Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HMT R04 Nov Dec 2007
Uploaded by
balakaleesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HMT R04 Nov Dec 2007
Uploaded by
balakaleesCopyright:
Available Formats
B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2007.
Sixth Semester (Regulation 2004) Mechanical Engineering ME 1351 - HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER (Common to B.E. (Part-Time) Fifth Semester Regulation 2005) Time: Three hours Maximum: 100 marks
Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables are permitted. Answer ALL questions. PART A - (10 x 2 = 20 marks) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the main advantage of parabolic fins? What is sensitivity of a thermocouple? Define critical radius thickness of insulation. Mention the importance of Biot Number. Write an equation for Fouling Resistance. Write a note on LMTD correction factor? What must be the colour of an umbrella to reduce the absorption of Solar Radiation? Why? State Kirchhoffs Law of Radiation. Define Fick's law of Diffusion.
8. 9.
10. Define mass-average velocity.
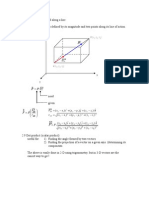
PART B - (5 x 16 = 80 marks) 11. (a) Derive the general one-dimensional differential equation of heat conduction in Cartesian coordinates and deduce it to Poisson and Laplace Equations. (16) Or (b) (i) The average heat produced by ripening Oranges is estimated as 300 W/m2 Taking the average radius as 0.04 m with k = e. I 5 W/mk, Calculate the temperature at the core when the surface temperature is 10C. (ii) Derive the log mean area of a cylinder used to transform into an equivalent slab. Assuming that a man can be represented as a cylinder of 0.30 m radius and height 1. 7 m with a surface temperature of 30C, Calculate the heat he would lose while standing in a 36 kmlhour wind at 10C. (8)
(8)
12. (a)
(i)
(8)
(ii)
Air stream of 30C moves with a velocity of 0.3 m/s across a 100 W electric bulb at 130C. If the bulb is approximated by a 0.06 m diameter sphere, estimate the rate and the percentage lost due to convection alone. (8) Or
(b)
(i)
Air at 8 kN/m2 and 242C flows over a flat plate of 0.3 m wide and 1 m long at a velocity of 8 m/s. If the plate is maintained at a temperature of 78C, estimate the heat to be removed continuously from the plate. (8) A 0.30 m long glass plate at 77C is hung vertically in air at 27C. Calculate the boundary layer thickness at the trailing edge and the average Nusselt number of the plate. (8)
(ii)
13. (a)
Derive the heat transfer equation of a parallel flow Heat exchanger stating the assumptions. Or
(16)
(b)
(i)
Saturated Steam at 120C condenses on the outer tube surface of a single pass heat exchanger. Determine the surface area to heat 1000 kglhour of water from 20C to 90C. Find the mass of the 2 Condensate Take Heat transfer Coefficient Uo = 1800 W/m and Hfg = 2200 kJ/kg. (8) Water is heated from 20C to 50C by condensing steam at 120C. If the inlet temperature of water falls to 15C with flow remaining constant, what will be the new outlet temperature? (8)
(ii)
14. (a)
(i)
Derive the Equivalent Emissivity of a two large parallel gray planes. The intensity of radiation emitted by the Sun is maximum at a wave length of 0.5 Il. As a black body, determine it's surface temperature and the emissive power.
(8)
(ii)
(8)
Or
(b) (i) Deduce the generalized equation for heat transfer of a system of two parallel plates separated by "n" screens. Emissivities of two large parallel plates at 800C and 300C are 0.3 and 0.5 respectively Find the net energy transfer rate per square metre. (8) Compare diffusion and convective mass transfer.
(8)
(ii)
15. (a)
(i) (ii)
(8)
Dry air at 27C and 1 bar flows over a wet plate 0.5 m long at a velocity of 50 mls. Calculate the mass transfer coefficient of water vapour in air at the end of the plate. (8)
Or
(b) (i) The mole fraction of H2 in a mixture of H2 and 02 is 0.4. If H2 moves with a velocity of 1 mls and 02 is stationary, find the mass and molar average velocities, mass and molar fluxes across the stationary surface. (8) Estimate the Diffusion rate of water at 27C from the bottom of a test tube of 0.02 m diameter and 0.04 m long into dry air at 27C. Take diffusion coefficient of water in air as 0.26 x 10-4 m2/s. (8)
(ii)
You might also like
- Chap54 7Document6 pagesChap54 7balakaleesNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Three-Dimensional Force Systems Again, Just Like in 2-Dimension, Newton's First Law Must Be SatisfiedDocument6 pages3.4 Three-Dimensional Force Systems Again, Just Like in 2-Dimension, Newton's First Law Must Be SatisfiedbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Statics Notes: 188268082.doc Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesStatics Notes: 188268082.doc Page 1 of 7balakaleesNo ratings yet
- DTS PDFDocument18 pagesDTS PDFaadhan100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering - Workshop Practice - Laboratory ManualDocument77 pagesMechanical Engineering - Workshop Practice - Laboratory Manualrajeevranjan_br100% (4)
- Chap47 9Document3 pagesChap47 9balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Chap47 9Document3 pagesChap47 9balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Anna University Theory Examination Nov/Dec 2013 Psna College of Engineering & Technology, DindigulDocument2 pagesAnna University Theory Examination Nov/Dec 2013 Psna College of Engineering & Technology, DindigulbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Gearbox Design IitDocument25 pagesGearbox Design IitSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Three-Dimensional Force Systems Again, Just Like in 2-Dimension, Newton's First Law Must Be SatisfiedDocument6 pages3.4 Three-Dimensional Force Systems Again, Just Like in 2-Dimension, Newton's First Law Must Be SatisfiedbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- I SEM Common Syllabus BE BTechDocument16 pagesI SEM Common Syllabus BE BTechrjthilakNo ratings yet
- Chap28 9Document7 pagesChap28 9balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Panel Format-I SemesterDocument22 pagesPanel Format-I SemesterbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R08 Nov Dec 2011Document4 pagesHMT R08 Nov Dec 2011balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg Nov 2013 Practical BatchDocument6 pagesMechanical Engg Nov 2013 Practical BatchbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R08 Apr May 2010Document2 pagesHMT R08 Apr May 2010balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.jgkgopiNo ratings yet
- HMT R04 Nov Dec 2009Document4 pagesHMT R04 Nov Dec 2009balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Practical Slot I SemesterDocument3 pagesPractical Slot I SemesterbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R08 Nov Dec 2010Document3 pagesHMT R08 Nov Dec 2010balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R08 Apr May 2010Document2 pagesHMT R08 Apr May 2010balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R08 Nov Dec 2010Document3 pagesHMT R08 Nov Dec 2010balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R07 May Jun 2010Document4 pagesHMT R07 May Jun 2010balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R04 May Jun 2007Document4 pagesHMT R04 May Jun 2007balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT Nov Dec 2007Document4 pagesHMT Nov Dec 2007balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R04 May Jun 2009Document3 pagesHMT R04 May Jun 2009balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT R04 May Jun 2009Document3 pagesHMT R04 May Jun 2009balakaleesNo ratings yet
- HMT Nov Dec 2005Document3 pagesHMT Nov Dec 2005balakaleesNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Rankine-Hugoniot Curve: CJ: Chapman JouguetDocument6 pagesRankine-Hugoniot Curve: CJ: Chapman Jouguetrattan5No ratings yet
- Government of West Bengal:: Tata Motors LTD: Abc 1 1 1 1 NA 0 NA 0Document1 pageGovernment of West Bengal:: Tata Motors LTD: Abc 1 1 1 1 NA 0 NA 0md taj khanNo ratings yet
- AD1 Elements of Architectural Composition For Placemaking PDFDocument4 pagesAD1 Elements of Architectural Composition For Placemaking PDFAndre Yap100% (1)
- Earth Sciences Notes Csir-Ugc Net JRFDocument57 pagesEarth Sciences Notes Csir-Ugc Net JRFmanas773No ratings yet
- Zincanode 304 pc142Document3 pagesZincanode 304 pc142kushar_geoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Course PhillStocking 4.2Document48 pagesAircraft Design Course PhillStocking 4.2ugurugur1982No ratings yet
- Serial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Document34 pagesSerial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Rohit PhalakNo ratings yet
- Imbinari Teava Fibra de Sticla PDFDocument1 pageImbinari Teava Fibra de Sticla PDFplex015No ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument9 pagesVentricular Septal DefectpepotchNo ratings yet
- Biomediacal Waste Project FinalDocument43 pagesBiomediacal Waste Project Finalashoknr100% (1)
- Eating With Chloe Lets EatDocument150 pagesEating With Chloe Lets Eatemily.jarrodNo ratings yet
- Rido, Rudini - Paediatric ECGDocument51 pagesRido, Rudini - Paediatric ECGFikriYTNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Cable Trays & Cable Ladders InstallationDocument7 pagesMethod Statement For Cable Trays & Cable Ladders InstallationJamal Budeiri0% (1)
- Of The Month Is Live. 100+ Subjects. Participate Now!: Sanfoundry Certification ContestDocument4 pagesOf The Month Is Live. 100+ Subjects. Participate Now!: Sanfoundry Certification ContestBaydaa QaidyNo ratings yet
- Biologically Active Compounds From Hops and Prospects For Their Use - Karabín 2016Document26 pagesBiologically Active Compounds From Hops and Prospects For Their Use - Karabín 2016Micheli Legemann MonteNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: C.X. Dong, A.K.H. Kwan, J.C.M. HoDocument14 pagesEngineering Structures: C.X. Dong, A.K.H. Kwan, J.C.M. HoElieser SinagaNo ratings yet
- ODA X9 2SL DatasheetDocument8 pagesODA X9 2SL DatasheetYudy UtamaNo ratings yet
- Pre RmoDocument4 pagesPre RmoSangeeta Mishra100% (1)
- Full Download Short Term Financial Management 3rd Edition Maness Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Short Term Financial Management 3rd Edition Maness Test Bankcimanfavoriw100% (31)
- Brief Summary of Catalytic ConverterDocument23 pagesBrief Summary of Catalytic ConverterjoelNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Cruise ControlDocument5 pagesAdaptive Cruise ControlIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Stanley B. Alpern - Amazons of Black Sparta - The Women Warriors of Dahomey-New York University Press (2011)Document308 pagesStanley B. Alpern - Amazons of Black Sparta - The Women Warriors of Dahomey-New York University Press (2011)georgemultiplusNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Tubing: Catalogue 5210/UKDocument15 pagesThermoplastic Tubing: Catalogue 5210/UKGeo BuzatuNo ratings yet
- Binet Kamat Test For General Mental AbilitiesDocument54 pagesBinet Kamat Test For General Mental AbilitiesSana Siddiq100% (14)
- Ask A Monk EnlightenmentDocument16 pagesAsk A Monk EnlightenmentPetruoka EdmundasNo ratings yet
- QuantAssay Software Manual 11-Mar-2019Document51 pagesQuantAssay Software Manual 11-Mar-2019LykasNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Mechanical Systems and Electrical SystemsDocument49 pagesMathematical Modeling of Mechanical Systems and Electrical SystemsMary DunhamNo ratings yet
- Updated SAP Cards Requirement JalchdDocument51 pagesUpdated SAP Cards Requirement Jalchdapi-3804296No ratings yet
- Bhagwati School Strap Report AnalysisDocument60 pagesBhagwati School Strap Report AnalysisReverse Minded100% (1)
- Tsel Manual ThermoselDocument25 pagesTsel Manual ThermoselPedro AlvelaisNo ratings yet