Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inherited and Developmental Disorders
Uploaded by
Jack PaiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inherited and Developmental Disorders
Uploaded by
Jack PaiCopyright:
Available Formats
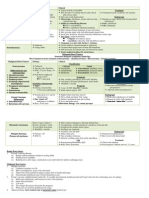
Disease
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Brittle Bones
Etiology Hereditary. Abnormal synthesis of type 1 collagen Type 1& 3: AD Type 2: AR Type 3: teeth involvement
Clinical General symptoms: Recurrent fractures generalized osteopenia Thin sclera with blue hue Hypermobility joint laxity Deafness: inner and middle ear bone Bruising thin dermis Type 1 Fractures Blue sclera Hearling loss Little progress after puberty Type 2 Stillborn, crushed into bones Type 3 Variable severity Fractures Skeletal deformities Normal sclera Sometimes DI
Osteopetrosis Marble bone/AlbersSchonberg disease
Hereditary: decrease osteoclast fxn Decreased resorption and thick sclerotic bone.
Cleidocranial dysplasia
AD disorder of bony development
Achondroplasia
Most common form of inherited dwarfism AD, affects FGF receptor 3 on chromosome 4 Inhibits cartilage synthesis at epiphyseal growth plate Decreased endochondral bone Premature ossification of growth plates Rare, unencapsulated, M =F, young adults Differential: diagnosed from ossifying fibroma wellcircumscribed borders. Complication: osteosarcoma
5 symptoms: Increased bone density and cortex thickening. Bone thickening fractures easy Myelophthistic process medullary fibrosis, extramedullary hematopoeisis CN compression: blind, deaf, palsies Hydrocephalus: CSF obstruction Oral Symptoms Multiple supernumerary, unerupted, Bones Affected Jaws, bones and clavicle malaigned teeth Absent collar bones, depressed nasal bridge Heavy protruding jaws Prominent frontal, parietal, occipital bones with open sutures Affected bones: short and thick long bones Spared bones: cranial and vertebral normal intelligence and life span Pituitary dwarfism: undersecretion of growth hormone Facial features Forehead bulging, Frontal bossing, Saddle nose, Mandibular prognathism Oral: Delayed eruption and shedding Small clinical crown and roots Smaller dental arch malocclusion and underdeveloped mandible. Treatment: surgical recontouring Radiation therapy possible malignant transformation Usually stops after puberty. Radiographically: Radiopaque mass, irregular borders: ground/frosted glass Chinese character
Fibrous Dysplasia
Monostotic
Most common form 80% One bone: ribs and femur are most common Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: more than maxilla involved. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the jaw Maxilla: 80% Bone expansion and deformity Tooth displacement Thickening of skull base
Polyostotic 1st decade, females before puberty McCune-Albright
Segmental distribution of involved bones Long bones, face, clavicles, pelvic bones Initial sign: limp, pain and fracture on affected side Triad: polyostotic, caf-au-lait, precocious puberty Frequent bone fractures Always involve mandible either alone or with maxilla Bilateral symmetrical swelling of 1/ both jaws Very round face and regional lymphadenopathy Less noticeable as child ages Upward eyes Intraoral: Premature primary exfoliation Delayed/abnormal eruption of permanent Pathognomonic: perivascular collagen condensation
COMPLICATION OSTEOSARCOMA, mainly polyostotic
Cherubism
AD disorder of the jaws in children Age 5, M>F
Treatment Cautious waiting, should stabilizes after puberty No treatment Dont use radiation therapy Radiographic Multiple, well defined radiolucency Soap-bubble
Inherited and Developmental BONE diseases 1. Cherubism: bilateral intraosseous fibrous proliferation soon after birth (a) Self-limiting, bony lesions regress with minor deformity at puberty 2. Cleidocranial dysostosis: (a) Affects skull, teeth, jaws, and shoulder girdle (b) Delayed eruption of permanent (c) Delayed fontanelle closure (d) High palate, absent clavicles (e) Decreased cellular cementum (f) Numerous impacted supernumerary in incisor and premolar area 3. Osteopetrosis: (a) If diagnosed in a child = MOST SEVERE rarely survive adolescence (b) Death from infection / anemia (c) Classic bone within bone due to greatly thickened cortices and medullary space obliteration 4. Cleidocranial dysplasia (a) Large head and brachycephalic (b) Broad-based nose with depressed nasal bridge 5. Fibrous dysplasia: SMOOTH expansion of alveolar ridge and adjacent bone
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- CHP 11 Moderate Nonskeletal Problems in Preadolescent ChildrenDocument6 pagesCHP 11 Moderate Nonskeletal Problems in Preadolescent ChildrenJack Pai0% (2)
- Drug Interactions in Dentistry: Understanding the Cytochrome SystemDocument15 pagesDrug Interactions in Dentistry: Understanding the Cytochrome SystemJack PaiNo ratings yet
- Systemic AntibioticsDocument13 pagesSystemic AntibioticsJack PaiNo ratings yet
- Idj Vision 2020 FinalDocument14 pagesIdj Vision 2020 FinalJack PaiNo ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument2 pagesBone TumorsJack PaiNo ratings yet
- Cast OutlineDocument1 pageCast OutlineJack PaiNo ratings yet
- 4.0 General Consierations ProstheticsDocument2 pages4.0 General Consierations ProstheticsJack PaiNo ratings yet
- MosbyDocument15 pagesMosbyJack PaiNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone DiseaseDocument1 pageMetabolic Bone DiseaseJack PaiNo ratings yet
- Seminar No 1Document3 pagesSeminar No 1Jack PaiNo ratings yet
- LinesDocument2 pagesLinesJack Pai100% (1)
- Seminar No 3Document10 pagesSeminar No 3Jack PaiNo ratings yet
- Chicken PotpieDocument38 pagesChicken PotpieJack PaiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Javier Couso, Alexandra Huneeus, Rachel Sieder Cultures of Legality Judicialization and Political Activism in Latin America Cambridge Studies in Law and SocietyDocument290 pagesJavier Couso, Alexandra Huneeus, Rachel Sieder Cultures of Legality Judicialization and Political Activism in Latin America Cambridge Studies in Law and SocietyLívia de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Ariel StoryDocument2 pagesAriel StoryKKN Pasusukan2018No ratings yet
- Design of Efficient Serial Divider Using HAN CARLSON AdderDocument3 pagesDesign of Efficient Serial Divider Using HAN CARLSON AdderInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report - 1st and 2nd SemDocument41 pagesAccomplishment Report - 1st and 2nd Semshailean azulNo ratings yet
- Banking & Finance Awareness 2016 (Jan-Nov) by AffairsCloudDocument167 pagesBanking & Finance Awareness 2016 (Jan-Nov) by AffairsCloudkaushikyNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Risks of Dexamethasone in Noncardiac Surgery: Clinical Focus ReviewDocument9 pagesBenefits and Risks of Dexamethasone in Noncardiac Surgery: Clinical Focus ReviewAlejandra VillaNo ratings yet
- Autism AspergerDocument24 pagesAutism AspergerusavelNo ratings yet
- Dreams and Destiny Adventure HookDocument5 pagesDreams and Destiny Adventure HookgravediggeresNo ratings yet
- The Army Crew Team Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesThe Army Crew Team Case Analysisarshdeep199075% (4)
- Lived Experiences of Elementary Teachers in A Remote School in Samar, PhilippinesDocument14 pagesLived Experiences of Elementary Teachers in A Remote School in Samar, Philippinesルイス ジャンNo ratings yet
- Prayer BuddyDocument42 pagesPrayer BuddyJoribelle AranteNo ratings yet
- Bob Jones - Science 4Document254 pagesBob Jones - Science 4kage_urufu100% (4)
- Universitas Alumni Psikotest LolosDocument11 pagesUniversitas Alumni Psikotest LolosPsikotes BVKNo ratings yet
- 2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidenceDocument16 pages2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidencebaridinoNo ratings yet
- ANTENATAL ASSESSMENT Form 13Document4 pagesANTENATAL ASSESSMENT Form 13Kaku ManishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Quiz Corrections ADocument4 pagesChapter 5 Quiz Corrections Aapi-244140508No ratings yet
- Week 1 Amanda CeresaDocument2 pagesWeek 1 Amanda CeresaAmanda CeresaNo ratings yet
- Neoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismDocument16 pagesNeoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismErika EludoNo ratings yet
- Primer To Using Stampplot® Pro Standard User LicensedDocument21 pagesPrimer To Using Stampplot® Pro Standard User LicensedSandy Rachman AdrianNo ratings yet
- Femap-58 Volume2 508Document357 pagesFemap-58 Volume2 508vicvic ortegaNo ratings yet
- Think Like An EconomistDocument34 pagesThink Like An EconomistDiv-yuh BothraNo ratings yet
- Christian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Document78 pagesChristian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Nwaozuru JOHNMAJOR ChinecheremNo ratings yet
- Modern Mathematical Statistics With Applications (2nd Edition)Document13 pagesModern Mathematical Statistics With Applications (2nd Edition)Alex Bond11% (28)
- Grade 10 To 12 English Amplified PamphletDocument59 pagesGrade 10 To 12 English Amplified PamphletChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Reading Comprehension Test 03Document5 pagesIntermediate Reading Comprehension Test 03MZNo ratings yet
- Leading a Community Through Integrity and CourageDocument2 pagesLeading a Community Through Integrity and CourageGretchen VenturaNo ratings yet
- GSM ZTE Paging Feature GuideDocument17 pagesGSM ZTE Paging Feature Guidemikepadilla82100% (1)
- New Text DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Text DocumentDhaniNo ratings yet
- Web Search - One People's Public Trust 1776 UCCDocument28 pagesWeb Search - One People's Public Trust 1776 UCCVincent J. CataldiNo ratings yet
- Psychology - A Separate PeaceDocument2 pagesPsychology - A Separate PeacevasudhaaaaaNo ratings yet