Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Function of Antibodies in The Immune System.
Uploaded by
alto1shipOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Function of Antibodies in The Immune System.
Uploaded by
alto1shipCopyright:
Available Formats
The function of antibodies in the immune system.
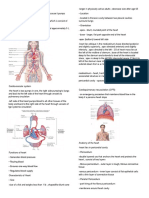
Our body is constantly defended against organisms from around us and against other attacking invaders by our vital immune system. The soldiers that will perform this function are called antibodies. The malicious attackers that try to invade our body and create infections and diseases are called antigens. How is this defense line organized, how do antibodies in the immune system function? This is how the immune system works and how the antibodies in the immune system do their main job. When the immune system is threatened by attacks from substances and/or organisms, invading the body and so cause diseases, there will be a counter reaction: the response of the antibodies in the immune system. This response consists of a series of reactions, in which all defensive elements of the immune system will work together in the right order. These elements are cells, tissues, and organs, all participating together to protect our body. The cells mentioned here are the white blood cells, also called leukocytes. There are two basic types of leukocytes, capable of detecting and destroying substances and organisms that can cause diseases. These two kinds of white blood cells are the phagocytes, cells that will consume attacking organisms, and the lymphocytes, cells that make it possible for the immune system of our body to remember and recognize attackers from previous invasions and help the system to destroy them. So lymphocytes play an enormous part in the functioning of antibodies in the immune system. As they remember the important information of former attacks on the body with stuff that tries to make us ill, they are able to respond very early when the body is under attack by a known ill maker. This means a very quick and apt action can be taken by our immune system. The two kinds of lymphocytes that will perform these actions are called B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes, also called B-cells and T-cells. All lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow. When they stay there, they will develop into B-cells. When they move to the thymus, they will grow up as T-cells. These two types of lymphocytes or cells have different functions to perform. The B-cells are able to detect the invading organisms and organize the defensive actions of the combined forces of the immune system. They do this by producing different and specialized proteins, which are the antibodies. For every specific antigen a specific antibody will be produced. Once these antibodies exist in our body, the will stay present, even after defeating the invading organisms. The memory function of the B-cells make it possible to recognize the same invaders by a next attack, so that the existing antibodies can react in an early stage and prevent us from getting a disease we already had in our life. For most diseases it means that you will get it only once in a lifetime.
This is the reason why immunizations help the system preventing certain diseases. Some small dose of antigens will not make us sick, but will trigger the immune system to make the right antibodies, that will stay in our body and defend us. So antibodies can detect and recognize antigens, they need help in the destruction of the antigens. destroying it without help. When the enemy is spotted and tagged, T-cells, of which a part develop into the specialized T- Killer-cells, will destroy the invaders. Next to this important job the T-cells help signaling other cells in the immune system to play their part in the defense system and assist the antibodies in the immune system. what are antibodies news
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Week 3 - Muscles LabDocument19 pagesWeek 3 - Muscles LabMarx AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Unique Presentation of Submandibular Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUnique Presentation of Submandibular Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Case Report and Review of LiteratureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 300 MCQsDocument62 pages300 MCQsZhuolu PanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Health Science Tool Kit Text BookDocument278 pagesHealth Science Tool Kit Text BookAidan Glasby100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Tetanus Case StudyDocument41 pagesTetanus Case StudyFAt Ty100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Chapter 5 - AmphibiansDocument39 pagesChapter 5 - AmphibiansJuan Carlos SánchezNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- 5 - Cluster 1 - Maintaining A Healthy Body - Manitoba - Grade 5 Science UnitDocument75 pages5 - Cluster 1 - Maintaining A Healthy Body - Manitoba - Grade 5 Science UnitZabrinaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Muscle of Mastication: Presented By:-Dr. Shaifali Mdspg1 YearDocument72 pagesMuscle of Mastication: Presented By:-Dr. Shaifali Mdspg1 YearAtul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemMitchy SunNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- LEVEL 5. Unit 1. The Human BodyDocument2 pagesLEVEL 5. Unit 1. The Human BodyAna Rosa Camacho CornejoNo ratings yet
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)Document1 pageCBC (Complete Blood Count)Roshan kumar giriNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Radiology Examination For Tractus Digestivus Chairunnisa, Dr. SP - RadDocument100 pagesRadiology Examination For Tractus Digestivus Chairunnisa, Dr. SP - RadDiana OCtavinaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Biology - Life Processs Key NotesDocument18 pagesCBSE Class X Biology - Life Processs Key NotesBhavesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Human Skeleton F3 NoradinDocument5 pagesHuman Skeleton F3 NoradinIbnu RaxaabNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Urinay SystemDocument14 pagesUrinay SystemAficionadoNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Workbook3 ExcretionDocument12 pagesWorkbook3 ExcretionDarambazar GantulgaNo ratings yet
- Ends With 2 Cells Original Homologous Pairs Separate Ending Human Cells Have 46 Starts With One Cell Sister Chromatids SeparateDocument18 pagesEnds With 2 Cells Original Homologous Pairs Separate Ending Human Cells Have 46 Starts With One Cell Sister Chromatids SeparateProThaThaKing ClashNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- HeartDocument11 pagesHeartKei GauranoNo ratings yet
- Histo - Course HeroDocument16 pagesHisto - Course HeroNatalie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Activity 11 The Tongue and The SkinDocument7 pagesActivity 11 The Tongue and The SkinRoi Vincent VillaraizNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Circulatory SystemDocument74 pagesCirculatory Systemmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- A New Approach To Breast Cancer Terminology Based On The A - 2022 - European JouDocument21 pagesA New Approach To Breast Cancer Terminology Based On The A - 2022 - European JouWang YuNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Human BodyDocument17 pagesOsteology of The Human BodyAyuba EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Physio CAT 2 AnsweredDocument34 pagesPhysio CAT 2 AnsweredJohn KennedyNo ratings yet
- Final Physiology... Medical 2Document12 pagesFinal Physiology... Medical 2Ishaq DerbashiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16-Urinary SystemDocument24 pagesChapter 16-Urinary SystemSekar ArumNo ratings yet
- Nutrients and Waste Transport SystemDocument22 pagesNutrients and Waste Transport SystemItsPotatoQueen MaeNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Anaphy PrelimDocument12 pagesAnaphy PrelimPrecious MapehNo ratings yet
- Class-14 - Plasma Lipoproteins - EnzymesDocument39 pagesClass-14 - Plasma Lipoproteins - EnzymesAyi FurqonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex ActivityDocument53 pagesChapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activityramadan100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)