Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Berger Paints Pakistan
Uploaded by
gritty92Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Berger Paints Pakistan
Uploaded by
gritty92Copyright:
Available Formats
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED INTRODUCTION ____________________________________________________________ 3 PURPOSE OF STUDY ________________________________________________________ 4 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY______________________________________________________ 5 BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
________________________________________ 6
INTRODUCTION ________________________________________________________________ 6 MISSION ________________________________________________________________________ 7 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS _______________________________________________________ 8
BALANCE SHEET ______________________________________________________________________ 8 PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT __________________________________________________________ 10
RATIO ANALYSIS __________________________________________________________ 11 LEVERAGE RATIOS ________________________________________________________ 12
LONG TERM DEBT RATIO ______________________________________________________ 12
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 12 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 12
DEBT EQUITY RATIO __________________________________________________________ 13
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 13 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 13
TOTAL DEBT RATIO ___________________________________________________________ 14
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 14 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 14
TIME INTEREST EARNED ______________________________________________________ 15
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 15 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 15
CASH COVERAGE RATIO _______________________________________________________ 16
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 16 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 16
LIQUIDITY RATIOS ________________________________________________________ 17
CURRENT RATIO ______________________________________________________________ 17
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 17 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 17
QUICK RATIO__________________________________________________________________ 18
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 18 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 18
CASH RATIO ___________________________________________________________________ 19
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 19 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 19
NET WORKING CAPITAL _______________________________________________________ 20
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 20 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 20
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
NET WORKING CAPITAL TO ASSETS ____________________________________________ 21
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 21 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 21
EFFICIENCY RATIOS_______________________________________________________ 22
TOTAL ASSET TURNOVER ______________________________________________________ 22
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 22 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 22
AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD _______________________________________________ 23
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 23 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 23
INVENTORY TURNOVER _______________________________________________________ 24
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 24 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 24
DAYS SALES IN INVENTORIES _________________________________________________ 25
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 25 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 25
PROFITABILITY RATIOS____________________________________________________ 26
OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN __________________________________________________ 26
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 26 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 26
GROSS PROFIT MARGIN _______________________________________________________ 27
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 27 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 27
NET PROFIT MARGIN __________________________________________________________ 28
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 28 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 28
RETURN ON ASSETS ___________________________________________________________ 29
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 29 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 29
RETURN ON EQUITY ___________________________________________________________ 30
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 30 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 30
EARNING PER SHARE __________________________________________________________ 31
INTERPRETATION _____________________________________________________________________ 31 CONCLUSION _________________________________________________________________________ 31
OTHER FACTORS AFFECTING COMPANY ____________________________________ 32
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
INTRODUCTION
In the current economic conditions, to understand the financial workings and get the assistance about the competition in business is the key to success. The analysis of financial statement is important to analyze the companys performance. Financial statements tell about the past period and predict the future. Therefore, it is important to have the authentic information for correct decision making which leads to success. Managers always refer the financial ratios because they indicate the performance of business units and the company. Managers are also concerned with the companys ability that whether it is able to finance its future expansion or not. The ratio analysis helps the financial analysts to study the performance of investments and determine the value of company by forecasting its future earnings. In this report, we have been assigned a project in which the ratio analysis of the company is extracted and interpreted. In this report, we have tried our best to express our learning throughout the semester. The ratio analysis is extracted to show the companys strength and weaknesses and determines whether the company is sufficiently liquid to meet its current obligations or not. It shows the companys credit worthiness, efficient utilization of its assets and profitability. This report analyzes the financial statements of Berger Paints Pakistan Limited for five years in which the contrast of companys performance is also measured for each year. This report provides information obtained through ratio analysis regarding the profitability, liquidity and financial stability of Berger Paints Pakistan Limited for five years. This report will pay particular attention to the earning power, liquidity & credit management, inventory management and debt management. It will also highlight major strengths and weaknesses with explanation for observed changes. The report will also comment on the prospects of the company and make recommendations that would improve Berger Paints Pakistans current performance.
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
PURPOSE OF STUDY
The purpose of this study is to analyze the financial statements of Berger Paints Pakistan and to extract and interpret the ratio analysis by the data provided in the financial statements. In this report, the applications of finance are applied through financial ratios and the results are interpreted to bring the light upon the performance of Berger Paints Pakistan. The financial ratios are taken of the five years and they are compared with the base year and thus, the performance of Berger Paints is studied with the graphical representation. In accordance with the result, the prospects for the company and recommendations are passed on.
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The ratio analysis of Berger Paints Pakistan Limited has been extracted and interpreted for five years. Interpretation has been followed through by considering 2008 as base year. According to the analysis, Berger Paints Pakistan Limited is considered to be highly leveraged because of high long term debt ratio, high debt equity ratio and high total debt ratio. This indicates the higher risk for the company especially under the fluctuations of interest rates because the equity and capital and less than the companys debt. Furthermore, time interest earned has increased but it is still too minimal to be considered as ideal. So, the companys earnings are more than its interest payable but not the ideal one whereas the companys ability to pay for its cash has been decreased as compare to the base year, therefore, little amount is left for other operations. The liquidity ratios for Berger Paints show that the company is able to pay for its current liabilities with minor fluctuations over the years. The Quick Ratio analysis shows that the companys present conditions are fair enough but not the ideal ones because the potential reservoir of cash (net working) capital becomes negative after meeting the current liabilities. The companys cash reservoirs appear to be lower than its assets. The efficiency ratio shows that the company has worked close to its capacity and the trend for asset turnover increases whereas the average collection period has become quite efficient. The companys ability to turnover its inventories has also increased by the period of time and the company possesses sufficient inventory to maintain its sales which benefits the company from the continuous appraisal in the cost of raw materials and inflation. The profitability ratios show that the companys operating profit margin has increased whereas gross profit margin has decreased. The utilization of assets has seen increasing trend whereas shareholders equity throughout the year has decreased. The Earnings per share have improved as compared to the base year. The company depends on the activities in real estate and construction business. Companys sales are good but it also have an area to grow because infrastructure development activities are taking place in the country. The rising prices of raw materials, packaging and advertisements has hurt the companys gross profit due to which the equity has decreased. The interpretation of ratio analysis has also come with some recommendation to improve the companys current condition. The company has become dependent on debt therefore, company should decrease its debt and start increasing its equity with the help of decreasing its expenses, becoming more cost efficient, increasing its sales volume and selling its outstanding number of shares.
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
INTRODUCTION
Berger was established two centuries ago and now it has grown to become one of the worlds largest paints manufacturer. In Pakistan, history of Berger is as old as history of Pakistan. Berger started its operations in Pakistan in 1950 and was the first organized Paint Company to offer premium products through import from the United Kingdom. BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LTD. became a public limited company in 1974, when 49.38% of its shares were acquired by Pakistani investors, while the remaining 50.62% were held by U.K. parent company, Jenson & Nicholson Limited. In 1991 Slotrapid Limited, a U.K. based company with diversified business interests, acquiring control of Berger Paints Pakistan Limited by gaining 50 .62% shares of the company.
Berger established its first local manufacturing facility in Karachi in 1955. As the countrys economic and industrial sector expanded the demand for quality paints also grew and Berger continued to make extensions in its product range to meet these requirements. In 2006, Berger established state of the art manufacturing facility in Lahore. This plant has provided Berger an edge over its competition through enhanced production. It has enabled Berger to meet the growing demands of its valued customers across Pakistan. Berger Paints Head office is located in Lahore. Consistent quality has always been Bergers trait. This has been the driving force in making it the leading brand name backed by premium quality across Pakistan. Berger has the most comprehensive product range for various paint market segments at different price points. Berger has earned the admiration and trust of customers by virtue of its superior technology, product quality and a very high level of customized services. Berger has entered into a number of technical collaboration arrangements with leading international manufacturers. These include the largest paint company in Japan, which enables Berger to develop Automotive, Vehicle Refinishes and Industrial Paints conforming to international standards; a Japanese chemical company, for Bumper Paints; PCS Powders, UK for Powder Coatings; DPI Sendirian Berhad, Malaysia for Road & Runway Markings; Cerachem for
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED Construction Chemicals and Asian Paints for Decorative Paints. Recently, Berger acquired distribution rights of DuPont for Pakistans vehicle refinish paint segment. Berger is also operating Resin manufacturing facility at its Lahore factory. The resin plant has high production capacity and has enabled Berger to meet its entire resin needs for the manufacturing of a wide range of quality paints. Berger was the first paint company in Pakistan to set up its own resin production facility. The company has regional offices in Karachi, Lahore, Islamabad and Territorial Offices in Gujranwala, Multan, Faisalabad, Peshawar and Hyderabad. A large team of sales personnel and a wide network of dealers and distributors serve customers in all urban centers across the country.
MISSION
Despite many challenges, Berger Paints has succeeded in staying at the forefront of Pakistans paint industry. Innovation and technological development has enabled the company to achieve corporate success through its commitment to provide products of the highest quality and ensuring the ultimate satisfaction of customers. The companys employees are constantly encouraged to pursue the Corporate Mission Statement: We will stay at the forefront of innovation and technological development in the paint industry. We will achieve corporate success through an unwavering commitment to provide our customers high quality products to their ultimate satisfaction. We will vigorously promote and safeguard the interests of our employees, our shareholders, our suppliers and all business associates. We will play our role as a good corporate citizen and serve community where we do business.
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
BALANCE SHEET
ASSETS NON CURRENT ASSETS Property, plant and equipment Assets subject to finance lease Intangible asset - in progress Goodwill Long term investments (subsidiaries and an associate) Long term loans Long term deposits Deferred taxation CURRENT ASSETS Stores Stock in trade Trade debts Loans and advances Trade deposits and short term Prepayments Other receivables Taxation net Short term investments Cash and bank balances TOTAL ASSETS 634,304 14,513 40,750 4,086 15,437 19,263 176,685 905,038 10,778 987,881 694,265 42,764 12,654 45,082 141,906 20,080 144,013 2,099,423 3,004,461 (Rupees in `000) 686,898 715,499 6,468 13,513 40,750 40,750 5,567 6,962 14,742 17,119 131,685 910,274 8,574 1,099,616 655,993 26,920 12,127 37,487 130,503 257,449 2,228,669 3,138,943 9,928 13,580 96,022 889,209 8,375 966,347 599,377 47,633 19,638 65,928 105,508 282,170 2,094,976 2,984,185 1,052,460 40,750 13,849 13,916 15,337 80,146 1,216,458 7,109 1,011,893 552,117 60,918 24,526 112,984 75,772 170,875 2,016,194 3,232,652 614,447 52,350 13,849 14,034 8,038 37,718 740,436 6,028 873,297 569,402 84,686 18,171 391,845 40,096 192,281 2,175,806 2,916,242 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
SHARE CAPITAL AND RESERVERS Share capital Reserves Surplus on revaluation of fixed assets - net of tax NON CURRENT LIABILITIES Long-term financing Staff retirement benefits Liabilities against assets subject to finance lease CURRENT LIABILITIES Trade and other payables Accrued mark-up Current maturity of long-term financing Current maturity of liabilities against assets subject to finance lease Short term borrowings TOTAL LIABILITES Contingencies and commitments
2012 181,864 219,307 401,171 187,720
2011 181,864 219,469 401,333 197,997
2010 181,864 277,593 459,457 210,343
2009 81,864 114,787 196,651 526,650
2008 81,864 213,449 295,313 154,744
115,000 47,865 7,675
220,000 47,352 2,644
4,023
50,000 -
116,666 -
1,096,443 41,008 105,000 1,883 1,000,696 2,245,030 2,415,570
1,140,731 48,460 105,000 -
960,277 44,420 50,000 2,112
894,303 50,785 50,000 1,464,263 2,459,351 2,509,351
989,484 43,524 66,667 1,249,844 2,349,519 2,466,185
447 974,979 1,253,553 2,269,617 2,310,362 2,539,613 2,314,385
3,004,461
3,138,943 2,984,185
3,232,652
2,916,242
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
2012 Net sales Cost of sales Gross profit Distribution cost Administrative expenses 4,052,009 3,253,590 798,419 534,128 143,872 678,000 120,419 87,528 207,947 9,265 205,762 215,027 -7,080 3,359 -10,439 -0.57 2011
(Rupees in `000)
2010 3,359,276 2,577,550 781,726 601,954 133,335 735,289 46,437 126,321 172,758 48,323 252,734 301,057 -128,299 -12,078 -116,221 -8.91
2009 3,580,302 2,745,755 834,547 594,941 138,654 733,595 100,952 266,875 367,827 66,625 253,906 320,531 47,296 20,160 27,136 2.21
2008 3,123,311 2,519,880 603,431 609,415 92,880 702,295 -98,864 37,162 -61,702 35,229 138,257 173,486 -235,188 -60,971 -174,217 -25.1
3,571,510 2,831,240 740,270 521,739 141,669 663,408 76,862 69,504 146,366 2,592 214,435 217,027 -70,661 -191 -70,470 -3.87
Operating profit Other operating income Other charges Finance cost
(Loss)/ profit before
taxation Taxation
(Loss)/ profit after taxation
(Loss)/ earnings per share basic and diluted
10
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
RATIO ANALYSIS
2012
Long Term Debt Ratio Debt Equity Ratio Total Debt Ratio Time Interest Earned Cash Coverage Ratio Current Ratio Quick Ratio Cash Ratio Net Working Capital NWC to Assets Total Asset Turnover Average Collection Period Inventory Turnover Days Sales in Inventories Operating Profit Margin Gross Profit Margin Ratio Net Profit Margin Return on Assets Return on Equity Earning per Share
2011 0.59 75.89% 0.8 0.6 time 0.6 0.98 time 0.5 time 0.11 -40948 -0.013 3.92 5.28 days 3.2
2010 0.423 73.42% 0.775 0.49 time 18.43 0.91 time 0.49 time 0.12 -215384 -0.072 3.78 9.71 days 3.5
2009 0.47 88.83% 0.776 1.18 time 0.82 time 0.41 time 0.07 -443157 -0.137 25.73 days 3
125.30 days
2008 0.28 39.50% 0.84 -0.7 time 0.93 time 0.55 time 0.08 -173713 0.059 -
LEVERAGE RATIOS
0.4 74.63% 0.8 0.9 time 1.017 0.94 time 0.5 time 0.06 -145607 -0.049 4.48 3.71 days 4.1
LIQUIDITY RATIOS
EFFICIENCY RATIOS
117.09 days 133.17 days 140.06 day PROFITABILITY RATIOS
3% 19.70% -3% 0.07 -0.02 -0.57
2% 20.73% -2% 0.09 -0.17 -3.87
1.38% 23.27% -3.45% 0.03 0.09 -8.9
2.82% 23.30% 0.75% 0.09 0.08 2.22
-3.16% 19.32% -5.58% -0.01 -25.1
11
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
LEVERAGE RATIOS
LONG TERM DEBT RATIO
2008 0.28 2009 0.47 2010 0.423 2011 0.59 2012 0.4
LONG TERM DEBT RATIO
0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 year 2008 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, Long Term Debt Ratio is low which means that company is not highly leveraged because debt is 0.28 which shows that 0.28 cents of every dollar from capital is in the form of long term debt. In 2009, Long Term Debt Ratio is the higher than the base year 2008, which shows that the large amount of capital is in form of long term debt as compared to year 2008. In 2010, Long Term Debt Ratio is has increased than the base year 2008 which represents the increase in amount of capital in the form of long term debt as compared to year 2008. In 2011, Long Term Debt Ratio is the highest than the base year 2008 which shows that the companys amount of capital in the form of long term debt is has too much increased as compared to year 2008. In 2012, Long Term Debt Ratio has decreased but it is still higher than the base year 2008 which represents that the increase exists in amount of capital in the form of long term debt as compared to the year 2008.
CONCLUSION
The Long Term Debt Ratio has increased but it is has decreased when we compare it with the past 5 years performance. Therefore, in order to decrease Long Term Debt Ratio, company should decrease its debt from its equity. In this way companys leverage can be decreased.
12
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
DEBT EQUITY RATIO
2008 39.50% 2009 88.83% 2010 73.42% 2011 75.89% 2012 74.63%
DEBT EQUITY RATIO
100.00% 80.00% 60.00% 40.00% 20.00% 0.00% year 2008 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Debt Equity Ratio is lower which represents that debt is lower than the equity which shows the lower risk for company in bad times. In 2009, the Debt Equity Ratio has increased to a great extent base year 2008 which shows that debt is higher than the equity and represents risk for the company. In 2010, the Debt Equity Ratio is slightly lower than the base year 2008 which shows that debt is still higher than the equity and risk exists for the company. In 2011, the Debt Equity Ratio for the company is higher as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the debt is much higher than the equity and therefore, the risk is also the higher. In 2012, the Debt equity Ratio for the company is higher as compared to the base year 2008 which represents the debt is much increased than the equity and the risk has also increased for the company.
CONCLUSION
The Debt Equity Ratio is higher as compared to the five years analysis of the company. Therefore, in order to decrease the Debt Equity Ratio, the company should decrease its long term debt and increase its equity. As a matter of fact, equity can be increased by increasing revenues, decreasing expenses, selling and increasing outstanding number of shares etc.
13
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
TOTAL DEBT RATIO
2008 0.84 2009 0.776 2010 0.775 2011 0.8 2012 0.8
TOTAL DEBT RATIO
0.85 0.84 0.83 0.82 0.81 0.8 0.79 0.78 0.77 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Total Debt Ratio is 0.84 which shows that 0.84 cents of every dollar from capital is in the form of total debt (short term debt and long term debt). This represents that the company is highly leveraged and fluctuations in interest rate will cause higher risk for the company as the equity is much lower than the total debt. In 2009, the Total Debt Ratio is decreased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the debt and risk are decreased. In 2010, the Total Debt Ratio for the company is decreased as compared to the base year 2008, which represents that in 2010 the debt, and risk were much lower and equity was higher than the year 2008. In 2011, the Total Debt Ratio for the company was decreased but it was relatively low as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the debt and risk has minor decrease and equity was increased. In 2012, the Total Debt Ratio for the company was lower as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that debt and risk were decreased and the equity was increased.
CONCLUSION
The Total Debt Ratio is higher but fluctuations are seen in the five years analysis of the company. Therefore, the company is considered to be as highly leveraged and in order to decrease the total debt ratio, company should decrease its debt and increase its equity which can be increased by generating revenues, decreasing expenses, selling and increasing outstanding number of shares etc.
14
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
TIME INTEREST EARNED
2008 -0.7 time 2009 1.18 time 2010 0.49 time 2011 0.6 time 2012 0.9 time
TIME INTEREST EARNED
1.5 1 0.5 0 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -0.5 -1
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Time Interest Earned also knows as Margin of Safety is -0.7 times which shows that the earnings of the company are 0.7 times less than its interest payable. In 2009, the Time Interest Earned is increased to a great extent that it has become positive as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that companys earnings are higher than its interest payable. In 2010, the Time Interest Earned has slight increase which shows that the earnings of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 and the company is still able to meet its interest payable with its earnings. In 2011, the Time Interest Earned has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the earnings of the company have also increased. In 2012, the Time Interest Earned has increased as compared to the base year which shows that companys earnings are higher than its interest payable.
CONCLUSION
The Time Interest Earned has fluctuation which shows that during the five years, the companys ability to pay interest from its earnings was in negative and with the passage of time, the company managed to increase its Time Interest Earned and became able to pay its interest payable but the company still needs to increase its interest payable which can be increased by increasing the earnings of the company.
15
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
CASH COVERAGE RATIO
2008 2009 2010 18.43 2011 0.6 2012 1.017
CASH COVERAGE RATIO
year 2010
year 2011
year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2010, the Cash Coverage Ratio shows that the company has the highest cash from the operations to pay its interest payments with cash. Although, 1.017 is not sufficient to pay because then very little amount will be left for other operations but still company is able to pay its interest payments. In 2011, the Cash Coverage ratio is decreased as compared to the base year 2010 which represents that the companys ability to pay its interest payments with cash has decreased. In 2012, the Cash Coverage Ratio has decreased as compared to the base year 2010 which shows that the companys ability to pay its interest payments with its cash has also decreased. Although, 1.017 is not sufficient to pay because then very little amount will be left for other operations but still company is able to pay its interest payments.
CONCLUSION
The Cash Coverage Ratio of the company through the overall analysis of three years shows the companys ability to pay its interest by cash was highest in the beginning but with the passage of time, it started declining but minor improvements are seen in the last two year. Therefore, in order to increase the Cash Coverage Ratio, the company must increase its earnings and should make depreciation conservative because depreciation is the amount which never goes out of the company and its helps the company to decrease its payables.
16
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
LIQUIDITY RATIOS
CURRENT RATIO
2008 0.93 time 2009 0.82 time 2010 0.91 time 2011 0.98time 2012 0.94time
CURRENT RATIO
1 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 year 2008 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Current Ratio of the company is 0.93 which shows the companys ability to pay (currents assets) is 0.93 times than its current liabilities. This value is not so high to be considered as ideal as the value is too minimal. In 2009, the Current Ratio of the company has decreased as compared to the base year 2008 due to which companys ability to pay its current liabilities has decreased to a great extent. In 2010, the Current Ratio of the company was slightly decreased as compared to the base year 2008 and the companys ability to pay its current liabilities decreased. In 2011, the Current Ratio of the company was high as compared to the base year 2008 which comprises of that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities was increased. In 2012, the Current Ratio of the company was slightly higher than its base year 2008 which represents that the company was able to pay its current liabilities as they fell due.
CONCLUSION
The Current Ratio has minor fluctuations over the time of five years which represents that the company is able to pay its current liabilities with the help of its current assets but this extent is not considered as ideal because the companys liquidity is too minimal. Therefore, the company must increase its current assets by increasing its receivables (increasing sale) & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
17
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
QUICK RATIO
2008 0.55 time 2009 0.41 time 2010 0.49 time 2011 0.5time 2012 0.5time
QUICK RATIO
0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 year 2008 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Quick Ratio of the company shows the companys ability to pay (current assets apart from inventory) is 0.55 times than its current liabilities. This value is not so high to be considered as ideal as the value is too minimal. In 2009, the Quick Ratio of the company is decreased as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities has decreased. In 2010, the Quick Ratio of the company is decreased to a small extent as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities has also decreased. In 2011, the Quick Ratio of the company has decreased as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities was much lower than the base year. In 2012, the Quick Ratio of the company is decreased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities has decreased.
CONCLUSION
The Quick Ratio of the company has slight fluctuations which show that over the period of five years the companys ability to pay has not increased to a high extent apart from its inventories. Therefore, the company possesses low liquidity. However, the company can increase its liquidity by increasing sales to increase its accounts receivables and by selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
18
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
CASH RATIO
2008 0.08 2009 0.07 2010 0.12 2011 0.11 2012 0.06
CASH RATIO
0.15 0.1 0.05 0 year 2008 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Cash Ratio of the company is 0.08 which represents the companys most liquid assets to pay its current liabilities. The Cash Ratio of the company is not considered as ideal as the value is too minimal. In 2009, the Cash Ratio of the company has decreased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities has also decreased. In 2010, the Cash Ratio of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities has also increased. In 2011, the Cash Ratio of the company has a slight increase as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the companys ability to pay its current liabilities is also increased. In 2012, the Cash Ratio of the company has decreased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the company is not able to pay for its current liabilities.
CONCLUSION
The Cash Ratio of the company has fluctuations which represents that during the five years analysis the companys ability to pay for its current liabilities from its most liquid assets has decreased and the company is not ideally liquid to pay for its current liabilities. Therefore, company should increase its cash by increasing sales and by selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
19
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
NET WORKING CAPITAL
2008 -173713 2009 -443157 2010 -215384 2011 -40948 2012 -145607
NET WOKRING CAPITAL
0 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -100000 -200000 -300000 -400000 -500000
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Net Working Capital of the company is negative which represents that the companys potential reservoir of cash is too low that the value has become negative after meeting the companys current liabilities. In 2009, the Net Working Capital of the company has decreased as compared to the base year 2008 and negativity has decreased to a large extent. In 2010, the Net Working Capital of the company remains negative as compared to the base year 2008 and the negativity has decreased to a great extent. In 2011, the Net Working Capital of the company remains negative as compared to the base year 2008 but the negativity has further decreased to a great extent. In 2012, the Net Working Capital of the company has remained negative as compared to the base year 2008 but the negativity has increased to a great extent.
CONCLUSION
The Net Working Capital of the company has fluctuation over the period of five years analysis but during this time the Net Working Capital of the company has remained negative. Therefore, it is highly recommended that the company should increase its Net Working Capital by increasing its current assets which can be increased by increase in sales, accounts receivables & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
20
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
NET WORKING CAPITAL TO ASSETS
2008 0.059 2009 -0.137 2010 -0.072 2011 -0.013 2012 -0.049
NET WORKING CAPITAL TO ASSETS
0.1 0.05 0 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -0.05 -0.1 -0.15
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Net Working Capital to Assets is 0.059 which represents the companys potential reservoir of cash with proportion to the asset. Therefore, companys cash reservoir is higher than its assets. In 2009, the Net Working Capital to Assets has decreased to a great extent as compared to the base year 2008 and it has become negative which shows that the companys cash reservoir too negative that is not even backed by the companys total assets. In 2010, the Net Working Capital to Assets has decreased as compared to the base year 2008 and stays negative. In 2011, the Net Working Capital to Assets has decreased in comparison with the base year 2008 which shows that it has become negative. In 2012, the Net Working Capital to Assets has decreased to a great extent in comparison with the base year 2008 and it has become negative. Therefore, companys cash reservoir is not able to be backed by companys total assets.
CONCLUSION
The Net Working Capital to Assets of the company has fluctuations during the five years analysis which was positive at the start and then remained negative for the following years. However, it is highly recommended to increase the companys Current Assets by increasing its accounts receivables & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares to make the companys cash reservoir positive so that the Net Working Capital can also be increased.
21
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
EFFICIENCY RATIOS
TOTAL ASSET TURNOVER
2008 2009 2010 3.78 2011 3.92 2012 4.48
TOTAL ASSET TURNOVER
4.5 4 3.5 3 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2010, the Total Asset Turnover is 3.78 which represent that how hard the companys assets are being put to use. Therefore, its obvious that each dollar of asset has produced 3.78 dollars of sale and the company is working close to its capacity. In 2011, the Total Asset Turnover has increased as compared to the base year 2010 which shows that the company has worked closer to its capacity. In 2012, the Total Asset Turnover has increased as compared to the base year 2010 which shows that the company has more utilized its assets for sales.
CONCLUSION
The Total Asset Turnover of the company has been analyzed for three years which shows that the companys Total Asset Turnover was low in the beginning but it increased during its following years. In order to further increase of Total Asset Turnover, the company should increase its sales.
22
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD
2008 2009 25.73 days 2010 9.71 days 2011 5.28 days 2012 3.71 days
AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD
30 25 20 15 10 5 0 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2009, the Average Collection Period is 25.73 days which shows that the company recovers its receivables from its credit customers in about 25.73 days. This collection period is not efficient because the value is not too minimal. In 2010, the Average Collection Period has decreased as compared to the base year 2009 which shows that the company efficiently recovers its receivables from its credit customers. In 2011, the Average Collection Period has again decreased as compared to the base year 2009 which shows that the company recovers its receivables from its credit customers more efficiently. In 2012, the Average Collection Period has decreased to a great extent as compared to the base year 2009 which represents that the company recovers its receivables efficiently.
CONCLUSION
The Average Collection Period of the company has been analyzed for four years which shows that the good performance with decrease in Average Collection Period with the passage of time. Therefore, to recover the receivables more efficiently the company can increase its sales which will increase its receivables and thus the Average Collection Period will also be increased.
23
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
INVENTORY TURNOVER
2008 2009 3 2010 3.5 2011 3.2 2012 4.1
INVENTORY TURNOVER
5 4 3 2 1 0 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2009, the Inventory Turnover of the company is 3 which represent the rate at which the company is turning over its inventories. In 2010, the Inventory Turnover of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2009 which shows they companys ability for turning over its inventory has increased. In 2011, the Inventory Turnover of the company has a slight increased as compared to the base year 2009 which represents that the companys ability for turning over its inventory has again increased. In 2012, the Inventory Turnover of the company has increased to a large extent as compared to the base year 2009 which shows that the companys ability for turning over its inventory has increased to a large extent.
CONCLUSION
The Inventory Turnover of the company has minor fluctuations during the analysis of four years which shows that the inventory turnover has increased which is a good remark. Therefore, company should increase its sales volume which will increase its cost of goods sold which will lead to the increase in its Inventory Turnover.
24
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
DAYS SALES IN INVENTORIES
2008 2009 125.30 days 2010 140.06 days 2011 133.17 days 2012 117.09 days
DAYS' SALES IN INVENTORIES
150 140 130 120 110 100 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2009, the Days Sales in Inventories is 125.30 which represents that on average the company has sufficient inventory to maintain sales for 125.30 days. In 2010, the Days Sales in Inventories was increased as compared to the base year 2009 which represents that the company had more inventories to maintain its sales. In 2011, the Days Sales in Inventories was increased as compared to the base year 2009 which shows that the company had more inventories to maintain its sales. In 2012, the Days Sales in Inventories has decreased as compared to the base year 2009 which shows that the inventory has decreased but still has sufficient to maintain its sales.
CONCLUSION
The Days Sales in Inventories has been analyzed for four years which shows that throughout the analyzed period the company had sufficient inventories to meet its daily sales.
25
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
PROFITABILITY RATIOS
OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN
2008 -3.16% 2009 2.82% 2010 1.38% 2011 2% 2012 3%
OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN
4.00% 3.00% 2.00% 1.00% 0.00% 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -1.00% -2.00% -3.00% -4.00%
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Operation Profit Margin of the company is -3.16% which represents that the companys revenue (inclusive of debt) throughout the year is -3.16% which determines that the company didnt earn revenue and the company incurred loss during the year. In 2009, the Operating Profit Margin of the company increased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys revenue (inclusive of debt) increased that it is no more negative. In 2010, the Operating Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys revenue (inclusive of debt) has also increased. In 2011, the Operating Profit Margin of the company has a slight increase as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the companys revenue (inclusive of debt) has a slight increase in it. In 2012, the Operating Profit Margin of the company increased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the companys revenue (inclusive of debt) has also increased.
CONCLUSION
The Operating Profit Margin of the Company has been analyzed for five years which shows extreme fluctuations. Therefore, company should increase its Net Income by becoming more cost efficient & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
26
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
GROSS PROFIT MARGIN
2008 19.32% 2009 23.30% 2010 23.27% 2011 20.73% 2012 19.70%
GROSS PROFIT MARGIN
25.00% 20.00% 15.00% 10.00% 5.00% 0.00% year 2008 year 2009 year 2010 year 2011 year 2012
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Gross Profit Margin of the company is 19.32% which represents the gross profit earned by the company. This margin is not too ideal because the value is too minimal. In 2009, the Gross Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the gross profit earned by the company has increased. In 2010, the Gross Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the gross profit earned by the company has increased. In 2011, the Gross Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the gross profit earned by the company has increased. In 2012, the Gross Profit Margin of the company has slightly increased as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that the gross profit earned by the company has slightly increased.
CONCLUSION
The Gross Profit Margin of the company has been analyzed for five years and minor fluctuations have been seen in it. Although, the company has earned its gross profit margin but no intense increase has been seen in it.
27
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
NET PROFIT MARGIN
2008 -5.58% 2009 0.75% 2010 -3.45% 2011 -2% 2012 -3%
NET PROFIT MARGIN
2.00% 1.00% 0.00% 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -1.00% -2.00% -3.00% -4.00% -5.00% -6.00%
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Net Profit Margin of the company is -5.58% which represents that the revenue earned by the company is 5.58% which indicates loss in it. In 2009, the Net Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but it has become positive but the value is too minimal to be ideal. In 2010, the Net Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but has still remained negative. In 2011, the Net Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but still it is negative. In 2012, the Net Profit Margin of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but it remains negative.
CONCLUSION
The Net Profit Margin of the company has been analyzed for five years which shows that the companys net profit was negative in the beginning but then it increased in its following years but yet remained negative. Therefore, it is highly recommended that the company should increase its Net Income by becoming more cost efficient & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
28
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
RETURN ON ASSETS
2008 -0.01 2009 0.09 2010 0.03 2011 0.09 2012 0.07
RETURN ON ASSETS
0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -0.02
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Return on Assets of the company is -0.01 which represents the return on companys assets is -0.01%. This return in not considered as ideal because the value is negative and the assets are not utilized. In 2009, the Return on Assets of the company has increased to a great extent that it is no more negative as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the assets are more utilized in this year. In 2010, the Return on Assets of the company has increased to be the positive as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the assets are utilized in this year. In 2011, the Return on Assets of the company has increased to a large extent as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the assets are more utilized in this year. In 2012, the Return on Assets of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 which shows that the assets are utilized in this year.
CONCLUSION
The Return on Assets of the company has been analyzed for five years and it has been found that the company earned return on its assets but the return was too minimal to be considered as ideal. However, the companys assets are not fully utilized. Therefore, company should increase its Net Income by becoming more cost efficient & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
29
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
RETURN ON EQUITY
2008 2009 0.08 2010 0.09 2011 -0.17 2012 -0.02
RETURN ON EQUITY
0.15 0.1 0.05 0 2008.5 -0.05 -0.1 -0.15 -0.2 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5
INTERPRETATION
In 2009, the Return on Equity of the company is 0.08 which represents that the return on shareholders equity throughout the year. In 2010, the Return on Equity of the company has a slight increase which shows that the return on shareholders equity has also slightly increased as compared to the base year 2009. In 2011, the Return on Equity of the company has decreased to a great extent which shows that the return on shareholders equity has become negative as compared to the base year 2009. This return is not considered as ideal as the return is in negative. In 2012, the Return on Equity of the company has decreased to a large extent as compared to the base year 2009 which shows that the return on shareholders equity has decreased and is slightly negative.
CONCLUSION
The Return on Equity of the company has been analyzed for four years and it has been concluded that the company equity has decreased during the period of time. Therefore it is highly recommended that the company should increase its Return on Equity by increasing its Net Income which can be increased by being more cost efficient & selling and increasing outstanding number of shares.
30
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
EARNING PER SHARE
2008 -25.1 2009 2.22 2010 -8.9 2011 -3.87 2012 -0.57
EARNING PER SHARE
5 0 2007.5 2008 2008.5 2009 2009.5 2010 2010.5 2011 2011.5 2012 2012.5 -5 -10 -15 -20 -25 -30
INTERPRETATION
In 2008, the Earning per Share of the company is -25.1 which represents that the companys earning with proportion to its shares in -25.1. This is not an ideal condition because the value is in negative. In 2009, the Earning per Share of the company has increased and is no more negative as compared to the base year 2008 which represents that that companys earnings with proportion to its shares has also slightly increased. In 2010, the Earning per Share of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but it remains negative. In 2011, the Earning per Share of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but the companys earnings with proportion to its shares have not increased because the value is in negative. In 2012, the Earning per Share of the company has increased as compared to the base year 2008 but the companys earnings with proportion to its shares have not increased because the value is in negative.
CONCLUSION
The Earning per Share of the company is analyzed for five years and it has been found that the companys earning with proportion to its shares has fluctuations but still it has remained negative for the period of time. Therefore, it is recommended for the company to increase its Net Income to increase its Earnings per Share by being more cost efficient and increasing its sales.
31
BERGER PAINTS PAKISTAN LIMITED
OTHER FACTORS AFFECTING COMPANY
The factors affecting companys performance except companys ratio analysis are:
RELIANCE ON DEBT FINANCING: The Company has become reliant on debt
financing due to which the companys liquid position has become insecure.
POLITICAL UNCERTAINTY: Political Uncertainty has caused the progress of real
estate and construction business due to which companys business is at disadvantage.
POWER CRISIS: The shortage and increasing power (electricity) prices and caused the
company to a great extent.
LAW AND ORDER SITUATION: In Central and Northern Region of the country, law
and order situation is not stable due to which business is negatively affected.
RAW MATERIAL AND PACKAGING: The raw material used for production has
become more expensive due to which operating expenses of the company have increased.
ADVERTISING COST: Advertisement has become more costly due to which operating
expenses of the company are increased.
32
You might also like
- Pakistan Paint Industry ReportDocument43 pagesPakistan Paint Industry ReportHamza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Final Report 12Document72 pagesStrategic Management - Final Report 12Aryan Smarty67% (3)
- A. Using The Concept of Net Present Value and Opportunity Cost, Explain When It Is RationalDocument2 pagesA. Using The Concept of Net Present Value and Opportunity Cost, Explain When It Is RationalLê Thành Danh100% (1)
- Business Studies Notes For o LevelDocument2 pagesBusiness Studies Notes For o LevelNuzhat TariqNo ratings yet
- Report On Berger Paints Pakistan LTDDocument7 pagesReport On Berger Paints Pakistan LTDJahangirKhanNo ratings yet
- Final Project Berger PaintsDocument22 pagesFinal Project Berger PaintsIsma Ishtiaq100% (1)
- FARR CeramicsDocument35 pagesFARR CeramicsKawsurNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis of Berger Paints Ltd.Document70 pagesMarket Analysis of Berger Paints Ltd.NAVZA0% (1)
- Berger Final Case Study OnlyDocument23 pagesBerger Final Case Study OnlyKhalid Mehmood0% (1)
- Mitchell S Fruit Foods LimitedDocument43 pagesMitchell S Fruit Foods LimitedRahila Saeed0% (1)
- Shoaib Akhtar Assignment-1 Marketting Research On Mochari Shoes BrandDocument5 pagesShoaib Akhtar Assignment-1 Marketting Research On Mochari Shoes BrandSHOAIB AKHTARNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument49 pagesAnalysis of Financial Statementsnimra farooq0% (1)
- Diamond PaintsDocument20 pagesDiamond Paintsialimughal75% (4)
- Lemon Max Advertising Strategy PakistanDocument3 pagesLemon Max Advertising Strategy PakistanZaka Ul Hassan100% (1)
- Computer-Bases Inforation Systems Building A DSS in Excel Part IDocument3 pagesComputer-Bases Inforation Systems Building A DSS in Excel Part IEduardo Vidal Cid100% (1)
- ACCA P3 Business Analysis Exam Focused Study Text BookDocument102 pagesACCA P3 Business Analysis Exam Focused Study Text Bookzurwahmirza100% (2)
- SHiELd PaintsDocument23 pagesSHiELd Paintsanonymous dcNo ratings yet
- Berger Paints Final ReportDocument45 pagesBerger Paints Final ReportMuhammad Jahanzeb AamirNo ratings yet
- Paint Industry AnalysisDocument25 pagesPaint Industry AnalysisRAJASHEKAR REDDY SNo ratings yet
- Berger PaintsDocument10 pagesBerger PaintsRamsha SohailNo ratings yet
- Berger Paints Pakistan Limited: Marketing Report OnDocument13 pagesBerger Paints Pakistan Limited: Marketing Report OnSafeer SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Berger Paints Pakistan Ltd.Document22 pagesBerger Paints Pakistan Ltd.Aimen KhatanaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report: Berger Paints Pakistan LimitedDocument28 pagesInternship Report: Berger Paints Pakistan LimitedAr Arunima RaneNo ratings yet
- Nippon Paint Pakistan Marketing ProjectDocument17 pagesNippon Paint Pakistan Marketing ProjectSalman Ahmad Kahloon100% (1)
- Paint IndustryDocument35 pagesPaint IndustryRajan Kashyap100% (3)
- Packages and MitsDocument15 pagesPackages and Mitssarakhan0622No ratings yet
- Brighto Paints: Hamza Fiaz Roll No.198 Bilal Randhawa Roll No.186 Muhammad Tariq Roll No.188 Afnan Masood Roll No.219Document7 pagesBrighto Paints: Hamza Fiaz Roll No.198 Bilal Randhawa Roll No.186 Muhammad Tariq Roll No.188 Afnan Masood Roll No.219Bilal RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Brighto Paints Final ReportDocument13 pagesBrighto Paints Final ReportMuhsin Rajpoot100% (1)
- Brighto Paints: Course: Presented ToDocument13 pagesBrighto Paints: Course: Presented ToAmna FarooquiNo ratings yet
- The Prudential Regulations of State Bank PakistanDocument33 pagesThe Prudential Regulations of State Bank PakistanSaad Bin Mehmood88% (17)
- Internship Report On Boss Plastic IndustryDocument71 pagesInternship Report On Boss Plastic IndustryShahzaibNo ratings yet
- Environmental Analysis of Mater TilesDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Analysis of Mater TilesMaher Zohaib Ahmed100% (1)
- Elite Paint RebrandingDocument41 pagesElite Paint RebrandingKamrul Hasan ShaonNo ratings yet
- Darson Securities PVT LTD Internship ReportDocument90 pagesDarson Securities PVT LTD Internship Report333FaisalNo ratings yet
- Atlas HondaDocument17 pagesAtlas Hondaanum fatimaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception Towards Kajaria TilesDocument33 pagesConsumer Perception Towards Kajaria TilesNitishKumar100% (2)
- Decision Making at Asian PaintsDocument12 pagesDecision Making at Asian PaintsTamil SelvamNo ratings yet
- English Biscuit ManufacturedDocument8 pagesEnglish Biscuit ManufacturedAdnan MajeedNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis 1Document13 pagesMarket Analysis 1zaighum sultan100% (4)
- FINI619 Internship Report Finance On ICI Paints PakistanDocument57 pagesFINI619 Internship Report Finance On ICI Paints Pakistantrillion5No ratings yet
- Assignment On Berger PaintsDocument13 pagesAssignment On Berger PaintsZeeLeeman100% (1)
- Paint Dealers Questionnaire PDFDocument3 pagesPaint Dealers Questionnaire PDFOjonimi AdegbeNo ratings yet
- Boss Moulded Furniture An Internship ReportDocument54 pagesBoss Moulded Furniture An Internship ReportMuhammad Ibtasam33% (6)
- Yunus TextileDocument10 pagesYunus TextileSaba RizwanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Report of Bake ParlorDocument3 pagesMarketing Report of Bake ParlorDania Sherwani67% (3)
- EFE of Pak SuzukiDocument4 pagesEFE of Pak SuzukishahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Fauji Fertilizer FinalizedDocument43 pagesFauji Fertilizer Finalizedeali09457% (7)
- Lucky Cement Case StudyDocument16 pagesLucky Cement Case StudyAni AbiNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractSohaib Riaz100% (2)
- Honda Atlas CarsDocument100 pagesHonda Atlas CarsShery AwanNo ratings yet
- Gul Ahmed Annual Report 2007Document73 pagesGul Ahmed Annual Report 2007AISHASABAHATNo ratings yet
- Final Slides Supply ChainDocument33 pagesFinal Slides Supply ChainghaziaNo ratings yet
- Packages Internship ReportDocument110 pagesPackages Internship ReportWaqas97986% (7)
- Market Study of Roxy PaintDocument22 pagesMarket Study of Roxy PaintMd. Syed Delwer RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Mitchals FruitDocument135 pagesRatio Analysis of Mitchals FruitNafeesa Naz50% (2)
- Financial Position of Nishat Mills LimitedDocument87 pagesFinancial Position of Nishat Mills Limitedzeshan khaliq80% (5)
- Asian Paints ReportDocument10 pagesAsian Paints ReportAMAZING FACTSNo ratings yet
- Suzuki Annual Report 2020Document85 pagesSuzuki Annual Report 2020Zeeshan MeharNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints Internship ReportDocument39 pagesAsian Paints Internship Reportrakibulislammbstu01100% (1)
- Objectives of The StudyDocument9 pagesObjectives of The Studysarvesh.bhartiNo ratings yet
- S&OP Finance InvolDocument112 pagesS&OP Finance InvolPhantrungsonNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios at B.D.K. Ltd. Hubli PROJECT REPORTDocument69 pagesFinancial Ratios at B.D.K. Ltd. Hubli PROJECT REPORTBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- Balangoda Plantations PLC and Madulsima Planrtations PLC (1193)Document21 pagesBalangoda Plantations PLC and Madulsima Planrtations PLC (1193)Bajalock VirusNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project: A Financial Statement Analysis and Interpretation of Certstore SolutionsDocument72 pagesSummer Internship Project: A Financial Statement Analysis and Interpretation of Certstore SolutionsDibyaranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- The House of Commons - PoliticsDocument6 pagesThe House of Commons - Politicsgritty92No ratings yet
- ClimatThe Response of Oil and Gas Industry Towards The Climate Changee ChangeDocument15 pagesClimatThe Response of Oil and Gas Industry Towards The Climate Changee Changegritty92No ratings yet
- Guns in Space: Is That Is and EnlightenDocument5 pagesGuns in Space: Is That Is and Enlightengritty92No ratings yet
- Nto Investigate The Impact of Prevailing Microbiological Contamination in The Ground and Surface WaterDocument71 pagesNto Investigate The Impact of Prevailing Microbiological Contamination in The Ground and Surface Watergritty92No ratings yet
- To Isolate Phosphate Solubilizing MicroorganismDocument33 pagesTo Isolate Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganismgritty92No ratings yet
- 2014 1 SpecDocument136 pages2014 1 Specgritty92No ratings yet
- Importance of Human Resource ManagementDocument3 pagesImportance of Human Resource Managementgritty92No ratings yet
- IskySoft (Scam)Document12 pagesIskySoft (Scam)gritty92No ratings yet
- How To Save and Backup Messages On IphoneDocument10 pagesHow To Save and Backup Messages On Iphonegritty92No ratings yet
- How To Send Messages From IphoneDocument13 pagesHow To Send Messages From Iphonegritty92No ratings yet
- Delete Messages From IphoneDocument11 pagesDelete Messages From Iphonegritty92No ratings yet
- How To Save and Backup Messages On IphoneDocument11 pagesHow To Save and Backup Messages On Iphonegritty92No ratings yet
- The House of Commons - PoliticsDocument6 pagesThe House of Commons - Politicsgritty92No ratings yet
- Brand IExploring The Impact of Apple Brand Image On The Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loyalty and Commitment in The UKDocument93 pagesBrand IExploring The Impact of Apple Brand Image On The Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loyalty and Commitment in The UKgritty92100% (2)
- Central Depository CompanyDocument2 pagesCentral Depository Companygritty92No ratings yet
- ClimatThe Response of Oil and Gas Industry Towards The Climate Changee ChangeDocument15 pagesClimatThe Response of Oil and Gas Industry Towards The Climate Changee Changegritty92No ratings yet
- Nto Investigate The Impact of Prevailing Microbiological Contamination in The Ground and Surface WaterDocument71 pagesNto Investigate The Impact of Prevailing Microbiological Contamination in The Ground and Surface Watergritty92No ratings yet
- Time-Series Analysis Forecasting 03Document26 pagesTime-Series Analysis Forecasting 03gritty92No ratings yet
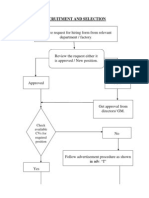
- Recruitment and Selection ChartDocument3 pagesRecruitment and Selection Chartgritty92No ratings yet
- To Isolate Phosphate Solubilizing MicroorganismDocument33 pagesTo Isolate Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganismgritty92No ratings yet
- LouisDocument8 pagesLouisgritty92No ratings yet
- Training and Development ChartDocument3 pagesTraining and Development Chartgritty92No ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal ChartDocument2 pagesPerformance Appraisal Chartgritty92No ratings yet
- Mima Group FinalDocument13 pagesMima Group Finalgritty92No ratings yet
- Good Earth ResourcesDocument36 pagesGood Earth ResourcesCptJohn HayabusaNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of HSLDocument151 pagesFinancial Performance of HSLNareshkumar Koppala100% (2)
- OM - (Forecasting) - M & L ManufacturingDocument3 pagesOM - (Forecasting) - M & L ManufacturingNeelNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Management and Profitability: A Case Study of Listed Manufacturing Companies in Sri LankaDocument5 pagesLiquidity Management and Profitability: A Case Study of Listed Manufacturing Companies in Sri Lankaeditor_ijtel100% (1)
- NDCC Consulting CasebookDocument185 pagesNDCC Consulting CasebookjonnyNo ratings yet
- Spending Power Cards Strategy SeriesDocument12 pagesSpending Power Cards Strategy SeriesyippiyooNo ratings yet
- Customer Service: Training Manual Corporate Training MaterialsDocument10 pagesCustomer Service: Training Manual Corporate Training MaterialsJennifer Penta BirkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Managerial EconomicsKran Lin100% (2)
- Edu 713 Educational Management and SupervisionDocument132 pagesEdu 713 Educational Management and SupervisionNoel Velante50% (2)
- Mithila ThesisDocument40 pagesMithila Thesisanupa bhattarai100% (1)
- Sykes EnterprisesDocument8 pagesSykes EnterprisesSamantha Green AquinoNo ratings yet
- Steps in Job CostingDocument8 pagesSteps in Job CostingBhagaban DasNo ratings yet
- Ej MicroDocument18 pagesEj MicronoegaesNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Marketing: Maxwell RanasingheDocument39 pagesNature and Scope of Marketing: Maxwell RanasingheKiran BabuNo ratings yet
- Computerized AccountingDocument50 pagesComputerized AccountingRam VasuNo ratings yet
- Example Open Items Via Direct InputDocument8 pagesExample Open Items Via Direct InputSri RamNo ratings yet
- CHPT 01Document23 pagesCHPT 01Tejaswini KotianNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Shakarganj Sugar Mill by SYED AHMAD MUSTAFADocument21 pagesInternship Report On Shakarganj Sugar Mill by SYED AHMAD MUSTAFAAhmad Mustafa100% (2)
- P6UK 2014 Dec ADocument12 pagesP6UK 2014 Dec APOUNo ratings yet
- LPP Formulation and Graphical MethodDocument22 pagesLPP Formulation and Graphical MethodKarthik AC100% (2)
- Application For Dealership - Hyundai Motor India LimitedDocument16 pagesApplication For Dealership - Hyundai Motor India LimitedVikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- IRIS Corporation Berhad - Rimbunan Kaseh To Come in Next Quarter - 120827Document2 pagesIRIS Corporation Berhad - Rimbunan Kaseh To Come in Next Quarter - 120827Amir AsrafNo ratings yet
- Tririga and Managing Capital Projects-3Document7 pagesTririga and Managing Capital Projects-3April Angela Ilao TaggsNo ratings yet
- 4 Success StoriesDocument11 pages4 Success StoriesAgana Sidney Bao-idangNo ratings yet
- Swedbank's Year-End Report 2015Document58 pagesSwedbank's Year-End Report 2015Swedbank AB (publ)No ratings yet
- BANKING Sector India and Swot AnalysisDocument16 pagesBANKING Sector India and Swot AnalysisPrateek Rastogi93% (14)