Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Grammar - Modal Meanings
Uploaded by
butterball0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
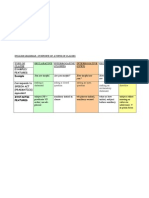
753 views2 pagesCAN Core concept: potential can Circumstances Interpretation animate agent-subject as source Physical action, mental activity social authority as source social transaction (social) Absence of agent-source Situation acknowledged, (+ but) not marked as relevant Interpretation permission May I come in? Examples weak possibility concession the bus may be late. I may be old, but am not crazy!
Original Description:
Original Title
English Grammar -Modal Meanings
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCAN Core concept: potential can Circumstances Interpretation animate agent-subject as source Physical action, mental activity social authority as source social transaction (social) Absence of agent-source Situation acknowledged, (+ but) not marked as relevant Interpretation permission May I come in? Examples weak possibility concession the bus may be late. I may be old, but am not crazy!
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
753 views2 pagesEnglish Grammar - Modal Meanings
Uploaded by
butterballCAN Core concept: potential can Circumstances Interpretation animate agent-subject as source Physical action, mental activity social authority as source social transaction (social) Absence of agent-source Situation acknowledged, (+ but) not marked as relevant Interpretation permission May I come in? Examples weak possibility concession the bus may be late. I may be old, but am not crazy!
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Extracts adapted from : EXPLAINING ENGLISH GRAMMAR, George Yule, OUP, 1998
Summary Box - The meanings of may
Core concept: possible may
Circumstances Interpretation Examples
Source is human authority
or social regulations (personal) permission May I come in?
Source is speaker's knowledge
Situationally specified
Equals may not (epistemic) weak possibility The bus may be late.
Situation acknowledged, concession I may be old, but am not crazy!
(+ but) not marked
as relevant
Summary Box - The meanings of CAN
Core concept: potential can
Circumstances Interpretation Examples
Animate agent-subject as source
Physical action, mental activity ability Jim can speak Spanish.
Social authority as source
Social transaction (social) permission The teacher says you can leave.
Absence of agent-source
Situationally specified (logical) possibility Grammar can be fun!
Summary Box - The meanings of will
Core concept: likely will
Circumstances Interpretation Examples
Speaker as source
Planned future action
Desirable (= promise)
Undesirable (= threat) intention I will call the police!
Animate agent subject
Physical action/activity
Second person questions as requests
Aspect rare
Negation applies to modal
Social transaction (social) willingness Will you help me?
Non-animate subjects common
Third person, non-specific subjects
Aspect common
Logical statements (If A, then B.)
Common in technical texts
Negation applies to main verb
(logical) prediction The weather will be nice.
Summary Box The meanings of should
Core concept: required should
Circumstances Interpretation Examples
Expressing appropriate behavior,
correct ways of doing things,
suggestions, advice (personal) weak obligation You should think of
others.
Expressing reasonable
assumptions, probable
occurrences (logical) probability The work should soon
be finished.
Summary Box The meanings of must
Core concept: necessary must
Circumstances Interpretation Examples
Present and future actions
with animate subjects
Aspect is rare
Negation is common (personal) obligation You must wear a seatbelt.
Past and present states
and some actions
Also with non-animate subjects
Perfect and progressive aspect
Negation is rare (logical) conclusion It must be cold up there.
Summary Box -Modals and negatives
Modals Interpretations Examples
with negative
can (= potential) NOT able (action) I can’t dance. We couldn't swim.
NOT permit (action) You can't go. They couldn't eat here.
NOT possible (action) It can't happen. It couldn't be done.
may (= possibility) NOT permit (action) You may not leave.
possible (NOT action) They may not come.
concede (NOT action) It may not be finished, but...
must(= necessity) oblige (NOT action) You mustn't shout.
NOT oblige (action) You don't have to stay.
conclude (NOT action) She must not have much money or
She can't have much money.
will(= likelihood) NOT intend (action) They won't do it.
NOT willing (action) She won't help. He wouldn't listen.
predict (NOT action) He won’t win. You wouldn’t like it.
should oblige (NOT action) You shouldn’t smoke.
(= requirement) probable (NOT action) It shouldn't last long.
You might also like
- English Grammar - Non Finite Forms of VerbsDocument3 pagesEnglish Grammar - Non Finite Forms of Verbsbutterball100% (3)
- English Grammar-Adverbial ClausesDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar-Adverbial Clausesbutterball100% (4)
- English Grammar - PrepositionsDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar - Prepositionsbutterball100% (3)
- English Grammar - AdjectivesDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar - Adjectivesbutterball100% (2)
- English Grammar - Tense and Time ReferencesDocument3 pagesEnglish Grammar - Tense and Time Referencesbutterball100% (1)
- English Grammar - Overview of 4 Types of Basic ClauseDocument1 pageEnglish Grammar - Overview of 4 Types of Basic ClausebutterballNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - CoordinationDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar - Coordinationbutterball100% (6)
- English Grammar CohesionDocument1 pageEnglish Grammar Cohesionbutterball100% (1)
- English Grammar - Overview of The English VerbDocument11 pagesEnglish Grammar - Overview of The English Verbbutterball100% (1)
- GRAMMAR - Proforms and Ellipsis For ScribdDocument2 pagesGRAMMAR - Proforms and Ellipsis For Scribdbutterball100% (3)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Ring Game: Order of Adjectives: Teacher'S NotesDocument2 pagesThe Ring Game: Order of Adjectives: Teacher'S NotesOana-Janina VisenicaNo ratings yet
- Structure Part B: Error With PrepositionDocument14 pagesStructure Part B: Error With PrepositionDelia RasmawatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 6A - Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument22 pagesUnit 6A - Gerunds and InfinitivesDavid EstrellaNo ratings yet
- After School Workshop ChecklistDocument2 pagesAfter School Workshop ChecklistMiah MurrayNo ratings yet
- Ingles 4° 2021Document101 pagesIngles 4° 2021freddy william montalban palaciosNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument3 pagesRelative ClausesAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Can/ Can T Exercise 1 1. Turn The Given Sentences Into Affirmative Sentences, Negative Sentences or QuestionsDocument3 pagesCan/ Can T Exercise 1 1. Turn The Given Sentences Into Affirmative Sentences, Negative Sentences or QuestionsadrianNo ratings yet
- Spelling List: Permai School Term 1 Worksheet 2021 - 2022Document9 pagesSpelling List: Permai School Term 1 Worksheet 2021 - 2022VeradsNo ratings yet
- Petrashkevich N P Grammarperfect Form To Function PraktichesDocument222 pagesPetrashkevich N P Grammarperfect Form To Function PraktichesПолина Новик0% (1)
- All Ug Courses - Language (Ba/Bsc/Bca/Bba/Bbm/Bcom/Bcom (Ca), Bcom (Co-Op)Document136 pagesAll Ug Courses - Language (Ba/Bsc/Bca/Bba/Bbm/Bcom/Bcom (Ca), Bcom (Co-Op)tfacultyNo ratings yet
- Australian CurriculumDocument8 pagesAustralian CurriculumKBNo ratings yet
- ApproachfinalDocument22 pagesApproachfinalChristian ConsignaNo ratings yet
- Extra Grammar Exercises (Unit 5, Page 52) : Top Notch 3, Third EditionDocument2 pagesExtra Grammar Exercises (Unit 5, Page 52) : Top Notch 3, Third EditionGia Minh LêNo ratings yet
- Comparison ExercisesDocument17 pagesComparison ExercisesnguyenngocquynhchiNo ratings yet
- Listening: 1 Listen and Circle The Correct AnswersDocument2 pagesListening: 1 Listen and Circle The Correct AnswersFuat BayramovNo ratings yet
- The Passive 3: Infinitive, - Ing, It Is Said ... : PresentationDocument2 pagesThe Passive 3: Infinitive, - Ing, It Is Said ... : PresentationAle Alejan100% (1)
- ENGLISH MATERIAL Affirmative AgreementDocument3 pagesENGLISH MATERIAL Affirmative AgreementMariatul afniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans - The Night The Moon FellDocument8 pagesLesson Plans - The Night The Moon Fellapi-190608850No ratings yet
- Analysis FrozenDocument87 pagesAnalysis FrozenAas Yulia DasirNo ratings yet
- Pronoun-Antecedent Rules: Group 2Document22 pagesPronoun-Antecedent Rules: Group 2Kons kirby LubiganNo ratings yet
- 1 - SNR - English - 19 - Ia3 - AsrDocument7 pages1 - SNR - English - 19 - Ia3 - AsrEoghan KuiperNo ratings yet
- Adjective TheoryDocument12 pagesAdjective TheoryAdi PopoviciNo ratings yet
- Bhasa InggrisDocument3 pagesBhasa InggrisRon Wisley100% (1)
- Unidad I Can-Do StatementsDocument1 pageUnidad I Can-Do Statementsapi-416535519No ratings yet
- Notes On AdverbsDocument8 pagesNotes On AdverbsIrene Tan100% (1)
- BC Review With NotesDocument10 pagesBC Review With NotesMai DangNo ratings yet
- IJLTR Volume7 Issue1 Pages119-139Document22 pagesIJLTR Volume7 Issue1 Pages119-139anasNo ratings yet
- Focgb4 Ak Utest VG 5Document2 pagesFocgb4 Ak Utest VG 5simple footballNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect Indirect Speech09-LUTHFIATUL A'YUNINNo ratings yet