Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Identification
Uploaded by
Lemuel KimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Identification
Uploaded by
Lemuel KimCopyright:
Available Formats
Identification LESSON 1: VIEWS ABOUT LEARNING Learning is a way of knowing things o is an increase of knowledge o refers to the method of acquiring
information o is a way of thinking, means the process of storing ideas o is defined as a process of memorization, is one way of storing information that can be reproduced, retrieved, and used when it is needed o is a means through which we make sense out of this world o is a way of interpreting and understanding realities and is a way through which we conceptualize the world. o is viewed as experiential process resulting in a relatively permanent change in behavior that cannot be explained by temporary states, maturation, or innate response tendencies o has also been defined as a reorganization of the cognitive structures o a change in behavior due to practice. a relatively permanent change in ones behavior as a result of his interaction in the environment. o involves change in knowledge and behavior o is acquisition of knowledge, involves experience o it describes accumulation of knowledge Learning is a heartbeat of society Jacques Lucien Jean Delors Understanding is created b6 individuals as they interact with the world and with people around them. LEARNER-CENTERED PSYCHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES is divided into cognitive and metacognitive, motivational and affective, developmental and social, and individual differences factors. Independence it means that learners have to posses their own learning. Creativity it means that learners should posses the ability to develop new ideas and especially in an artistic way. Self-motivation the learners should be responsible for their own motivations, Resilience the learners should posses the ability to recover quickly from setback failures. Assessment provides relevant information to both learners and teachers at all stages of learning process. LESSON 2 LEARNING METAPHORS Metaphor is a cognitive tool that enables us to see one thing in terms of another. - Give meanings to new experiences or events in a symbolic manner. - It means that if things are perceived to be similar, then we intend to transfer their meanings to other objects. - Are assumptions about learning; they are cognitive systematizations to our experiences to facilitate our thoughts about learning. - Is a process of utilizing the embodied of our personal experiences. Effective Teaching leads to effective learning Poor Teaching leads to poor learning Hearing and vision are receptors of knowledge and not expressers of such knowledge. LESSON 3: TYPES OF KNOWLEDGE Knowledge -is very important. -it is what we use in everything we do in our everyday in our life -should be integrate between the old and new facts to maintain the equilibration -is of powerful for it can make and unmake us even our strongest relationships. Episodic Knowledge refers to our biographical memory reflecting not only what happened, but also when it happened. Semantic Knowledge deals with memories and information that are not tied to our personal biographies. Declarative Knowledge deals with the statement of truth; it also deals with what we know about the world. Accounts for knowing what. Episodes these are specific events in a certain story which has its essentials elements such as setting, plot, climax, style, point of view, denouncement and others. Generalizations are statements of conclusions that are derived from and can be applied in a number of situations. Principles these are statements of generalizations that expresses rules or relationships that exist between or among events. Procedural knowledge - is the knowledge about how things are to be done. Accounts for knowing how. Conditional knowledge - Accounts for knowing when. The appropriate time and condition in which certain information is to be used. Rational- if it is based on correct premise. Empirical - if it is can be verified. Pragmatic- if it is based on practical results.
Facts are things that are known to be true are very specific bits of information that relate to a specific events , person, object, or situation. -never stand alone, they are always interpreted and have ascribed meaning. Data are the things gathered through the process of research. Information is a definite knowledge. -superhighway Internet is an incredibly rich source of information on virtually all aspects and disciplines. Ideas are maybe suggestions, impressions, or opinion. Wisdom - is gained through experiences. Concepts are labels given to categories of information or things that have common characteristics. these are commonly single words that label a category or class of persons, things, objects or events. -basic units of thinking. -is general categories of things, events, and qualities that are linked by common features. Properties- are common characteristics shared by all of the example concepts. Generalizations are statements that contain the if-then or predictive characteristics. LESSON 4: PRIOR KNOWLEDGE Prior knowledge is a mental structure that describes our knowledge and experiences gain during the course of our life and how old experiences are used to understand new ones. Schemata are called mental organizers. - are cognitive structures that help us make sense of the world around us. Schema Theories support the idea that new information is constructed to fit information currently existing in the mind. Organizational Schema is one of many approaches to understand how our memory works. Schemas are organizational hierarchies of information established in our brain that provide blueprints for perceiving, interpreting, and remembering incoming information. Deep Learning occurs when students digest are nourished by their learning and able to make sense out of it. -entails the use of metacognition that encapsulates our ability to recognized, organized, and develop the learning process and such leads to what we know as ownership of learning. Learner autonomy is one of the new paradigms of learning. Superficial Learning knowing facts without their use in acquiring other forms of knowledge for its only focused on signs and symbols. -it is the knowledge of what one is not how one is. -it deals with the quantitative aspects of learning. Chunking -it is the process of breaking a whole thing into small and workable components. -is another way to maintain the information in STM. Outlining -it gives the readers a birds eye view of what will be discussed in the material. Highlighting students can easily locate the most important points in lesson. Questioning if we provide students with organizing information, we need to give them guide questions before we expose them to a certain task. LESSON 5: TRANSFER OF LEARNING Transfer of Learning is one of the basic concerns of educational practitioners. Transfer is a process of extending knowledge acquire in one context to other contexts. Transfer of knowledge and skills - is a major concern of every teacher. Positive Transfer it occurs when students have the ability to harness strong associations for some recall in the future. - is what we develop among our students Negative Transfer it occurs when students find two events or items similar when in fact they are not. -happens when two materials are different. Vertical Transfer occurs when complex skills are more easily learned because of simple skills that are acquired earlier. Lateral Transfer refers to the students ability to generalized knowledge or skill to a novel situation. LESSON 9: COGNITIVE THEORY Cognitive Theory is influenced by Gestalt movement and later by Swiss psychologist, Jean Piaget, and Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky. American cognitive theorist such as Tolman, Bruner. Gestalt Theory was developed by three psychologist Wolfgang Kohler, Max Weitheimer, and Kurt Koffka. Gestalt - is of German origin which means pattern, shape or form. Law of Continuity the law states that we link individual elements together so they form a continuous pattern that makes sense.
Law of Closure this law holds the idea that incomplete figures tend to perceived as complete Law of Similarity this law holds that similar things appear to be group together. O O O O O ******* Law of Proximity this law states that things that other appear to be group together. Q Q Q Q Q ******* Law of Pragnanz the word pragnanz is a German word which means good figure. -A.K.A. law of simplicity and law of good figure. 00000 -this holds the beliefthat all possible organization could be perceived in a stimulus array one that possesses the best, the simplest, and themost stable form. O Cognitive Development Jean Piaget popularized the cognitive development. Jean Piaget born on August 9, 1896 and died on September 16, 1980. Genetic Epistemology refers to the formation of meaning of knowledge. Scheme - the knowledge structure responsible for our ability to reason and adapt to the environment. Schemes are specific patterns of mental activities for acquiring information about the environment. Assimilation is the process of fitting information into existing schemes. Accommodation is a process of modifying our scheme in order to interact with the world around us. Assimilation and Accommodation are inseparable processes. Equilibration is responsible for reducing cognitive conflicts in order to create a balance cognitive state. Domains are specific areas of knowledge which share a specific focus and are distinct from each other. -are concepts such as morality, number, socialization, feelings, perception, illustration and others. Sensorimotor stage birth 2 years. Children begin to make sense of the world by using their sensory impressions and motor actions. Knowledge of objects is reflected in the childs understanding that object is permanent. Object permanence states that the objects still exist even they are out of sight. Knowledge of causation is reflected in the childs ability to understand perceived causes. Knowledge of space is manifested in the childs ability to probe the inside of containers. Knowledge of time is evident in various activities. Pre operational Stage- 2 7 years, the childs language increasingly becomes an important tool in dealing with the environment. The development of semiotic function which is the ability of the childs to use symbols, is activated. -are represented by the childs deferred imitation, mental imaginary, symbolic play, and language. Mental Imaginary is affected by what the child has seen or experienced in the past. Centration is the tendency to focus the attention only in one aspect of situation. Concrete-operational stage 7-11 years, the child posses operative schemes that necessitate him to think in logical terms. Classification is the childs ability to group a set of objects and then to group around a common category of attributes. Seriation the child develops the ability to order objects according to height, length or width. Horizontal decalage it deals with tempo difference in levels of performance that a child shows between various cognitive domains or activities within a given stage of development. -it refers to the childs tendency to solve some kind of concrete operational problems earlier than others. Decalage is of French word which means SHIFT Formal operational stage 11 years older the development of abstract reasoning is the benchmark of formal operational stage. Sensory Registers this is a separate register to each sensory modality (e.g. visual, auditory, tactile, kinesthetic, or olfactory) which is expected to hold large amount of information, but only for a matter of milliseconds. Information Processing Approach/Theory there are two theoretical ideas considered fundamental to cognitive psychology and the information processing framework. Chunk is any meaningful unit of information. TOTE or Test operate test exit should replace the stimulus response as the fundamental unit of behavior. The Short Term Memory functions into two important ways. -organizes information by integrating new information with the existing information. -it temporarily stores information for the learners use. -A.K.A. working memory.
.... . o o
The Long Term Memory information that stays at the LTM is expected to be stored indefinitely. -is labeled as verbal or visual information for future use; it contains the episodic and semantic knowledge. -A.K.A. warehouse of knowledge. -A.K.A. data bank that store information. -is the repository of stored information. -a permanent storage of information. Primary means the capacity of the brain to remember the best information that is learned recently. 7 Sins of Memory Transience this sin refers to the gradual forgetting of information over time. Absent-mindedness the second sin deals with our failure to fully attend to the actual encoding process that causes us to forget. Blocking the third sin accounts for our memory that is present but inaccessible. Misattribution the forth sin maintain the idea that the memory is presented but it is attributed to the incorrect source. Suggestibility the fifth sin of memory pertains to the incorrect information that is unknowingly incorporate into the memory representation. Bias the sixth sin is about the formation of bias. Persistence the last sin accounts for the memory that is highly intrusive or obsessive.
Illustration INFORMATION PROCESSING THEORY
Routes traveled by the information in the INFORMATION PROCESSING THEORY
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Region Division District School Address S.Y. Grade Section SEX Teacher I School Principal IVDocument34 pagesRegion Division District School Address S.Y. Grade Section SEX Teacher I School Principal IVLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Stage 3 Act Step 10: Check ProgressDocument1 pageStage 3 Act Step 10: Check ProgressLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Health Declaration FormDocument2 pagesHealth Declaration FormLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 2018 Smea 1st QuarterDocument21 pages2018 Smea 1st QuarterLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
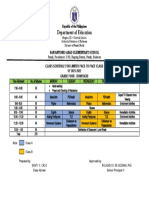
- Class Schedule For Limited f2fDocument1 pageClass Schedule For Limited f2fLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Rosaly A. Manisan: CertificationDocument3 pagesRosaly A. Manisan: CertificationLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Project Love InterventionsDocument3 pagesProject Love InterventionsLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Ict Action PlanDocument3 pagesIct Action PlanLemuel Kim80% (5)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Public Policy Analysis: An: William N. Dunn Associate Dean and Professor University of PittsburgDocument34 pagesPublic Policy Analysis: An: William N. Dunn Associate Dean and Professor University of PittsburgLemuel Kim100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Division of Bulacan Pandi North District San Antonio Abad Elementary School Pandi Residences 2 RS Bagong Barrio, Pandi Bulacan 3014Document1 pageRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Division of Bulacan Pandi North District San Antonio Abad Elementary School Pandi Residences 2 RS Bagong Barrio, Pandi Bulacan 3014Lemuel KimNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Techer's Day CertificatesDocument10 pagesTecher's Day CertificatesLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- CBRC English - BocaueDocument3 pagesCBRC English - BocaueLemuel Kim100% (2)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Progress Report Card: Lemuel Kim C. Belen Juan A. Dela CruzDocument2 pagesProgress Report Card: Lemuel Kim C. Belen Juan A. Dela CruzLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Prof EdDocument8 pagesProf EdLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Lemuel Kim C. BelenDocument1 pageDaily Lesson Plan: Lemuel Kim C. BelenLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Dr. Carl E. Balita Review Center Tel. No. 735-4098/7350740 - 1Document5 pagesDr. Carl E. Balita Review Center Tel. No. 735-4098/7350740 - 1Lemuel Kim100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 1Document3 pages1Lemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- MetDocument2 pagesMetLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Leslie D. Miemban: Certificate of AttendanceDocument1 pageLeslie D. Miemban: Certificate of AttendanceLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Not Valid Without Lgu Permit/Clearance: Ecember, 2016 Anuary 31, 2017Document2 pagesNot Valid Without Lgu Permit/Clearance: Ecember, 2016 Anuary 31, 2017Lemuel Kim100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Certificate of ClearanceDocument1 pageCertificate of ClearanceLemuel Kim100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Daily Attendance Report of Learners School Form 2 (SF2) Prepared By: Ma. Lovie C. Belen Teacher I Attested By: Ma. Cecilia J. Bernardo Princip Al IIDocument1 pageDaily Attendance Report of Learners School Form 2 (SF2) Prepared By: Ma. Lovie C. Belen Teacher I Attested By: Ma. Cecilia J. Bernardo Princip Al IILemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Subject: Bungalow House - For Sale (Price Is Negotiable) Address: 437 Magsaysay RD., Tangos, Baliwag, BulacanDocument1 pageSubject: Bungalow House - For Sale (Price Is Negotiable) Address: 437 Magsaysay RD., Tangos, Baliwag, BulacanLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Recognition Certificate of RecognitionDocument12 pagesCertificate of Recognition Certificate of RecognitionLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- The Good Teacher Makes The Poor Student Good and The Good Student SuperiorDocument6 pagesThe Good Teacher Makes The Poor Student Good and The Good Student SuperiorLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- RevDocument3 pagesRevLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Lemuel Kim C. Belen: Birth Date: April 11, 1996 Age: 19 Civil Status: Single Height: 5'0" Weight: 65 KGDocument2 pagesLemuel Kim C. Belen: Birth Date: April 11, 1996 Age: 19 Civil Status: Single Height: 5'0" Weight: 65 KGLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- MetDocument2 pagesMetLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- DFA E-Passport ApplicationDocument7 pagesDFA E-Passport ApplicationLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Summat IveherhrehDocument3 pagesSummat IveherhrehLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- Walkthrough Grade10 P.EDocument1 pageWalkthrough Grade10 P.EEdz Libre GayamoNo ratings yet
- Sample Narrative Report and Documentation 2024 InsetDocument3 pagesSample Narrative Report and Documentation 2024 InsetWILSON CASTRONo ratings yet
- Aman Gupta - 343 - Aman - GuptaDocument1 pageAman Gupta - 343 - Aman - GuptaPulokesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Pdca Cycle SampleDocument7 pagesPdca Cycle SampleSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- 3a.roles of Family, Education EtcDocument3 pages3a.roles of Family, Education Etcvijay pal100% (1)
- Teaching Internship Portfolio Grading SystemDocument20 pagesTeaching Internship Portfolio Grading Systemanalyn.bucoNo ratings yet
- Edx CoursesDocument3 pagesEdx CoursesdavidrojasvNo ratings yet
- B.ed Course OutlinesDocument29 pagesB.ed Course OutlinesZaib Rehman100% (1)
- Minutes of The 13th Deans Committee MeetingDocument4 pagesMinutes of The 13th Deans Committee MeetingRazia KanwalNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Identification of Invertebrate Taxonomic Character JadiDocument8 pagesIdentification of Invertebrate Taxonomic Character Jadipratiwi kusumaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Error Types Made by Nursing Students Using eMAR TechnologyDocument11 pagesIdentifying Error Types Made by Nursing Students Using eMAR TechnologyRahman KholilNo ratings yet
- Application Form (Smaw NC Ii)Document4 pagesApplication Form (Smaw NC Ii)Dhess Dulay BambaNo ratings yet
- Plan Lista PonasanjaDocument14 pagesPlan Lista Ponasanjaenamuli1No ratings yet
- Getting Your Needs Meet Rhonda Britten FinalDocument46 pagesGetting Your Needs Meet Rhonda Britten FinalIvaylo Yordanov100% (1)
- Activity 12 Finding Fibonacci Patterns in NatureDocument8 pagesActivity 12 Finding Fibonacci Patterns in Naturenines1983No ratings yet
- Laporan Ulbs 2019Document9 pagesLaporan Ulbs 2019Grace RaymondNo ratings yet
- Comparison Contrast Analogy Paragraph SamplesDocument3 pagesComparison Contrast Analogy Paragraph Sampleshappiness1234No ratings yet
- Mean, Median and Mode For Ungropued Data and For Grouped DataDocument8 pagesMean, Median and Mode For Ungropued Data and For Grouped DataNiels DaveNo ratings yet
- The Fragmentation of Being PDFDocument333 pagesThe Fragmentation of Being PDFDontu Maria100% (2)
- Stanford Invitational Speech and Debate Tournament Invitation and Information PacketDocument6 pagesStanford Invitational Speech and Debate Tournament Invitation and Information PacketamborddNo ratings yet
- Learning+Power+Muscles UnlockedDocument2 pagesLearning+Power+Muscles UnlockedWill TeeceNo ratings yet
- Co Education System Vs Separate Education in PakistanDocument2 pagesCo Education System Vs Separate Education in PakistanPervaiz Shahid0% (1)
- Notre Dame University College of Engineering and Computer Studies Notre Dame Avenue, Cotabato CityDocument31 pagesNotre Dame University College of Engineering and Computer Studies Notre Dame Avenue, Cotabato CityAIMAN ABBASNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson Grade 4 - GradedDocument14 pagesSocial Studies Lesson Grade 4 - Gradedapi-313976131No ratings yet
- Coach Steve LudwigDocument9 pagesCoach Steve Ludwigapi-389096885No ratings yet
- MATH 109 101 Final ExamDocument11 pagesMATH 109 101 Final ExamshannonroxxNo ratings yet
- Jackson Era Direct TeachDocument5 pagesJackson Era Direct Teachapi-289579265No ratings yet
- The Same Yet Different: Comparing Ancient Athens and SpartaDocument7 pagesThe Same Yet Different: Comparing Ancient Athens and SpartaElle AurelioNo ratings yet
- Action Plan School Governing CouncilDocument2 pagesAction Plan School Governing Counciljamel mayor100% (65)
- Paragraph WritingDocument4 pagesParagraph WritingdooblahNo ratings yet
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pharmaceutical Dispensing and CompoundingFrom EverandPharmaceutical Dispensing and CompoundingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Common Core Science 4 Today, Grade 3: Daily Skill PracticeFrom EverandCommon Core Science 4 Today, Grade 3: Daily Skill PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)