Professional Documents
Culture Documents
102 Lab Exam4 Reviewer - Parts
Uploaded by
Jan Marvin Lichauco MendozaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
102 Lab Exam4 Reviewer - Parts
Uploaded by
Jan Marvin Lichauco MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
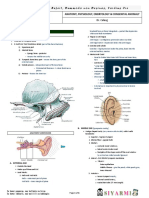
BIO 102 LAB PE4 CAT DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYS
PART FUNCTION/DESCRIPTION SALIVARY GLANDS -outgrowths of oral epithelium Excretes saliva (ptyalin) moistens food Secretes digestive enzymes OTHERS
Parotid gland (penetrates upper lip) Submaxillary gland Sublingual gland Molar gland Lips Cheeks Vestibule Hard palate Soft palate Nasopalatine ducts Tongue Filiform papillae Fungiform papillae Vallate papillae
ORAL CAVITY Bounds oral cavity Separates lips and teeth Anterior of roof of oral cavity; houses nasopalatine ducts Posterior part; houses nasopharynx Connect mouth and nasal cavities through incisive foramina Anterior; hard and spine-like (pointed posteriorly) Remainder of the tongue 4-6 fungiform papillae in a V-shaped row
Supported by pre/maxillary and palatine bones Lacks bony support
Amniote definitive tongue: -fused 4 swellings (primary tongue + tuberculum impar + 2 lateral lingual swellings -invaded by voluntary muscles (from hypobranchial muscles) th -innervated by 12 cranial nerve (hypoglossal) *papillae: with microscopic taste buds
Frenulum Flattened papillae
Isthmus of the fauces Tonsillar fossa Palatine tonsil Glassopalatine arch Pharyngopalatine arch Nasopharynx Posterior nares / choanae Eustachian tubes Esophagus
Fold for attachment of tongue to oral cavity floor Bears openings of ducts of submaxillary and sublingual glands PHARYNX Opening of the free border of the palate; leads into pharynx Contains palatine tonsil nd Filters air; proliferate from 2 gill pouches Anterior fold/boundary of tonsillar fossa Posterior fold/boundary of tonsillar fossa Part of pharynx dorsal to soft palate Internal ends of nasal passages Connect pharynx with cavity of middle ear Passage of food (mouth stomach); DORSAL to the larynx
Shoved backward to separate food and respiratory passages Lined by stratified epithelium (*crop/ingluvies: enlargement in birds) Lies in the mediastinum
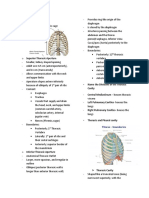
Epiglottis Body of the hyoid Anterior horn or cornua Posterior horn or cornua Larynx Glottis (voice box) Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage constitutes Arytenoids the True vocal cords Adams (medial) apple False vocal cords (lateral) Trachea / wind pipe Thyroid gland Isthmus of the thyroid gland Pleural cavity / pleural sac Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Mediastinal septum Mediastinum Diaphragm
Guards entrance into respiratory tract (larynx) HYOID APPARATUS, LARYNX, TRACHEA, ESOPHAGUS nd rd -from 2 and 3 gill arches Narrow bar of bone -supports base of tongue Long, slender; chain of 4 bony pieces (last: -for muscle origin and insertion articulates w/ tympanic bulla) Short; united to larynx Opening of the larynx th th Supports ventral wall of larynx Shield-shaped; from 4 and 5 gill arch Forms ring around larynx Supports dorsal rim of glottis Produce sound Not cords, but folds of lateral wall of larynx
Passage of air Has secretion for normal growth and sexual development Connects caudal ends of 2 lobes of thyroid glnad PLEURAL AND PERICARDIAL CAVITIES Houses the lungs Lines the pleural cavity; forms mediastinal septum Lines the lungs Partition from heart to median ventral line Space between mediastinal septum Separates pleural from peritoneal cavity Used in respiration (contracts flattens air rushes into lungs) Insertion of the diaphragm For respiration *composed of alveoli (air cells) Attachment of lungs Attachment of lung to dorsal thoracic wall Supports postcaval vein From liver to heart (bring deoxygenated blood) Tissue enclosing the heart
Walls stiffened by cartilaginous rings Flat elongated body; epithelial invagination from pharyngeal floor
From inner and outer wall of the hypomere Consist of 2 median walls of pleural sacs; separates at the heart Muscle: originribs, sternum, vertebrae; insertioncentral tendon Fused pleuroperitoneal fold + transverse septum
Central tendon of the diaphragm Lungs Left lobe Right lobe Radix / root of the lung Pulmonary ligament Caval fold Postcaval vein Pericardial sac / parietal pericardium
Anterior, middle (larger) and posterior lobes (Larger than left) Ant, middle, post lobes (medial, lateral lobules) Found: artery, vein, bronchus/air tube Fold of the pleura Dorsal fold of mediastinal septum
Pericardial cavity Visceral pericardium Thymus
Houses the heart; space between pericardial sac and heart Lines the heart (inseparably adherent) Mass of gland tissue; part of immune system
Portion of the coelom Continuous w/ pericardial sac where blood vessels enter Younger specimen = larger thymus Derived from endodermal lining of embryo gill pouches Lies in the mediastinum
Dorsal aorta Abdominal / peritoneal cavity Peritoneum Parietal peritoneum Visceral peritoneum / serosa Dorsal mesentery Ventral mesentery Stomach Cardia Cardiac end of stomach Lesser curvature Greater curvature Fundus Body of stomach Pylorus Pyloric valve Rugae Gastrosplenic ligament Mesogaster Greater omentum Lesser peritoneal sac Lesser omentum / gastrohepato-duodenal ligament) Gastrohepatic ligament Hepatoduodenal ligament Liver (right, left, caudate lobes)
Largest artery, carries oxygenated blood PERITONEAL CAVITY Houses digestive tract Lines the peritoneal cavity Lines the body wall Lines the viscera Double-walled membrane formed when visceral & parietal walls meet Area of junction of stomach and esophagus Region of stomach adjacent to cardia Concave anterior surface of stomach Larger convex posterior surface Saclike bulge to the left of the cardia Remainder of the stomach Junction of stomach and small intestine Constriction marking the junction/pylorus Marked ridges for greater absorptive area Portion of the greater omentum between spleen and stomach Peritoneum covering the stomach Covers the liver; extension of the mesogaster Protects abdominal viscera Cavity within greater omentum Portion of the mesogaster; passes from lesser curvature to posterior surface of liver Portion of lesser omentum from lesser curvature to liver Portion of lesser omentum from liver to small intestine Contains the bile duct and hepatic portal vein Secretes bile: assist in digestion of fat Store excess glycogen, produce urea, control of substances in the blood Passage of bile from gall bladder Passage of bile to the intestine Union of cystic and hepatic ducts; bile to duodenum Right and dorsal to bile duct Entrance into cavity of omentum From between the 2 medial lobes of the liver to the medial ventral line Attaches liver to the central tendon of the diaphragm Absorptive function in digestion Part of dorsal mesentery supporting the duodenum Attaches duodenum to the right kidney Portions beyond the duodenum Finger-like projections of mucous membrane; increase surface area Elevation at the junction of large and small intestine Secrete pancreatic juice into duodenum (impt for digestion) *Islets of Langerhans: produce insulin for carb metabolism Passage of pancreatic juices Swollen chamber where bile and pancreatic ducts unite Slight projection at the junction of small and large intestine Absorbs water
Intact in mammals Persists only in liver and urinary bladder
Consist of 2 separate walls Owes its origin to the rotation of the stomach
Lobes subdivided: median and lateral (large: left lateral, right median) Diverticulum from small intestine
Gall bladder Cystic duct Bile duct Common bile duct Hepatic portal vein Foramen epiploicum Falciform ligament Coronary ligament Intestine Mesoduodenum Duodenum Duodorenal st -1 portion ligament Jejunum Ileum Small intestine villi Ileocolic valve Pancreas
Stalk of liver outgrowth
Anterior connection of liver to septum Contains the pancreas
Dorsal to greater curvature of stomach
Pancreatic ducts Ampulla of Vater Large Caecum intestine Ascending, transverse, descending Mesocolon Rectum Urinary bladder Medial ligament Lateral ligament Lymph glands Lymph nodules / Peyers patches
Joins common bile duct where it enters the duodenum
Mesentery of the colon Terminal portion of descending colon Pear-shaped reservoir for urine Ventral mesentery; extends to medial ventral line Near exit of bladder from peritoneal cavity Part of lymphatic system Aggregations of lymph nodules (portions of lymphatic system)
Completely separated from urogenital ducts (no cloaca!) In amniote embryos: allantois (respiratory function)
CAT UROGENITAL SYS
KIDNEYS AND DUCTS Right and left kidneys Bean shaped METANEPHROI; Retroperitoneal *collecting tubules, pelvis, ureter: outgrowth of mesonephric duct In females: dorsal to horns of uterus; Males: dorsal to ductus deferens
Hilus Ureter (metanephric duct) Renal sinus (*renal artery, renal vein) Renal pelvis Renal papilla Cortex Medulla Urinary bladder Apex / vertex Fundus Medial and lateral ligaments Urethra Rectovesical pouch (male) Vesico-uterine pouch (female) Ovaries Graafian follicles Muellerian ducts / oviducts Uterine / Fallopian tube Ostium with fimbriae Horn of uterus Broad Mesovarium ligament of Mesosalpinx the uterus Mesometrium Round ligament of the uterus Body of uterus
Concavity in the medial face (ourside) Passage of urine Cavity within hilus; where renal artery & vein and beginning of ureter pass Expanded beginning of ureter Where openings of collecting tubules are Peripheral; contains renal corpuscles and looped portions of kidney tubules Central; marked by collecting tubules Reservoir of urine Free anterior end of bladder Posterior portion Neck of the bladder Pouch between bladder and rectum Pouch between bladder and uterus FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYS Egg production Contains egg/ovum Ducts of the ovaries Uppermost portion of oviduct (Slit) where fallopian tube opens Posterior part of oviduct Mesentery of the ovary Mesentery of the Fallopian tube Peritoneum supporting the horns of the uterus Extends from horn to the body wall Single tube where the horns unite
In the renal pelvis Collecting tubules + renal papilla = renal pyramid
Covered by peritoneum and median & lateral ligaments
In embryos: urethra = urogenital sinus
*corpora lutea (if preggers): represent follicles from which the eggs were discharged
*Fimbriae: border of ostium; overarching the ovary
Perpendicular to broad ligament *Womb = body + horns *Bipartite type: vagina fused, lower parts of uteri fused *Cervix: lower end of uterus
Vagina Labia major and vulva Clitoris Urogenital canal/sinus Anal glands/sacs Scrotum Spermatic cord External & Internal inguinal rings Urogenital canal/sinus Prostate gland Bulbourethral glands / Cowpers gland Penis Glans of the penis Urogenital opening Corpora cavernosa Cavernous urethra Crura of the penis Prepuce Testis Vaginal sac Tunica vaginalis Mesorchium Gubernaculum Epididymal duct (head, body tail)
Posterior to uterus (Homologous to the penis) Where urethra and vagina unite Secrete odoriferous substance of sexual nature MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYS Houses the testes Contains ductus deferens/vas deferens, blood vessels and nerves Ends of the inguinal canal Common tube to deferent duct and urethra Secretion casues secretion of seminal vesicles to coagulate produce plug Swellings in urogenital canal Pointed projection of the penis Tip of the glans; exit of urine and sperm Cylindrical bodies in the penis; distended with blood during copulation to project penis out of the prepuce Portion of the urogenital canal in the penis; dorsal Where the 2 cavernous bodies diverge Covers the penis Cavity where the testis lies Lines the vaginal sac Between testis and wall of vaginal sac Ligament in scrotal wall where testis is attached Coiled ductus deferens on dorsal surface of testis; conducts sperm Head: receives efferent ductules from testis Tail: where gubernaculum is attached AMNIOTE EMBRYO Sac around embryo Connection between embryo and maternal tissues Conveys umbilical blood vessels to and from embryonic part of placenta *no direct connection bet embryo and mother
To either side of rectum
Enlargement in junction between deferent duct and urethra
Bears spines for copulation
Attached to ischia Part of peritoneal cavity
Homologous to round ligament of uterus Derived from mesonephros
Amnion Placenta Umbilical cord
CHORIOALLANTOIC PLACENTA; ZONARY type
SHARK DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYS
Pleuroperitoneal cavity Parietal peritoneum PLEUROPERITONEAL CAVITY Houses pleural and peritoneal viscera Lines pleuroperitoneal cavity
Liver (left, right, median lobe) Gall bladder Esophagus-stomach Pylorus Spleen Intestine (duodenum) Bile duct Pancreas (dorsal and ventral) Valvular intestine (*spiral valve) Rectal / digitiform gland Cloaca Anus Abdominal pores Dorsal (from meddorsal line to digestive tract) Ventral (remnants only) Mesogaster Gastrosplenic ligament Mesentery Mesorectum Mesovarium Mesorchium Mesotubarium Gastro-hepatoduodenal ligament Hepatoduodenal ligament Gastrohepatic ligament Suspensory / falciform ligament Coronary ligament (transverse septum)
Anterior end; large brownish or grayish Located in median lobe of liver J-shaped Constriction; marks termination of stomach Along posterior margin of the stomach bend; part of lymphatic system Beyond pylorus, extending into anus From gall bladder to duodenum Ventral: in curve of duodenum; dorsal: dorsal to stomach and duodenum Part of small intestine with spiral valve (to increase absorptive surface) Hyman: secretes mucus; Now: secretes salt for osmoregulation Receives both urinary and genital ducts Opening of cloaca Communication to the exterior MESENTERIES Supports stomach Mesogaster from spleen to stomach Supports small intestine In the region of the rectal gland Supports ovary Supports testis Supports oviducts Lesser omentum; from right side of stomach to liver and duodenum Lesser omentum from liver to duodenum Lesser omentum from stomach to liver and duodenum From midventral surface of liver to midventral line
If with papillaeesophagus; Rugaestomach
Runs in a strip of mesentery; passes to dorsal side of duodenal wall
Attached to colon
Contains bile duct and blood vessels
Parietal pericardium Visceral pericardium Sinus venosus
Buccal / oral cavity Primary tongue Pharynx Spiracle Elongated gill slits (5)
Partition separating the cavities *Coronary ligament: attaches liver to septum PERICARDIAL CAVITY Lines pericardial cavity Lines the heart (attached only at anterior and posterior ends) Fan-shaped chamber at the posterior end of the heart Wall continuous with transverse septum Have venous channels through which venous blood is returned to the heart ORAL & PHARYNGEAL CAVITIES AND RESPI SYS Enclosed by jaws and gill arches Immovable projection -have no muscles or glands nd -supported by 2 or hyoid gill arch Posterior to mandibular arch (Internal) Passage from pharynx to exterior Cavities where internal gill slits open into Opening to the exterior Tissue between successive gill pouches Continuation of brachial bar to body surface; bears gill lamellae Half-gill; on one face of the septum Gill; 2 demibranchs of a spetum Afferent: brings venous blood to the gills; Efferent: carries aerated blood from gills Respiratory mechanism; where blood obtains oxygen and gives up CO2
Gill pouches External gill slits Branchial bar (visceral arch) Interbranchial septum Demibranch Holobranch Afferent and efferent branchial blood vessels Gill lamellae
Epithelium: ectodermal Inner thickened part: cartilaginous gill arch; external: gill rays
*oxygen: from water (flows through gill pouches by movements of gill apparatus)
SHARK UROGENITAL SYS
Ovaries Mesovarium Kidneys Chromaffine masses (suprarenal bodies) Oviducts Mesotubaria Ostium Shell gland / nidamental gland Uterus Cloaca (urodeaum and coprodaeum) FEMALE Where ovum are produced Mesentery of the ovaries Thinner anterior portion: no urinary function; Thicker posterior portion: excretion Light spots near medial border Immature: ventral face of kidneys, no mesentery; Mature: large tubes Mesentery of oviducts (in mature females) Where 2 oviducts unite in falciform ligament Secretes membrane to enclose eggs Coprodaeum: ventral, opening of intestine Urodaeum: dorsal, urogenital region of cloaca Dorsal to liver Retroperitoneal, MESONEPHROI (opisthonephroi) Same as in males
Formed by fusion of peritoneal funnels of pronephros Enlargement in the oviducts
Urinary papilla Muellerian duct / mesonephric duct Testes Mesorchium Wolffian duct / mesonephric duct Efferent ductules Epididymis Ductus deferens Leydigs gland Seminal vesicle Sperm sac Cloaca (uro and coprodaeum) Urogenital sinus Urinary papilla MALE Where sperm are produced (specifically, seminiferous tubules) Mesentery of the testes
In middorsal wall of urodaeum Along ventral face of kidney
Dorsal to liver
Connects testis to opisthonephros to convey sperm into Wolffian duct Part of opisthonephros penetrated by efferent ductules Part of Wolffian duct; connected to tubules of epididymis Secretes fluid beneficial to sperm Ductus deferens part of caudal opisthonephros Terminal of seminal vesicle Where 2 sperm sacs unite
Larger than in females; run along ventral face of kidneys Run in the mesorchium
Behind epididymis Have papillae where seminal vescicles open into
You might also like
- BIO 102: First Lab Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesBIO 102: First Lab Exam Study GuideDanielle Jann Manio Concepcion100% (1)
- LMR ANATOMY by DR Shilpi Agarwal PDF Filename UTF 8''LMR ANATOMY PDFDocument12 pagesLMR ANATOMY by DR Shilpi Agarwal PDF Filename UTF 8''LMR ANATOMY PDFadiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderDocument10 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderAdam IrsyaddyraNo ratings yet
- Neck Axilla BackDocument24 pagesNeck Axilla BackmoregutsNo ratings yet
- Clerks Manual Ay 2016-2017 PDFDocument20 pagesClerks Manual Ay 2016-2017 PDFJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pranic HealingDocument73 pagesPranic HealingShah Alam67% (3)
- Bio 235 Midterm 1 NotesDocument53 pagesBio 235 Midterm 1 NotesNita JosephNo ratings yet
- Ebook Developing Human 9Th Edition Moore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesEbook Developing Human 9Th Edition Moore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStacieSharpnocje88% (8)
- Form 6 Biology Second Term Practical PDFDocument13 pagesForm 6 Biology Second Term Practical PDFWalter100% (9)
- Girdle endoskel crescent shape, on Trunk FxnDocument3 pagesGirdle endoskel crescent shape, on Trunk FxnJune Francis Ang MongeNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THDocument6 pagesManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OverviewDocument12 pagesRespiratory System OverviewNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- 3 Hyman Digestive SystemDocument7 pages3 Hyman Digestive SystemJoachimNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissuememe bolongonNo ratings yet
- Superficial Back Proximal Insertion Distal Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Function Latissimus DorsiDocument23 pagesSuperficial Back Proximal Insertion Distal Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Function Latissimus Dorsimeyouhere100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology MnemonicsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology MnemonicsLalajimNo ratings yet
- Ascending Tracts Spinal CordDocument1 pageAscending Tracts Spinal CordChristopher Samuel0% (1)
- Last Minute Revision Tips for FMGE ExamDocument54 pagesLast Minute Revision Tips for FMGE Examswetha100% (3)
- MOCK QUIZ - Head & Neck EmbryoDocument3 pagesMOCK QUIZ - Head & Neck EmbryoLanz RomuloNo ratings yet
- Inguinal CanalDocument4 pagesInguinal CanalspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & HandDocument27 pagesAnatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & Handgdubs215No ratings yet
- Openings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedDocument19 pagesOpenings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedMacy Peralta100% (1)
- Development of Branchial ArchesDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Branchial ArchesFidz LiankoNo ratings yet
- TubeGuide PDFDocument1 pageTubeGuide PDFalberto100% (1)
- Peritoneal Anatomy Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesPeritoneal Anatomy Lecture Noteschc300No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologygirlwithbrowneyesNo ratings yet
- #Anatomy of External & Middle EarDocument2 pages#Anatomy of External & Middle EarameerabestNo ratings yet
- Bsci201 Anatomy Class NotesDocument101 pagesBsci201 Anatomy Class NotesSahel UddinNo ratings yet
- Upper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallDocument18 pagesUpper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallHessa AlamiraNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesakexisNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonDocument4 pagesLecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonLopez Manilyn CNo ratings yet
- Esphagus Stomach Duodenum Gross AnatomyDocument9 pagesEsphagus Stomach Duodenum Gross AnatomyWinchester LoapedNo ratings yet
- Disease Signs & SymptomsDocument3 pagesDisease Signs & SymptomsJose Dangali AlinaoNo ratings yet
- Recommended Dosage For DrugsDocument2 pagesRecommended Dosage For DrugsJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of AirwaysDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Airwaysgdubs215No ratings yet
- Skeleton of The SharkDocument12 pagesSkeleton of The SharkJoachimNo ratings yet
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 pagesSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴No ratings yet
- Pelvic Cavity PDFDocument10 pagesPelvic Cavity PDFRigor MortisNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY: Pelvic 2Document16 pagesANATOMY: Pelvic 2Nur Liyana MohamadNo ratings yet
- PONS: NeuroanatomyDocument20 pagesPONS: NeuroanatomyHassan IlyasNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The ThoraxDocument4 pagesMuscles of The ThoraxKieth Roland PalosoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract ReciewDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract ReciewRobert LotzerNo ratings yet
- COMPARATIVE CIRCULATORY SYSTEMSDocument15 pagesCOMPARATIVE CIRCULATORY SYSTEMSSmartcool SoNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Neck PDFDocument1 pageMuscles of The Neck PDFEdreyn DellosaNo ratings yet
- 1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2Document18 pages1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2DrVasu Mudiraj100% (1)
- Idoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFDocument6 pagesIdoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFhieulee84No ratings yet
- Axillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4Document14 pagesAxillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4foster18No ratings yet
- 15 PharynxDocument9 pages15 Pharynxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Elbow AnatomyDocument2 pagesElbow Anatomyapi-195986134No ratings yet
- 11 MusclesDocument9 pages11 MusclesElaine Loreen Villanueva100% (1)
- Embryological DerivativesDocument1 pageEmbryological DerivativesDr Ishtiaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Step-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - SampleDocument8 pagesStep-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - Samplecsbully913No ratings yet
- MTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Excretory SystemDocument9 pagesMTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Excretory SystemJaeri HuangNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves and BranchesDocument5 pagesCranial Nerves and Branchesballer0417No ratings yet
- 1a. Upper Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument21 pages1a. Upper Anatomy & PhysiologyDliya UlhaqNo ratings yet
- 04 Mediastinum, HeartDocument27 pages04 Mediastinum, HeartShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms: by WWW - Ipostforyou.infoDocument38 pagesAnatomical Terms: by WWW - Ipostforyou.infoShahid Maqbool100% (1)
- Diaphragm Gross AnatomyDocument3 pagesDiaphragm Gross AnatomyCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- EAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyDocument6 pagesEAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy-Review NotesDocument56 pagesGross Anatomy-Review NotesJohnNo ratings yet
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocument100 pagesHistology of Digestive SystemFadhila Putri Palupi100% (2)
- Anatomy of The Digestive SystemDocument46 pagesAnatomy of The Digestive Systemprincess joy sustiguerNo ratings yet
- The Abdomen: Stuart M BuntDocument36 pagesThe Abdomen: Stuart M BuntEmmy BankzNo ratings yet
- 7th-The Alimentary SystemDocument25 pages7th-The Alimentary Systemprasun_v100% (1)
- Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Otitis Media in ChildrenDocument45 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Otitis Media in ChildrenJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- LU3 HS 201 Paz Y EnteDocument2 pagesLU3 HS 201 Paz Y EnteJan Marvin Lichauco Mendoza100% (1)
- Evaluation and Management of Pediatric Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument46 pagesEvaluation and Management of Pediatric Community-Acquired PneumoniaJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - GBSDocument28 pagesCase Presentation - GBSJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- LU3 HS 201 Paz Y EnteDocument2 pagesLU3 HS 201 Paz Y EnteJan Marvin Lichauco Mendoza100% (1)
- FORM - 5A - 2010-21978 - Second Semester AY 2013-2014Document1 pageFORM - 5A - 2010-21978 - Second Semester AY 2013-2014Jan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Approved Academic Calendar 2014-2015Document2 pagesApproved Academic Calendar 2014-2015Jan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unknown Analysis TESTSDocument4 pagesUnknown Analysis TESTSJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- UP Med CurriculumDocument21 pagesUP Med CurriculumJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen MetabolismDocument31 pagesNitrogen MetabolismJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- UP College of Law Curriculum PDFDocument1 pageUP College of Law Curriculum PDFFroilan Richard RamosNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Flow ChartDocument3 pagesChem 16 Flow ChartJan Marvin Lichauco Mendoza100% (1)
- Movies To DownloadDocument1 pageMovies To DownloadJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 56 The DiaphragmDocument64 pagesCHAPTER 56 The DiaphragmAbeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument16 pagesRespiratory PhysiologyYsabel Salvador DychincoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Movements and MusclesDocument48 pagesRespiratory Movements and MusclesMomentaNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) NotesDocument3 pagesSheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) Notesdevu fav MohanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Today Transition and Trends 9th Edition Zerwekh Test BankDocument25 pagesNursing Today Transition and Trends 9th Edition Zerwekh Test BankShellyGriffinjacb100% (48)
- Abnormal Bowel Gas PatternDocument136 pagesAbnormal Bowel Gas PatternEdward ElricNo ratings yet
- hw410 Stress Management and Prevention Program Resource Unit 9Document40 pageshw410 Stress Management and Prevention Program Resource Unit 9api-376064259No ratings yet
- Yoga For Pregnant Ladies EnglishDocument44 pagesYoga For Pregnant Ladies EnglishDrAjey BhatNo ratings yet
- Embryology Notes emDocument25 pagesEmbryology Notes emAnonymous IwWT90VyNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErica Denice CastilloNo ratings yet
- Everyday Enlightenment PDFDocument26 pagesEveryday Enlightenment PDFMarcela SanchezNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument262 pagesMechanical VentilationShalini Garg0% (1)
- Watch Your Weight While at HomeDocument26 pagesWatch Your Weight While at HomeNikita SNo ratings yet
- Cervical PlexusDocument4 pagesCervical PlexusIshant SinghNo ratings yet
- Mentoring Doctors for Justicistic SuccessDocument9 pagesMentoring Doctors for Justicistic Successsk100% (1)
- Chapter 27 Chest Injuries Final TermDocument4 pagesChapter 27 Chest Injuries Final Termluwi vitonNo ratings yet
- Bio4 5Document11 pagesBio4 5HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- Diaphragmatic breathing: A concise guide to this important breathing techniqueDocument23 pagesDiaphragmatic breathing: A concise guide to this important breathing techniqueSonia guptaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Respiratory System LessonsDocument19 pagesGrade 7 Respiratory System LessonsclaireNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in Obstetrics GynaecologyDocument90 pagesPhysiotherapy in Obstetrics Gynaecologyمركز ريلاكس للعلاج الطبيعيNo ratings yet
- Philippine Supreme Court Decision on Murder Conviction and SentencingDocument17 pagesPhilippine Supreme Court Decision on Murder Conviction and SentencingNor-Alissa M DisoNo ratings yet
- Thoracic CavityDocument2 pagesThoracic CavityMaria Isabela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sadhana Intensive CourseDocument16 pagesSadhana Intensive Courseapi-241382210No ratings yet
- Exercising Your Speech and Voice SystemDocument2 pagesExercising Your Speech and Voice SystemTyler SanchezNo ratings yet
- Breathing ExercisesDocument19 pagesBreathing ExercisesvarunNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall AnatomyDocument62 pagesThoracic Wall AnatomyMohib S. MeahNo ratings yet