E. (Mechanical Engineering I) 2007Mukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Report For: Home My Test My ProfileDocument5 pagesSolution Report For: Home My Test My ProfilekalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Asia Report 2016 OnlineDocument21 pagesAsia Report 2016 OnlinekalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 2 PDFDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper 2 PDFfotickNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Chapt 14Document25 pagesChapt 14kalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument12 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- 1D Finite Element IIDocument15 pages1D Finite Element IIthanhphucbr87No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Machine Elements: Powerpoint PresentationkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Anti InfectiveDocument9 pagesAnti InfectiveMae DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Vendors for H.T. Line MaterialsDocument587 pagesVendors for H.T. Line MaterialsAnonymous RjIueYSlNo ratings yet
- DIY Underground Greenhouse For Organic FarmingDocument29 pagesDIY Underground Greenhouse For Organic Farmingwire-of-Information100% (7)
- TaguigDocument25 pagesTaguigChan ReyNo ratings yet
- TCD42A10N0Document1 pageTCD42A10N0jeancharfan8353No ratings yet
- Descriptive Text Purpose:: ( (: The Use of Adjectives and Compound AdjectivesDocument3 pagesDescriptive Text Purpose:: ( (: The Use of Adjectives and Compound AdjectivesEka Nur Laela Mar'atus SholikhaNo ratings yet
- Key Benefits: Benefit TableDocument12 pagesKey Benefits: Benefit TableRaaj ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cylinder Configuration: Options TabDocument4 pagesAdvanced Cylinder Configuration: Options TabJose RattiaNo ratings yet
- Activity1 Group6Document4 pagesActivity1 Group6Castor, Cyril Nova T.No ratings yet
- Electronic Properties of Band-Inverted HeterojunctionsDocument7 pagesElectronic Properties of Band-Inverted HeterojunctionsArmapezoNo ratings yet
- University of Calgary: New Measurement-While-Drilling Surveying Technique Utilizing Sets of Fiber Optic Rotation SensorsDocument289 pagesUniversity of Calgary: New Measurement-While-Drilling Surveying Technique Utilizing Sets of Fiber Optic Rotation SensorsJames ConnerNo ratings yet
- Micro Programmable Logic Controller: User's ManualDocument643 pagesMicro Programmable Logic Controller: User's Manualcasmadi casmadiNo ratings yet
- U.K. Shakyawar - ERDMPDocument32 pagesU.K. Shakyawar - ERDMPPanchdev KumarNo ratings yet
- QAQC Objective & Key Career AchievementsDocument3 pagesQAQC Objective & Key Career Achievementssaffririzal4237100% (2)
- High Performance Epoxy Tile GroutDocument3 pagesHigh Performance Epoxy Tile GroutShaik J MohamedNo ratings yet
- Snow White Is A Gangster (MHSG Sequel) COMPLETEDDocument459 pagesSnow White Is A Gangster (MHSG Sequel) COMPLETEDReign Candarell67% (3)
- Canal of Nuck Hernia in An Elderly Patient A Case ReportDocument8 pagesCanal of Nuck Hernia in An Elderly Patient A Case ReportAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy - NCS, Mumbai UniversityDocument28 pagesSolar Energy - NCS, Mumbai UniversityVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet - Grade 10Document14 pagesPhysics Worksheet - Grade 10Faran AssifNo ratings yet
- Frac SandDocument3 pagesFrac Sandcrazy boyNo ratings yet
- Jamaica Kincaid NotesDocument16 pagesJamaica Kincaid NotesDaniela Gomez RiveraNo ratings yet
- Helling2014 - Ton That Tung's LiversDocument8 pagesHelling2014 - Ton That Tung's Livershoangducnam100% (1)
- Mail From Yoichi Shimatsu Regarding Nano Travel 04 Jan 2022Document4 pagesMail From Yoichi Shimatsu Regarding Nano Travel 04 Jan 2022tavdeash238No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle (Scitable)Document2 pagesCell Cycle (Scitable)LibrofiloNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Types of PollutionsDocument14 pagesAir Pollution: Types of PollutionsJia Ping Jia PingNo ratings yet
- Guitar Interactive 25 2014 Gus GDocument302 pagesGuitar Interactive 25 2014 Gus GNeil Carroll100% (1)
- Black Metal Distortion Guitar PatchDocument1 pageBlack Metal Distortion Guitar PatchPedro Carmelo SoaresNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Design Rev-0Document2 pagesSwimming Pool Design Rev-0Haytham Samir75% (4)
- How To Increase Flow In Lamy Fountain PensDocument21 pagesHow To Increase Flow In Lamy Fountain PensPHILL.MARTIN3356No ratings yet
- Studies of Religion - Islam 2Document3 pagesStudies of Religion - Islam 2Lachlan BrownNo ratings yet