Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isopropanol Identification
Uploaded by
AlisameimeiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Isopropanol Identification
Uploaded by
AlisameimeiCopyright:
Available Formats
More information: http://www.guidechem.com/cas-67/67-63-0.
html
Isopropanol Identification
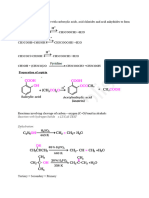
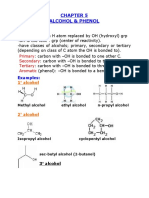
Isopropanol is a common name for a chemical compound with the molecular formula C3H8O or C3H7OH. It is a colorless, flammable chemical compound with a strong odor. It is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms sometimes shown as (CH3)2CHOH. It is a structural isomer of propanol. Isopropanol is denatured for certain uses, in which case the NFPA 704 rating is changed to 2,3,1. Name:Isopropanol EINECS:200-661-7 Molecular Formula:C3H8O CAS Registry Number:67-63-0 Appearance:colourless liquid Molecular Weight:60.09 Density:0.785 Boiling Point:81-83 Melting Point:-89.5 Flash Point:12 Storage Temperature:Flammables area Refractive index:1.376-1.378 Solubility:Miscible Chemical Properties: colourless liquid with slight alcohol odour Usage: When compared to ethanol, 50% less is required for nucleic acid precipitation, thus minimizing the total volume to be centrifuged for DNA or RNA recovery.
More information: http://www.guidechem.com/cas-67/67-63-0.html
Usage: Suitable for HPLC, spectrophotometry, environmental testing General Description :Volatile, colorless liquid with a sharp musty odor like rubbing alcohol. Flash point of 53F. Vapors are heavier than air and mildly irritating to the eyes, nose, and throat. Density approximately 6.5 lb / gal. Used in making cosmetics, skin and hair preparations, pharmaceuticals, perfumes, lacquer formulations, dye solutions, antifreezes, soaps, window cleaners. Sold in 70% aqueous solution as rubbing alcohol. Air & Water Reactions: Highly flammable. Water soluble. Reactivity Profile: Isopropanol reacts with air or oxygen to form dangerously unstable peroxides. Contact with 2-butanone increases the rate of peroxide formation. An explosive reaction occurs when Isopropanol is heated with (aluminum isopropoxide + crotonaldehyde). Forms explosive mixtures with trinitromethane and hydrogen peroxide. Reacts with barium perchlorate to form a highly explosive compound. Ignites on contact with dioxygenyl tetrafluoroborate, chromium trioxide and potassium-tert-butoxide. Vigorous reactions occur with (hydrogen + palladium), nitroform, oleum, COCl2, aluminum triisopropoxide and oxidizing agents. Reacts explosively with phosgene in the presence of iron salts. Incompatible with acids, acid anhydrides, halogens and aluminum . Isopropanol can react with PCl3, forming toxic HCl gas. Health Hazard: Vapors cause mild irritation of eyes and upper respiratory tract; high concentrations may be anesthetic. Liquid irritates eyes and may cause injury; harmless to skin; if ingested causes drunkenness and vomiting. Fire Hazard: highly flammable , Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
You might also like
- LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) - MsdsDocument3 pagesLPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) - MsdsN KannanNo ratings yet
- Rest Part of AlcoholsDocument6 pagesRest Part of Alcoholswww.seemasainirox123No ratings yet
- Week 8 Monohydric Alcohols ClassificationDocument8 pagesWeek 8 Monohydric Alcohols Classificationsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolDocument59 pagesHydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Alcohol EtherDocument104 pagesChap 2 Alcohol EtherNurhazimah Adibah EdrisNo ratings yet
- Ss2 WK 10 Hydrocarbon and Crude OilDocument8 pagesSs2 WK 10 Hydrocarbon and Crude Oilamakaemilia5No ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument9 pagesHydroxy Compoundschong56No ratings yet
- Alkohol...Document47 pagesAlkohol...R.Afr26 0403No ratings yet
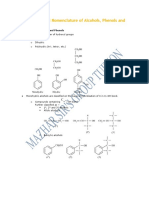
- Classification and Nomenclature of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesClassification and Nomenclature of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- 11.3B AlcoholsDocument34 pages11.3B AlcoholsЕлнур ИкимбаевNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Phenols A Level A2 Chemistry CIEDocument4 pagesReactions of Phenols A Level A2 Chemistry CIErayaNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I (MPC 102T) UNIT-III: Synthetic Reagents & ApplicationsDocument13 pagesADVANCED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I (MPC 102T) UNIT-III: Synthetic Reagents & ApplicationsZofishanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols ChemistryDocument24 pagesAlcohols ChemistryBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Alcoholpresentation 111029054727 Phpapp01Document27 pagesAlcoholpresentation 111029054727 Phpapp01Namra SarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, EthersDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, Ethersjane kangNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Alcohols 13-18Document6 pagesHydrocarbons Derivatives - Alcohols 13-18Ahmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 11 NotesHibba IsrarNo ratings yet
- DDT and BHC PesticidesDocument5 pagesDDT and BHC PesticidesAleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2) 1.1 Pro BackgroundDocument20 pages2) 1.1 Pro BackgroundMohd AizatNo ratings yet
- Phenols: Ahmet Kaan Dikici 03130021005Document23 pagesPhenols: Ahmet Kaan Dikici 03130021005Ahmet Kaan DikiciNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document10 pagesExp 7Nuur HidayahNo ratings yet
- Isopropanol ProductionDocument51 pagesIsopropanol Productionيزيد العزانيNo ratings yet
- Methanol Project PDFDocument50 pagesMethanol Project PDFPaola Nair M ChNo ratings yet
- Pengertian Alkohol, Sifat, Kegunaan, Isomer, Dampak, Bahaya, Pembuatan, Sintesis, Identifikasi, KimiaDocument45 pagesPengertian Alkohol, Sifat, Kegunaan, Isomer, Dampak, Bahaya, Pembuatan, Sintesis, Identifikasi, KimiaTitin solihatNo ratings yet
- Midterms Quiz 1 (Acao)Document3 pagesMidterms Quiz 1 (Acao)Natasha AcaoNo ratings yet
- Alcohol & Phenol: Primary Secondary Tertiary AromaticDocument32 pagesAlcohol & Phenol: Primary Secondary Tertiary AromaticcikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Pollutants Pulp FinalDocument3 pagesPollutants Pulp FinalLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol, and Ethers:: "Their Structures, Physical Properties and Nomenclature"Document33 pagesAlcohol, Phenol, and Ethers:: "Their Structures, Physical Properties and Nomenclature"AmanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Alcohols Phenols Ethers NotesDocument23 pagesClass 12 Alcohols Phenols Ethers NotesIpsita SethiNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDocument10 pagesCape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideAshli GrantNo ratings yet
- MSDS BenzolDocument11 pagesMSDS Benzolasnandy100% (2)
- Organic Compounds Classification and PropertiesDocument14 pagesOrganic Compounds Classification and PropertiesakshodhiniNo ratings yet
- Production Of Methanol From Natural GasDocument219 pagesProduction Of Methanol From Natural GasMary Grace VelitarioNo ratings yet
- Propylene DerivativesDocument25 pagesPropylene DerivativesMahendraTorati100% (1)
- Alcohols NotesDocument4 pagesAlcohols Notesjohn mNo ratings yet
- Alcohols ChemistryDocument12 pagesAlcohols ChemistryDIEGO ANTONIO ABITIA NU�EZNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Phenol Structures and PropertiesDocument5 pagesAlcohol and Phenol Structures and PropertiesFableNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL PROPERTIESDocument51 pagesCHEMICAL PROPERTIESMemeowwNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument20 pagesPhenolUmar TahirNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Structure and Synthesis 2Document82 pagesAlcohols-Structure and Synthesis 2Diana Cárdenas MuñozNo ratings yet
- Identification of Alcohols and PhenolsDocument15 pagesIdentification of Alcohols and PhenolsSALIFU91% (22)
- Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Properties of Organic CompoundsDocument18 pagesLaboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Properties of Organic CompoundsSaraNo ratings yet
- 3B Reactions of Alcohols and ThiolsDocument27 pages3B Reactions of Alcohols and ThiolsAnloraine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AreneDocument37 pagesArene'Aqilah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Document28 pages5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Marivic TayabanNo ratings yet
- Unit 11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark Questions: Ans: EthanolDocument10 pagesUnit 11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark Questions: Ans: EthanolDeva RajNo ratings yet
- Redox WrkshtsDocument5 pagesRedox WrkshtsMaxine TaeyeonNo ratings yet
- Alcohol molecul-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesAlcohol molecul-WPS OfficeUSCLOUD MINERNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Thiol and EtherDocument8 pagesAlcohol, Thiol and EtherbatacsidneyemmanuelNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument91 pagesAlcoholsWAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNo ratings yet
- Organic MCQ 2010 ANS Updated 22-05-2013Document100 pagesOrganic MCQ 2010 ANS Updated 22-05-2013Turfy YanNo ratings yet
- Dahdahchemlab ProjDocument3 pagesDahdahchemlab ProjXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy Compounds: (Alcohols)Document71 pagesHydroxy Compounds: (Alcohols)NorsyazaEdmiraNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument34 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersJoshua Johnson100% (2)
- Alco and PhenoDocument5 pagesAlco and PhenofastrackeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesBuana SandilaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument21 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EtherAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ALCOHOLDocument65 pagesChapter 1 ALCOHOLNURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NOR100% (1)
- F322 AlcoholsDocument9 pagesF322 AlcoholsDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Cyclohexanone ApplicationDocument2 pagesCyclohexanone ApplicationAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Beta-Carotene Sources in The DietDocument2 pagesBeta-Carotene Sources in The DietmeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of sulfur Sulfur (α)Document2 pagesAllotropes of sulfur Sulfur (α)AlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- How Does Docetaxel WorksDocument3 pagesHow Does Docetaxel WorksAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Where can you buy Sulfur (α)Document2 pagesWhere can you buy Sulfur (α)AlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Information About Sulfamic AcidDocument3 pagesInformation About Sulfamic AcidAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- What's MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesWhat's MetronidazoleAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- The Studies of CyclohexanoneDocument3 pagesThe Studies of CyclohexanonemeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- Intro to Sulfur (α)Document3 pagesIntro to Sulfur (α)AlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Sulfamic AcidDocument2 pagesChemical Properties of Sulfamic AcidAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Intro To Calcium FormateDocument2 pagesIntro To Calcium FormateAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Benzyl AlcoholDocument2 pagesIdentification of Benzyl AlcoholAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- What's Folic AcidDocument2 pagesWhat's Folic AcidAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Accelerating Calcium Formate and Calcium ChlorideDocument2 pagesAccelerating Calcium Formate and Calcium ChlorideAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Sulfuric AcidDocument3 pagesHazard of Sulfuric AcidAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- CompoundsZinc ChlorideDocument2 pagesCompoundsZinc ChlorideAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Information About Zinc ChlorideDocument2 pagesInformation About Zinc ChlorideAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Sulfuric AcidDocument3 pagesIdentification of Sulfuric AcidAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- The Application of 1,2,3-PropanetriolDocument2 pagesThe Application of 1,2,3-PropanetriolAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Identification of 1,2,3-PropanetriolDocument2 pagesIdentification of 1,2,3-PropanetriolAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Calcium Carbonate PropertiesDocument2 pagesCalcium Carbonate PropertiesAlisameimeiNo ratings yet
- Russian Overkill WeaponsDocument35 pagesRussian Overkill WeaponsJuris Poet100% (1)
- Geoactive 290Document4 pagesGeoactive 290Cath LeslieNo ratings yet
- 12 Film ReviewsDocument4 pages12 Film ReviewsFulguraNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesScience 5 Reaction PaperJan GoNo ratings yet
- Flame Arresters: The Last Line of DefenseDocument6 pagesFlame Arresters: The Last Line of DefenseArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Us3320883 PDFDocument3 pagesUs3320883 PDFchecolonoskiNo ratings yet
- Peril in Pompeii! - 240213 - 114920Document2 pagesPeril in Pompeii! - 240213 - 114920Tanakha MaziwisaNo ratings yet
- Before The Atomic BombDocument6 pagesBefore The Atomic BombhistoryfreaksNo ratings yet
- Bath School DisasterDocument7 pagesBath School Disasterapi-491093397No ratings yet
- All About ZXCDocument27 pagesAll About ZXCapi-314239332No ratings yet
- ChernobylDocument4 pagesChernobylhweta173No ratings yet
- GYSDocument24 pagesGYSsyaiful.idzwanNo ratings yet
- Flash Point Fire Rescue Illustrated Cheat SheetDocument1 pageFlash Point Fire Rescue Illustrated Cheat SheetSamuel Lam100% (1)
- 1972 nuclear tests on Glade Park shook residents and earthDocument3 pages1972 nuclear tests on Glade Park shook residents and earthmtnmike73No ratings yet
- Asphalt Emulsion: Material Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesAsphalt Emulsion: Material Safety Data Sheetsmanoj354No ratings yet
- Nuclear ProliferationDocument39 pagesNuclear ProliferationDasuni De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Zanette and TaylorDocument2 pagesZanette and TaylorLVNewsdotcomNo ratings yet
- Random Cypher Additional Effect: Click Here To Randomize!Document21 pagesRandom Cypher Additional Effect: Click Here To Randomize!Ramon DulesNo ratings yet
- Forces of Valor Battle Tactics Game RulesDocument5 pagesForces of Valor Battle Tactics Game Rulessupergrover6868No ratings yet
- STORIES OF THE UNDEAD INFERNODocument14 pagesSTORIES OF THE UNDEAD INFERNOAnonymous YjP3GZYXNo ratings yet
- Big Fireworks ExplosionDocument4 pagesBig Fireworks Explosiondimi danNo ratings yet
- QRA Rule SetDocument3 pagesQRA Rule Setamollakare100% (1)
- 709 Turbocharger ExplosionDocument2 pages709 Turbocharger ExplosionTimmyJuriNo ratings yet
- Blizzard of Glass Book Report 1Document3 pagesBlizzard of Glass Book Report 1api-269004789No ratings yet
- Explosives Akhavan PDFDocument196 pagesExplosives Akhavan PDFbbnchem86% (7)
- Explosive Compaction PDFDocument2 pagesExplosive Compaction PDFJustin100% (1)
- Chernobyl Case Study: World's Worst Nuclear AccidentDocument3 pagesChernobyl Case Study: World's Worst Nuclear AccidentHarry PotterNo ratings yet
- Thuoret Et. Al. 2007Document24 pagesThuoret Et. Al. 2007Roger WaLtersNo ratings yet
- The Mexico City Explosion of 1984 FinalDocument18 pagesThe Mexico City Explosion of 1984 FinalAnoop PrajapatiNo ratings yet