Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Urinary System
Uploaded by
api-236094936Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Urinary System
Uploaded by
api-236094936Copyright:
Available Formats
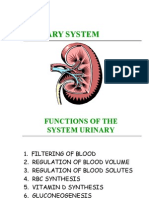
The Urinary System The urinary system consists of the organs, tubes, muscles and nerves that work
together to create, store and carry urine. It includes two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder and urethra. Waste products (nitrogen) are released into the bloodstream (urea, creatinine and uric acid). The urinary system removes them from the blood. Then, the kidneys filter the blood. The kidneys also regulate water, electrolytes, and acids in body fluids. Homeostasis takes place because of the stability provided by the urinary system. Renin and erythropoietin are hormones secreted by the kidneys. Renin is an enzyme for blood pressure regulation. Erythropoietin stimulates BBC production in bone marrow. The kidneys are retroperitoneal in the lumbar area. In other words, they are located above the waist, towards the back. Each kidney is fist-sized and weighs around four-six oz. each. The outer portion of the kidney is known as the cortex. The middle/inner portion is known as the medulla. The hilum is the depression/area where blood vessels past through. The collection point for urine is located in the renal pelvis. Blood first enters the renal arteries. Next, it enters into the arterioles. Last, it goes to capillaries. A tiny ball of capillaries is known as a glomerulus. In each kidney, there are approximately one million glomeruli. A Bowmans capsule surrounds each glomerulus. The ureters are around sixteen-eighteen inches long. Each ureter is lined with a mucous membrane. Their function is to move urine to bladder via peristalsis. The bladder is a hollow muscular sac. Its function is to hold urine until voluntary release. The urethra is a membranous tube. A female urethra is around one and one-half inches long. A male urethra is much longer, measuring at eight inches long and goes through the male prostate. Its function is to carry urine out of the body. The external opening is called the urinary meatus. Urine production comes in three steps: filtration, reabsorption and secretion. This occurs in the nephrons (found in the kidneys). In filtration, nitrogenous wastes leave the bloodstream. Next, reabsorption occurs. Water, sugar and salt are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream. Last, secretion occurs. Secretion is when acids, drugs, potassium, etc. leave the body in the form of urine. The ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) and aldosterone are the two hormones that control the amount of urine that the nephrons produce. Urine is normally straw colored to clear. It is composed of ninety-five percent water. Other terms for urinating are voiding or micturition.
You might also like
- Melanoma PPDocument11 pagesMelanoma PPapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Seizure DogsDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Seizure Dogsapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument1 pageIntegumentary Systemapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Integumentary DiseasesDocument1 pageIntegumentary Diseasesapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Renal Failure PamphletDocument2 pagesRenal Failure Pamphletapi-236094936No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageThe Endocrine Systemapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DiseasesDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Diseasesapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Power PointDocument9 pagesPower Pointapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument6 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Definitions of Nervous System DiseasesDocument1 pageDefinitions of Nervous System Diseasesapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Definitions of Respiratory DiseasesDocument1 pageDefinitions of Respiratory Diseasesapi-236094936No ratings yet
- Definitions of Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument1 pageDefinitions of Cardiovascular Diseasesapi-236094936No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Acid-Base PhysiologyDocument27 pagesAcid-Base PhysiologyANDRES GUARDIA CAYONo ratings yet
- Urinary System A&p 2Document187 pagesUrinary System A&p 2Ritari KimyunjongNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal GinjalDocument28 pagesKumpulan Soal GinjalTheddyon BhenlieNo ratings yet
- Sample of QuestionsDocument16 pagesSample of QuestionsAhmed Kh. Abu WardaNo ratings yet
- Concentration of Urine: Maj DR Shavana R.L RanaDocument22 pagesConcentration of Urine: Maj DR Shavana R.L RanaChandan Sah100% (1)
- SHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionDocument61 pagesSHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionAzlan YasirNo ratings yet
- Case Study Nephrotic SyndromeDocument26 pagesCase Study Nephrotic SyndromeDimpal Choudhary0% (2)
- Syllabus For B.H.M.S. (Degree) CourseDocument78 pagesSyllabus For B.H.M.S. (Degree) CourseBeat cretblast. 708.0% (1)
- Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument5 pagesAnatomic and Physiologic OverviewShannen Alija M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Module 17 - Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesModule 17 - Urinary SystemSam TagardaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Joson - WaterDiuresisDocument10 pagesWorksheet Joson - WaterDiuresisJoson Joyfactor67% (3)
- Urine FormationDocument16 pagesUrine Formationsajid_saiyad0% (1)
- Lecture 1 Excrection of Drugs Pharm D 4th Year BPKDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Excrection of Drugs Pharm D 4th Year BPKDaisy Arora KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 5-x Exam 5-Study Guide-Urinary SystemDocument9 pages5-x Exam 5-Study Guide-Urinary SystemAllison GajadharNo ratings yet
- Overview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedDocument34 pagesOverview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedAnnisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Urinary SystemDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Urinary SystemHannah Grace GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology813 cafeNo ratings yet
- Excretory System ResonanceDocument40 pagesExcretory System ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Aubf Review UermDocument18 pagesAubf Review UermZhiddah Japzon0% (1)
- Drug ClearanceDocument65 pagesDrug ClearanceSyed Umair100% (1)
- Drug Therapy Considerations Across The LifespanDocument43 pagesDrug Therapy Considerations Across The LifespanhealingnurseNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument49 pagesUrinary SystemSalum AhmadiNo ratings yet
- CH 15 Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument9 pagesCH 15 Excretion and Osmoregulationprachi98601No ratings yet
- Osmotic Regulation and ExcretionDocument46 pagesOsmotic Regulation and ExcretionKhent SyNo ratings yet
- A Summary Table of Reabsorption and Secretion Along The Nephron - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument2 pagesA Summary Table of Reabsorption and Secretion Along The Nephron - Anatomy & Physiologyshirley118650% (2)
- Urinary System NotesDocument5 pagesUrinary System NotesValerie Bete100% (4)
- Excretory System (Excercise)Document17 pagesExcretory System (Excercise)Shadab HanafiNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2014 Biology Question Paper With SolutionsDocument10 pagesWBJEE 2014 Biology Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 33 Cisplatin A ReviewDocument18 pages33 Cisplatin A Reviewtrifamonika23No ratings yet
- Insights in Physiology - Sudha Vinayak Khanorkar PDFDocument793 pagesInsights in Physiology - Sudha Vinayak Khanorkar PDFioan dumitrescuNo ratings yet