Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P6
Uploaded by
Harold LimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P6
Uploaded by
Harold LimCopyright:
Available Formats
Harold C.
Lim IV-Calungsod
Machines
A machine is a tool containing one or more parts that uses energy to perform an intended action. Machines are usually powered by mechanical, chemical, thermal, or electrical means, and are often motorized. Historically, a power tool also required moving parts to classify as a machine. However, the advent of electronics technology has led to the development of power tools without moving parts that are considered machines. A simple machine is a device that simply transforms the direction or magnitude of a force, but a large number of more complex machines exist. Examples include vehicles, electronic systems, molecular machines, computers, television, and radio. Since there are thousands of different machines, they all work different but similar in nature. For any machine to be called a machine, it must be able to do its job. Machines work by using force to lift, push or move an object. Different machines operate in their own unique ways. Let's take a pulley (a simple machine) for instance. A pulley works by running a rope through it, by pulling on one end of the rope you can raise or lower items.
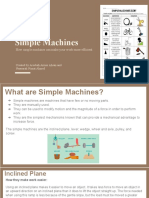
Simple Machines
A simple machine is a non-motorized device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, a simple machine can be defined as one of the simplest mechanisms that provide mechanical advantage (also called leverage). Usually the term refers to the six classical simple machines which were defined by Renaissance scientists:
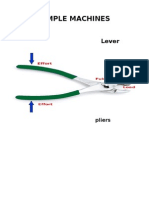
Inclined Plane A plane is a flat surface. For example, a smooth board is a plane. Now, if the plane is lying flat on the ground, it isn't likely to help you do work. However, when that plane is inclined, or slanted, it can help you move objects across distances. And, that's work! A common inclined plane is a ramp. Lifting a heavy box onto a loading dock is much easier if you slide the box up a ramp--a simple machine. Wedge Instead of using the smooth side of the inclined plane, you can also use the pointed edges to do other kinds of work. For example, you can use the edge to push things apart. Then, the inclined plane is a wedge. So, a wedge is actually a kind of inclined plane. An axeblade is a wedge. Think of the edge of the blade. It's the edge of a smooth slanted surface. That's a wedge! Screw Now, take an inclined plane and wrap it around a cylinder. Its sharp edge becomes another simple tool: the screw. Put a metal screw beside a ramp and it's kind of hard to see the similarities, but the screw is actually just another kind of inclined plane. How does the screw help you do work? Every turn of a metal screw helps you move a piece of metal through a wooden space. And, that's how we build things! Lever Try pulling a really stubborn weed out of the ground. You know, a deep, persistent weed that seems to have taken over your flowerbed. Using just your bare hands, it might be difficult or even painful. With a tool, like a hand shovel, however, you should win the battle. Any tool that pries something loose is a lever. A lever is an arm that "pivots" (or turns) against a "fulcrum" (or point). Think of the claw end of a hammer that you use to pry nails loose. It's a lever. It's a
curved arm that rests against a point on a surface. As you rotate the curved arm, it pries the nail loose from the surface. Wheel and Axle The rotation of the lever against a point pries objects loose. That rotation motion can also do other kinds of work. Another kind of lever, the wheel and axle, moves objects across distances. The wheel, the round end, turns the axle, the cylindrical post, causing movement. On a wagon, for example, the bucket rests on top of the axle. As the wheel rotates the axle, the wagon moves. Pulley Instead of an axle, the wheel could also rotate a rope or cord. This variation of the wheel and axle is the pulley. In a pulley, a cord wraps around a wheel. As the wheel rotates, the cord moves in either direction. Now, attach a hook to the cord, and you can use the wheel's rotation to raise and lower objects. On a flagpole, for example, a rope is attached to a pulley. On the rope, there are usually two hooks. The cord rotates around the pulley and lowers the hooks where you can attach the flag. Then, rotate the cord and the flag raises high on the pole. A simple machine is an elementary device that has a specific movement (often called a mechanism), which can be combined with other devices and movements to form a machine. Thus simple machines are considered to be the "building blocks" of more complicated machines. This analytical view of machines as decomposable into simple machines first arose in the Renaissance as a neoclassical amplification of ancient Greek texts on technology, and is still a central part of engineering in today's age of applied science. For example, wheels, levers, and pulleys are all used in the mechanism of a bicycle. Between the simple machines and complex assemblies, several intermediate classes can be defined, which may be termed "compound machines" or "machine elements".
The mechanical advantage of a compound machine is simply the product of the mechanical advantages of the simpThere are three different kinds of levers.
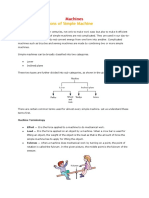
Types of Levers
A first-class lever is a stick where the fulcrum is between the weight and the energy moving the weight (your hands, for example). Some common first-class levers are see-saws, crowbars, pliers, scissors (which use two first-class levers together), and a hammer pulling a nail. An example is a see-saw.
A second-class lever is a stick where the fulcrum is at one end of the stick, you push on the other end, and the weight is in the middle of the stick. Some common second-class levers are doors, staplers, wheelbarrows, and can openers.
A third-class lever is a stick where the fulcrum is at one end of the stick, you push on the middle, and the weight is at the other end of the stick. With a third-class lever, you
have to put in more energy than you would just lifting the weight, but you get the weight to move a longer distance in return. Some common examples are a broom, a hoe, a fishing rod, a baseball bat, and our own human arms.
You might also like
- Simple Machines : The Way They Work - Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandSimple Machines : The Way They Work - Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Simple MachineDocument4 pagesSimple MachineEzio AuditoreNo ratings yet
- The Six Types of Simple MachinesDocument3 pagesThe Six Types of Simple MachinesYang Yo JeongNo ratings yet
- Simple machines make work easierDocument6 pagesSimple machines make work easierDainelle Angelo A. LabutonNo ratings yet
- The Six Types of Simple MachinesDocument4 pagesThe Six Types of Simple MachinesmarroNo ratings yet
- What Is A Simple MachineDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Simple Machinenorazane86% (7)
- Kinds of Simple MachineDocument8 pagesKinds of Simple MachineGiga NetNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Janve M. BungayDocument11 pagesSubmitted By: Janve M. Bungay做挾持No ratings yet
- Simple Machines: Facts: The LeverDocument2 pagesSimple Machines: Facts: The LeverJoyce PrivadoNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument3 pagesSimple MachinesAna GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ingles 1Document6 pagesIngles 1Avimael Nayter Fuentes GuzmanNo ratings yet
- STD 5 Unit 7 Simple Machines Study MaterialDocument6 pagesSTD 5 Unit 7 Simple Machines Study MaterialCool WritzNo ratings yet
- YashDocument9 pagesYashaditya nimbalkarNo ratings yet
- SImple Machines 4Document4 pagesSImple Machines 4g26091993No ratings yet
- Basic Simple MachinesDocument5 pagesBasic Simple MachinessridharNo ratings yet
- Force Simple MachinesDocument17 pagesForce Simple MachinesTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Lever and Simple Machines: The FundamentalsDocument11 pagesLever and Simple Machines: The FundamentalsJhenalyn PerladaNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine Assessment Study GuideDocument1 pageSimple Machine Assessment Study GuideKristen Pietrowski LiportoNo ratings yet
- MachinesDocument20 pagesMachinesletslive2050No ratings yet
- A Simple Machine Is A Mechanical Device That Changes The Direction or Magnitude of A ForceDocument2 pagesA Simple Machine Is A Mechanical Device That Changes The Direction or Magnitude of A ForcefarhanieNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument27 pagesLathe MachineRAGHVENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine HandoutDocument3 pagesSimple Machine HandoutLouis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- SIMPLE MACHINES: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF TECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesSIMPLE MACHINES: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF TECHNOLOGYJordan RamosNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines ExercisesDocument3 pagesSimple Machines Exercisesyensy morel ureñaNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument3 pagesSimple MachinesMarium BilleNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines (Lessons)Document3 pagesSimple Machines (Lessons)patcris moncadaNo ratings yet
- Machine Tool Rotates Workpiece to Shape ObjectsDocument3 pagesMachine Tool Rotates Workpiece to Shape ObjectsbansalsajalNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument7 pagesSimple MachinesAtupan M. MaritesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1cymonitmawile27No ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument12 pagesSimple MachinesCharlote MontefalconNo ratings yet
- 2.+class7 Week18 Science Activity2 Simple - MachineDocument4 pages2.+class7 Week18 Science Activity2 Simple - MachineKetsia DjibrilNo ratings yet
- PPT5Document24 pagesPPT5SAMARTH SWAROOPNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument37 pagesSimple MachinesJay SalesNo ratings yet
- Examples of Simple Machines: Inclined Plane: Easy LiftingDocument3 pagesExamples of Simple Machines: Inclined Plane: Easy LiftingQqq espirituNo ratings yet
- q3 Week 6 Science 6Document51 pagesq3 Week 6 Science 6Morris BanoeyNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines-Taking ActionDocument10 pagesSimple Machines-Taking ActionArham Aariz AhsanNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Simple Machines - Science 6Document13 pagesDifferent Types of Simple Machines - Science 6ilagan.haqqi0321No ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument10 pagesSimple MachinesKristen Pietrowski LiportoNo ratings yet
- Lathe WikipediaDocument71 pagesLathe WikipediaMark Angelo M. BubanNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Principals For Fourth Graders Final IterationDocument19 pagesBasic Mechanical Principals For Fourth Graders Final IterationGia BeNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines Study Guide 2014Document6 pagesSimple Machines Study Guide 2014Janet Pam100% (1)
- Kinds and Functions of Simple Machine: MachinesDocument8 pagesKinds and Functions of Simple Machine: MachinesAman LilaniNo ratings yet
- Science-and-technology (1)Document49 pagesScience-and-technology (1)Doris ParatoNo ratings yet
- Science and TechnologyDocument43 pagesScience and TechnologyDoris ParatoNo ratings yet
- Types of Pulleys and Their UsesDocument2 pagesTypes of Pulleys and Their UsesJejeLyan AmbaNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 14Document9 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 14megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Simple machine guideDocument48 pagesSimple machine guideUnknown Music LabNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines: Provided by TryengineeringDocument15 pagesSimple Machines: Provided by TryengineeringRehpsaj VicenteNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 8.3 - NazarroDocument8 pagesLab Report 8.3 - NazarroMATTHEW NAZARRONo ratings yet
- Project IN ScienceDocument25 pagesProject IN ScienceBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- Rolling Motion ExplainedDocument2 pagesRolling Motion ExplainedzidaaanNo ratings yet
- Science8 LaneDoughertyStuber May6Document11 pagesScience8 LaneDoughertyStuber May6Novita WinarniNo ratings yet
- PAWAR PUBLIC SCHOOL CHAPTER ON SIMPLE MACHINESDocument22 pagesPAWAR PUBLIC SCHOOL CHAPTER ON SIMPLE MACHINESSamiksha NairNo ratings yet
- 6 Simple Machines That Make Work EasierDocument5 pages6 Simple Machines That Make Work EasierPingky AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Lathe MachinesDocument23 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Lathe MachinesNeeraj JithuNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines Study GuideDocument1 pageSimple Machines Study GuideKristen Pietrowski LiportoNo ratings yet
- Forces, Energy and Simple Machines ExplainedDocument4 pagesForces, Energy and Simple Machines ExplainedBeena Santhosh50% (2)
- Simple MachinesDocument16 pagesSimple Machinesapi-176501107No ratings yet
- Unit 5, Story 4 How Do Simple Machines Help Us?Document2 pagesUnit 5, Story 4 How Do Simple Machines Help Us?asmaNo ratings yet
- READMEDocument1 pageREADMEHarold LimNo ratings yet
- Gameplay and Game Mechanics Design: A Key To Quality in VideogamesDocument18 pagesGameplay and Game Mechanics Design: A Key To Quality in VideogamesyiahNo ratings yet
- Content OutlineDocument4 pagesContent OutlineHarold LimNo ratings yet
- AwakeningDocument2 pagesAwakeningHarold LimNo ratings yet
- Lim - ResumeDocument2 pagesLim - ResumeHarold LimNo ratings yet
- Template LP Simplified 2012Document4 pagesTemplate LP Simplified 2012Harold LimNo ratings yet
- 30 January 2015 Liane Peña Alampay Associate Professor Department of Psychology Ateneo de Manila UniversityDocument1 page30 January 2015 Liane Peña Alampay Associate Professor Department of Psychology Ateneo de Manila UniversityHarold LimNo ratings yet
- Survey About Internet UsageDocument1 pageSurvey About Internet UsageHarold LimNo ratings yet
- June 2016 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics AS-LevelDocument28 pagesJune 2016 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics AS-LevelDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper - 1 (Question Paper)Document7 pagesPhysics Paper - 1 (Question Paper)garyNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Document15 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine Assessment Study GuideDocument1 pageSimple Machine Assessment Study GuideKristen Pietrowski LiportoNo ratings yet
- Statics engineering problems and solutionsDocument30 pagesStatics engineering problems and solutionsbok davidNo ratings yet
- Rolling On An Inclined PlaneDocument10 pagesRolling On An Inclined PlaneRichard Puni75% (4)
- Physics: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Document24 pagesPhysics: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Bruce RussellNo ratings yet
- Delcam - PowerMILL 2017 Training Course 5-Axis en - 2016Document274 pagesDelcam - PowerMILL 2017 Training Course 5-Axis en - 2016Вадим ФурсовNo ratings yet
- Operator Manual ECB3035Document114 pagesOperator Manual ECB3035ErnNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument13 pagesSimple Machinespetunia1008554No ratings yet
- 1st Law of MotionDocument14 pages1st Law of Motionbasaallen566No ratings yet
- Statics - Assignment 8: MCE 111 MechanicsDocument4 pagesStatics - Assignment 8: MCE 111 MechanicsOmar NabilNo ratings yet
- M1 Statics - Equilibrium ProblemsDocument30 pagesM1 Statics - Equilibrium ProblemsDarla FennNo ratings yet
- 1 Inclined Plane Problems SOLUTIONSDocument8 pages1 Inclined Plane Problems SOLUTIONSAntonov Vodka100% (4)
- The Fruit Reception StationDocument11 pagesThe Fruit Reception StationArifal100% (1)
- Calculate mine slope parametersDocument6 pagesCalculate mine slope parametersarmadi harisNo ratings yet
- Lab - 11 PHET Energy Skate ParkDocument4 pagesLab - 11 PHET Energy Skate ParkBa ShaNo ratings yet
- Hanoi high school entrance exam English test paperDocument5 pagesHanoi high school entrance exam English test paperNg Hoang Hoai HuongNo ratings yet
- TPT-6 - Paper With SolutionsDocument14 pagesTPT-6 - Paper With SolutionsMahesh guptaNo ratings yet
- M1 Oct 2019 Ial QP PDFDocument28 pagesM1 Oct 2019 Ial QP PDFSham-aan AliNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument5 pagesSimple MachinestpgovindNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration On An InclineDocument3 pagesVelocity and Acceleration On An InclineUgur ASİT100% (3)
- Intuitive Physics: The Straight-Down Belief and Its OriginDocument15 pagesIntuitive Physics: The Straight-Down Belief and Its OriginJavier Jechu Soto MardonesNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.1: SolutionDocument227 pagesProblem 8.1: SolutionPaul Reyna Rojas0% (1)
- Phys101 8 hw2Document2 pagesPhys101 8 hw2mirsad türkerNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PRF1016 (Student)Document48 pagesTutorial PRF1016 (Student)yongshengtang596No ratings yet
- NCCCO Rigger Reference Booklet PDFDocument9 pagesNCCCO Rigger Reference Booklet PDFFOZCANNo ratings yet
- Lalbhai Dalpatbhai Museum concrete beams structural designDocument7 pagesLalbhai Dalpatbhai Museum concrete beams structural designYash PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Montacargas Clark PDFDocument108 pagesMontacargas Clark PDFJaime FlórezNo ratings yet
- Calculations or Solution To Any Problem Are Supposed To Be On The PaperDocument19 pagesCalculations or Solution To Any Problem Are Supposed To Be On The PaperEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachFrom EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryFrom EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo ratings yet
- Radium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935From EverandRadium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Exercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeFrom EverandExercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionFrom Everand3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionArnaud PerrotNo ratings yet
- One Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthFrom EverandOne Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthJoana C. PrataNo ratings yet
- Autophagy in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandAutophagy in Health and DiseaseBeverly RothermelNo ratings yet
- The Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straightforward Guide to Functional Safety: IEC 61508 (2010 Edition), IEC 61511 (2015 Edition) and Related GuidanceFrom EverandThe Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straightforward Guide to Functional Safety: IEC 61508 (2010 Edition), IEC 61511 (2015 Edition) and Related GuidanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet