Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Tetralogy of Fallot?: Congenital Heart Defect
Uploaded by
Glenn Asuncion PagaduanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Tetralogy of Fallot?: Congenital Heart Defect
Uploaded by
Glenn Asuncion PagaduanCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy (teh-TRAL-o-je) of Fallot (fah-LO) is a congenital heart defect. This is a problem with the heart's structure that's present at birth. Congenital heart defects change the normal flow of blood through the heart. Tetralogy of Fallot is a rare, complex heart defect. It occurs in about 5 out of every 10,000 babies. The defect affects boys and girls equally. To understand tetralogy of Fallot, it helps to know how a healthy heart works. The Health Topics How the Heart Works article describes the structure and function of a healthy heart. The article also has animations that show how your heart pumps blood and how your heart's electrical system works.
Overview
Tetralogy of Fallot involves four heart defects:
A large ventricular septal defect (VSD) Pulmonary (PULL-mun-ary) stenosis Right ventricular hypertrophy (hi-PER-tro-fe) An overriding aorta
Ventricular Septal Defect
The heart has an inner wall that separates the two chambers on its left side from the two chambers on its right side. This wall is called a septum. The septum prevents blood from mixing between the two sides of the heart. A VSD is a hole in the septum between the heart's two lower chambers, the ventricles. The hole allows oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to mix with oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle.
Pulmonary Stenosis
This defect involves narrowing of the pulmonary valve and the passage from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. Normally, oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle flows through the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary artery. From there, the blood travels to the lungs to pick up oxygen. In pulmonary stenosis, the pulmonary valve cannot fully open. Thus, the heart has to work harder to pump blood through the valve. As a result, not enough blood reaches the lungs.
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
With this defect, the muscle of the right ventricle is thicker than usual. This occurs because the heart has to work harder than normal to move blood through the narrowed pulmonary valve.
Overriding Aorta
This defect occurs in the aorta, the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. In a healthy heart, the aorta is attached to the left ventricle. This allows only oxygenrich blood to flow to the body. In tetralogy of Fallot, the aorta is located between the left and right ventricles, directly over the VSD. As a result, oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle flows directly into the aorta instead of into the pulmonary artery.
Outlook
With tetralogy of Fallot, not enough blood is able to reach the lungs to get oxygen, and oxygenpoor blood flows to the body.
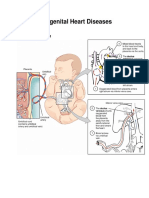
Cross-Section of a Normal Heart and a Heart With Tetralogy of Fallot
Figure A shows the structure and blood flow inside a normal heart. Figure B shows a heart with the four defects of tetralogy of Fallot.
Babies and children who have tetralogy of Fallot have episodes of cyanosis (si-ah-NO-sis). Cyanosis is a bluish tint to the skin, lips, and fingernails. It occurs because the oxygen level in the blood leaving the heart is below normal. Tetralogy of Fallot is repaired with open-heart surgery, either soon after birth or later in infancy. The timing of the surgery will depend on how narrow the pulmonary artery is. Over the past few decades, the diagnosis and treatment of tetralogy of Fallot have greatly improved. Most children who have this heart defect survive to adulthood. However, they'll need lifelong medical care from specialists to help them stay as healthy as possible.
You might also like
- #15 Review and NACC Final ExaminationDocument3 pages#15 Review and NACC Final ExaminationGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies Promoting Active Learning in Healthcare EducationDocument14 pagesTeaching Strategies Promoting Active Learning in Healthcare EducationGlenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Tetralogy of Fallot Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Lesson PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument93 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseManjunatha HR100% (1)
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument28 pagesTetralogy of FallotArdyansyah Nasution, M.DNo ratings yet
- Free Logical Reasoning Questions AnswersDocument13 pagesFree Logical Reasoning Questions AnswersIdhonna Abihay100% (1)
- Your Name 407-111 Your Street, City, ProvinceDocument1 pageYour Name 407-111 Your Street, City, ProvincemmottolaNo ratings yet
- Kerry Layne Author Albert Ferro Author 100 Cases in Clinical PharmacologyDocument249 pagesKerry Layne Author Albert Ferro Author 100 Cases in Clinical Pharmacologyteju100% (3)
- What is Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesWhat is Tetralogy of FallotJamaica Cruz San Pedro100% (1)
- What Is Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesWhat Is Tetralogy of FallotJyedenn PonceNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesTetralogy of FallotMiLody NajeNo ratings yet
- TOFDocument17 pagesTOFMaryel PascualNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot Is A Combination of Four Congenital AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Is A Combination of Four Congenital AbnormalitiesJoanne TolopiaNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot ExplainedDocument9 pagesTetralogy of Fallot ExplainedLaurice BarronNo ratings yet
- 12 - Semiotics of Cardiovascular Disorders. Semiotics of Congenital Hert Diseases in Children.Document30 pages12 - Semiotics of Cardiovascular Disorders. Semiotics of Congenital Hert Diseases in Children.Omowunmi KadriNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument38 pagesTetralogy of FallotJohn Paul MedalloNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument28 pagesTetralogy of FallotconcozNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument8 pagesTetralogy of FallotHillary Faye FernandezNo ratings yet
- Tricuspid Atresia Heart Defect ExplainedDocument5 pagesTricuspid Atresia Heart Defect ExplainedCassyDelaRosaNo ratings yet
- CVS - Session 3 - CHDDocument3 pagesCVS - Session 3 - CHDkotecha.rheaNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument9 pagesTetralogy of FallotPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- TOF Pathophysiology ExplainedDocument30 pagesTOF Pathophysiology ExplainedArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument28 pagesTetralogy of FallotLaurice Grace Zamayla BaelNo ratings yet
- Atrial Septal DefectDocument5 pagesAtrial Septal DefectalmorsNo ratings yet
- TOF Heart Defect Guide: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument8 pagesTOF Heart Defect Guide: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatmentdecembergirl92No ratings yet
- TYPES OF HEART DEFECTSDocument11 pagesTYPES OF HEART DEFECTSJuliet Marie MiomioNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument5 pagesTetralogy of FallotCharity OaniaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Tetralogy of Fallot: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Tetralogy of Fallot: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentJoanna Bee Rose MagyawiNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot Heart Defect ExplainedDocument26 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Heart Defect ExplainedMaria VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot: What Is It?Document3 pagesTetralogy of Fallot: What Is It?Anditha Namira RSNo ratings yet
- 1) Understand The Basic Development of The Heart and Great VesselsDocument7 pages1) Understand The Basic Development of The Heart and Great VesselsFizza HussainNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Stenosis: Narrowing of The Pulmonary Valve and Outflow Tract or Area BelowDocument1 pagePulmonary Stenosis: Narrowing of The Pulmonary Valve and Outflow Tract or Area BelowGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot.......Document7 pagesTetralogy of Fallot.......Sam AlipioNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot: (A Congenital Heart Disease)Document7 pagesTetralogy of Fallot: (A Congenital Heart Disease)Sunil Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument7 pagesTetralogy of FallotAshok Kumar JangirNo ratings yet
- What Are Congenital Heart Defects?Document15 pagesWhat Are Congenital Heart Defects?Echi InartiangatNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument6 pagesTetralogy of FallotArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AathifDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System Aathifl881539No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Dr. Eman Badr 2020Document182 pagesCardiovascular System Dr. Eman Badr 2020Amina DinarNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot FinaleDocument8 pagesTetralogy of Fallot FinaledawnieciousNo ratings yet
- Lapkas Dian and DamboDocument34 pagesLapkas Dian and DamboDian Primadia PutriNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument31 pagesTetralogy of FallotAnditha Namira RS100% (1)
- How The Heart Works: Septum Lungs OxygenDocument22 pagesHow The Heart Works: Septum Lungs OxygenSuzan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Transposition of Great Artery: 1. AbstractDocument7 pagesTransposition of Great Artery: 1. AbstractA. Fajar AprianiNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot SP B.inggrisDocument19 pagesTetralogy of Fallot SP B.inggrisSoraya VerinaNo ratings yet
- Tricuspid AtresiaDocument14 pagesTricuspid AtresiaPretty AjursNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease Is One or More Problems With The Heart's Structure ThatDocument37 pagesCongenital Heart Disease Is One or More Problems With The Heart's Structure Thatneelimawanker chinnariNo ratings yet
- Conginital Heart DiseaseDocument19 pagesConginital Heart DiseaseSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing NCM 103 DeliverablesDocument6 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing NCM 103 DeliverablesNoelle HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Embryology of the Heart Tube FormationDocument65 pagesEmbryology of the Heart Tube Formationnisha24No ratings yet
- What Causes Increased Pulmonary Blood FlowDocument11 pagesWhat Causes Increased Pulmonary Blood FlowJc Pauline PabustanNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument10 pagesTetralogy of FallotanggiehardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument7 pagesTetralogy of FallotWidelmark FarrelNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot: Normal Heart FunctionDocument4 pagesTetralogy of Fallot: Normal Heart FunctionSoekarno HattaNo ratings yet
- TOF Patient EducationDocument8 pagesTOF Patient EducationMia MiaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Atrial Septal Defect and Ventricular Septal DefectDocument28 pagesCase Report: Atrial Septal Defect and Ventricular Septal DefectDian Primadia PutriNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument31 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseSandeep ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Tetrallogy of FallotDocument33 pagesPresentation ON Tetrallogy of Fallotvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument65 pagesTetralogy of FallotEndrati WidiastutiNo ratings yet
- Cardiopatias CongenitasDocument4 pagesCardiopatias CongenitasKEVIN SANTIAGO SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Acquired Heart DXDocument39 pagesAcquired Heart DXFauziana Abd JabarNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Diseases, A Simple Guide to these Medical ConditionsFrom EverandCongenital Heart Diseases, A Simple Guide to these Medical ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Mitral Stenosis (A Heart Valve Disease), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Mitral Stenosis (A Heart Valve Disease), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lecture EndocrineDocument16 pagesNursing Lecture EndocrineAedge010100% (3)
- Diagnostic Exam All Areas 2016Document37 pagesDiagnostic Exam All Areas 2016Glenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Certification: Esther C. Remigio, M.DDocument2 pagesCertification: Esther C. Remigio, M.DGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Glenn A. Pagaduan: Registered NurseDocument3 pagesGlenn A. Pagaduan: Registered NurseGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- 15 Toughest Interview Questions and Answers!: 1. Why Do You Want To Work in This Industry?Document8 pages15 Toughest Interview Questions and Answers!: 1. Why Do You Want To Work in This Industry?johnlemNo ratings yet
- Pediatric BulletsDocument36 pagesPediatric Bulletswinner gift flowersNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion ActivityDocument1 pageHealth Promotion ActivityGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Dec GlennDocument2 pagesDec GlennGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- The Nursing ProcessDocument1 pageThe Nursing ProcessGedyn OlaerNo ratings yet
- Overview CyanideDocument3 pagesOverview CyanideGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument30 pagesPharmacologyapi-3818438100% (3)
- For People Like Kiko PangilinanDocument4 pagesFor People Like Kiko PangilinanGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Summary of CancerDocument8 pagesSummary of CancerGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- AdeyemiDocument2 pagesAdeyemiGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Bedside TeachingDocument13 pagesBedside TeachingGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Villaverde ChapterDocument1 pageVillaverde ChapterGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- DOH Nurse Deployment Project 2014 Application FormDocument1 pageDOH Nurse Deployment Project 2014 Application FormjamieboyRNNo ratings yet
- DohDocument10 pagesDohGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- GGBBDocument4 pagesGGBBGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Assessing and Evaluating Learning Outcomes (Edited)Document11 pagesStrategies For Assessing and Evaluating Learning Outcomes (Edited)Glenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- BookkeepingDocument11 pagesBookkeepingGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Microskills Clinical TeachingDocument5 pagesMicroskills Clinical TeachingGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Transsphenoidal Hypophysectomy March 2014Document3 pagesTranssphenoidal Hypophysectomy March 2014Glenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Knowing in NursingDocument1 pageActivity 2 Knowing in NursingGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Dwarfism: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pagesPituitary Dwarfism: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal KurapDocument3 pagesJurnal Kurapbunga farnadaNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Digestive-SystemDocument179 pagesCH 14 Digestive-SystemAntonio Calleja IINo ratings yet
- Disease Research PaperDocument6 pagesDisease Research PaperJose PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Singkatan MedisDocument16 pagesSingkatan MedisfarizaNo ratings yet
- Blood ReportDocument15 pagesBlood ReportSaadNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Score Sheet For CASE Write-UpDocument30 pagesFaculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Score Sheet For CASE Write-UpJared Khoo Er HauNo ratings yet
- Overview HyperparatiroidDocument5 pagesOverview HyperparatiroiddyahNo ratings yet
- Lesson A 6-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesLesson A 6-WPS OfficeRestuNo ratings yet
- ABC Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesABC Lecture NotesLady Shayne YapNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument10 pagesIntroductionNareman Alaa50% (2)
- Respiratory AcidosisDocument5 pagesRespiratory Acidosisapi-376421583% (6)
- Review of Influenza as a Seasonal and Pandemic DiseaseDocument12 pagesReview of Influenza as a Seasonal and Pandemic DiseaseFreddy SueroNo ratings yet
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome inDocument17 pagesMyofascial Pain Syndrome inEdogawa RakhmanNo ratings yet
- Generi Life Physician Statement FormDocument1 pageGeneri Life Physician Statement FormVennus RacraquinNo ratings yet
- Chinese Herbal Medicine For RelaxationDocument9 pagesChinese Herbal Medicine For RelaxationLinda PrideNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Allergic Contact DermatitisDocument5 pagesEtiology of Allergic Contact DermatitisChichi Dita VirllianaNo ratings yet
- Designated Medical Event Dme List enDocument3 pagesDesignated Medical Event Dme List enAmany HagageNo ratings yet
- Complete Physical Exam AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesComplete Physical Exam Abbreviationseal772328No ratings yet
- Calorimetría Indirecta EsencialDocument12 pagesCalorimetría Indirecta EsencialPaulina ToledoNo ratings yet
- Rehab Advances for Spinal Cord InjuriesDocument45 pagesRehab Advances for Spinal Cord InjurieskaushikawebNo ratings yet
- 9164 62159 1 PBDocument12 pages9164 62159 1 PBjenegneNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Nursing QuizDocument15 pagesFundamental of Nursing QuizDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (1)
- 2023 - ACRM - Diagnositc - CriteriaDocument13 pages2023 - ACRM - Diagnositc - CriteriaRobinNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaDocument30 pagesLaporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaShifa Ali JannatinNo ratings yet
- JevaxDocument2 pagesJevaxjovedNo ratings yet
- " Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics" "Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics"Document7 pages" Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics" "Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics"kookiescreamNo ratings yet
- Dinakaran 2017Document16 pagesDinakaran 2017Chirac OanaNo ratings yet
- Mrcem Primary June 2022 Recalls Compiled by DR Sumair HameedDocument4 pagesMrcem Primary June 2022 Recalls Compiled by DR Sumair HameedSHK100% (1)
- Overview of Digestive System 16-01-23Document20 pagesOverview of Digestive System 16-01-23erisericssonNo ratings yet