Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Materials and Metallurgy
Uploaded by
abdulhere4uOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Materials and Metallurgy
Uploaded by
abdulhere4uCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY
Anna university 2 marks
UNIT-1 1. State peritectic and peritectoid reactions? 2. Distinguish between steel and cast iron. Also classify steel with respect to carbon percentage? 3. What are interstitial solid solutions and intersitisal compounds? 4. Differentiate between eutectic and eutectoid phase reactions? 5. Define solid solutions? 6. How are steels classified? 7. What do you mean by substitution solid solution? Briefly explain the rules governing the formation of subsitutional solid solution? 8. Name and explain any one type of binary solid to solid state transformation reaction with ideal phase diagram? 9. Why carbon solubility is more in austenite? 10. List the advantages of alloy steels as compound to plain carbon steels? 11. Give examples of eutectoid reactions? 12. Distinguish between hypo-eutectoid reactions? 13. Define the terms ferrite and austenite in iron carbon alloy system? 14. What are the effects of crystal structure and atomic radii on formation of solid solution between two metallic elements?
UNIT-II 1. Enumerate any two differences between annealing and normalizing? 2. Explain the term inducing hardening? 3. Define critical cooling rate? 4. What is final microstructure in austempering of steels? 5. When will you prefer carbonitriding? 6. Define hardness? 7. Name and explain any one subcritical case hardening treatment? 8. With heat treatment cycle, explain the conventional normalizing treatment for hypereutectoid steel? 9. What are the principal advantages of austempering over conventional quench and temper method? 10. Mention few application of induction hardening? 11. Can mild steel be induction hardened? Substantiate. 12. What is the need for providing a tempering treatment after quench hardening of steels? 13. What is the principle of surface hardening in induction hardening process? 14. A low carbon steel is in the normalized condition is stronger than the same steel in the annealed condition. Why?
15. Case carburizing heat treatment is not generally carried out for medium carbon steels. Why? 16. What is carbonitiriding?
UNIT-III 1. What is twinning in metals? 2. What is difference between HRB and HRC? 3. Define fatigue? 4. List the testing methods of metals? 5. What is difference between slip and twinning? 6. What is creep? Draw typical creep curve and show different creep stages on it? 7. What slip bands? 8. What are different types of loadings available for fatigue testing? 9. Why is impact specimens notched? 10. How will you express the deformation characteristics of a material through tension test? 11. In general HCP metals are hard and brittle while FCC metals are soft and ductile. Why?
12. Draw the sketch of a standard specimen used for charpy v-notch impact testing? 13. What is endurance limit in fatigue test? 14. What properties are determined from tension testing of metallic products?
UNIT-IV 1. List the parameters that can be determined from the tension test? 2. Mention some of the disadvantages of brinell's hardness test? 3. What are the effects of adding Si in steel? 4. Differentiate brass from bronze? 5. Name the alloying elements in high speed steels? 6. State the applications of tool steels? 7. Write short notes on the type of stainless steel? 8. With composition, property and application explain (A) tin bronze (B) naval bronze? 9. List different types of tool steels? 10. Mention any two aluminum base alloys and their applications? 11. Distinguish between grey cast iron and spheroidal graphite cast iron in terms of microstructures and the mechanical properties?
12. What is the composition of 18-4-1 type high speed steel? 13. What is the effect of chromium and molybdenum in low alloy steels? 14. What is the purpose of magnesium treatment in producing iron? 15. What is the main strengthening mechanism in high strength aluminum alloys? 16. Compare the marten site that is formed in managing steels with the marten site that is formed in carbon steels?
UNIT-V 1. Name any two polymers and state their applications? 2. Mention any four attractive proper ties of engineering ceramics? 3. What are PMMA and PET polymers? What are their uses? 4. What are uses of alumina? 5. Define degree of polymerization? 6. State any two properties of ceramics? 7. Write the general mechanical properties of ceramics? 8. Write the property and applications of; explain the following polymers (a) PVC (b) PMMA? 9. What do you mean by copolymers? 10. How are refractories classified?
11. Name any four common engineering polymers? 12. What are the uses of aluminum oxide? 13. Write the molecular structure of either phenol-formaldehyde polymer or urea-formaldehyde polymer? 14. Give two examples of particulate reinforced metal matrix composite? 15. Draw the molecular structure of polyethylene and polypropylene? 16. Give one examples of each metal matrix composites and ceramics matrix composites? 17. Name four enthenic polymers? 18. What are important uses of alumina and silicon nitride?
ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY
Anna University 16-marks
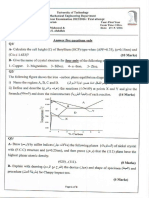
UNIT-I 1. Draw iron carbon diagram neatly with explanation? 2. Elements A and B melt at 700c and 1000c respectively .draw a typical phase diagram between A and B? 3. Elements A and B melt at 1000c respectively they form a eutectic at 35% A at temperature 500c.Draw a typical phase diagram between A and B. 4. Metal A has melting point of 1000c .Metal B has melting point of 500c .draw one phase diagram for each of the following conditions. (i) the two elements exhibits unlimited solid solubility .ii) the alloy system shows formation of two terminal solid solution and a eutectic point, at 50% A and at 700c.iii) the alloy system shows formation of an intermolecular phases with the chemical formula A2B. 5. Estimate the carbon content of carbon steel whose microstructure in the annealed conditions shows 75% pearlite and 25% ferrite. 6. Two elements A and B have melting point 800c and 600c respectively (i) draw the phase diagram between A and B if they exhibit unlimited solid solubility. (ii) Draw phase diagram between A and B if eutectic reaction occurs at composition 40% B and at temperature 400c.Asusume that the maximum solid solubility in either case is5% and the room temperature solubility is either case is 1%.
7. Metal A and B having melting point respectively 270c,320c are assumed to be completely soluble in the liquid state and completely soluble in the liquid state and completely insoluble in solid state. They form eutectic at 140c containing 40%B.i)draw the equilibrium diagram and label all lines and areas and ii)for an alloy containing 30%A.give the temperature of initial and final solidification and relative amounts of phases present at 180c. 8. How are solid solutions classified? Give two examples of each./ 9. Discuss Hume-Rothery rules for the formation of solid solution? 10. Define i)solid solution ii)polymorphism iii)allotropy IV)phase v)equilibrium diagram. UNIT-II 1. Draw and explain CCT curve? 2. Draw and explain TTT curve? 3. Explain Jomny end quench test? Define hardenability? 4. Explain heat treatment process? 5 .Estimate steps in care carburizing of steels? 6 .Explain the construction procedure of isothermal transformation diagram for 1080 steel. Neatly sketch the diagram ,indicating different phases on it. 7. Distinguish between hardness and hardenability . 8. Distinguish between "annealing" and "tempering". 9. Compare between austempering and martempering. 10 .Discuss different types of annealing process?
UNIT-III 1.Write the compositions and properties of i)austenitic stainless steel ii0high speed steel iii)martensite iv)maraging steel v)ferritetic steel vi)brasses vii)cu-zn viii)caritdge ix)naval brasses x)muntz brasses. 2.How will you classify brasses based on the composition of zinc? Explain the properties and applications of the main types of brasses. 3.Explain the steps involved in precipitation hardening treatment? 4.Discuss strengthening mechanism, composition and properties of any one type of maraging steels. 5. Discuss the steps involved in precipitation hardening treatment using any one aluminum alloy as example. 6. What are alpha brasses and brasses ?what are their properties and applications 7. Using AL-CU alloy system as example, explain the concept of precipitation heat treatment? 8. Explain how a machinability heat treatment will convert a white cast iron to a malleable Cast iron? 9.What are HSLA steels? How can high strength and toughness be obtained in them? 10.Discuss the influence of each of the following alloying elements on the properties of steel. i)molybdenum ii)chromium iii)magnesium IV)titanium v)tungsten VI)vanadium.
UNIT-IV 1.Describe the molecular structure, properties and applications of ,PVC ,PS ,PET alumina silicon carbide ,silicon nitride ,sialum ,polymethyl methacynate,PTF,ABS,PTFE,PEP,PMMA. 2.Difference between thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. 3. Short notes on i)ceramics ii)polymer iii)formaldehyde iv)reinforced composite. 4.What properties and uses of reinforced composites?
UNIT-V 1.Explain the mechanism of plastic deformation of metal by slip and twinning? 2.Explain the characteristics of ductile fracture and brittle fracture? 3.Explain the testing procedure for Vikers hardness test? 4. Explain the testing procedure for Izod impact test? 5. Explain the testing procedure for Charpys impact test? 6. Explain the testing procedure for Brinell hardness test? 7. Explain the testing procedure for Rockwell hardness test? 8.Draw SN curve for MS and Al and explain in features .Explain the procedure used to obtain SN diagram? 9. What is fatigue failure? How fatigue test is carried out? Explain? 10. Difference between ductile and brittle fracture?
11. Define and explain plastic deformation, creep tensile test for metal, hardening test. 12. Explain i) mechanical ii) thermal behavior iii) electrical behavior.
You might also like
- Sterlization of Water Using Bleaching Powder PDFDocument20 pagesSterlization of Water Using Bleaching Powder PDFradha krishnanNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument10 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgykannan100% (1)
- Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankDocument7 pagesEngineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankJOHN PAUL V67% (3)
- Emm Question BankDocument6 pagesEmm Question BankMurugesan JeevaNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsFrom EverandDie Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Steel and Timber Report Compiled (Aaa) PDFDocument42 pagesSteel and Timber Report Compiled (Aaa) PDFLee Chen ChoonNo ratings yet
- ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBDocument3 pagesME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Emm Lab QuestionsDocument9 pagesEmm Lab QuestionsVijai KaladadNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution and Its PropertiesDocument19 pagesThe Normal Distribution and Its Propertiessherdan genistonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material AssignmentDocument3 pagesEngineering Material AssignmentSharjeel Faisal100% (1)
- 4 Me MQ EMMDocument2 pages4 Me MQ EMMBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Question Papers - Heat TreatmentDocument9 pagesQuestion Papers - Heat TreatmentSrilakshmi Shunmugaraj100% (3)
- ME6403 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY UNIT 1.ALLOYS AND PHASE DIAGRAMDocument6 pagesME6403 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY UNIT 1.ALLOYS AND PHASE DIAGRAMjamunaa83No ratings yet
- UNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-ADocument7 pagesUNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-AkarthisanNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument12 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgysanthanam102No ratings yet
- Engineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - IDocument4 pagesEngineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - Ijamunaa83No ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 MarksDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 Marks17TUME212 ROHITH.MNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesMetallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyMANYAM. HARI KRISHNA MECHANICAL ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Principles of Material Selection Question BankDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Material Selection Question BankGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Anna University Questions on Phase Diagrams, Heat Treatment and MaterialsDocument4 pagesAnna University Questions on Phase Diagrams, Heat Treatment and Materials10BShalini.B IgmmNo ratings yet
- 9 - Phase DiagramsDocument13 pages9 - Phase DiagramsJohny SkNo ratings yet
- ME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument10 pagesME8491 IQ 02 - by LearnEngineering - inDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ME1253-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument0 pagesME1253-Engineering Materials and MetallurgybalajimeieNo ratings yet
- Previous Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesDocument10 pagesPrevious Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesRajeev SaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 &4 Question BankDocument4 pagesUnit 3 &4 Question BankcprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- MM Question BankDocument22 pagesMM Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ME-8491 EM QB For UT1Document2 pagesME-8491 EM QB For UT1ajaymNo ratings yet
- G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankDocument12 pagesG. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur: Mechanical Engineering Department Question BankRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- BF1113 Assignment 2Document2 pagesBF1113 Assignment 2sanasieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4kaushikNo ratings yet
- 9A03301 Materials Science and EngineeringDocument4 pages9A03301 Materials Science and EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Material ScienceDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Material Sciencetheamg7272No ratings yet
- Material Science Important Questions For AMIE Section-ADocument8 pagesMaterial Science Important Questions For AMIE Section-AThota Sai Swaroop67% (3)
- VSB Engineering College Question BankDocument53 pagesVSB Engineering College Question BankHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- Part A SUGUDocument2 pagesPart A SUGUAnbu SelvanNo ratings yet
- Material Science & Metallurgy Question BankDocument4 pagesMaterial Science & Metallurgy Question BankJay SathwaraNo ratings yet
- Regulation 2010 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy ExamDocument4 pagesRegulation 2010 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy ExambalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Ph8251 Ms Rejinpaul Iq Am19Document1 pagePh8251 Ms Rejinpaul Iq Am19JairusNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test Properties Mechanical TestsDocument14 pagesTensile Test Properties Mechanical TestsBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Chemy 2 QBDocument6 pagesChemy 2 QBPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09Document3 pages1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09praiselovesscienceNo ratings yet
- سنوات سابقة خواصDocument64 pagesسنوات سابقة خواصmechanical depNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Metallurgy Question BankDocument3 pagesMaterial Science and Metallurgy Question BankVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Questions Set - 4 (Module 4)Document1 pageAssignment Questions Set - 4 (Module 4)nkar037No ratings yet
- Material Science and Metallurgy Question BankDocument11 pagesMaterial Science and Metallurgy Question BankMohamed SohaibNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgy PDFDocument10 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgy PDFRaviggg0% (1)
- Engineering Metallurgy IAE III QP Question BankDocument2 pagesEngineering Metallurgy IAE III QP Question BankJawaharNo ratings yet
- CH 6604 Materials Science and Technology Part B Questions Unit IDocument3 pagesCH 6604 Materials Science and Technology Part B Questions Unit Ichitra123No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties and Its Testing MethodDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties and Its Testing MethodMohammad Khairul Azmi Mohd KassimNo ratings yet
- Two Marks With AnswersDocument19 pagesTwo Marks With AnswersNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes on Abrasives, Refractories, Lubricants, Corrosion and PolymersDocument6 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes on Abrasives, Refractories, Lubricants, Corrosion and PolymersLohanathan VkNo ratings yet
- 금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Document10 pages금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Li Ken LokNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- PMSM ALL IMP 3rd Sem Mechatronics GTU QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesPMSM ALL IMP 3rd Sem Mechatronics GTU QUESTIONSSwastik PanchalNo ratings yet
- Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsFrom EverandUltra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsWilliam G. FahrenholtzNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Nanomaterials: Advances in Energy, Environment, and Polymer NanocompositesFrom EverandHybrid Nanomaterials: Advances in Energy, Environment, and Polymer NanocompositesSuneel Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Automobile and Aeronautical EngineeringDocument4 pagesMechanical Automobile and Aeronautical Engineeringkaushikv88No ratings yet
- Instruction 2015BDocument3 pagesInstruction 2015Babdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Syllabus R2013 PDFDocument105 pagesSyllabus R2013 PDFlogeshboy007No ratings yet
- WGFDGCBDDocument1 pageWGFDGCBDabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Basic and Applied Thermodynamics - WebviewDocument10 pagesBasic and Applied Thermodynamics - Webviewabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Instruction 2015BDocument3 pagesInstruction 2015Babdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) AUPtancetmathsDocument4 pages(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) AUPtancetmathsabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: in This Project Used Different Materials. There AreDocument5 pagesSynopsis: in This Project Used Different Materials. There Areabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Sri Subramanya College of Engineering & Technology Palani Me2304-Engineering Metrology and MeasurementsDocument1 pageSri Subramanya College of Engineering & Technology Palani Me2304-Engineering Metrology and Measurementsabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Course File CHECK LIST For RoboticsDocument1 pageCourse File CHECK LIST For Roboticsabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- 2.ic Engine Nov - Dec-2013Document18 pages2.ic Engine Nov - Dec-2013abdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Chimney: Dense PressureDocument1 pageChimney: Dense Pressureabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- CCTV User Group Guide For Small Users Private and CommercialDocument15 pagesCCTV User Group Guide For Small Users Private and Commercialabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Ram ResumeDocument3 pagesRam Resumeabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- AHP 2 It 2Document1 pageAHP 2 It 2abdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Final Pro EDocument2 pagesFinal Pro Eabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Part - A Answer All The Questions (5x2 10)Document1 pagePart - A Answer All The Questions (5x2 10)abdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Tower 3300 Instruction ManualDocument23 pagesTower 3300 Instruction ManualMark RobertsNo ratings yet
- ContentServer PDFDocument16 pagesContentServer PDFdaniel leon marinNo ratings yet
- Armando Anaya Guenter y Zender - Sak Tz'iDocument14 pagesArmando Anaya Guenter y Zender - Sak Tz'iAngel Sanchez GamboaNo ratings yet
- CE 205 - Analyzing Hydrographs and Deriving Unit HydrographsDocument17 pagesCE 205 - Analyzing Hydrographs and Deriving Unit HydrographsUmange RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Design of RC Building - ExerciseDocument6 pagesDesign of RC Building - Exercisesajeerala100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 18 (Final)Document3 pagesLesson Plan 18 (Final)ryan agustianNo ratings yet
- Insight: Mini C-Arm Imaging System Technical Reference ManualDocument21 pagesInsight: Mini C-Arm Imaging System Technical Reference ManualTyrone CoxNo ratings yet
- Deformation of Ceramics and PolymersDocument41 pagesDeformation of Ceramics and PolymersJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- WCB Customized Superior Quality Slewing Ring GearDocument173 pagesWCB Customized Superior Quality Slewing Ring GearWCB BEARINGNo ratings yet
- Atht Model Ques 2017Document1 pageAtht Model Ques 2017Jeyakumar VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Emc VNX Vnxe3300: Installation GuideDocument28 pagesEmc VNX Vnxe3300: Installation GuideAnkit JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide To Arrows in ChemistryDocument1 pageA Short Guide To Arrows in ChemistryJefferson RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Mos PDFDocument194 pagesMos PDFChoon Ewe LimNo ratings yet
- Same Denominator or Numerator Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSame Denominator or Numerator Worksheet 1Jenny KimNo ratings yet
- Multistage Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument29 pagesMultistage Amplifier Frequency ResponseMuhammad HafizNo ratings yet
- Financial Modelling Assignment - Ghizal Naqvi (Attock Petroleum Limited)Document13 pagesFinancial Modelling Assignment - Ghizal Naqvi (Attock Petroleum Limited)Ghizal NaqviNo ratings yet
- SUDOKU DocumentDocument37 pagesSUDOKU DocumentAmbika Sharma33% (3)
- Understanding the Strength and Limitations of DES EncryptionDocument32 pagesUnderstanding the Strength and Limitations of DES EncryptionArya KumariNo ratings yet
- Primary-Side Regulation PWM Power Switch General Description FeaturesDocument10 pagesPrimary-Side Regulation PWM Power Switch General Description FeaturespopoNo ratings yet
- B1698Document23 pagesB1698Esteban OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Carbon 06 00052Document17 pagesCarbon 06 00052Elbahi DjaalabNo ratings yet
- 2011 Nov P1 Maths L2Document9 pages2011 Nov P1 Maths L2nhlanhlamhlambi3No ratings yet
- Star and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesStar and Its PropertiesRemond BalabaNo ratings yet
- Guide For Dynamic Report Generator - EndsfsdfsdfsdfsdfDocument15 pagesGuide For Dynamic Report Generator - Endsfsdfsdfsdfsdfmtech structuresNo ratings yet
- Pages 296-298 Module 6 ReviewDocument4 pagesPages 296-298 Module 6 Reviewapi-332361871No ratings yet
- Test Automation Design PrinciplesDocument15 pagesTest Automation Design PrinciplesSujay KumarNo ratings yet
- Ups Lyonn Modelo: Ult St5-100 KS: 10KVA A 120KVADocument1 pageUps Lyonn Modelo: Ult St5-100 KS: 10KVA A 120KVASebastian Matias CruzNo ratings yet