Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical and Process Thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Zakariya MohamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical and Process Thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Zakariya MohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical and Process Thermodynamics
Third Edition
B. G. Kyle
Emeritus Professor of Chemical Engineering Kansas State University
Prentice Hall PTR Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
CONTENTS
Preface Notation 1 Introduction
1-1 1-2 1-3 1-4 1-5 1-6 The Anatomy ofThermodynamics The Terminology ofThermodynamics The Variables and Quantities of Thermo Equilibrium and the Equilibrium State The Phase Rule The Reversible Process
2 The First Law of Thermodynamics
2-1 2-2 2-3 2-4 The First Law and Internal Energy The Enthalpy The Heat Capacity The First Lawfor Open Systems Problems
3 The Behavior of Fluids
3-1 3-2 3-3 3-4 3-5 The P VT Behavior of Fluids Equations of State The Ideal Gas The Compressibility Factor Generalized Equations of State Problems
4 The Second Law ofThermodynamics
4-1 4-2 Heat Engines and the Carnot Cycle The Ideal-Gas Carnot Cycle
viii
Contents
4-3 4-4 4-5 4-6 4-7 4-8 4-9 4-10
The Absolute Temperature Scale The Entropy Function Entropy and the Spontaneity of Natural Processes Calculation of Entropy Changes Open Systems Applications of the Second Law The Microscopic View of Entropy The ThirdLaw of Thermodynamics Problems
74 76 78 79 87 88 95 97 98
5 The Thermodynamic Network
5-7 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 5-6 5-7 5-8* 5-9* The Free Energy Functions The Clausius Inequality and the Fundamental Equation The Thermodynamic Network Measurable Quantities Calculation ofK and'S asFunctions o/P and T Property Estimation from Corresponding States Property Estimation Via Generalized Equations of State The MethodofJacobians The Generality ofthe Thermodynamic Method Problems
103
104 104 106 108 109 114 118 124 132 138 149 150 151 154 154 155 161 166 173 176 189 197 198 200 203 206 208 214 215
Heat Effects 6-1 6-2 6-3 6-4 6-5 6-6 6-7 6-8 6-9 The Computational Path Heat Effects Due to Change of Temperature Heat Effects Due to Change of Pressure Heat Effects Due to Change of Phase Mixing Heat Effecfts Enthalpy-Concentration Diagrams Chemical Heat Effects Heats of Formation in Solution Applied Thermochemistry Problems
Equilibrium and Stability 7-1 7-2 7-3 7-4 7-5* 7-6* Criteria of Equilibrium The Chemical Potential Application ofthe Equilibrium Criteria The Essence of Thermodynamics Stability Constraints, Equilibrium and Virtual Variations Problems
Contents
ix
8 Thermodynamics of Pure Substances
8-1 8-2 8-3 8-4 8-5 The Phase Diagram The Clapeyron Equation Solid-Liquid Equilibrium Solid- Vapor and Liquid- Vapor Equilibrium Presentation of Thermodynamic Property Data Problems
217
217 220 223 225 229 233
9 Principles of Phase Equilibrium
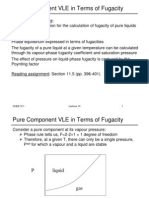
9-1 9-2 9-3 9-4 9-5 9-6 9-7 9-8 9-9 9-10 9-11 9-12 9-13 Presentation of Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data Determination of Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data The Thermodynamic Basis for the Phase Rule The Fugacity Determination ofFugacities ofPure Substances Determination ofFugacities in Mixtures Ideal Systems The Activity Coefficient Experimental Determination ofActivity Coefficients Henry's Law Activity Coefficient Equations Phase Equilibrium Via an Equation of State The Thermodynamic Approach to Phase Equilibrium Problems
239
240 244 246 247 249 258 261 270 274 278 279 291 299 302 309 313 319 325 327 332 337 340 346 350 352 359 362
10
Applied Phase Equilibrium 10-1 The Consummate Thermodynamic Correlation of Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium 10-2 Constant-Pressure VLEData 10-3 Total Pressure Data 10-4 Azeotropes 10-5 Thermodynamic Consistency Tests 10-6 Multicomponent Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium 10-7 Phase Behavior in Partially Miscible Systems 10-8 Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium 10-9* Ternary Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium 10-10 Estimates from Fragmentary Data 10-11 Recapitulation Problems
Contents
11
Additional Topics in Phase Equilibrium 11-1 11-2 11-3 11-4* 11-5* 11-6* 11-7* 11-8* Partial Molar Properties Experimental Determination q/Mixture and Partial Molar Properties Mixture Properties for Ideal Solutions Activity Coefficients Based on Henry 's Law The Solubility of Gases in Liquids Solid-Liquid Equilibria Solid-Supercritical Fluid Equilibrium Prediction of Solution Behavior Problems
375 375 3 78 384 386 390 394 410 412 420
12 Chemical Equilibrium
12-1 12-2 12-3 12-4 12-5 12-6 12-7 12-8 12-9 12-10* 12-11* 12-12* Generalized Stoichiometry The Condition of Equilibrium for a Chemical Reaction Standard States and AG Temperature Dependence ofthe Equilibrium Constant Experimental Determination ofThermochemical Data Other Free Energy Functions Homogeneous Gas-Phase Reactions Heterogeneous Chemical Equilibrium Reactions in Solution Reactions in Aqueous Solution Electrolyte Solutions Coupled Reactions Problems
433
435 437 440 444 446 454 456 462 468 478 486 505 511 529 530 548 55 7 571 579 581
13
Complex Chemical Equilibrium 13-1 The Phase Rulefor Reacting Systems 13-2* Analyzing Complex Chemical Equilibrium Problems 13-3 * Formulating Complex Chemical Equilibrium Problems 13-4* The CHO System and Carbon Deposition Boundaries 13-5* The Si-Cl-H System and Silicon Deposition Boundaries Problems
14 Thermodynamic Analysis of Processes
14-1 14-2 14-3 Work and Free Energy Functions The Availability Mixing and Separation Processes
589
589 591 600
Contents
xi
14-4* 14-5
Heat Exchange Systems Involving Chemical Transformations Problems
607 614 632
15 Physicomechanical Processes
15-1 15-2 15-3 15-4 15-5 15-6 15-7 Compression and Expansion of Gases The Joule-Thomson Expansion Liquefaction of Gases Refrigeration Heat Pumps Power Generation Cogeneration of Steam and Power Problems
639
640 643 645 654 661 662 667 671
16 Compressible Fluid Flow
16-1 16-2 16-3 16-4 16-5 The Basic Equations of Fluid Mechanics Sonic Velocity Isentropic Flow Isentropic Flow Through Nozzles Nonisentropic Flow Problems
677
678 681 683 685 689 693
17 Thermodynamics and Models
17-1* 17-2* 17-3* Standard Models Ad Hoc Models Evaluation of Models Problems
697
698 703 719 722 729
Appendix A Table A-l FigureA-1 Appendix B Table B-l Molar Heat Capacities of Gases at Zero Pressure Critical Constants of Selected Substances Equilibrium Constants for Selected Reactions
729 731 732 732
xii
Contents
Appendix C
Table C-l Table C-2 Thermodynamic Properties of Saturated Steam Thermodynamic Properties ofSuperheated Steam
734
734 737
Appendix D
Table D-l Table D-2 Table D-3 Appendix E Inventory ofthe CD-ROM Appendix F Properties ofDeterminants Index
742
Enthalpies and Free Energies of Formation of Selected Organic Compounds 742 Enthalpies and Free Energies of Formation of Selected Inorganic Compounds 744 Free Energies of Formation of Selected Ions in the Aqueous State 745 746 746 751 751 753
You might also like
- Transport Phenomena for Chemical Reactor DesignFrom EverandTransport Phenomena for Chemical Reactor DesignRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Thermal Fluid Sciences 6Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesFundamentals of Thermal Fluid Sciences 6Th Edition Full Chapterrobert.luckman563100% (28)
- Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 2nbsped 812032790x 9788120327900 CompressDocument720 pagesFundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 2nbsped 812032790x 9788120327900 Compresssweetyjun161998No ratings yet
- Conventional and Alternative Power Generation: Thermodynamics, Mitigation and SustainabilityFrom EverandConventional and Alternative Power Generation: Thermodynamics, Mitigation and SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Thermo FluidsDocument7 pagesThermo FluidsjuanmanuelrodriNo ratings yet
- 013101367X TocDocument6 pages013101367X TocIrham Hikmawan RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Supercritical Fluids: A Spreadsheet-based ApproachFrom EverandIntroduction to Supercritical Fluids: A Spreadsheet-based ApproachNo ratings yet
- Credits: 4 Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesCredits: 4 Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsSubrata PaulNo ratings yet
- Chemical, Biochemical, and Engineering Thermodynamics: Stanley I. SandlerDocument5 pagesChemical, Biochemical, and Engineering Thermodynamics: Stanley I. SandlerAriadne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Perry BookmarkDocument10 pagesPerry BookmarkFrancis Val FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsvp02091988No ratings yet
- Methanol Dehydration To Dimethyl Ether PDFDocument6 pagesMethanol Dehydration To Dimethyl Ether PDFJC Jane BarnesNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentFrom EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentNo ratings yet
- ME 311 Thermodynamics Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesME 311 Thermodynamics Course SyllabusSuga MilkNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Processing from Midstream to DownstreamFrom EverandNatural Gas Processing from Midstream to DownstreamNimir O. ElbashirNo ratings yet
- 2.thermal EngineeringDocument7 pages2.thermal EngineeringVikram Rao100% (1)
- Liquids and Liquid Mixtures: Butterworths Monographs in ChemistryFrom EverandLiquids and Liquid Mixtures: Butterworths Monographs in ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Process CalculationsDocument535 pagesStoichiometry and Process CalculationsAndrés Ceverisae76% (38)
- Engineering Thermodynamics35MDocument876 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics35MTara Collier100% (4)
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Thermal EnggDocument7 pagesThermal EnggVikram RaoNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of EngineeringDocument8 pagesFundamentals of EngineeringArun Victor PaulrajNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Thermodynamics - GhoshDocument314 pagesMetallurgical Thermodynamics - GhoshFormula FirestormNo ratings yet
- S A M S AC R P: Hortcut Pproach T O Odeling A N D Imulation O F Atalytic Eforming RocessDocument6 pagesS A M S AC R P: Hortcut Pproach T O Odeling A N D Imulation O F Atalytic Eforming RocessLuis Enrique Jiménez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics: D. Eastop A. Mccon EYDocument14 pagesApplied Thermodynamics: D. Eastop A. Mccon EYJayPisonNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of A Riser Type Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC)Document12 pagesModeling and Control of A Riser Type Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC)krg09100% (1)
- Untitled 0Document46 pagesUntitled 0Agam Duma Kalista WibowoNo ratings yet
- Maths review gases thermo electrochemistryDocument6 pagesMaths review gases thermo electrochemistryELben RescoberNo ratings yet
- Processcalculation PDFDocument1 pageProcesscalculation PDFRajeevNo ratings yet
- TD Course FileDocument18 pagesTD Course FileBadari Narayan P100% (1)
- Thermodynamics of The Single-Step SynthesisDocument9 pagesThermodynamics of The Single-Step SynthesischemmmmmNo ratings yet
- A Textbook Of: Hemical Ngineering HermodynamicsDocument11 pagesA Textbook Of: Hemical Ngineering HermodynamicsAiswarya RaviNo ratings yet
- ChE SyllabusDocument30 pagesChE SyllabusSubodh DwivediNo ratings yet
- ChE SyllabusDocument30 pagesChE SyllabusRavindra Kumar NiranjanNo ratings yet
- 352361670Document8 pages352361670Emanuel Heinze0% (1)
- Reactive DistillationDocument36 pagesReactive Distillationzorro21072107No ratings yet
- Aspen Tutorial Guide to Process Simulation SoftwareDocument28 pagesAspen Tutorial Guide to Process Simulation SoftwareJustin DeVitoNo ratings yet
- Prico Process PDFDocument13 pagesPrico Process PDFcorkynhoNo ratings yet
- Francis W. Sears, Gerhard L. Salinger-Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory, and Statistical Thermodynamics-Addison Wesley (1975)Document462 pagesFrancis W. Sears, Gerhard L. Salinger-Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory, and Statistical Thermodynamics-Addison Wesley (1975)João Felipe Feitosa FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Single Event Kinetic Modeling of The Methanol-to-Olefins Process On SAPO-34Document14 pagesSingle Event Kinetic Modeling of The Methanol-to-Olefins Process On SAPO-34estudio91No ratings yet
- Michael V. Lurie: Modeling of Oil Product and Gas Pipeline TransportationDocument17 pagesMichael V. Lurie: Modeling of Oil Product and Gas Pipeline TransportationDanAlexandruJoitaNo ratings yet
- Regime Analysis and Scale DownDocument13 pagesRegime Analysis and Scale Downtiffanyyy000% (1)
- Applied Thermodynamics, 3rd EditionDocument2,105 pagesApplied Thermodynamics, 3rd Editionirkaidirfais100% (5)
- CRude Oil Fouling Experi EncesDocument5 pagesCRude Oil Fouling Experi EncesPedro DiazNo ratings yet
- Simulation Studies On A Cross Flow Plate Fin Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesSimulation Studies On A Cross Flow Plate Fin Heat ExchangerHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Dali Cha Ouch 89Document249 pagesDali Cha Ouch 89Arie JuliantoNo ratings yet
- COURSESDocument9 pagesCOURSESshushuNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil FoulingDocument5 pagesCrude Oil FoulingJenny Carter100% (1)
- Dynamic Modelling and Optimized Model Predictive Control Strategies For The ORCDocument24 pagesDynamic Modelling and Optimized Model Predictive Control Strategies For The ORCYodha YudhistraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics (MEEG 207) Reference Textbook: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8 Edition in SI Units (Author-Cengel and Boles)Document1 pageEngineering Thermodynamics (MEEG 207) Reference Textbook: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8 Edition in SI Units (Author-Cengel and Boles)Roshan0% (1)
- Engineering Thermodynamics (MEEG 207) Reference Textbook: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8 Edition in SI Units (Author-Cengel and Boles)Document1 pageEngineering Thermodynamics (MEEG 207) Reference Textbook: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8 Edition in SI Units (Author-Cengel and Boles)RoshanNo ratings yet
- Design of a Plug Flow Reactor (PFR) SimulationDocument10 pagesDesign of a Plug Flow Reactor (PFR) SimulationDee RajanNo ratings yet
- Problem 6.1. SolutionDocument4 pagesProblem 6.1. SolutionZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 PDFDocument23 pagesLecture 4 PDFZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- H83BCE Life's Building Blocks & ProcessesDocument16 pagesH83BCE Life's Building Blocks & ProcessesZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Distillation 1Document42 pagesDistillation 1Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Tryout Exam - SolutionDocument8 pagesTryout Exam - SolutionZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- 2.2.fats and ProteinsDocument25 pages2.2.fats and ProteinsZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document40 pagesLecture 3Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modelling of Chemical ProcessesDocument17 pagesMathematical Modelling of Chemical ProcessesZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena Module Covers Heat, Mass, MomentumDocument8 pagesTransport Phenomena Module Covers Heat, Mass, MomentumZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroorganismsDocument25 pages1 MicroorganismsZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroorganismsDocument25 pages1 MicroorganismsZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Adsorption Isotherms: Kazi Monzure KhodaDocument17 pagesAdsorption Isotherms: Kazi Monzure KhodaHarsha Ramakrishna KashyapNo ratings yet
- H83BCE Life's Building Blocks & ProcessesDocument16 pagesH83BCE Life's Building Blocks & ProcessesZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Answer For PLD Final ExamsDocument3 pagesAnswer For PLD Final ExamsZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Example Class-1 (Enzyme Kinetics)Document2 pagesExample Class-1 (Enzyme Kinetics)Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- H83DPX Spring AssessmentDocument11 pagesH83DPX Spring AssessmentZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Isotherm DervDocument9 pagesIsotherm DervZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument8 pagesReferenceZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Week 1 CYJ Mole Balance-PrintDocument25 pagesWeek 1 CYJ Mole Balance-PrintZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- L04Document31 pagesL04Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Modeling in The Presence of Catalyst DeactivationDocument16 pagesModeling in The Presence of Catalyst DeactivationZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Hen II - Pta & GCCDocument8 pagesLecture 8 - Hen II - Pta & GCCZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- L04Document31 pagesL04Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy PrinciplesDocument19 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy PrinciplesZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial OneDocument2 pagesTutorial OneZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Extra TPH02 1Document3 pagesExtra TPH02 1Zakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Hen III - PDMDocument11 pagesLecture 9 - Hen III - PDMZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - HEN I - CCDocument6 pagesLecture 7 - HEN I - CCZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Pump SelectionDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Pump SelectionZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- CH 06 Binary PhaseDocument56 pagesCH 06 Binary PhaseJhonnBeikerAnccasiLachoNo ratings yet
- Entropy is important for two main reasonsDocument11 pagesEntropy is important for two main reasonsGerman ChiappeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Phase Diagram of Naphthalene-BiphenylDocument7 pages3 - Phase Diagram of Naphthalene-Biphenyldidikkris100% (3)
- PGTRB 2021 - Chemistry - 1Document69 pagesPGTRB 2021 - Chemistry - 1selvisolomon80No ratings yet
- Introduction To Phase Equilibria & SeparationsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Phase Equilibria & SeparationsShawn ChanNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument19 pagesPhase Diagramsget2csNo ratings yet
- Roaa PDFDocument24 pagesRoaa PDFRo'a ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mark With AnswerDocument16 pagesEtd 2mark With AnswerERKATHIR100% (1)
- Pertemuan Ke-3 Dan 4Document32 pagesPertemuan Ke-3 Dan 4Habib Faisal YahyaNo ratings yet
- Ch-27.3 Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramDocument58 pagesCh-27.3 Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramasjfgauojfgfNo ratings yet
- 2. Phase RuleDocument59 pages2. Phase RuleR TharunishNo ratings yet
- 5) Phase RuleDocument17 pages5) Phase RuleSHANJIDA ALI RIA100% (1)
- Accurate Prediction of Equilibrium PropertiesDocument10 pagesAccurate Prediction of Equilibrium PropertiesAhmed MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics and Materials Glossary of Terms: Chemical Potential 1Document7 pagesThermal Physics and Materials Glossary of Terms: Chemical Potential 1matt gerard perezNo ratings yet
- Kannur University B.SC Chemistry PDFDocument55 pagesKannur University B.SC Chemistry PDFJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- Chemistry Syllabus Mapping IITJAM NET GATE BSC MSCDocument39 pagesChemistry Syllabus Mapping IITJAM NET GATE BSC MSCAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- Assessment of High Alumina Refractories by Phase Diagram EvaluationsDocument5 pagesAssessment of High Alumina Refractories by Phase Diagram EvaluationsNhocSkyzNo ratings yet
- Gas Production Eng.-Sanjay KumarDocument326 pagesGas Production Eng.-Sanjay Kumargmikhil100% (6)
- CHM271 - Chapter 6 - Phase EquilibriumDocument93 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 6 - Phase Equilibriumhidayahtul adhaNo ratings yet
- CH 06 Binary PhaseDocument63 pagesCH 06 Binary PhaseNiranjan MohantyNo ratings yet
- One Compenent Water SystemDocument7 pagesOne Compenent Water Systemslchem75% (4)
- Chemical, Biochemical, and Engineering Thermodynamics: Stanley I. SandlerDocument5 pagesChemical, Biochemical, and Engineering Thermodynamics: Stanley I. SandlerAriadne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Process modelling thermodynamic selection guideDocument48 pagesProcess modelling thermodynamic selection guidevictorvikramNo ratings yet
- 1997 - Nowak - Kleinrahm - Wagner - Measur and Correl of PRoT Rel of Nitrogen - Sautated Liquid and Saturated VaporDocument18 pages1997 - Nowak - Kleinrahm - Wagner - Measur and Correl of PRoT Rel of Nitrogen - Sautated Liquid and Saturated VaporAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Pet 326: Reservoir Phase Behaviour: Lecture NotesDocument79 pagesPet 326: Reservoir Phase Behaviour: Lecture NotesAkande Ayodeji100% (2)
- Calculating Fugacity of Pure Liquid n-PentaneDocument8 pagesCalculating Fugacity of Pure Liquid n-PentanescienziatoNo ratings yet
- ASPEN PLUS (v7.3) (2011-03) - Aspen Physical Property System - Physical Property MethodsDocument245 pagesASPEN PLUS (v7.3) (2011-03) - Aspen Physical Property System - Physical Property Methodsthiarap23No ratings yet
- Cetd Unit 4Document37 pagesCetd Unit 4Laxmi PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Process ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesChemical and Process ThermodynamicsZakariya MohamedNo ratings yet
- III SEM Question BankDocument110 pagesIII SEM Question BankGowtham SNo ratings yet
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaFrom EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNo ratings yet
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- 35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980From Everand35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (241)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureFrom EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (124)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceFrom EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (586)
- Across the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsFrom EverandAcross the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsNo ratings yet
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseFrom EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (12)
- Recording Unhinged: Creative and Unconventional Music Recording TechniquesFrom EverandRecording Unhinged: Creative and Unconventional Music Recording TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (50)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyFrom EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterFrom EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Fallout: The Hiroshima Cover-up and the Reporter Who Revealed It to the WorldFrom EverandFallout: The Hiroshima Cover-up and the Reporter Who Revealed It to the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- The Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914From EverandThe Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (124)