Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TVM-Q's - Gitman
Uploaded by
Nikita AgarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TVM-Q's - Gitman
Uploaded by
Nikita AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
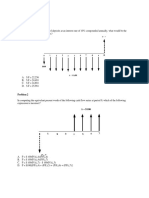
For each of the cases shown in the following table, calculate the future values of the cash flow deposited today that will be available at the end of the deposit period if the interest is compounded annually at the rate specified over the given period Case A B C D E F Single cash flow 200 4500 10000 25000 37000 40000 Interest rate 5 8 9 10 11 12 Deposit period (years) 20 7 10 12 5 9
2. You have Rs. 1500 to invest today at 7 percent interest compounded annually. A. find how much you will have accumulated in the account at the end of (1) 3 years (2) 6 years, and (3) 9 years. B. Use your findings in part a to calculate the amount of interest earned in in the (1) first 3 years (2) yr. 4 to 6 and (3) yr. 7 to 9 C. Compare and contrast your findings in part b. explain why the amount of interest earned increases I each succeeding 3 year period.
3. You can deposit rs. 10,000 into an account paying 9% annual interest either today or exactly 10 years from today. How much better off will you be at the end of 40 years if you decide to make the initial deposit today rather than 10 years from today? 4. For each of the cases shown in the following table, calculate the present value of cash flow, discounting at the rate given and assuming that the cash flow is received at the end of the given period noted. case A B C D E Single cash flow 7000 28000 10000 150000 45000 Discount rate 12 8 14 11 20 End of period (yrs) 4 20 12 6 9
5. Jam nance has been offered a future payment of Rs.500 three yrs from today. If his opportunity cost is is 7% compounded annually, what value should he place on his opportunity today? What is the most he should pay to purchase the payment today?
6. In exchange for a Rs. 20,000 payment today, a well known company will allow you to choose one of the alternatives shown in the following table. Your opportunity cost is 11% Alternative Single amount A 28500 @ end of 3 yrs B 54000 @ end of 9 yrs C 160000 @ end of 20 yrs
a. Find the value today of each alternative b. Are all the alternatives acceptable- that is, worth 20,000 today? c. Which alternative, if any, will you take? 7. Assume that you just won the state lottery. Your prize can be taken either in the form of Rs.40000 at the end of the next 25 yrs (i.e, Rs.1,000,000 over 25 yrs) or as a single amount of Rs.500000 paid immediately. a. If you expect to be able to earn 5% annually over next 25 yrs on your investment, ignoring taxes, which alternative would you take? b. Would your decision change if you could earn 7% over the next 25 years on your investment? c. On a strictly economic basis, at approximately what earnings rate would you be indifferent between the two plans? 8. Consider the data in the following table. Perpetuities Annual amount A 20000 B 100000 C 3000 D 60000 Determine, for each of these perpetuities: a. The appropriate PV interest factor b. The PV
Discount rate 8 10 6 5
9. An insurance agent is trying to sell you an immediate retirement annuity, which for a single amount paid today will provide you with Rs.12000 at the end of each yr. for the next 25 yrs. You currently earn 9% On low risk investments comparable to the retirement annuity. Ignoring taxes, what is the most you would pay for this annuity? 10. Rishi singh has Rs. 1500 to invest. His counselor suggests investment that pays no stated interest but will return Rs.2000 at the end of 3 yrs. What annual rate of return will rishi earn with this investment? Rishi is considering other investment, of equal risk, that earns an annual return of 8%. What investment should he make, and why?
You might also like
- CFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CFA Level 1 Calculation Workbook: 300 Calculations to Prepare for the CFA Level 1 Exam (2023 Edition)From EverandCFA Level 1 Calculation Workbook: 300 Calculations to Prepare for the CFA Level 1 Exam (2023 Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Time Value of Money (Problems)Document4 pagesTime Value of Money (Problems)Mohammad RashidNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Chapter 2Document5 pagesPractice Problems For Chapter 2Lacey Blankenship100% (2)
- Quiz - Practice Problems Chapter 4 8 and 9Document12 pagesQuiz - Practice Problems Chapter 4 8 and 9abhilash.mandal.meNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2,3Document8 pagesAssignment 2,3HASSAN AHMADNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Chapter 5: Time Value of Money P5-5 Time Value: 2. 6 YearsDocument11 pagesTutorial 4 Chapter 5: Time Value of Money P5-5 Time Value: 2. 6 YearsrizqighaniNo ratings yet
- Midterm1 134A Sp22 CDocument9 pagesMidterm1 134A Sp22 CviennayungNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document4 pagesCH 2Sayandeep Nag0% (1)
- Fin302 MCQs PDFDocument13 pagesFin302 MCQs PDFkhushi mishaNo ratings yet
- CVFDDVDocument2 pagesCVFDDVPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- TUTORIALDocument10 pagesTUTORIALViễn QuyênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Time Value of MoneyDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Time Value of MoneyLayla MainNo ratings yet
- Solution of Assignment On Time Value of MoneyDocument11 pagesSolution of Assignment On Time Value of MoneyArif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Present ValueDocument16 pagesProblem Sets Present ValueJoaquín Norambuena EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money - AsadDocument15 pagesTime Value of Money - AsadKamran KhanNo ratings yet
- 3530 SU23 Final Exam - Type X - Questions (Post)Document13 pages3530 SU23 Final Exam - Type X - Questions (Post)combatapple25No ratings yet
- CFP Mock Test Introduction To Financial PlanningDocument7 pagesCFP Mock Test Introduction To Financial PlanningDeep ShikhaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets 15 - 401 08Document72 pagesProblem Sets 15 - 401 08Muhammad GhazzianNo ratings yet
- The Questions Marked WithDocument36 pagesThe Questions Marked WithMark Smith100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Harris JamilNo ratings yet
- FM A Assignment 19-40659-1Document11 pagesFM A Assignment 19-40659-1Pacific Hunter JohnnyNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Quiz 3Document4 pagesBusiness Finance Quiz 3deeplabuNo ratings yet
- TVM Practice Questions Fall 2018Document4 pagesTVM Practice Questions Fall 2018ZarakKhanNo ratings yet
- IE 360 Engineering Economic Analysis: Name: Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDocument11 pagesIE 360 Engineering Economic Analysis: Name: Read The Following Instructions CarefullyjohnhenryyambaoNo ratings yet
- Solution Key To Problem Set 3Document8 pagesSolution Key To Problem Set 3Ayush RaiNo ratings yet
- TVF Practice Sum - 2Document14 pagesTVF Practice Sum - 2Rashi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument8 pagesTime Value of MoneyChethan KumarNo ratings yet
- Quiz #3.2-Time Value of Money-SolutionsDocument2 pagesQuiz #3.2-Time Value of Money-SolutionsChrisNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomyDocument37 pagesEngineering EconomyxxkooonxxNo ratings yet
- Problem SetsDocument69 pagesProblem SetsAnnagrazia ArgentieriNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 Time Value of MoneyDocument5 pagesSheet 1 Time Value of MoneyAhmed RagabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONSDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONSMariem JabberiNo ratings yet
- Práctica 1 Fin I 2021Document2 pagesPráctica 1 Fin I 2021Brenda123No ratings yet
- Engineering Economy PDFDocument37 pagesEngineering Economy PDFSummer Wynn DacwagNo ratings yet
- ACC501 Mid Term Preparation FileDocument28 pagesACC501 Mid Term Preparation FileMujtaba AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Camilo Andres MesaNo ratings yet
- FM - Hosp - Tutorial 5Document7 pagesFM - Hosp - Tutorial 5Sylvia AnneNo ratings yet
- Bs204 Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument13 pagesBs204 Frequently Asked QuestionsTakudzwa GwemeNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 - Problems - 01+02Document2 pagesCh. 2 - Problems - 01+02NazmulAhsanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics Midterm ExamDocument8 pagesEngineering Economics Midterm ExamRIZZI JOY LUMAGUINo ratings yet
- Assignment#2Document3 pagesAssignment#2Wuhao KoNo ratings yet
- BBA 207 Exam 2 - Chapters 4, 5 & 6Document6 pagesBBA 207 Exam 2 - Chapters 4, 5 & 6AdrtyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONSDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONSSolutionz Manual67% (3)
- PracticeDocument8 pagesPracticehuongthuy1811No ratings yet
- Chap5 - Discounted CFDocument39 pagesChap5 - Discounted CFhichichic0% (1)
- TVM ProblemsDocument4 pagesTVM Problemsshikha_asr2273No ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument12 pagesTime Value of Money Practice Problems and Solutionsalice horanNo ratings yet
- Midterm F08 With SolutionsDocument11 pagesMidterm F08 With SolutionsSupri awasthiNo ratings yet
- HIGGINS Chapter 7 - Course AidesDocument6 pagesHIGGINS Chapter 7 - Course AidesParul BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Topic 1 (Answers)Document4 pagesExercises On Topic 1 (Answers)Anis NabilaNo ratings yet
- CH 04 EOC Solutions 4e StudentDocument15 pagesCH 04 EOC Solutions 4e StudentMary Shannon DeeringNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Practice QuestionshahaheheNo ratings yet
- Annuity SolutionDocument15 pagesAnnuity Solution신동호No ratings yet
- Engineering EconomicsDocument10 pagesEngineering EconomicsRalph CastilloNo ratings yet
- CFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Economic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetFrom EverandEconomic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetNo ratings yet
- Should Municipal Bonds be a Tool in Your Retirement Planning Toolbox?From EverandShould Municipal Bonds be a Tool in Your Retirement Planning Toolbox?No ratings yet
- Personal Money Management Made Simple with MS Excel: How to save, invest and borrow wiselyFrom EverandPersonal Money Management Made Simple with MS Excel: How to save, invest and borrow wiselyNo ratings yet
- A Haven on Earth: Singapore Economy Without Duties and TaxesFrom EverandA Haven on Earth: Singapore Economy Without Duties and TaxesNo ratings yet
- Extension of Time Claim ProcedureDocument108 pagesExtension of Time Claim ProcedureAshish Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Putnam C Ounty NewsDocument25 pagesPutnam C Ounty NewsPCNRNo ratings yet
- Dividend PolicyDocument9 pagesDividend Policyjimmy rodolfo LazanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Analaysis GLOBEDocument2 pagesHorizontal Analaysis GLOBEjerameelnacalaban1No ratings yet
- Cetking GK Shot Test - Feb 2019Document213 pagesCetking GK Shot Test - Feb 2019harshit rajNo ratings yet
- Cacao Production in MindanaoDocument17 pagesCacao Production in MindanaoBREN G. CATUNAONo ratings yet
- Kansai Nerolac Software TDSDocument17 pagesKansai Nerolac Software TDSkumargaurav21281No ratings yet
- Colliers Market ResearchDocument6 pagesColliers Market ResearchMcke YapNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Ukulima Sacco Audited Accounts Year 2014Document27 pages2.2 Ukulima Sacco Audited Accounts Year 2014sebichondoNo ratings yet
- Revised Taxation Reading MaterialsDocument38 pagesRevised Taxation Reading MaterialsNardsdel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Acs 01Document23 pagesAcs 01Astha Srivastava100% (1)
- LBC-STRATEGIC-PAPER - Rev.1 22021Document42 pagesLBC-STRATEGIC-PAPER - Rev.1 22021Dennis Alea100% (5)
- BS - May 1Document14 pagesBS - May 1Lingesh SivaNo ratings yet
- 2006-2007 Dartmouth Tuck CC Case BookDocument103 pages2006-2007 Dartmouth Tuck CC Case Bookr_oko100% (3)
- VEC For EmbassiesDocument8 pagesVEC For Embassiescatherine joy sangilNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - Roque (Summarized)Document5 pagesCapital Budgeting - Roque (Summarized)Ivan BendiolaNo ratings yet
- Budget Process in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesBudget Process in EthiopiaEbenezerMebrate100% (1)
- Detailed Project Report For: Bus - OfficeDocument15 pagesDetailed Project Report For: Bus - OfficeRohit ManeNo ratings yet
- BTC Trading Inc TokyoDocument15 pagesBTC Trading Inc Tokyobtctradinginctokyo1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Josalyn Cervantes AbudaNo ratings yet
- Mgt401 Midterm 2010 McqsDocument35 pagesMgt401 Midterm 2010 McqsMèhàŕ MàŕiàNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis - PPT (25!06!2013)Document18 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis - PPT (25!06!2013)servicenagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Strauss Printing Services Statement of Cash Flows For The Year Ended December 31, 2013 Cash Flow From Operating ActivitiesDocument2 pagesStrauss Printing Services Statement of Cash Flows For The Year Ended December 31, 2013 Cash Flow From Operating ActivitiesChristian Shino Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- How To Swing TradeDocument270 pagesHow To Swing Tradejegonax73396% (28)
- Solved Ballou Corporation Distributes 200 000 in Cash To Its Sharehold PDFDocument1 pageSolved Ballou Corporation Distributes 200 000 in Cash To Its Sharehold PDFAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing For Decision Making & CVP Analysis - BudgetingDocument15 pagesMarginal Costing For Decision Making & CVP Analysis - BudgetingSravya MagantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 - AnswerDocument3 pagesChapter 26 - Answerlooter198No ratings yet
- Pseudo Code 1Document6 pagesPseudo Code 1Michelin FernandezNo ratings yet
- Financial Management (Final)Document143 pagesFinancial Management (Final)Java Spring Part 1No ratings yet
- Period When Returns Are Filed: BIR Form 1801Document4 pagesPeriod When Returns Are Filed: BIR Form 1801I Am Not DeterredNo ratings yet