Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technical Drawing: Paper II (A) - Ordinary Level (Engineering Applications)
Uploaded by
stdropboxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Drawing: Paper II (A) - Ordinary Level (Engineering Applications)
Uploaded by
stdropboxCopyright:
Available Formats
2007.
M82
Coimisin na Scrduithe Stit
State Examinations Commission
Leaving Certificate Examination 2007
Technical Drawing
Paper II(A) Ordinary Level (Engineering Applications)
(200 Marks)
Friday 15 June Afternoon, 2.00 - 5.00
Instructions
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Ensure that you have received examination paper M82(L) which accompanies this paper. Answer question 1 and two other questions. Drawings and sketches should be in pencil unless otherwise stated. Where dimensions are omitted they may be estimated. Credit will be given for neat orderly presentation of work. Work on one side of the paper only. Your Examination Number should be written on each drawing sheet used.
Note: The following drawings are shown on examination paper M.82(L) which accompanies this paper: Fig. 1, Fig. 5(a), Fig. 5(b), and Fig. 5(c).
Page 1 of 5
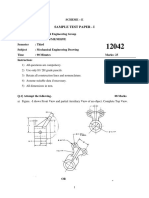
1.
Details of a Roller Support Bracket are shown in Fig.1 with a parts list tabulated below. PART 1 2 3 4 5 6 Base Plate Bracket Roller Bush Shaft Set Screw NAME REQUIRED 1 2 1 2 1 2
(a) Assemble the parts and draw, full size, the following views: (i) a sectional elevation on plane A-A; (ii) a plan projected from (i). (b) Insert the following on your drawing: (i) Title:- ROLLER SUPPORT BRACKET; (ii) ISO projection symbol; (iii) Four principal dimensions.
(100 marks)
2.
Fig.2 shows the elevation and end elevation of a cylindrical pipe which is connected to a triangular duct. A pictorial view is also shown.
The pictorial view shows material thickness which may be ignored for the purposes of your drawing.
(a) Draw the given elevation and end elevation. (b) Draw a surface development of the cylindrical pipe with C-C as the seam line. (50 marks)
Fig. 2
Page 2 of 5
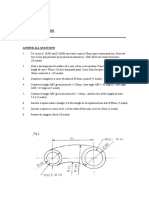
3.
(a)
A radial plate cam has a minimum radius of 42mm and a camshaft diameter of 20mm. The cam rotates in a clockwise direction and imparts the following motion to an inline knife-edge follower: 0 to 30 Dwell;
30 to 210 Rise 54mm with uniform acceleration and retardation; 210 to 270 Fall 14mm with uniform velocity; 270 to 360 Fall 40mm with simple harmonic motion. Draw the profile of the cam. Include the displacement diagram as part of the solution.
(b)
Fig. 3 shows a link mechanism. Crank OA rotates in an anti-clockwise direction about the fixed point O. A and B are pin joints. Crank BC pivots about the fixed point C. (i) (ii) Using a line diagram to represent the mechanism, plot the locus of point P for one revolution of the crank OA. Draw the profile of a simple machine guard about the mechanism with a minimum clearance of 15mm. (50 marks)
OA = 40 AP = 150 AB = 100 BC = 100 Fig. 3
Page 3 of 5
4.
(a)
Using the data table below make a fully dimensioned drawing of the machine part in Fig. 4(a), showing all specifications. Fig. 4(a)
1 2 3 4 5 6
Diameter 40, Length 50, Chamfer 6 x 6, Fillet radius 10, Screwthread Metric 20, Pitch 2.5, Depth of thread 20 Diameter 84, Length 28, Chamfer 4 x 4, Finish diamond knurl Diameter 50, Length 36, Diameter 16 hole through centre Minimum diameter 30, Length 40 Undercut 4 x 4 Length 30, Screwthread Metric 20, Pitch 2.5
(b)
Fig. 4(b) shows a part section through a portion of a typical engine. (i) Draw a parts list, in table format, which includes the item number and name for each of the parts 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. Explain, with the aid of freehand sketches, the operation of the engine mechanism.
(ii)
Fig. 4(b)
(c)
Using large freehand sketches, explain the following engineering terms associated with an engine: (i) Piston; (ii) Connecting rod; (iii) Gudgeon pin. (50 marks)
Page 4 of 5
5.
Answer SECTION A or SECTION B but not both. SECTION A (a) Fig.5(a) shows the elevation and end elevation of a machine casting. Draw an isometric view of the casting with the portion in front of the section plane A-A removed. Point P is to be the lowest point on the drawing. Using large freehand sketches illustrate the following: (i) Splined shaft; (ii) Keyway; (iii) Stud. (50 marks) OR SECTION B (a) (b) List six CAD commands necessary to produce the drawing in Fig.5(b). By means of sketches and a short note, explain the purpose of the following commands: (i) Mirror; (ii) Break; (iii) Extend. (c) (d) Using a large freehand sketch, draw the object shown in Fig. 5(c) as a wireframe representation. Draw, full size, the object that would be displayed on a CAD system when the following commands are executed: (All points (X,Y) are specified using absolute co-ordinates. The origin (0,0) is located at the lower left corner of the display) A rectangle is drawn with its lower left corner at (30,30) and its upper right corner at (190,65) The upper corners of the rectangle are chamfered 15 x 15 A line joins the lower ends of the chamfer lines A line AB is drawn using the following co-ordinates: A (75,65) B (75,115) The line AB is offset 70mm to the right. This new line is indexed CD (point C is on top) A circular arc is drawn to pass through points B, C and point E (110,215) A 30mm diameter circle is drawn concentric with the arc A 16mm diameter circle is drawn with its centre at point (110,195) The circle is the subject of a circular (polar) array consisting of a total of 5 items. The centre of the array is located at the centre of the three point arc A rectangle is drawn with its lower left corner at (85,78) and its upper right corner at (135,102) (50 marks)
(b)
Page 5 of 5
Blank Page
You might also like
- CBSE Class 12 Engineering Graphics Sample Paper-01 (For 2012)Document11 pagesCBSE Class 12 Engineering Graphics Sample Paper-01 (For 2012)cbsesamplepaperNo ratings yet
- 12042-Mechanical Engineering Drawing PDFDocument13 pages12042-Mechanical Engineering Drawing PDFIshara Sanjeewa PereraNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Engineering Drawing With CadDocument10 pagesAircraft Engineering Drawing With CadShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- 4 Hours / 100 MarksDocument7 pages4 Hours / 100 MarkswarekarNo ratings yet
- 9A21301 Aircraft Engineering Drawing With CADDocument9 pages9A21301 Aircraft Engineering Drawing With CADsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- DJF - Model Question PaperDocument6 pagesDJF - Model Question PaperMohammedRafficNo ratings yet
- Jig and Fix Model QPDocument4 pagesJig and Fix Model QPDharmaraj ParamasivamNo ratings yet
- 9A21301 Aircraft Engineering Drawing With CADDocument4 pages9A21301 Aircraft Engineering Drawing With CADsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - 2012Document29 pagesEngineering Graphics - 2012Pranav PoorniNo ratings yet
- 2010 - May - June-06ME44Document2 pages2010 - May - June-06ME44nitte5768No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Engineering Graphics Sample Paper-03 (For 2012)Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Engineering Graphics Sample Paper-03 (For 2012)cbsesamplepaperNo ratings yet
- 06 ME 36A/ 06 ME 46A: Model Question PaperDocument2 pages06 ME 36A/ 06 ME 46A: Model Question PaperRavi karanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing II TutorialDocument29 pagesEngineering Drawing II TutorialManoj Paudel67% (6)
- Machine Drawing SyllabusDocument8 pagesMachine Drawing SyllabusShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- 1492680818Document10 pages1492680818Asprilla MangombeNo ratings yet
- DJFDocument2 pagesDJFRamesh VeerNo ratings yet
- 4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoDocument12 pages4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NowarekarNo ratings yet
- FE6Document109 pagesFE6Jyoti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoDocument11 pages4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NowarekarNo ratings yet
- Be Summer 2020Document3 pagesBe Summer 2020M.I.K 72No ratings yet
- Mech 260-Final ExamDocument3 pagesMech 260-Final ExamwerewaroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing-Marking Schemes Science Subjects-XII-2007Document20 pagesEngineering Drawing-Marking Schemes Science Subjects-XII-2007ranydiNo ratings yet
- Prac 2 DrawingDocument8 pagesPrac 2 DrawingOscar KhanyeNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1 08 12 2017Document3 pagesIndividual Assignment 1 08 12 2017Fahad Khalef Al BarwanNo ratings yet
- Emg 3212 Metrology SuppDocument4 pagesEmg 3212 Metrology SuppkiokocurtisNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Engineering Drawing Solved Sample Paper-02 (For 2011)Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Engineering Drawing Solved Sample Paper-02 (For 2011)cbsesamplepaperNo ratings yet
- R5100107 Engineering GraphicsDocument2 pagesR5100107 Engineering GraphicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument45 pagesQuestionsMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument5 pagesEngineering Drawingrsinha.0604No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals: College of Engineering Sciences Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument2 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals: College of Engineering Sciences Mechanical Engineering DepartmentOmar RefeNo ratings yet
- Course: Maximum Marks: 100: Computer Aided Machine DrawingDocument3 pagesCourse: Maximum Marks: 100: Computer Aided Machine DrawingVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- ME8691 CADM Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesME8691 CADM Important QuestionsUdamanNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - CBSE Class 12 Engineering Drawing Sample Paper 3Document21 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - CBSE Class 12 Engineering Drawing Sample Paper 3saded05No ratings yet
- Caribbean Examinations: Resr CouncDocument7 pagesCaribbean Examinations: Resr CouncDarrion BruceNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Draughting N4 QP Aug 2019Document9 pagesMechanical Draughting N4 QP Aug 2019patel.ayushl2018No ratings yet
- Punjab Uni 2012 EnggDrawing QueDocument2 pagesPunjab Uni 2012 EnggDrawing QueAkter SuriyaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Engineering Drawing I: August 2019Document28 pagesPractice Problems For Engineering Drawing I: August 2019ribbyNo ratings yet
- Mee2001 Digital AssignmentDocument3 pagesMee2001 Digital Assignmentdude_udit321771No ratings yet
- Practice Problemsfor Engineering Drawing IDocument28 pagesPractice Problemsfor Engineering Drawing IV Pankaj NathNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Engineering Drawing IDocument28 pagesPractice Problems For Engineering Drawing IYasmin ArebNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. (Sem.: Roll No. ...................... Total No. of Ques Ions: 09) (Total No. of Pages: 04Document4 pagesB.Tech. (Sem.: Roll No. ...................... Total No. of Ques Ions: 09) (Total No. of Pages: 04Jaswinder SinghNo ratings yet
- End Sem TA101AA Sem I - 2020-2021Document6 pagesEnd Sem TA101AA Sem I - 2020-2021tHEhOODYgANGNo ratings yet
- Assignment CAD NME-701Document5 pagesAssignment CAD NME-701Shah GhanimNo ratings yet
- Cat 1 - 2 and Assignment 2Document3 pagesCat 1 - 2 and Assignment 2Nashon MutuaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Engineering Drawing I: August 2019Document28 pagesPractice Problems For Engineering Drawing I: August 2019a c s KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Exercise 3Document3 pagesEngineering Drawing Exercise 3Charlee EdsonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing II Tutorial PDFDocument38 pagesEngineering Drawing II Tutorial PDFskumaranspNo ratings yet
- EG New Data Sheet 2022 - R1Document9 pagesEG New Data Sheet 2022 - R1Shivamxerox 2022No ratings yet
- Bmsce Mechanical Engineering Dept.: CAMD Test I - 3 Sem B' SectionDocument3 pagesBmsce Mechanical Engineering Dept.: CAMD Test I - 3 Sem B' SectionAll_regNo ratings yet
- Machine Drawing PDFDocument8 pagesMachine Drawing PDFBv Rajesh RëälNo ratings yet
- CSEC Technical Drawing June 2010 P032Document6 pagesCSEC Technical Drawing June 2010 P032Patrick ClarkeNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsFrom EverandA Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsNo ratings yet
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsFrom EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Autodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressFrom EverandAutodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- ConicsDocument30 pagesConicsstdropboxNo ratings yet
- MPQDocument93 pagesMPQstdropboxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanisms: Rapid Design Through Virtual and Physical PrototypingDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Mechanisms: Rapid Design Through Virtual and Physical PrototypingstdropboxNo ratings yet
- CamsDocument32 pagesCamsNot my documentsNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit Microcontroller With 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega16 Atmega16LDocument358 pages8-Bit Microcontroller With 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega16 Atmega16LKhoerun Nisa SNo ratings yet
- ABS Data SheetDocument2 pagesABS Data Sheetom12315No ratings yet
- Exercise 1&2Document2 pagesExercise 1&2stdropboxNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument12 pagesWorksheetstdropboxNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit With 8K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega8 Atmega8LDocument308 pages8-Bit With 8K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega8 Atmega8LtataraseanuNo ratings yet
- Release NotesDocument2 pagesRelease NotesstdropboxNo ratings yet
- SandFlea Datasheet v1 - 0Document1 pageSandFlea Datasheet v1 - 0stdropboxNo ratings yet
- Headline Daily 11 Oct 2011Document1 pageHeadline Daily 11 Oct 2011stdropboxNo ratings yet
- SandFlea Datasheet v1 - 0Document1 pageSandFlea Datasheet v1 - 0stdropboxNo ratings yet
- Problem of Ageing Population in Hong Kong andDocument19 pagesProblem of Ageing Population in Hong Kong andstdropboxNo ratings yet
- Headline Daily 17 Nov 2011Document1 pageHeadline Daily 17 Nov 2011stdropboxNo ratings yet
- Project Title: Proposed One-Storey Residential Building Governing Codes and SpecificationDocument8 pagesProject Title: Proposed One-Storey Residential Building Governing Codes and SpecificationPamela Joanne Falo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Led LCD TV: Service ManualDocument60 pagesLed LCD TV: Service ManualFrank VillaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument12 pagesPPTajaydev2224No ratings yet
- Power Plant and Calculations - 15-Equipments Efficiency Calculation in Power PlantDocument12 pagesPower Plant and Calculations - 15-Equipments Efficiency Calculation in Power PlantRajeshNo ratings yet
- Ductless Fume Hood Brochure - FEB19Document2 pagesDuctless Fume Hood Brochure - FEB19Musz MusaNo ratings yet
- Matacid AsDocument4 pagesMatacid Asraju.dhNo ratings yet
- Viper SM 21203788CDocument158 pagesViper SM 21203788CarodassanchezNo ratings yet
- HSE Guide For Hot Tapping Part 1-13Document4 pagesHSE Guide For Hot Tapping Part 1-13abhisheknharanghat100% (1)
- Jumbo DrillDocument4 pagesJumbo DrillJose Antonio Quispealaya HernandezNo ratings yet
- EZ Clean 1500Document4 pagesEZ Clean 1500sebasalinashjNo ratings yet
- Laser Consumables PDFDocument1 pageLaser Consumables PDFAnonymous cXX1tYY2No ratings yet
- Bayblend T88 GF 20 - en - 56968672 00003567 20081863Document3 pagesBayblend T88 GF 20 - en - 56968672 00003567 20081863Mattia Terri TerrandoNo ratings yet
- TitaniumDocument6 pagesTitaniumzonearthNo ratings yet
- Project Report On GearsDocument40 pagesProject Report On Gearsjai70% (27)
- Combustion SectionDocument31 pagesCombustion SectionKusmaliah OksaNo ratings yet
- Dupont Freon 22 Refrigerant: Safety Data SheetDocument12 pagesDupont Freon 22 Refrigerant: Safety Data Sheetmanu elmerNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Text DocumentsadsdNo ratings yet
- DP Test ProcedureDocument8 pagesDP Test ProcedureAjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Nexans Olex Handbook 2017 OnlineDocument112 pagesNexans Olex Handbook 2017 OnlinenitinrajuNo ratings yet
- DokwegII - Auxiliary - Maintenance Compressed Air SystemDocument62 pagesDokwegII - Auxiliary - Maintenance Compressed Air SystemCarlin BabuchasNo ratings yet
- Non-Cycling Refrigerated Dryer 200-800 SCFMDocument24 pagesNon-Cycling Refrigerated Dryer 200-800 SCFMCarlos Jiménez100% (1)
- Using The Failure Assessment Diagram Method With Fatigue Crack Growth To Determine Leak-before-RuptureDocument15 pagesUsing The Failure Assessment Diagram Method With Fatigue Crack Growth To Determine Leak-before-RuptureMohammed EljammalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 02 - AnswerDocument8 pagesTutorial Chapter 02 - AnswerFateh Hakeem100% (4)
- Tugas PPM Deny Saputro Arifin 113170039Document9 pagesTugas PPM Deny Saputro Arifin 113170039Vira IrnandaNo ratings yet
- Design Principles Common To Jigs and FixturesDocument3 pagesDesign Principles Common To Jigs and FixturesTahir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Week 2-Basic Cost ManagementDocument21 pagesWeek 2-Basic Cost ManagementRichard Oliver CortezNo ratings yet
- Strategic MGMT Ch-3Document30 pagesStrategic MGMT Ch-3Desu MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Flow Measuring Instruments: (An ISO 9001-2008 Company)Document4 pagesFlow Measuring Instruments: (An ISO 9001-2008 Company)I. Murali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BS 812-124 1989Document29 pagesBS 812-124 1989Muhamed RiskhanNo ratings yet
- Condensate Chemistry DiscussDocument12 pagesCondensate Chemistry DiscussMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet