Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macro Chap 20 & 21
Uploaded by
vivianguo23Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Macro Chap 20 & 21
Uploaded by
vivianguo23Copyright:
Available Formats
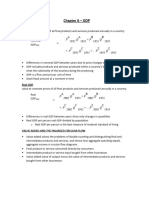
MACROECONOMICS CHAP 20 Unemployment rate = #U/#LF Frictional unemployment = short-term unemployment that arises from the process of matching
workers with jobs Structural unemployment = unemployment that arises from a persistent mismatch between the skills and attributes of workers and the requirements of jobs Cyclical unemployment = unemployment caused by a business cycle recession Natural rate of unemployment = the normal rate of unemployment, consisting of frictional unemployment plus structural unemployment Inflation rate = the percentage increase in the price level from one year to the next Consumer price index (CPI) = an average of the prices of the goods and services purchased by the typical urban family of four CPI = (Expenditures in the current year / Expenditures in the base year) x 100 Four biases that cause changes in CPI to overstate true inflation rate by 0.5 percentage point to 1 percentage point: Substitution bias Increase in quality bias New product bias Outlet bias
Producer price index (PPI) = an average of the prices received by producers of goods and services at all stages of the production process MACROECONOMICS CHAP 21 Business cycle = alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession Long-run economic growth = the process by which rising productivity increases the average standard of living (real GDP per capita)
Long-run economic growth due to: Technology (patents, R&D) Capital accumulation Human capital (education)
Increases in real GDP per capita depend on increases in labor productivity. Labor productivity = the quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of worked Capital = manufactured goods that are used to produce other goods and services Technology = processes a firm uses to turn inputs into outputs of goods and services Potential GDP = the level of real GDP attained when all firms are producing at capacity To calculate how many years it will take real GDP per capita to double: Rule of 70 Number of years to double = 70/Growth rate Business cycle
Real GDP increase smoothly in an expansion to a business cycle peak and then decreases smoothly in a recession to a business cycle trough, which is followed by another expansion. A recession = losing 2 quarters of output Y = C + I + G + NX Closed economy: Y = C + I + G Sprivate = Y + TR C T Spublic = T G TR S = Sprivate + Spublic
S=YCG S=I In the case of a budget deficit, T < G + TR (public saving is negative)
You might also like
- Macro-Economic Concepts and National Income Identities World Bank InstituteDocument23 pagesMacro-Economic Concepts and National Income Identities World Bank InstituteRitika GargNo ratings yet
- Review SessionDocument7 pagesReview SessionKelvin LamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandFundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Labour ProductivityDocument2 pagesLabour Productivityabdul WahabNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- VIVADocument6 pagesVIVAkoushikNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Remigio G. TiambengDocument40 pagesRemigio G. TiambengRaissa Ericka RomanNo ratings yet
- Labor ProductivityDocument13 pagesLabor ProductivityMaleeha WaheedNo ratings yet
- Chap 23Document11 pagesChap 23Phạm Hồng Trang Alice -No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document6 pagesChapter 6bbm12345678900No ratings yet
- Economics For Engineers - Final 1Document20 pagesEconomics For Engineers - Final 1Umut KocabayNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics IIA ECON20401: Paul MiddleditchDocument39 pagesMacroeconomics IIA ECON20401: Paul MiddleditchMara PopescuNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Ganesh Kumar NDocument44 pagesMacroeconomics Ganesh Kumar NRahul AuddyNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 NotesDocument15 pagesModule - 4 NotesKrishnaprabha K TNo ratings yet
- Eco202 Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesEco202 Exam Reviewaoi.ishigaki101No ratings yet
- 2 1 The Level of Overall Economic ActivityDocument3 pages2 1 The Level of Overall Economic ActivityjohnssNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting PPT at MBADocument58 pagesNational Income Accounting PPT at MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- 2 National Accounting - Lecture 2.Ppt (Autosaved)Document32 pages2 National Accounting - Lecture 2.Ppt (Autosaved)Darren MgayaNo ratings yet
- What Is National Final)Document49 pagesWhat Is National Final)Tong KakitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - National Income AccountsDocument49 pagesLecture 2 - National Income AccountsPia Tanya UyNo ratings yet
- GDP RevisedDocument27 pagesGDP RevisedtamiokdNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Fundamental Concepts of Macroeconomics and Macroeconomic ProblemsDocument33 pagesChapter Six: Fundamental Concepts of Macroeconomics and Macroeconomic ProblemsOromay EliasNo ratings yet
- 1.GDP&NationalIncome (54) - Read-OnlyDocument32 pages1.GDP&NationalIncome (54) - Read-Onlykunjal pasariNo ratings yet
- Productivity Engineering and ManagementDocument28 pagesProductivity Engineering and Managementبسمة أمل33% (3)
- Productivity ModelsDocument8 pagesProductivity ModelsSuhas FundeNo ratings yet
- Productivity NotesDocument30 pagesProductivity NotesPhoneix12No ratings yet
- Chapter Six: MacroeconomicsDocument51 pagesChapter Six: MacroeconomicsetNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 4Document51 pagesPrinciples of Economics 4reda gadNo ratings yet
- Economics PresentationDocument28 pagesEconomics PresentationVibhor JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 The Level of Overall Economic ActivityDocument8 pagesChapter 8 The Level of Overall Economic ActivityHieptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI Macroeconomics PartDocument44 pagesChapter VI Macroeconomics PartBereket MuniyeNo ratings yet
- 2Document118 pages2Arpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument20 pagesNational IncomeoggyNo ratings yet
- Assignment AnswerDocument12 pagesAssignment AnswerPg HandmadesNo ratings yet
- NI Acounting - FDocument33 pagesNI Acounting - Fmonalishas_1No ratings yet
- Ch08 - National Income AccountingDocument37 pagesCh08 - National Income AccountingSarah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Macro NotesDocument28 pagesMacro NotesAlexis RheinNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 8 Determination of Gross Domestic ProductDocument50 pagesLearning Unit 8 Determination of Gross Domestic ProductKelvinNo ratings yet
- Macro EcDocument34 pagesMacro EcSeymaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument26 pagesNational IncomerajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Economics FormulasDocument8 pagesEconomics FormulasInam AghaNo ratings yet
- 07 Macro GDP GDPDeflator CPI InflationDocument6 pages07 Macro GDP GDPDeflator CPI InflationAaryan ModiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - MacroeconomyDocument33 pagesQuiz 1 - Macroeconomysantiago.paredes.molinaNo ratings yet
- ECON1011 Principles of Economics Agrarian Reform Taxation: National Income AccountingDocument10 pagesECON1011 Principles of Economics Agrarian Reform Taxation: National Income AccountingJan Mark MujalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2definition SetDocument3 pagesUnit 2definition SetFathimath ShiunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - GDP and CPI - EngDocument48 pagesChapter2 - GDP and CPI - EngvietzergNo ratings yet
- Measuring The EconomyDocument34 pagesMeasuring The EconomyJoanaMarie CaisipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7Kajal YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document23 pagesLecture 9Hyder AliNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument13 pagesNational IncomeEashwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Measuring The National Income AccountsDocument23 pagesMeasuring The National Income AccountsSchmelNo ratings yet
- Ch08 - National Income AccountingDocument58 pagesCh08 - National Income AccountingDhruv PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Measuring GDP and Economic GrowthDocument4 pagesChapter 20 Measuring GDP and Economic GrowthAnsonNo ratings yet
- Mee - 2 - Data of Macro (2013) - ClassDocument60 pagesMee - 2 - Data of Macro (2013) - Classsnata92No ratings yet
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product) GrowthDocument6 pagesGDP (Gross Domestic Product) GrowthBilal Hussain LonghaniNo ratings yet
- AP MacroEconomics Study GuideDocument14 pagesAP MacroEconomics Study GuideRon GorodetskyNo ratings yet
- Productivity ManagementDocument21 pagesProductivity ManagementDebajani DeoriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - The Is-Lm/Ad-As ModelDocument20 pagesChapter 9 - The Is-Lm/Ad-As Modelvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Group Ex Fall 2014Document2 pagesGroup Ex Fall 2014vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Bribery PDFDocument10 pagesBribery PDFvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Labor Capital Natural Resources Entrepreneur Entrepreneurial AbilityDocument3 pagesLabor Capital Natural Resources Entrepreneur Entrepreneurial Abilityvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chap 04 PDFDocument34 pagesChap 04 PDFvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Lecture Sept 30Document1 pageLecture Sept 30vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Trade-Offs, Comparative Advantage, and The Market System: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument28 pagesTrade-Offs, Comparative Advantage, and The Market System: Chapter Summary and Learning Objectivesvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document3 pagesChapter 10vivianguo23No ratings yet
- Economic Growth, The Financial System, and Business Cycles: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument24 pagesEconomic Growth, The Financial System, and Business Cycles: Chapter Summary and Learning Objectivesvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chap 05 PDFDocument28 pagesChap 05 PDFvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chap 03 PDFDocument30 pagesChap 03 PDFvivianguo23No ratings yet
- The Total Market Value of All Final Goods and Services Produced Within The Borders of An Economy in A Given YearDocument4 pagesThe Total Market Value of All Final Goods and Services Produced Within The Borders of An Economy in A Given Yearvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Technology, Production, and Costs: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesTechnology, Production, and Costs: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesseriosulyawksomNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 PDFDocument28 pagesChap 10 PDFvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Review SheetDocument1 pageReview Sheetvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chap 15 PDFDocument30 pagesChap 15 PDFvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument33 pagesFirms in Perfectly Competitive Markets: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesseriosulyawksomNo ratings yet
- Unemployment and Inflation: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument27 pagesUnemployment and Inflation: Chapter Summary and Learning Objectivesvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Long-Run Economic Growth: Sources and Policies: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument25 pagesLong-Run Economic Growth: Sources and Policies: Chapter Summary and Learning Objectivesvivianguo23No ratings yet
- GDP: Measuring Total Production and Income: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesGDP: Measuring Total Production and Income: Chapter Summary and Learning Objectivesvivianguo23No ratings yet
- PNP Ki in July-2017 AdminDocument21 pagesPNP Ki in July-2017 AdminSina NeouNo ratings yet
- Existentialism in LiteratureDocument2 pagesExistentialism in LiteratureGirlhappy Romy100% (1)
- Calculus For The Life Sciences 2nd Edition Greenwell Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesCalculus For The Life Sciences 2nd Edition Greenwell Solutions ManualSharonPerezozqy100% (56)
- Angel C. Delos Santos: Personal DataDocument8 pagesAngel C. Delos Santos: Personal DataAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Seizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Document14 pagesSeizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Sulaman AbdelaNo ratings yet
- Brahms Symphony No 4Document2 pagesBrahms Symphony No 4KlausNo ratings yet
- John Wren-Lewis - NDEDocument7 pagesJohn Wren-Lewis - NDEpointandspaceNo ratings yet
- Omnitron CatalogDocument180 pagesOmnitron Catalogjamal AlawsuNo ratings yet
- Cpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3Document128 pagesCpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3christianwood0117No ratings yet
- Ti05001 PDFDocument1 pageTi05001 PDFanggieNo ratings yet
- LFF MGDocument260 pagesLFF MGRivo RoberalimananaNo ratings yet
- EX200Document7 pagesEX200shubbyNo ratings yet
- PGCRSM-01-BLOCK-03 Research Design ExperimentalDocument29 pagesPGCRSM-01-BLOCK-03 Research Design ExperimentalVijilan Parayil VijayanNo ratings yet
- Etextbook PDF For Pharmacology Connections To Nursing Practice 3rd EditionDocument61 pagesEtextbook PDF For Pharmacology Connections To Nursing Practice 3rd Editionkarla.woodruff22798% (45)
- L5V 00004Document2 pagesL5V 00004Jhon LinkNo ratings yet
- Procter and Gamble - MarketingDocument10 pagesProcter and Gamble - MarketingIvana Panovska100% (5)
- X - WORMWOOD EVENT IMMEDIATE - Paranormal - 4chanDocument7 pagesX - WORMWOOD EVENT IMMEDIATE - Paranormal - 4chanAnonymous dIjB7XD8ZNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management 2012 of HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LTD.Document98 pagesWorking Capital Management 2012 of HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LTD.Pratyush Dubey100% (1)
- Body Systems Portfolio - Tommy JDocument8 pagesBody Systems Portfolio - Tommy Japi-554072790No ratings yet
- Reaserch On Effect of Social Media On Academic Performance: Study On The Students of University of DhakaDocument27 pagesReaserch On Effect of Social Media On Academic Performance: Study On The Students of University of DhakaFatema Tuz Johoora88% (114)
- 32 Hyderabad HITEC City BisleriDocument23 pages32 Hyderabad HITEC City BisleriSridhar ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: The University of Lahore (Islamabad Campus)Document3 pagesStrategic Marketing: The University of Lahore (Islamabad Campus)Sumaira IrshadNo ratings yet
- LLM Letter Short LogoDocument1 pageLLM Letter Short LogoKidMonkey2299No ratings yet
- KMKT Pra PSPM ANS SCHEMEDocument16 pagesKMKT Pra PSPM ANS SCHEMEElda AldaNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject Proposaljiaclaire2998100% (1)
- CTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Document45 pagesCTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Resort1.7 Mri100% (1)
- Resistance & Resistivity: Question Paper 1Document15 pagesResistance & Resistivity: Question Paper 1leon19730% (1)
- Duo Interpretation Class PresentationDocument31 pagesDuo Interpretation Class PresentationPlanetSparkNo ratings yet
- Lesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446Document9 pagesLesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446BruntNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1John Patrick Famadulan100% (1)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationFrom EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- Workin' Our Way Home: The Incredible True Story of a Homeless Ex-Con and a Grieving Millionaire Thrown Together to Save Each OtherFrom EverandWorkin' Our Way Home: The Incredible True Story of a Homeless Ex-Con and a Grieving Millionaire Thrown Together to Save Each OtherNo ratings yet
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentFrom EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (92)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereFrom EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- When Helping Hurts: How to Alleviate Poverty Without Hurting the Poor . . . and YourselfFrom EverandWhen Helping Hurts: How to Alleviate Poverty Without Hurting the Poor . . . and YourselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (36)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsFrom EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- High-Risers: Cabrini-Green and the Fate of American Public HousingFrom EverandHigh-Risers: Cabrini-Green and the Fate of American Public HousingNo ratings yet
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Economics 101: How the World WorksFrom EverandEconomics 101: How the World WorksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaFrom EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo ratings yet
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyFrom EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Poor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyFrom EverandPoor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (263)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet