Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnifying Instruments
Uploaded by
Zoora SavioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnifying Instruments
Uploaded by
Zoora SavioCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnifying Instruments They are used to observe tiny objects, which we cannot see clearly with our eyes.
Common magnifying instruments are hand lenses and microscopes. Hand lenses They are convex lenses, which are used to enlarge small objects. They should be placed a short distance from the eye and the object under investigation. The object should be moved towards the lens until the enlarged image can be seen clearly. A typical hand lens has a magnifying power of ten i.e. the image of object is 10 times larger
Magnification =
Size of Image Size of Object
Microscopes icroscopes enable us to see much smaller objects e.g. !acteria, "roto#oa, etc. $xamples are% i. ii. &ight microscope $lectronic microscope
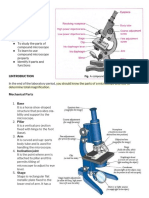
The width of objects seen though the light microscope is measured in micrometer. '( m) A micrometer e*uals 1+ 1,000 of a millimetre 'mm) 1000 mm , 1m 1000 (m , 1mm 1,000,000 (m , 1m -or white tiny objects we use on even smaller unit called Anemometer , 1+ 1,000,000 of a millimetre '10) 1 million manometers , 1mm '10) 1 billion manometers , 1m An electron microscope is used to see small objects that are too small to be seen with a light microscope e.g. virus. Parts of a light microscope
Functions of the parts of a light microscope 1. Eye piece lens; this lens magnifies objects, it can be removed and replaced with another of different magnification .. Object lens; this is the lens that is closer to the stage where objects to be observed are placed. /bjective lens can be removed and replaced with others of different magnification. 0. Iris diaphragm; 1t regulates the amount of light entering the microscope. 2. Mirror; it directs light through the microscope 3. Nosepiece; this is where objective lenses are fixed. 1t can be rotated to change from one objective to the other. The nosepiece is also called the turret. 4. Stage; this is a platform on which the specimen is placed. /n the stage are dips which hold the slide and to which the specimen is placed. The stage has an opening that admits light. 5. rm; it supports the body tube and focusing adjustments. each other. 8. "oarse and fine adjustment #nobs; they are used for focusing. The coarse adjustment 7nob moves the stage up and down to allow focusing. 1t is used with low power objective lens. The fine adjustment 7nob moves the stage up and down slightly to allow exact focusing. 1t is used with high power objective lens. 10. Foot$base; 1t supports the whole microscope. 6. !ody tube; 1t holds eyepiece and objective lenses at a proper wor7ing distance from
You might also like
- Lab Report General Biology (s1) - MicrosDocument11 pagesLab Report General Biology (s1) - MicrosNurul ZahidahNo ratings yet
- Measuring Microscopic ObjectsDocument7 pagesMeasuring Microscopic ObjectsPatriz CachoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MicrosDocument11 pagesUnit 1 MicrosDharviNo ratings yet
- THE Microscope: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesTHE Microscope: ObjectiveskimNo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentDocument15 pagesOptical InstrumentVinayKumar100% (1)
- The Light Microscope, Its Parts and Their FunctionsDocument64 pagesThe Light Microscope, Its Parts and Their FunctionsMarjorie Nebalasca GalongNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of CellsDocument16 pagesMicroscopic Examination of CellsShania MNo ratings yet
- Fungsi Mikroskop 1Document1 pageFungsi Mikroskop 1Andius SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Microscope Laboratory ActivityDocument6 pagesMicroscope Laboratory ActivityDaryl Boldios LoterteNo ratings yet
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of MicroscopeJohn Rey F. CastroNo ratings yet
- Proper Use of MicroscopeDocument7 pagesProper Use of MicroscopeRalc RamsNo ratings yet
- Microscope: Greek Instrument Microscopy MicroscopicDocument9 pagesMicroscope: Greek Instrument Microscopy MicroscopicBrian Lester Llanos DeeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Worksheet 3Document8 pagesGen Bio 1 Worksheet 3JJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Microscope: - Types - Parts & Functions - Microscope Terms - Slide Preparation - ExerciseDocument30 pagesIntroduction To The Microscope: - Types - Parts & Functions - Microscope Terms - Slide Preparation - Exercisesameera abedNo ratings yet
- 01 Zoology MicrosDocument10 pages01 Zoology MicrosJohn AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 1Document3 pagesLab Manual 1elizabeth shaw gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of a Compound Microscope - S7 Module 1Document69 pagesParts and Functions of a Compound Microscope - S7 Module 1AURORA () CARIAGANo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument3 pagesDiscussionFarra RadziNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of A Compound MicroscopeDocument15 pagesParts and Functions of A Compound MicroscopeKAREN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Microscopy: Compound Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesExperiment 4: Microscopy: Compound Light MicroscopeEhazNo ratings yet
- The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesThe Compound Light MicroscopeIsabela MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Telescope: 7.1 PurposeDocument10 pagesThe Telescope: 7.1 PurposeAlice Mengyao HeNo ratings yet
- Light Microscopy: Basics PrinciplesDocument5 pagesLight Microscopy: Basics PrinciplesArman AshiqNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesHow To Use A Light MicroscopebasondesaNo ratings yet
- 1 Mic125Document8 pages1 Mic125nadiazkiNo ratings yet
- Microscope LabDocument8 pagesMicroscope LabBe NjNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document10 pagesActivity 1Lovely Krish RazNo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentsDocument16 pagesOptical Instrumentsanand011100% (10)
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- Project On Microscop Maryam Sattar Roll No. Bsot-F21-030Document10 pagesProject On Microscop Maryam Sattar Roll No. Bsot-F21-030Maryam SattarNo ratings yet
- Optical Microscope Light Microscope Visible Light Lenses: Compound MicroscopesDocument2 pagesOptical Microscope Light Microscope Visible Light Lenses: Compound MicroscopesShanshah AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3.1 MicroscopeBasicsDocument22 pages3.1 MicroscopeBasicsJamaica Salas SuacilloNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument6 pagesManualapi-301455039No ratings yet
- How to Focus a MicroscopeDocument3 pagesHow to Focus a MicroscopeFati Andari AlmahdiniNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2 LAB MODULE 1 WorksheetDocument7 pagesGENBIO2 LAB MODULE 1 Worksheetgnye20No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab 1Document5 pagesAnaphy Lab 1DIANNE PLANANo ratings yet
- The science of investigating small objects using microscopesDocument6 pagesThe science of investigating small objects using microscopeslarry machonNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPE NOTES - 2018 by LN PDFDocument7 pagesMICROSCOPE NOTES - 2018 by LN PDFLuyando NzalaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts FunctionsDocument11 pagesMicroscope Parts FunctionsChristian AbordoNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument12 pagesMicroscopeHEXALANE E. LABRADORNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL LAB MANUAL FOR HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument37 pagesPRACTICAL LAB MANUAL FOR HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAjish joNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 The MicroscopeGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Compound Microscope: Parts and Focusing SpecimensDocument37 pagesThe Compound Microscope: Parts and Focusing SpecimensLeah RualesNo ratings yet
- Prelab Activity MPLDocument5 pagesPrelab Activity MPLAlthea Valenzuela100% (1)
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesActivity 1A MicroscopeClarito ManaayNo ratings yet
- Study of Compound MicroscopeDocument4 pagesStudy of Compound MicroscopeArman KhanxNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece and Objective Lenses: Key Parts of a MicroscopeDocument4 pagesEyepiece and Objective Lenses: Key Parts of a MicroscopeChristine Joy ArisgarNo ratings yet
- GBGuidelineDocument106 pagesGBGuidelinedoskuuunNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument2 pagesPracticalNim RaNo ratings yet
- Microscope CareDocument5 pagesMicroscope CareKate BlahblahNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab GuideDocument10 pagesMicroscope Lab GuideBrian Luo67% (3)
- Laporan MikroskopDocument29 pagesLaporan MikroskopAni NurHidayantiNo ratings yet
- Document JPGDocument17 pagesDocument JPGrahulNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Practical HandbookDocument41 pagesParasitology Practical Handbookmaximazarov100% (1)
- MicroscopeDocument6 pagesMicroscopeapi-267979304No ratings yet
- HumanAnatomy SA Raja PharmacyDocument50 pagesHumanAnatomy SA Raja PharmacyMAJEETH மஜீத் TIRUNELVELINo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Final DemoDocument8 pagesLesson Plan For Final DemoCetura VillaruzNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Using The Compound MicroscopeDocument3 pagesA Guide To Using The Compound MicroscopeReanna GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: (A) Discuss Why There Is A Need To Develop An Agreed International Conceptual Frame Work and TheDocument9 pagesChapter One: (A) Discuss Why There Is A Need To Develop An Agreed International Conceptual Frame Work and TheZoora SavioNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere and CombustionDocument5 pagesThe Atmosphere and CombustionZoora SavioNo ratings yet
- Butterflies and MothsDocument3 pagesButterflies and MothsZoora SavioNo ratings yet
- Joomla! 1.5 QuickstartDocument49 pagesJoomla! 1.5 QuickstartAmyStephen100% (107)
- CCNA 1 Chapter 1 V4.0 AnswersDocument4 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 1 V4.0 Answersccnadiscovery40% (1)
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Charm Banlaoi100% (1)
- Chapter 11Document52 pagesChapter 11Mike JingNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication PDFDocument24 pagesOptical Communication PDFgkreuginerajNo ratings yet
- IsotopsDocument13 pagesIsotopshenry castellNo ratings yet
- Abhijit Strategy For PhyDocument13 pagesAbhijit Strategy For PhyJAIVEERU37No ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument15 pagesCoordination Compoundsdivanshu2006yadavNo ratings yet
- Light Fundamentals: Radiant Energy, Vision and ColorDocument13 pagesLight Fundamentals: Radiant Energy, Vision and ColorMiko F. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Aplanatic Lenses: Proceedings of The Physical Society (1958-1967)Document7 pagesAplanatic Lenses: Proceedings of The Physical Society (1958-1967)Rafael Guillermo Gonzalez AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Variation of Er3+ Cross Section With Glass CompositionDocument13 pagesVariation of Er3+ Cross Section With Glass CompositionVastavikta SinghNo ratings yet
- Hazarika Pratim 2023Document176 pagesHazarika Pratim 2023Ant DtiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 Periodic TableDocument2 pagesWorksheet 5 Periodic TableVerna Santos-NafradaNo ratings yet
- Trends Periodic WorksheetDocument1 pageTrends Periodic WorksheetmydqueNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument15 pagesLaserMahnoor CheemaNo ratings yet
- MCQS Part 1Document27 pagesMCQS Part 1Uswa AzharNo ratings yet
- Electronic band structure explainedDocument9 pagesElectronic band structure explainedTeka KamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Chemical Context of Lifejohn doeNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopia RamanDocument6 pagesSpectroscopia Ramandanaaaa007No ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Atomic Structure Learning Objectives GRIDDocument4 pagesGCSE Chemistry Atomic Structure Learning Objectives GRIDRohina AkramNo ratings yet
- How To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementDocument6 pagesHow To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementRemartin MaglantayNo ratings yet
- Chem Topic 14 Questions + AnswersDocument18 pagesChem Topic 14 Questions + AnswersOscarHigson-Spence100% (1)
- P12.3 WSDocument4 pagesP12.3 WStholmesNo ratings yet
- The Process of Color SubtractionDocument2 pagesThe Process of Color SubtractionLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Holga ManualDocument20 pagesHolga ManualRoXana SellaNo ratings yet
- Syslog Trên Olt Huawei 99 Card Lt01Document35 pagesSyslog Trên Olt Huawei 99 Card Lt01Cong HiNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument20 pagesAtomic StructureshinNo ratings yet
- Measuring Quantum States of LightDocument259 pagesMeasuring Quantum States of LightbrianjsmithNo ratings yet
- Valence Electrons and Electron Configuration: Chemistry WorksheetDocument2 pagesValence Electrons and Electron Configuration: Chemistry Worksheetrobertkani2004No ratings yet
- IR Spectroscopy Identification GuideDocument28 pagesIR Spectroscopy Identification GuideAby JatNo ratings yet
- Back Button Focus Sharp Focus Photography Guide From Dave Morrow PhotographyDocument31 pagesBack Button Focus Sharp Focus Photography Guide From Dave Morrow PhotographyBlue EagleNo ratings yet
- A) A) B) C) B) : Make A Diffraction Grating From A DVD-R Cut and Fold Attach To A Webcam, Phone, or LaptopDocument2 pagesA) A) B) C) B) : Make A Diffraction Grating From A DVD-R Cut and Fold Attach To A Webcam, Phone, or LaptopDario OchoaNo ratings yet