Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review For Final Exam
Uploaded by
Ariel Paulo G. TabangayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review For Final Exam
Uploaded by
Ariel Paulo G. TabangayCopyright:
Available Formats
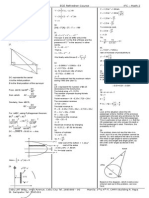
Exam
Name___________________________________
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Express the set using the roster method.
1) {x | x- N and x is greater than 7} 1)
A) {8,9,10,...} B) {7,8,9,...} C) {8,10,12,...} D) {8,9,10}
Express the set using set-builder notation. Use inequality notation to express the consition x must meet in order to be a
member of the set.
2) A ={12, 13, 14, 15, 16,...} 2)
A) {x | x- N and x 12} B) {x | x- N and x < 12}
C) {x | x- N and x >12} D) {x | x- N and x 16}
Are the sets equal?
3) {e, f, g, h}={f, h, g, e} 3)
A) Yes B) No
4) A ={13, 14, 15, 16, 17}
B={12, 13, 14, 15, 16}
4)
A) Yes B) No
Write or in the blank so that the resulting statement is true.
5) {c, a, n, d, i, d, a, t, e}_____ {a, c, d, e, i, t, a, n, d} 5)
A) _ B) _
6) {red, blue, green}_____ {blue, green, yellow, black} 6)
A) _ B) _
Calculate the number of subsets and the number of proper subsets for the set.
7) {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11} 7)
A) 64; 63 B) 62; 63 C) 63; 64 D) 63; 62
Let U= {q, r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z}
A= {q, s, u, w, y}
B= {q, s, y, z}
C= {v, w, x, y, z}. List the elements in the set.
8) (A . C)' 8)
A) {q, r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} B) {q, s, y, z}
C) {q, r, s, t, u, v, x, z} D) {w, y}
9) A' B 9)
A) {s, u, w} B) {q, s, t, u, v, w, x, y}
C) {q, r, s, t, v, x, y, z} D) {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, z}
10) C / 10)
A) {q, s, y, z} B) {q, s, u, w, y} C) {v, w, x, y, z} D) { }
1
Place the various elements in the proper regions of the following Venn diagram.
11) Let U ={g, h, j, k, m, n}and A ={g, h, n}. Find A'. Then use a Venn diagram to illustrate the
relationship among the sets U, A, and A'.
11)
A) A' ={j, k, m} B) A' =/
C) A' ={g, h, m} D) A' ={g, h, n}
Use set notation to identify the shaded region.
12) 12)
A) B. A' B) A' . B C) A' B D) (A . B)'
2
13) 13)
A) (A C) . B' B) (C . B') A C) B' . (A C) D) A C
Write the statement in symbolic form to determine the truth value for the statement.
14) 53=15 or French is a language. 14)
A) True B) False
Construct a truth table for the statement. Then determine if the statement is a tautology.
15) (q- p) - (~p V q) 15)
A)
p q q- p ~p ~p V q (q- p) - (~p V q)
T T T F T T
T F T F F F
F T F T T T
F F T T T T
Is not a tautology.
B)
p q q- p ~p ~p V q (q- p) - (~p V q)
T T T T T F
T F T F F F
F T F T T F
F F F T T T
Is not a tautology.
C)
p q q- p ~p ~p V q (q- p) - (~p V q)
T T T F T T
T F F F F T
F T T T T T
F F T T T T
Is a tautology.
D)
p q q- p ~p ~p V q (q- p) - (~p V q)
T T T F T T
T F T F F F
F T F T T F
F F T T T T
Is not a tautology.
Use an Euler diagram to determine whether the argument is valid or invalid.
16) All birds have feathers.
No mammal has feathers.
Therefore, no mammals are birds.
16)
A) valid B) invalid
3
17) All insects have six legs.
No spiders are insects.
Therefore, no spiders have six legs.
17)
A) valid B) invalid
Use a truth table to determine whether the symbolic form of the argument is valid or invalid.
18) (p - q) (q- p)
q
. p V q
18)
A)
p q p - q q- p [ (p - q) (q- p) ] p V q [ [( p - q) (q - p) ] q ] - (p V q)
T T T T T T T
T F F T F F T
F T T F F F T
F F T T T F F
Argument is invalid.
B)
p q p - q q- p [ (p - q) (q- p) ] p V q [ [(p - q) (q- p) ] q ] - (p V q)
T T T T T F T
T F F T F F T
F T T F F F T
F F T T T T F
Argument is invalid.
C)
p q p - q q- p [ (p - q) (q- p) ] p V q [ [( p - q) (q - p) ] q ] - (p V q)
T T T T T T T
T F F T F T T
F T T F F T T
F F T T T F T
Argument is valid.
D)
p q p - q q- p [ (p - q) (q- p) ] p V q [ [(p - q) (q- p) ] q ] - (p V q)
T T T T T T T
T F F T F T T
F T T F F T T
F F T T T F F
Argument is valid.
Convert the numeral to a numeral in base ten.
19) 54012
six
19)
A) 32,472 B) 336 C) 1106 D) 7352
Use divisions to convert the base ten numeral to a numeral in the given base.
20) 2,874 to base eight 20)
A) 4,572
eight
B) 5,427
eight
C) 4,527
eight
D) 5,472
eight
4
Solve the problem. Round all circumference and area calculations to the nearest whole number.
21) How much fencing is required to enclose a circular garden whoseradius is35 m? 21)
A) 220 m B) 55 m C) 3848 m D) 110 m
Find the area of the figure.
22) 29yd
8yd
24yd
7yd
22)
A) 400yd
2
B) 226yd
2
C) 241yd
2
D) 142yd
2
Find the volume of the figure. If necessary, round the answer to the nearest whole number.
23) Cone
2 in.
4 in.
23)
A) 50in.
3
B) 67in.
3
C) 17in.
3
D) 34in.
3
24)
12ft
13ft
24)
A) 490ft
3
B) 5881ft
3
C) 1470ft
3
D) 245ft
3
Find the measures of the parts of the right triangle that are not given. Round your answers to the nearest whole number.
25)
c
a
30
b=57 yd
25)
A) a=37 yd; c=64 yd; z B=60 B) a=33yd; c=64 yd; z B=60
C) a=33 yd; c=66 yd; z B=60 D) a=37 yd; c=66 yd; z B=60
5
Use the inverse trigonometric keys on a calculator to find the measure of angle A, rounded to the nearest whole degree.
26)
16 m
25 m
26)
A) 32 B) 33 C) 31 D) 34
Use the formula for
n
P
r
to solve.
27) A club elects a president, vice- president, and secretary- treasurer. How many sets of officers are
possible if there are13 members and any member can be elected to each position? No person can
hold more than one office.
27)
A) 858 B) 572 C) 1716 D) 17,160
Use the formula for
n
C
r
to evaluate the expression.
28) To win at LOTTO in a certain state, one must correctly select 6 numbers from a collection of 53
numbers ( one through 53.) The order in which the selections is made does not matter. How many
different selections are possible?
28)
A) 22,957,480 B) 720 C) 318 D) 20,358,520
You randomly select one card from a 52-card deck. Find the probability of selecting:
29) an ace or a8? 29)
A)
9
26
B) 9 C)
2
13
D)
13
2
A single die is rolled twice. The set of 36 equally likely outcomes is {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3),
(2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5,
6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6),}.
30) Find the probability of getting a sum of 3 or 4. 30)
A)
1
18
B)
1
6
C)
1
12
D)
5
36
A single die is rolled. Find the odds:
31) against getting a number less than 4. 31)
A) 2:1 B) 1:2 C) 1:1 D) 3:2
Solve the problem involving probabilities with independent events.
32) A single die is rolled twice. Find the probability of getting a3 the first time and a5 the second time. 32)
A)
1
3
B)
1
36
C)
1
12
D)
1
6
6
The table shows the number of employed and unemployed workers in the U.S., in thousands, in 2000.
Employed Unemployed
Male 67,761 2433
Female 58,655 2285
Assume that one person will be randomly selected from the group described in the table.
33) Find the probability of selecting a person who is employed, given that the person is male. 33)
A)
67,761
70,194
B)
2433
70,194
C)
2285
70,194
D)
2433
67,761
Find the mean for the data items in the given frequency distribution. Round to the nearest hundredth, if necessary.
34)
Score Frequency
x f
1 3
2 5
3 4
4 6
5 10
6 7
7 11
8 8
9 12
10 12
34)
A) 5.91 B) 5.15 C) 7.91 D) 6.54
Find the median for the group of data items.
35) 1.1, 2.4, 1.6, 2.5, 1.1, 2.4, 1.1, 8.3, 8.3, 1.9 35)
A) 1.9 B) 2.15 C) 2.4 D) 1.1
Find the mode for the group of data items.If there is no mode, so state.
36) 97, 97, 94, 44, 74, 97 36)
A) 94 B) 97 C) no mode D) 44
Find the range for the group of data items.
37) 7, 7, 7, 19, 24, 24, 24 37)
A) 31 B) 19 C) 17 D) 12
Find the standard deviation for the group of data items (to the nearest hundredth).
38) 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 38)
A) 2.5 B) 0 C) 1.58 D) 1.25
The scores on a driver's test are normally distributed with a mean of 100. Find the score that is:
39) Find the score that is 2 standard deviations below the mean, if the standard deviation is22. 39)
A) 56 B) 78 C) 144 D) 122
7
The correlation coefficient, r is given for a sample of n data points. Use the = 0.05 column in a correlation significance
table to determine whether or not we may conclude that a correlation does exist in the population.
40) n =37 r =- 0.395 40)
A) Yes, we may conclude that there is a correlation.
B) No, we may not conclude that there is a correlation.
A set of data items is normally distributed with a mean of 60. Convert the data item to a z-score, if the standard deviation
is as given.
41) data item: 80; standard deviation: 5 41)
A) 20 B) 5 C) 3 D) 4
Use a table of z-scores and percentiles to find the percentage of data items in a normal distribution that lie between:
42) z =- 0.2 and z =0.2 42)
A) 50% B) 42.07% C) 15.86% D) 57.93%
8
You might also like
- Math IFC 2 December 2013 Solution 26-50-1Document2 pagesMath IFC 2 December 2013 Solution 26-50-1Ariel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- Excel c1 DBTC Ifc6Document3 pagesExcel c1 DBTC Ifc6Ariel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- IECEP Questions (2-4-2014)Document140 pagesIECEP Questions (2-4-2014)Ariel Paulo G. Tabangay0% (1)
- IECEP Questions (2-4-2014)Document140 pagesIECEP Questions (2-4-2014)Ariel Paulo G. Tabangay0% (1)
- Geas PhysicsDocument3 pagesGeas PhysicsAriel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- Math IFC 2 December 2013 Solution 26-50-1Document2 pagesMath IFC 2 December 2013 Solution 26-50-1Ariel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- Memonics PDFDocument82 pagesMemonics PDFMelvin John Habla Banzuelo100% (2)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Chapter 2: Radio-Frequency CircuitsDocument17 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Chapter 2: Radio-Frequency CircuitsAriel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chap 6Document16 pagesMCQ Chap 6Ariel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- Communications Test YourselfDocument35 pagesCommunications Test Yourselfpatrick0308No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Kinematics AssignmentDocument17 pagesKinematics AssignmentMadhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Body in White Architecture For An Electric Vehicle ConceptDocument54 pagesBody in White Architecture For An Electric Vehicle ConceptJosue Enriquez Eguiguren100% (1)
- Individual Household Electric Power ConsumptionDocument29 pagesIndividual Household Electric Power ConsumptionVISHAL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Qau Course Outlines PDFDocument11 pagesQau Course Outlines PDFphooolNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocument502 pagesPlane and Solid GeometryRyan Tegio100% (5)
- Visual VocabDocument10 pagesVisual Vocabnellie_74023951No ratings yet
- Practice Paper: I. Candidates Are Informed That Answer Sheet Comprises TwoDocument19 pagesPractice Paper: I. Candidates Are Informed That Answer Sheet Comprises TwoRashid Ibn AkbarNo ratings yet
- Tut2 PDFDocument3 pagesTut2 PDFanshuljain226No ratings yet
- Corrada - Geometry - El Lissitzky PDFDocument9 pagesCorrada - Geometry - El Lissitzky PDFAnnie PedretNo ratings yet
- Rocket Equation Derivation NotesDocument7 pagesRocket Equation Derivation NotesSrikar GhooliNo ratings yet
- Srikanth External Lab AnswersDocument19 pagesSrikanth External Lab AnswersKumar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Process Synchronization and DeadlockDocument41 pagesProcess Synchronization and DeadlockRemy Kuswara Putra KelanaNo ratings yet
- Robert Talbert Statement of Teaching Philosophy DRAFTDocument2 pagesRobert Talbert Statement of Teaching Philosophy DRAFTRobert TalbertNo ratings yet
- CaissonDocument12 pagesCaissonjohnnyoliveiraNo ratings yet
- Data Coding TabulationDocument20 pagesData Coding TabulationShwetank Sharma100% (2)
- 1 1.1 ComputationDocument72 pages1 1.1 ComputationGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Classification Algorithms IIDocument9 pagesClassification Algorithms IIJayod RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- 55 The Vector Equation of A PlaneDocument37 pages55 The Vector Equation of A PlaneShammus SultanNo ratings yet
- Xy-Graph: Ordered PairsDocument14 pagesXy-Graph: Ordered PairsmsooflooNo ratings yet
- Practical Implementation of A Dependently Typed Functional Programming LanguageDocument270 pagesPractical Implementation of A Dependently Typed Functional Programming LanguageEdwin Brady100% (1)
- Last 2 Digits of PowersDocument3 pagesLast 2 Digits of PowersSreedhar JalapatiNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument15 pagesBinomial DistributionNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- Machines: Condition-Based Maintenance-An Extensive Literature ReviewDocument28 pagesMachines: Condition-Based Maintenance-An Extensive Literature ReviewSebastiao DuarteNo ratings yet
- ABACUS Features USDocument2 pagesABACUS Features USSuzanne StewartNo ratings yet
- Selection Course For Term 1626 - 22aug2016Document21 pagesSelection Course For Term 1626 - 22aug2016yvonneNo ratings yet
- Mathematics HL Paper 3 TZ2 Sets Relations and GroupsDocument3 pagesMathematics HL Paper 3 TZ2 Sets Relations and GroupsAastha NagarNo ratings yet
- Bridge ManualDocument13 pagesBridge ManualAzik KunouNo ratings yet
- Method of Differentiation DPP - 7Document3 pagesMethod of Differentiation DPP - 7tanayNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan May 23, 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan May 23, 2022Anagh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Q1 4TH Assessment Test MATHDocument2 pagesQ1 4TH Assessment Test MATHManila Hankuk AcademyNo ratings yet