Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tapiridae
Uploaded by
Dark_KiroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tapiridae
Uploaded by
Dark_KiroCopyright:
Available Formats
Tapir.
Taxonomi Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Scientific Name : amalia : chordata : mammalia : perissodactyla : tapiridae : tapirus indicus
Tapirs are mammals which are often confused with hippos, anteaters and capybaras Their closest li!ing relati!es are odd"toed ungulates #hoofed animals$,horses and rhinos % uni&ue feature that tapir posess is its fleshy prehensile nose that it uses to grab lea!es and e!en use as a snor'le while swimming Their hides are !ery tough but streamlined for easy maneu!ering in the forest Tapirs are (seed dispersers ( They eat seeds that are then dispersed in their scat which helps the forest to regenerate Tapirs are herbi!ores best suited to primary or old growth secondary forest, and their reproduction is slower than most mammal species due to a long gestation period #)*
months$ and to the fact that there is only one offspring per gestation Tapirs play a critical role in shaping and maintaining the biological di!ersity of tropical ecosystems The tapir is one of the first species in its habitat to be ad!ersely affected by human disturbance because of their si+e, and because of their sensiti!ity to habitat changes ,ocal e-tinction or population decrease may trigger ad!erse effects in the habitat, causing disruptions of some 'ey ecological processes #e g seed dispersal, nutrient recycling$, and e!entually compromising the long"term integrity and biodi!ersity of the ecosystem Ecology and Behaviour .alayan tapirs are primarily " although not e-clusi!ely " nocturnal They co!er large distances in their search for food, ma'ing fre&uent stops to eat /egularly used paths are used in these foraging e-cursions, and se!eral may lead to bodies of water 0ach animal occupies a large territory which o!erlaps that of its neighbours These paths and territories are mar'ed with urine, which is sprayed on small bushes and plants 1hen mo!ing, the .alayan tapir wal's slowly with its head down, which probably allows it to pic' up the scents of other tapirs 2ndi!iduals also communicate with shrill whistles The .alayan tapir is a good climber, scaling steep slopes with relati!e ease, and when alarmed gallops off with surprising speed Tapirs and Their Connection to the Ecosystem Tapirs play a critical role in shaping and maintaining the biological di!ersity of tropical forests and function as biological indicators of area re&uirements for the ecosystem The tapir is one of the first species in its habitat to be ad!ersely affected by human disturbance because of their si+e, and sensiti!ity to changes in their habitat range ,ocal e-tinction or population decrease may trigger ad!erse effects in the forest, causing disruptions of some 'ey ecological processes #e g seed predation and dispersal, nutrient recycling$, and e!entually compromising the long"term integrity and biodi!ersity of the ecosystem These factors, added to the destruction of tapir habitat in recent years, 3ustify the urgency for in!estigation of the status of the populations, and de!elopment and implementation of conser!ation and management plans
References 0isenberg, 4 F , C P 5ro!es, and K .acKinnon )667 Tapirs In 5r+ime'8s 0ncyclopedia of .ammals Edited by S P Par'er New 9or': .c5raw":ill ;olume <, pp =6>"?7@ .ohd Khan bin .omin Khan )66> Status and action plan of the .alayan tapir #Tapirus indicus$ In Tapirs " Status Sur!ey and Conser!ation %ction
Plan 2ACNBSSC Tapir Specialist 5roup Compiled by C . Droo's, / 0 Dodmer, and S .atola 2ACN, 5land, Swit+erland and Cambridge, AK %!ailable online at http:BBwww tapirbac' comBtapirgalBiucn"sscBtsgBaction6>Bdefault htm 1ilson, C 0 , and C . /eeder EeditorsF )66* .ammal Species of the 1orld #Second 0dition$ 1ashington: Smithsonian 2nstitution Press %!ailable online at http:BBnmnhwww si eduBmsw
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Experiment 1 CBB 20104 Shake FlaskDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 CBB 20104 Shake FlaskDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Tutorial 1: Fluid Mechanics (CLB 11003) Chapter 1: Introduction To Fluid SystemsDocument1 pageTutorial 1: Fluid Mechanics (CLB 11003) Chapter 1: Introduction To Fluid SystemsDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Acid Base Titration ExperimentDocument2 pagesAcid Base Titration ExperimentDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Metabolic EngineeringDocument10 pagesMetabolic EngineeringAlexandru TugutchiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- GeneticDocument34 pagesGeneticDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Metabolism (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesMetabolism (Compatibility Mode)Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- TapirDocument3 pagesTapirDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- MeiosisDocument6 pagesMeiosisDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Lab Manual Organic Analytical ChemistryDocument30 pagesLab Manual Organic Analytical ChemistryKayrol29100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument6 pagesMeiosisDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Gaza War SummaryDocument8 pagesGaza War SummaryDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Pulsed Column Liquid - Liquid Extraction Unit.: Experiment 4Document16 pagesPulsed Column Liquid - Liquid Extraction Unit.: Experiment 4Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular RespirationDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Chemistry Process of AmmoniaDocument1 pageChemistry Process of AmmoniaDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Etc (Electron Transport Chain)Document24 pagesEtc (Electron Transport Chain)Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Biotreatmenttypes PDFDocument5 pagesBiotreatmenttypes PDFDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
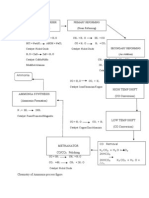
- NH 3Document4 pagesNH 3uetian729No ratings yet
- Active Sludge PDFDocument8 pagesActive Sludge PDFDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Airlift BioreactorDocument18 pagesAirlift BioreactorDark_Kiro100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidDocument7 pagesNucleic AcidDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Mini Research About Biomass by Using Tapioca PeelsDocument40 pagesMini Research About Biomass by Using Tapioca PeelsDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Project ChecklistDocument3 pagesProject Checklistarunurs1No ratings yet
- Festivals of IndiaDocument51 pagesFestivals of IndiaDhatchayani RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Virudhunagar: Department: Semester: Vi SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 6602Document34 pagesSri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Virudhunagar: Department: Semester: Vi SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 6602JEYA KUMARNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sustainabilty Report - ENDocument29 pages2020 Sustainabilty Report - ENGeraldNo ratings yet
- Lecture For ClassDocument97 pagesLecture For ClassRITHWIK DINESHNo ratings yet
- Auto Repair and Car Wash Business PlanDocument31 pagesAuto Repair and Car Wash Business PlanKiraYagamiNo ratings yet
- STPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Document19 pagesSTPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Sou Voyage0% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Biochemistry - Syllabus Marks EtcDocument8 pagesBiochemistry - Syllabus Marks EtcshahzebNo ratings yet
- Real Estate QuizzerDocument27 pagesReal Estate QuizzerRochelle Adajar-BacallaNo ratings yet
- Expansion ScrewsDocument32 pagesExpansion ScrewsJomar PortadoNo ratings yet
- The Interrelationship Between Fashion andDocument17 pagesThe Interrelationship Between Fashion andpushpak navandarNo ratings yet
- A Butterfly Effect Volume 1 (Years 1 - 2)Document362 pagesA Butterfly Effect Volume 1 (Years 1 - 2)xdyj2005No ratings yet
- Gujarat-Ports Sector ReportDocument17 pagesGujarat-Ports Sector ReportK. Ashok Vardhan ShettyNo ratings yet
- FPS Module 1Document28 pagesFPS Module 1RickNo ratings yet
- MCQ DTSDocument3 pagesMCQ DTSraja93satNo ratings yet
- Types of Welding Defects PDFDocument12 pagesTypes of Welding Defects PDFDhiab Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Bock09 - Video Compression SystemsDocument300 pagesBock09 - Video Compression SystemsWong_Ngee_SengNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document1 pageCovid 19Sadiq NaseerNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- T - Cell DifferentiationDocument24 pagesT - Cell DifferentiationAnand Prakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Ecological Fire MGMT Guidelines V5Document40 pagesEcological Fire MGMT Guidelines V5MeNo ratings yet
- Osawa Catalogue 2021Document708 pagesOsawa Catalogue 2021lorenzo.lima1706No ratings yet
- Marshall Abby - Chess Cafe - The Openings Explained - 1-63, 2015-OCR, 682pDocument682 pagesMarshall Abby - Chess Cafe - The Openings Explained - 1-63, 2015-OCR, 682pArtur MałkowskiNo ratings yet
- Castlegar & Slocan Valley Pennywise Dec. 9, 2014Document49 pagesCastlegar & Slocan Valley Pennywise Dec. 9, 2014Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet
- Marlinespike - Rope Breaking StrengthDocument7 pagesMarlinespike - Rope Breaking StrengthAnonymous ycFeyuLAt100% (1)
- Laura Gentile Letter On Hampden County CourthouseDocument6 pagesLaura Gentile Letter On Hampden County CourthouseMassLiveNo ratings yet
- PC-FT 403: Lecture (1) byDocument21 pagesPC-FT 403: Lecture (1) byFT 19 Suparno DasNo ratings yet
- Practice Tests - Tiếng Anh 7 I-learn Smart World TestDocument9 pagesPractice Tests - Tiếng Anh 7 I-learn Smart World TestnghiepNo ratings yet
- Rebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Document28 pagesRebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Manuel Velasco100% (1)
- Electrical Circuits 1 QPDocument7 pagesElectrical Circuits 1 QPKitty MinogueNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Pemisahan Kimia Pembuatan Membran Polysulfon (PSF)Document9 pagesJurnal Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Pemisahan Kimia Pembuatan Membran Polysulfon (PSF)Rizki AuNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)