Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Excretory System
Uploaded by
Maria Charlene OrpillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Excretory System
Uploaded by
Maria Charlene OrpillaCopyright:
Available Formats
EXCRETORY SYSTEM MARY ANNE P.
. ISIP, MD, MT(ASCPi) Functions: Filtration of cellular waste from blood Regulation of salt and water balance* Excretion of the waste and excess water as urine Endocrine function Erythropoietin and Renin* In Male, the urethra also serves the reproductive system* kidney Renal medulla Renal cortex Renal cortex Pars Convoluta Renal corpuscles or Malphigian corpuscles Glomerulus and Bowmans capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Distal Convoluted tubule Arch Collecting tubule Pars Recta Straight tubules Descending loop of Henle Ascending loop of Henle Straight Collecting tubules NEPHRONS 1-1.4Millions* Parts: Renal or Malphigian corpuscle Bowmans capsule Glomerulus PCT Descending and Ascending loop of Henle DCT Collecting tubule
glomerulus A tuft of capillaries enclosed in the Bowmans capsule Bowmans capsule 2 layers: Outer parietal layer Lined by single layer of squamous cells Inner visceral layer Formed of modified epithelial cells called PODOCYTES* Filtration barrier Filtration slits
Basal lamina Fusion of capillary and podocyte-produced basal lamina Endothelium of a glomerular capillary Mesangial cells Stellate-shaped Phagocytic*
Functions: Provide structural support and contraction* Phagocytosis* Secretion * Urinary or capsular space Between 2 capsular layers Receives the fluid filtered through the capillary wall and the visceral layer
Each renal corpuscle has a: Vascular pole* Tubular pole * Proximal convoluted tubule Longest and the most convoluted part
Lined by Simple cuboidal epithelium with brush border reabsorption Cells have granular cytoplasm, acidophilic* Reabsorb 60-65% water All glucose and amino acid 85% Sodium, Chloride Loop of henle U-shaped structure with a: Descending limb Thick:lined by Simple cuboidal epithelium Thin:line by Simple squamous epithelium
Ascending limb lined by Simple cuboidal epithelium without brush border Wider lumen Juxtamedullary nephrons Located near the corticomedullary junction It allows the kidney to produce concentrated hypertonic urine With short thick descending limb, long thin descending and ascending limbs and long thick ascending limbs Distal convoluted tubule Lined by Simple cuboidal cells without brush border Wider lumen Pale staining cytoplasm Sodium reabsorption and Potassium secretion by Sodium pump regulated by Aldosterone Secrete H+ and NH4 maintain acid-base Juxta glomerular apparatus Juxtaglomerular cells/ jg cells Rounded nuclei, basophilic cytoplasm* Secretes RENIN Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiotensin II
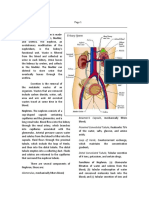
Aldosterone Na & H2O reabsorption o Increase blood pressure Lacis cells Aka Extraglomerular Mesangial cells Produce Erythropoietin Collecting tubules Last part of each nephron Join each other to form straight COLLECTING DUCTS Runs to the tips of the medullary pyramids Empty into the minor calyces Tubules: Simple cuboidal epithelium Ducts: Simple columnar epithelium Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Arginine vasopressin Makes the collecting duct more permeable to water Blood supply Excretory passages Structures that convey urine from the kidney parenchyma to the outside Renal pelvis main excretory duct of the Ureter kidney LE: Transitional epithelium/ Urothelium 3 walls Inner mucous layer Middle muscular layer Outer circular layer muscle layer Inner longitudinal muscle layer Outer adventitia layer loose collagenous t. Blood & lymph vessels, nerves 3 layers of urothelium
Single layer of small basal cells* Intermediate region containing 1-several layers of columnar cells Superficial layer of very large polyhedral or bulbous cells called UMBRELLA CELLS* RENAL PELVIS Flattened funnel-shaped end of the ureter in the hilum of the kidney, that branches into major and minor calyces Lined by transitional epithelium Lamina propia: scanty areolar c.t. Small blood vessels, lymphocytes NO GLANDS URETER Muscular tube that connects each kidney to the bladder Walls are much thicker than renal pelvis
Mucosa: lined by Transitional epithelium Forms longitudinal mucosal folds when empty giving the lumen stellate shaped appearance Collapsed state Columnar Distended - Cuboidal Lamina propia: dense supeficial part Loose superficial part NO glands Diffuse lymphatic tissue Muscular: Upper 2/3 thinner, 2 layers of muscle: Inner longitudinal Outer circular Lower 1/3 thicker, 3 layers: Inner longitudinal
Middle circular Outer longitudinal Terminal portion: NO circular muscle Inner longitudinal Outer longitudinal Tunica adventitia: loose collagenous t. Urinary bladder Hollow organ for the storage of urine Mucosa: lined by Transitional epithelium Lamina propia: highly vascularized Submucosa: Muscularis: 3 layers: Detrussor muscle Inner longitudinal Middle circular Outer longitudinal
Tunica adventitia: fibroelastic connective tissue Peritoneum covers the upper part of the urinary bladder The ureter pass through the wall of the bladder obliquely forming a sphincter of the bladder Male urethra Long, consist of 3 portions: Prostatic urethra 3-4cm long, extends through the prostate gland Lined by urothelium In the midline is the opening of the prostate utricle On the R & L are the slit like openings of the ejaculatory ducts Membranous urethra Short segment 1-1.5cm Lined by Stratified Columnar or Pseudostratified epithelium
Extending from the lower pole of the prostate to the bulb of the corpus spongiosum Spongy urethra Longest part 15cm Traversing the whole length of the corpus spongiosum* Lined by Pseudostratified or Stratified Columnar epithelium Terminal portion: Fossa Navicularis lined Stratified Squamous non-cornified epithelium
Mucosa: recesses or deep irregular outpocketings into the tunica propia which are called Lacunae of Morgagni Lamina propia: loose collagenous tissue with abundant elastic fibers and smooth muscle Few diffuse lymphocytes Several small mucus secreting glands called LITTERS GLAND Muscular: inner longitudinal Outer circular Tunica adventitia Areolar connective tissue Bigger blood vessels Nerve plexuses Female urethra Shorter 4-5cm Mucosa: lined by First part - Transitional epithelium Middle part Pseudostratified epithelium Terminal part SSNCE Lamina propia: loose c.t Elastic fibers & lymphocytes Litters gland Lacunae of Morgagni
Muscular: Inner longitudinal Outer circular Skeletal muscle urethral sphincter Tunica adventitia Areolar tissue Blood vessels, nerves
What you are right now is Gods gift to you, What you will become is your gift to God
You might also like
- Nervous System Part 1Document6 pagesNervous System Part 1rb YangzonNo ratings yet
- Glider Lesson Plan PDFDocument16 pagesGlider Lesson Plan PDFirontribeNo ratings yet
- Mission - Balsa Wood BridgeDocument34 pagesMission - Balsa Wood Bridgeapi-332158785No ratings yet
- Intrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentDocument24 pagesIntrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentIpan YustiartaNo ratings yet
- A&P 302 Digestive Notes: GI Anatomy, Functions, ProcessesDocument51 pagesA&P 302 Digestive Notes: GI Anatomy, Functions, ProcessesBethanyNo ratings yet
- 16 Sense OrgansDocument79 pages16 Sense OrgansvanderphysNo ratings yet
- ANA3203 (Neuroanatomy) Lecture, 2020-2021Document33 pagesANA3203 (Neuroanatomy) Lecture, 2020-2021M sarauta Tv100% (1)
- Body Composition Elements and CompoundsDocument22 pagesBody Composition Elements and CompoundsSophia RoseNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE Nervous SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- Notes Human EyeDocument9 pagesNotes Human EyeGeetanshi OberoiNo ratings yet
- Histo - Pituitary GlandDocument22 pagesHisto - Pituitary GlandRessam NazirNo ratings yet
- A&P 302 - Respiratory NotesDocument31 pagesA&P 302 - Respiratory NotesBethanyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocument19 pages3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesThe Urinary SystemNayan BhatiaNo ratings yet
- How Tia Lola Came To Stay Book ReportDocument2 pagesHow Tia Lola Came To Stay Book ReportMelissa Palacios100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemDara BMNo ratings yet
- Physiology NotesDocument4 pagesPhysiology NotesGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
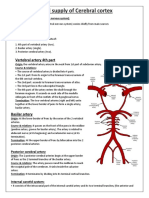
- Blood Supply of Cerebral CortexDocument3 pagesBlood Supply of Cerebral CortexashrafNo ratings yet
- Dr. Aaijaz Ahmed Khan Sr. Lecturer in Anatomy PPSP, UsmDocument38 pagesDr. Aaijaz Ahmed Khan Sr. Lecturer in Anatomy PPSP, UsmeliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy of BrainAlex Bañares Eusebio Jr.100% (1)
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Blood Supply To The BrainDocument6 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Blood Supply To The BrainsoyyosoloyoNo ratings yet
- ANP 300 Exam 3 ReviewDocument15 pagesANP 300 Exam 3 ReviewNerdy Notes Inc.No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument135 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyHrishikesh GokhaleNo ratings yet
- The answer is D. Bone Marrow. Primary lymphoid organs are where lymphocytes mature and differentiate. The bone marrow is the primary lymphoid organ where B cells and T cells develop from stem cellsDocument44 pagesThe answer is D. Bone Marrow. Primary lymphoid organs are where lymphocytes mature and differentiate. The bone marrow is the primary lymphoid organ where B cells and T cells develop from stem cellsZeyNo ratings yet
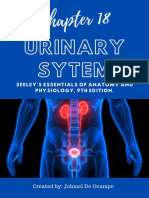
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Document12 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANSDocument5 pagesFEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANSYanie ZsofNo ratings yet
- Sensory Physiology Student ProtocolDocument18 pagesSensory Physiology Student ProtocolManuel Alejandro Chiguay GonzalezNo ratings yet
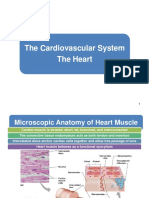
- 08 Human Physiology The HeartDocument107 pages08 Human Physiology The HeartsuNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument92 pagesCardiovascularRolinette DaneNo ratings yet
- Sweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesSweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- Excretory System Chapter 9thDocument4 pagesExcretory System Chapter 9thशंकराय नमोNo ratings yet
- Tissues 4Document65 pagesTissues 4marianisie448100% (2)
- Propagation of Nerve ImpulseDocument42 pagesPropagation of Nerve ImpulseRe UpNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Suchjeoffrey_castroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology1Document5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology1Roxanne Ganayo ClaverNo ratings yet
- Face and Scalp ANATOMYDocument60 pagesFace and Scalp ANATOMYpuliyogareNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of Kidney: NephronDocument3 pagesClinical Anatomy of Kidney: NephronNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemyannieNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture On Nerve Physiology by Dr. RoomiDocument12 pages3rd Lecture On Nerve Physiology by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesThe Excretory Systemapi-3759646100% (2)
- Encephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDocument4 pagesEncephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDivya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Pharmacology NotesDocument5 pagesFoundations of Pharmacology NotesSheril MarekNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System HistologyDocument32 pagesRespiratory System HistologyMohib HassanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- General Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyDocument4 pagesGeneral Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyChristine Rose EmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Introduction To The CvsDocument43 pagesIntroduction To The CvsParmesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BowelDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BowelholzzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Cavity Anatomy ReviewDocument15 pagesAbdominal Cavity Anatomy ReviewCaperlac MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology II Course OutcomesDocument50 pagesAnatomy and Physiology II Course OutcomesShirley LourdesNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis and Ovarian Cycle, Uterus, Menstrual Cycle ABORTION TERATOLOGYDocument72 pagesOogenesis and Ovarian Cycle, Uterus, Menstrual Cycle ABORTION TERATOLOGYElizabeth OmobolanleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyDocument14 pagesIntroduction To NeuroanatomyRosalie CalisinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PhysiologyDocument2 pagesEndocrine System PhysiologyLuisGabitoNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Histology of the Breast: Lobules, Alveoli and DuctsDocument2 pagesHistology of the Breast: Lobules, Alveoli and DuctsIbrahim SugiyonoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Ection I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALDocument9 pagesEction I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALNheil_Christop_4211No ratings yet
- Urinary Excretory System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDocument15 pagesUrinary Excretory System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Prepared By: Ma. Concepcion F. Columbres, MNDocument38 pagesUrinary System: Prepared By: Ma. Concepcion F. Columbres, MNAl Serenoso100% (1)
- General Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument62 pagesGeneral Anatomy of Urinary SystemSARABIA, ARVIN JR.No ratings yet
- RCS PreparationDocument3 pagesRCS PreparationMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument1 pageNursing DiagnosisMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAlbuterol Drug StudyMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Liver Flukes, Lung Flukes and Intestinal Flukes CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesLiver Flukes, Lung Flukes and Intestinal Flukes CharacteristicsMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- Excretory SystemDocument9 pagesExcretory SystemMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument3 pagesAntifungal DrugsMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- The Means of EnjoymentDocument3 pagesThe Means of EnjoymentMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- The Means of EnjoymentDocument3 pagesThe Means of EnjoymentMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Vascular DiseaseDocument61 pagesHypertensive Vascular DiseaseFedelyn Mae AcaylarNo ratings yet
- Dragons Touch - Weaknesses of HumanDocument6 pagesDragons Touch - Weaknesses of Humanprakharmishra902No ratings yet
- Blood Grouping & Transfusion: - DR Kaberi deDocument22 pagesBlood Grouping & Transfusion: - DR Kaberi deSrishti GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Mode of Action of SvedanaDocument6 pagesMode of Action of Svedanabharti guptaNo ratings yet
- Molar UprightingDocument8 pagesMolar UprightingNguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Bases Neurobiologicas Dificultades Aprendizaje PDFDocument5 pagesBases Neurobiologicas Dificultades Aprendizaje PDFMacarena MartínezNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Yearly Teaching Plan 2016Document15 pagesBiology Form 5 Yearly Teaching Plan 2016FidaNo ratings yet
- GULYA - Anatomy of The Temporal Bone With Surgical ImplicationsDocument378 pagesGULYA - Anatomy of The Temporal Bone With Surgical ImplicationsAlina Angelica100% (5)
- Chronic Hyperplastic PulpitisDocument30 pagesChronic Hyperplastic PulpitisGlory Pohan67% (3)
- 7&8 Tooth Extraction (Exodontia)Document28 pages7&8 Tooth Extraction (Exodontia)Muntather Muhsen100% (2)
- 1-Eruption of TeethDocument9 pages1-Eruption of TeethAhmed AbdNo ratings yet
- Absen Pembacaan Refarat Dan Lapsus Suci RamadhaniDocument2 pagesAbsen Pembacaan Refarat Dan Lapsus Suci Ramadhanisuci ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Pancreatita Acuta. Cancerul PancreaticDocument60 pagesPancreatita Acuta. Cancerul PancreaticElena CNo ratings yet
- Practice: Failures in Implant DentistryDocument7 pagesPractice: Failures in Implant DentistryDrMarkHoganNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Blood Lymph SystemsDocument29 pagesMedical Terminology Blood Lymph Systemsapi-268199514100% (1)
- Mechanisms of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis (Autosaved)Document60 pagesMechanisms of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis (Autosaved)Tom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- 14 The Central Nervous SystemDocument61 pages14 The Central Nervous SystemvanderphysNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Forms and Philosophies in Full Mouth Rehabilitation: A Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesOcclusal Forms and Philosophies in Full Mouth Rehabilitation: A Literature ReviewSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Human Body 11 Organ Systems FoldableDocument4 pagesHuman Body 11 Organ Systems Foldablenaeleti1899No ratings yet
- Bhatia LMR 2019 All Subjects PDFDocument675 pagesBhatia LMR 2019 All Subjects PDFPrince Trambadiya100% (1)
- Journal .Of Orthodontics and Oral Surgery: AmericanDocument11 pagesJournal .Of Orthodontics and Oral Surgery: AmericanShirley AliagaNo ratings yet
- Ap Psychology Unit 7 Overview Revised 2015Document5 pagesAp Psychology Unit 7 Overview Revised 2015api-262090199No ratings yet
- HAP1 Review: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument37 pagesHAP1 Review: Dr. Garry Niedermayersweta paudelNo ratings yet
- Neck DissectionDocument43 pagesNeck DissectionMeilina Elin WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids Compartments and ExchangeDocument21 pagesBody Fluids Compartments and ExchangeLIDIYA MOL P VNo ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy of The HeartDocument5 pagesSurface Anatomy of The HeartEglNo ratings yet
- GB 25Document2 pagesGB 25ray72roNo ratings yet
- Class HolothuroideaDocument2 pagesClass HolothuroideaSecretsoushiNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExamDocument6 pagesNeurological ExamTiti Daraban100% (2)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyTiffany Blanca Evangelista RaiNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Horse Training 101: Key Techniques for Every Horse OwnerFrom EverandHorse Training 101: Key Techniques for Every Horse OwnerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)
- You Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherFrom EverandYou Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherNo ratings yet
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (396)
- The Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionFrom EverandThe Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesFrom EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (56)
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesFrom EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfFrom EverandMitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)
- The Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceFrom EverandThe Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (45)
- Unthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsFrom EverandUnthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (50)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)