Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fossil Power Plant Components Failure Analysis Guideline
Uploaded by
abdulyunus_amirCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fossil Power Plant Components Failure Analysis Guideline
Uploaded by
abdulyunus_amirCopyright:
Available Formats
Fossil Power Plant Components Failure Analysis Guideline
Product ID:1018749 Date Published:31-Mar-2009 File size:12.83 MB Sector Name:Generation Document Type:Assembled Package FileType:Adobe PDF (.pdf) This product is available at no cost to funding members only. If you are a member, you must Log in to access. Price:$ 4,750 (US Dollars) If you are a non-funding individual or entity and wish to purchase this document, please contact the EPRI Order Center at 1-800313-3774 Option 2 or 650-855-2121. You may also send an e mail to orders@epri.com. Abstract The goal of engineering design is to obviate failures. However, this goal is only partially achievable because of the balance between cost and risk, potential deterioration during service, and the departure of actual operation from design assumptions. Thus, utility engineers are periodically faced with failures that span the gamut of power plant equipment and economic and safety consequences. Reaching a proper conclusion about the failure mechanism and the associated root cause is central to the postfailure decisions regarding permanent repair, temporary repair, replace in-kind, replace with an upgrade, or retire the associated equipment. The goal of this two-volume report is to provide guidance to utility teams that perform the failure analysis, with a focus on metallurgical and mechanical aspects of the failure. This failure analysis guideline provides a roadmap of the sequential steps for the investigation and the laboratory equipment to be used.
Objective
The challenge facing all fossil utilities is to maintain safe and reliable operation while facing a shrinking pool of expertise in the critical technologies. With retirement of fossil plants becoming a rarity, the aging equipment will encounter increasing failure rates unless a concerted effort is made to understand critical failures and react to them appropriately. The understanding of failures usually involves knowledge spread among several engineering disciplines, and the appropriate linkages and integration must be established in a comprehensive solution. The information provided in this failure analysis guideline will be valuable to mechanical, metallurgical, and system engineers at both power plants and central offices in establishing the root cause for a particular failure and in choosing the best options for repair or replacement to either minimize repeat failures or give extended life.
Approach
The primary objective of this project is to provide a comprehensive and detailed document that provides guidance to fossil utilities in either performing their own metallurgical failure analyses for a variety of power plant components or in directing organizations that are responsible for performing such work. The information will be valuable to mechanical, metallurgical, and system engineers at
both the power plant and the central office in establishing the root cause for a particular failure and choosing the best options for repair or replacement to either minimize repeat failures or give extended life. To achieve the goals, a comprehensive outline was developed and refined through successive iterations before project initiation. After the initial document was drafted, a review team of power plant failure analysis experts with over 100 years of combined experience was assembled, and the document was refined with a basic list of do's and don'ts, the inclusion of flowcharts, and the decision to split the guide into a two-volume set. The first volume identifies the instruments, equipment, and procedures that are used to perform failure analyses, as well as the sequential steps to be followed. The second volume provides detailed fossil power plant-specific information, including typical materials of construction, generic damage mechanisms, and characteristic damage for an assortment of key power plant components.
Results
A wealth of generic information exists regarding metallurgical failure analysis. However, the existing information is not specifically tailored for utility engineers, and it has redundant and superfluous information that is destined to confuse nonspecialists. Due to the universal challenges facing utilities in retaining technical expertise in metallurgy, welding, and mechanical design, the need for a readily accessible failure analysis guideline was identified as an Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) priority. This failure analysis guideline was developed in response to the utility need. This document has assembled the relevant information in a concise manner and logical order that fulfills the needs of utility engineers to correctly identify failure mechanisms and associated root causes. Whether the failure investigation is performed in-house or is contracted to others, the responsible utility engineers can use this failure analysis guideline to be confident in directing the effort. By following this document, utility engineers will be able to successfully complete the failure analysis and will be equipped to make enlightened decisions during the post-failure period.
Application, Value and Use
Failures in fossil power plant components are common occurrences. The tendency is to treat failures as single events, to treat the problem with immediate actions, and to move on to other challenges. This approach can squander the opportunity to determine the fundamental failure mechanism and the associated root cause. Without gaining such fundamental knowledge, history is destined to repeat itself, as evidenced by repeat failures in the same or similar units. By following this failure analysis guideline, personnel will document an understanding of each failure, which will lead to enlightened decisions and greater future equipment reliability.
EPRI Perspective
If it is true that knowledge is power, then lack of knowledge surely equates to weakness. This failure analysis guideline is one of a series of EPRI documents that seek to gather essential knowledge from disparate sources and distill it into utility-focused documents to broaden the knowledge base of utility personnel in an easy-to-comprehend presentation. Most of the information contained in this failure analysis guideline is well established, but it is scattered in dozens of books and publications, usually only familiar to technical specialists. Although the subject area demands a metallurgical emphasis, engineers from other disciplines will grasp most of the information and be able to put it to practical use. Newer Version Of
1012744-Fossil Power Plant Components Failure Analysis Guideline 1014184-Failure Analysis Guidelines for Power Plant Components
Program 2008 Program 87 Fossil Materials and Repair Keywords
Failure Analysis Failure mechanisms Metallographic examination Metallurgy Optical light microscopy Scanning electron microscopy Report 000000000001018749 Note
For further information about EPRI, call the EPRI Customer Assistance Center at (800) 313-3774 or email askepri@epri.com
Direct URL http://www.epri.com/abstracts/Pages/ProductAbstract.aspx?ProductId=000000000001018749 Email a link to the page
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Dpu4e - Dpu4fDocument5 pagesDpu4e - Dpu4fabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Support and Voltage Regulation in Power SystemDocument20 pagesReactive Power Support and Voltage Regulation in Power Systemabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- DAVR - ModulesDocument1 pageDAVR - Modulesabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Generator Earthing and Stator Earth Fault ProtectionDocument9 pagesGenerator Earthing and Stator Earth Fault ProtectionYousif_AbdalhalimNo ratings yet
- AREVA MiCOM Prot Relay DetailsDocument2 pagesAREVA MiCOM Prot Relay Detailsabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- 11 - 11KV (UE) 3C X 185 SQ MM Alu, Cable IndentDocument1 page11 - 11KV (UE) 3C X 185 SQ MM Alu, Cable Indentabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- India's Big and Messy Real Estate Ponzi Scheme, Just Got MessierDocument6 pagesIndia's Big and Messy Real Estate Ponzi Scheme, Just Got Messierabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Railway Services (Pension) Rules, 1993 - FormsDocument89 pagesRailway Services (Pension) Rules, 1993 - Formsabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- The 15 "Hottest" Electrical Problems You'Ll Find Lurking in FacilitiesDocument40 pagesThe 15 "Hottest" Electrical Problems You'Ll Find Lurking in Facilitiesabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Baroda Health Mediclaim Insurance PolicyDocument13 pagesBaroda Health Mediclaim Insurance Policyabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- WWW - Xilinx-What Is A CPLD-261016Document45 pagesWWW - Xilinx-What Is A CPLD-261016abdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- ModifiedNLC P343 Setting CalculationDocument13 pagesModifiedNLC P343 Setting CalculationFlorabel Tolentino Sera Josef100% (1)
- મેથી ની ભાજીDocument11 pagesમેથી ની ભાજીabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Actions To Be Taken On Death of A Pensioner To Claim Family PensionDocument6 pagesActions To Be Taken On Death of A Pensioner To Claim Family Pensionabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- GTU Civil Engineering: Home Date: 4 7 2016Document2 pagesGTU Civil Engineering: Home Date: 4 7 2016abdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Actions To Be Taken On Death of A Pensioner To Claim Family PensionDocument6 pagesActions To Be Taken On Death of A Pensioner To Claim Family Pensionabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Railway Services (Pension) Rules, 1993 - FormsDocument89 pagesRailway Services (Pension) Rules, 1993 - Formsabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- 1-Hydraulic Spring Type HMB4Document891 pages1-Hydraulic Spring Type HMB4abdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
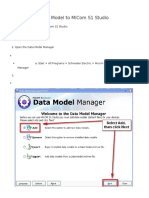
- How To Add A Data Model To MiCom S1 StudioDocument16 pagesHow To Add A Data Model To MiCom S1 Studioabdulyunus_amir0% (1)
- Vickers Parts SearchDocument11 pagesVickers Parts Searchabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Tentative - Schedule Diploma EnggDocument1 pageTentative - Schedule Diploma Enggabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Metallurgicaltesting 150416031439 Conversion Gate01Document26 pagesMetallurgicaltesting 150416031439 Conversion Gate01abdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- 5 Copper Busbar Jointing MethodsDocument12 pages5 Copper Busbar Jointing Methodsabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Effective Monitoring of AC MotorsDocument4 pagesEffective Monitoring of AC Motorsabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Capacitors For Power Factor CorrectionDocument5 pagesCapacitors For Power Factor CorrectionAswin Kumar KondurNo ratings yet
- OFTC Tap Change Testing RequirementDocument2 pagesOFTC Tap Change Testing Requirementabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- AD598 Vs AD698 LVDT Application DifferencesDocument2 pagesAD598 Vs AD698 LVDT Application Differencesabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- CT Busting: Engineering at Nipro India Corporation PVT Ltdtop ContributorDocument4 pagesCT Busting: Engineering at Nipro India Corporation PVT Ltdtop Contributorabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Capacitive and Inductive Reactive PowerDocument4 pagesCapacitive and Inductive Reactive Powerabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- DataDocument19 pagesDataabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Best CNC Machines For Beginners (The Ultimate Guide)Document11 pagesBest CNC Machines For Beginners (The Ultimate Guide)Squickmon's Engineering & AutomationNo ratings yet
- Kyletsai Aero ResumeDocument2 pagesKyletsai Aero ResumeKyle TsaiNo ratings yet
- Enr Top CM Firms June 2018Document1 pageEnr Top CM Firms June 2018emoriderNo ratings yet
- BY Alehegn Gashu Submitted To: Yibeltal Tarekegn (Asst - Professor)Document7 pagesBY Alehegn Gashu Submitted To: Yibeltal Tarekegn (Asst - Professor)ayanaNo ratings yet
- Academic General Seat MatrixDocument246 pagesAcademic General Seat Matrixmuthu kumarNo ratings yet
- Edibon GC enDocument160 pagesEdibon GC enPrathap ReddyNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Evaluation of Protective Relay Performance - REEES-2010 ITMDocument21 pagesFINAL - Evaluation of Protective Relay Performance - REEES-2010 ITMjaythakar8887No ratings yet
- English For Chemical EngineerDocument94 pagesEnglish For Chemical EngineerKresna Thufail ANo ratings yet
- Computer, ScienceDocument16 pagesComputer, ScienceAnonymous Cw1DGmRfNo ratings yet
- System Thinking and Project Management ProcessDocument31 pagesSystem Thinking and Project Management ProcessSunil K JauharNo ratings yet
- MCA-PE3 Technical Data SheetDocument10 pagesMCA-PE3 Technical Data Sheetsuman_civilNo ratings yet
- FRP VesselsDocument2 pagesFRP VesselsNaveenraj DadaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Highway and Railroad EngineeringDocument12 pagesSyllabus - Highway and Railroad Engineeringabel dequinaNo ratings yet
- Suitability of Fixed Base and Pinned Base PEB Structure With Pile FoundationDocument4 pagesSuitability of Fixed Base and Pinned Base PEB Structure With Pile FoundationKarthik SgNo ratings yet
- 52Document65 pages52Jaswanth SunkaraNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering 1 Assignment: Timber TestsDocument12 pagesStructural Engineering 1 Assignment: Timber Testsbrkn8No ratings yet
- Lab Manual Basic Mechanical Engineering LNCT BhopalDocument237 pagesLab Manual Basic Mechanical Engineering LNCT BhopalDeepakNo ratings yet
- Draft Discussions On 4TH Amendment of Is 456Document6 pagesDraft Discussions On 4TH Amendment of Is 456Santhosh Kumar BaswaNo ratings yet
- Element Topping Concrete: A I y y y Z Z Z e e E' BDocument6 pagesElement Topping Concrete: A I y y y Z Z Z e e E' BAistė VaitkuvienėNo ratings yet
- ECEN 3364 - Industrial Electronics and PLC ApplicationDocument6 pagesECEN 3364 - Industrial Electronics and PLC ApplicationItsMeRyanCNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument105 pagesBusiness PlanmarinelascribdNo ratings yet
- Studenthandbookfkk 2018Document72 pagesStudenthandbookfkk 2018Nordin SuhadatNo ratings yet
- Iec 44-2Document83 pagesIec 44-2Munkhbaatar ShagdarsurenNo ratings yet
- 530.1R-05 Specification For Masonry Structures and CommentaryDocument1 page530.1R-05 Specification For Masonry Structures and CommentaryCenteno NelsonNo ratings yet
- Crash Cushion Selection ProcedureDocument4 pagesCrash Cushion Selection ProcedureKOLD News 13No ratings yet
- SECTION 16010 General Provisions For Electrical Installation Part 1 - General 1.01 GENERALDocument22 pagesSECTION 16010 General Provisions For Electrical Installation Part 1 - General 1.01 GENERALabobeedoNo ratings yet
- Railway ReservationDocument42 pagesRailway Reservationshailesh singh100% (1)
- HelipadDocument53 pagesHelipadKandregulaPrameelaNo ratings yet
- Motor Starter Ready ReckonerDocument2 pagesMotor Starter Ready ReckoneranandpurushNo ratings yet
- Hexagon Simufact Welding PresentationDocument37 pagesHexagon Simufact Welding PresentationKhang NguyenNo ratings yet