Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B Along Axial and Equitorial Line
Uploaded by
surya_kotniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B Along Axial and Equitorial Line
Uploaded by
surya_kotniCopyright:
Available Formats
P age | 5
Wellfare Institute of Science, Technology & Management
Polytechnic - Magnetism K.Surya Prakash
DETERMINATION OF B ON THE AXIAL LINE OF A BAR MAGNET:
Def. of Axial line:
A straight line passing through the mid-point of a bar magnet and joining the two
poles of the bar magnet is called Axial line (or) Axis of the bar magnet. It is an imaginary line.
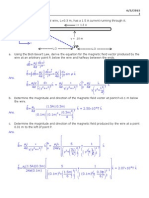
Derivation: consider a bar magnet of length 2l and pole strength m. Let A be a point on the
axial line at a distance d from the centre (O) of the magnet.
The magnetic inductinn B
N
at A due to north pole of the magnet, acting along NA is
given by
( )
2
4
o
N
m
B
NA
=
( )
( )
2
4
o
N
m
B NA d l
d l
= =
The magnetic induction B
S
at A due to the south
pole of the magnet, acting along AS is given by
( )
2
4
o
S
m
B
SA
=
( )
( )
2
4
o
S
m
B SA d l
d l
= = +
+
The resultant magnetic induction at A along NA is given by
N S
B B B =
( ) ( )
2 2
4 4
o o
m m
d l d l
=
+
( ) ( )
2 2
1 1
4
o
m
d l d l
(
= (
+
(
( ) ( )
( )
2 2
2
2 2
4
o
d l d l m
d l
(
+
(
=
(
( )
2
2 2
2 2
4
o
m l d
d l
( )
( )
2
2 2
2
2
4
o
Md
B m l M
d l
= =
The magnetic induction field strength at any point on the axial line of a bar magnet is
( )
2
2 2
2
4
o
Md
B
d l
When l <<d i.e., in the case of a very short bar magnet
( )
3
2
4
o
M
B
d
=
P age | 6
Wellfare Institute of Science, Technology & Management
Polytechnic - Magnetism K.Surya Prakash
DETERMINATION OF B ON THE EQUATORIAL LINE OF A BAR MAGNET:
Def: Equatorial line of a bar magnet is the perpendicular bisector of the axis of the magnet
Consider a bar magnet of magnetic length 2l and pole-
strength m. let P be a point on the equatorial line at a distance
d from centre (O) of the magnet.
The magnetic induction B
N
at P due to the north pole of
the magnet acting along NP is given by
( )
2
4
o
N
m
B
NP
=
( )
( )
2 2
2 2
4
o
N
m
B NE d l
d l
= = +
+
The magnetic induction B
S
at P due to the south pole of the magnet acting along EP is given by
( )
2
4
o
S
m
B
SE
=
( )
( )
2 2
2 2
4
o
S
m
B SE d l
d l
= = +
+
The vectors B
N
and B
S
are represented by the adjacent sides PA and PB of the parallelogram
PACB. Then the diagonal PC of the parallelogram gives the resultant induction field B.
From the fig. the triangles PAC and NPS are similar.
PC PA
NS NP
=
.( )
PA
PC NS
NP
=
2 2
.2
N
B l
PC
d l
=
+
( )
2 2
2 2
2
B .
4
o
m l
d l
d l
=
+
+
( )
3/2
2 2
B
4
o
M
d l
=
+
( ) 2 m l M =
When l << d, i.e., in the case of a very short bar magnet
3
B
4
o
M
d
=
Note : the direction of induction field B on the equatorial line is always opposite to the direction
of the magnetic moment.
You might also like
- Marion County School Board Meeting Observation ReportDocument3 pagesMarion County School Board Meeting Observation Reportapi-356450412No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Magnetic Feild 2016 ReviewedDocument160 pagesChapter 4 Magnetic Feild 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Magnetic InductionDocument6 pagesMagnetic InductionYugandhar Veeramachaneni0% (1)
- 04 3 Magnetic Induction PDFDocument6 pages04 3 Magnetic Induction PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of Material PDFDocument19 pagesMagnetic Properties of Material PDFavi taylorNo ratings yet
- Astons Mass Spectrograph by Sonu RaniDeptt. of PhysicsDocument4 pagesAstons Mass Spectrograph by Sonu RaniDeptt. of PhysicsDNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument42 pagesMagnetismAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Permanent MagnetDocument15 pagesPermanent MagnetthinkiitNo ratings yet
- 17 MagnetostaticsDocument29 pages17 MagnetostaticsChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Document24 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Bharati PatilNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force: B V F FDocument21 pagesMagnetic Field and Magnetic Force: B V F FscholsarNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and Magnetism 2Document43 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetism 2Mavn LoginNo ratings yet
- Magnetism & MatterDocument17 pagesMagnetism & Matterkartiksingh46648No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of CurrentDocument31 pagesMagnetic Effects of CurrentMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (3)
- SDASDASDSADocument17 pagesSDASDASDSAAkash BidhuriNo ratings yet
- Homework 10: Chapter 30: 14, 17, 25, 41Document9 pagesHomework 10: Chapter 30: 14, 17, 25, 41Moises TriguerosNo ratings yet
- 2009 Evolution of The Angle Between The Magnetic Moment and The Rotation Axis of Radio PulsarsDocument9 pages2009 Evolution of The Angle Between The Magnetic Moment and The Rotation Axis of Radio PulsarsheitoroliveiraNo ratings yet
- PHY13 Lesson 1 MagnetismDocument48 pagesPHY13 Lesson 1 MagnetismAmante Rivera JrNo ratings yet
- IITJEE 2014-Physics-School Handout-Magnetism and MatterDocument10 pagesIITJEE 2014-Physics-School Handout-Magnetism and MatterDikshant GuptaNo ratings yet
- BKM - MagnetismDocument26 pagesBKM - Magnetismdny001No ratings yet
- CUET Physics 2022 23rd Aug Slot 1Document71 pagesCUET Physics 2022 23rd Aug Slot 1NafeesNo ratings yet
- Phy213 CH29 Worksheet-KeyDocument5 pagesPhy213 CH29 Worksheet-KeynjparNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument3 pagesMagnetismalvin talaveraNo ratings yet
- PB Sheet 4 and Solutions LMODocument6 pagesPB Sheet 4 and Solutions LMOShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument33 pagesPhysics XIPavithra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Exam3 Problems SolDocument36 pagesExam3 Problems Solnancy maganaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Electromagnetism Textbook Suggested AnswersDocument23 pagesCH 4 Electromagnetism Textbook Suggested Answers黃淑敏No ratings yet
- Polarization and Modern OpticsDocument12 pagesPolarization and Modern OpticsCharles BernandoNo ratings yet
- Alok Phy Project 23-24Document19 pagesAlok Phy Project 23-24at8225997No ratings yet
- Sheet of Magnetic Effects of Current Sheet Student Copy With Ans 09-07-2021 1669900581763Document75 pagesSheet of Magnetic Effects of Current Sheet Student Copy With Ans 09-07-2021 1669900581763Tanay SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch26 SSMDocument22 pagesCh26 SSMFranko UrciaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics of NMRDocument75 pagesQuantum Mechanics of NMRmishs14No ratings yet
- 4 MagnetismDocument17 pages4 MagnetismThinkershub11No ratings yet
- 3 2 Formulae MagnetismDocument4 pages3 2 Formulae MagnetismNathanianNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and Magnetism (Edited)Document32 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetism (Edited)Akash BidhuriNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Document17 pagesLab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Sitaramaraju VengalarajuNo ratings yet
- q2 PDFDocument8 pagesq2 PDFSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument16 pagesMagnetism and MatterrajannaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter All DerivationsDocument5 pagesMagnetism and Matter All DerivationsRonit VaskarNo ratings yet
- 20 Magnetism and Matter: SolutionsDocument22 pages20 Magnetism and Matter: Solutionssunaarvind1922No ratings yet
- Magnetism ExerciseDocument17 pagesMagnetism ExerciseAnkit VatsaNo ratings yet
- CET Physics - 2012: R I I IDocument17 pagesCET Physics - 2012: R I I IAnumod IllathNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument19 pagesMagnetismAkash Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- MagnetDocument1 pageMagnetpeter_br3adNo ratings yet
- ch29 PDFDocument29 pagesch29 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- 02 08II. Electromagnetic Induction 215-225Document7 pages02 08II. Electromagnetic Induction 215-225eamcetmaterials0% (1)
- Problem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Document8 pagesProblem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Nicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- Physics Mapping Magnetic Field Lines of A Bar MagnetDocument18 pagesPhysics Mapping Magnetic Field Lines of A Bar Magnet7H VENOM TMNo ratings yet
- 4 Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument7 pages4 Moving Charges and MagnetismRajender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetic Effects of CurrentDocument10 pagesJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetic Effects of Currentvarunkohliin100% (1)
- Magnetism FORMULADocument1 pageMagnetism FORMULAMoni Kakati0% (1)
- XII Physics Chapter 5 - Magnetism Matter Saju HssliveDocument10 pagesXII Physics Chapter 5 - Magnetism Matter Saju HssliveVikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Physicsloncap 9 HelpDocument16 pagesCH 28 Physicsloncap 9 Helpjonjones666No ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 4Document34 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 4Infamous LegendsNo ratings yet
- A2Document6 pagesA2georgiNo ratings yet
- Fermi Surface IIIDocument67 pagesFermi Surface IIIImtiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- Aston's Mass SpectrographDocument3 pagesAston's Mass Spectrographlplc79178% (9)
- Subject:: Atomic and Molecular SpectrosDocument8 pagesSubject:: Atomic and Molecular SpectrosAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4th Class EVS 9Document4 pages4th Class EVS 9surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- 7 Teaching Learning MaterialDocument6 pages7 Teaching Learning Materialsurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Bhagavad GeethaDocument381 pagesBhagavad GeethaVenu GadadasuNo ratings yet
- Jan6-2012 Poly Technic Exam PaperDocument32 pagesJan6-2012 Poly Technic Exam PaperNooruddin SheikNo ratings yet
- Hindu Calender 2015Document12 pagesHindu Calender 2015pravin2projectsNo ratings yet
- Psychology Definitions1Document3 pagesPsychology Definitions1surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics Sem - 1Document349 pagesEngineering Physics Sem - 1Andrew NelsonNo ratings yet
- 10th Physical Science Bit BankDocument7 pages10th Physical Science Bit Banksurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Seagate Dashboard User Guide UsDocument20 pagesSeagate Dashboard User Guide UsPranav VyasNo ratings yet
- I YearDocument28 pagesI Yearsurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Bit Bank Physic (T.M)Document16 pages10th Class Bit Bank Physic (T.M)Rajasekhar ParaNo ratings yet
- 10th Chemistry Bit Bank EMDocument6 pages10th Chemistry Bit Bank EMsurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Magnetism ContentsDocument6 pagesMagnetism Contentssurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- 9th Beejiya SamasaluDocument31 pages9th Beejiya Samasalusurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Results of 2nd Stage Exam For NTPC (UG) (DOE-19.01.14)Document4 pagesResults of 2nd Stage Exam For NTPC (UG) (DOE-19.01.14)surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- 10 Science English 2013Document204 pages10 Science English 2013surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Engbooklet (1) 2014Document23 pagesEngbooklet (1) 2014surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- AP X Physics EMDocument352 pagesAP X Physics EMsurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Sakshi: ÑÐ) L ) Lä Æ ) L Ð) Låð) LçüDocument4 pagesSakshi: ÑÐ) L ) Lä Æ ) L Ð) Låð) LçümooorthuNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Path A Jali Yoga Sutra MuluDocument58 pagesPath A Jali Yoga Sutra MuluKovvuri Vnlnsrinivas100% (5)
- Magnetism 06Document8 pagesMagnetism 06surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Ãt Ûäyês¡+ 2 - Òæáãe) 2011: Á - Üc Nqtã+ Ûä+Document1 pageÃt Ûäyês¡+ 2 - Òæáãe) 2011: Á - Üc Nqtã+ Ûä+surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Èlç (™èlìz Ð) L Qå Çü Çœ$R ) Lë$: SakshiDocument4 pagesÈlç (™èlìz Ð) L Qå Çü Çœ$R ) Lë$: SakshiJagadeesh SaragadamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 8Document9 pagesElectromagnetism 8surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Electricity 7Document13 pagesElectricity 7surya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Pragnaa File FromDocument1 pagePragnaa File Fromsurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Mahaprasthanam in TeluguDocument54 pagesMahaprasthanam in TeluguTelugu Telugu100% (1)
- HCF and LCM - Practice SheetDocument6 pagesHCF and LCM - Practice SheetSakshi mishraNo ratings yet
- Mckenzie Murdock-1Document2 pagesMckenzie Murdock-1api-264700938No ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude Test2Document5 pagesQuantitative Aptitude Test2Kanimozhi PonnuchamyNo ratings yet
- Anacdotal RecordsDocument3 pagesAnacdotal Recordsapi-250007692No ratings yet
- Tappet ShapeDocument5 pagesTappet ShapeAshraful HimelNo ratings yet
- 11th & 12th Math CBSE Se JEE Tak PDFDocument4 pages11th & 12th Math CBSE Se JEE Tak PDFHarsh Shah67% (3)
- Kelsey Krumme ResumeDocument1 pageKelsey Krumme Resumeapi-356495784No ratings yet
- Ajitha ManiyaranDocument3 pagesAjitha Maniyaranapi-324809701No ratings yet
- My Life and My AchievementDocument2 pagesMy Life and My AchievementReynand MaitemNo ratings yet
- CERTIFICATIONDocument3 pagesCERTIFICATIONmary antonette manaloNo ratings yet
- Class 7 English MediumDocument12 pagesClass 7 English Mediumnaveen_halk0% (1)
- C Programming Lab ManualDocument8 pagesC Programming Lab Manualnalluri_08No ratings yet
- q3 Math 5Document6 pagesq3 Math 5nicaangelenecomiaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations TextDocument238 pagesDifferential Equations TextEANo ratings yet
- SET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Document8 pagesSET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Joel WallerNo ratings yet
- Complete Practice of Geometry by Gagan Pratap SirDocument69 pagesComplete Practice of Geometry by Gagan Pratap SirAnjali SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fractional NumeralDocument9 pagesFractional NumeralCorina SimionNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Math CHIJ ST Theresa Sec SA2 2017Document24 pagesSec 1 Math CHIJ ST Theresa Sec SA2 2017Yi QinNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaDocument8 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaSofiyah Sitorus PaneNo ratings yet
- Master Listing 11-18-13 TitleDocument36 pagesMaster Listing 11-18-13 Titleapi-234140657No ratings yet
- Theory EnglishDocument11 pagesTheory EnglishwanderedNo ratings yet
- 100 QA Number Systems (WWW - Qmaths.in)Document16 pages100 QA Number Systems (WWW - Qmaths.in)smodi20No ratings yet
- Horizons MathDocument29 pagesHorizons MathHomeschool BaseNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Chapter 8Document16 pagesSec 3 Chapter 8Edu 4 UNo ratings yet
- Girls 2010 Cross Country BracketDocument3 pagesGirls 2010 Cross Country BracketpaisaasportsNo ratings yet
- List of Pupils by Section KindergartenDocument6 pagesList of Pupils by Section KindergartenGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Liate and Tabular Intergration by PartsDocument3 pagesLiate and Tabular Intergration by Partsmarinos.stargazer7831No ratings yet
- E) Choose The Right Answer. F) Correct The Mistakes and Write The Right PronounsDocument1 pageE) Choose The Right Answer. F) Correct The Mistakes and Write The Right PronounsMOBA Mobile Legend100% (1)
- SystemsofEquations HandoutDocument44 pagesSystemsofEquations Handoutasdasdf1No ratings yet