Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO Unit 4 - Mock Exam
Uploaded by
alex_gaston_2Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO Unit 4 - Mock Exam
Uploaded by
alex_gaston_2Copyright:
Available Formats
Answer Sheet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 Answer 86-100 on the test.
Mock Exam 4
True (A) or False (B) 1. Translation in eukaryotes involves a sigma factor which allows the RNA polymerase to attach to the DNA strand. 2. A cell from your lung and another from your thigh bone have the same genome, but different proteomes. 3. Mendels law of independent assortment only applies to traits found on the same chromosome. 4. The Central Dogma refers to the three stages of translation. 5. A sex-influenced trait, such as balding, impacts males and females differently, may mimic a sex-linked trait, but is located on an autosome. 6. Interphase occurs prior to meiosis. 7. Multiple genes can be found on a DNA helix with the various templates located on both strands. 8. When lactose and glucose are present in low concentrations, E. coli produces proteins required to transport lactose across the membrane and metabolized it. 9. An operon is a series of genes that are controlled by the same regulatory region. 10. Checkpoint proteins are active in all cells and are the predominant form of mRNA recycling. 11. It is possible for two genetically identical individuals raised in different environments to express different phenotypes.
12. Which of the following is not true regarding tRNA? A. created by transcription B. it is often cloverleaf-shaped C. transports amino acids D. regulates DNA replication E. polymer made up of nucleotides 13. Which of the following would not play a role in gene regulation? A. DNA synthesis B. transcription C. RNA processing D. translation E. protein folding
14. Nonstructural genes code for A. proteins B. DNA C. RNA D. carbohydrates E. lipids 15. Which of the following is not true regarding Gregor Mendel? A. Austrian monk B. Father of Genetics C. performed experiments with peas and bees D. first to link genes with protein production E. first to establish rules associated with inheritance
16. Which of the following in not true regarding transcription? A. begins with initiation: RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter B. elongation: amino acids are linked together from 3 to 5 C. termination: RNA polymerase reaches the terminator D. after termination, prokaryotic mRNA is ready for translation E. eukaryotic mRNA requires processing to add a cap and poly A tail and remove introns 17. Which of the following is not part of the lac operon? A. multiple promoters B. multiple terminators C. CAP binding site D. gene for glucose catabolism E. gene for lactose transport 18. Which of the following types of cell division occur in eukaryotes? A. mitosis only B. meiosis only C. mitosis and meiosis D. binary fission E. transformation 19. Which of the following is not true regarding the stages of interphase? A. G1 stage seen in normal functioning cells B. S the mitotic spindle is completed and positioned C. G2 additional proteins and organelles are created D. G0 a paused or suspended stage experienced by some cells (i.e. nerve cells) 20. Which of the following is not true regarding mitosis? A. forms 4 haploid cells from a single diploid cell B. responsible for growth C. replaces dead or damaged cells D. allows for asexual reproduction
21. Which of the following is not true regarding a Punnett square? A. the letters along the top and side represent gametes B. the letters in the boxes represent the genotypes of offspring C. the process depicts a breeding event between two individuals D. it can be used to determine the phenotypic ratio of future offspring E. it can be used to determine if a trait is autosomal or sex-linked 22. You crossed a yellow flowering plant with a red flowering plant and produced offspring that have flowers with yellow and red spots. This is what type of inheritance? A. incomplete dominance B. codominance C. sex-linked D. mutant allele E. pleiotropy 23. When does crossing over occur? A. prophase B. prophase I C. metaphase D. metaphase II E. cytokinesis 24. What do you call the process, from start to finish, by which a gene is used to produce a protein? A. gene expression B. translation C. transcription D. interphase E. gene regulation 25. Which of the following attaches an amino acid to the correct tRNA? A. lac O B. operon C. pyruvate D. aminoacyl-tRNA synthase E. -galactosidae
26. Which of the following is not true regarding a monohybrid cross? A. Tt x tt B. produces a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio C. produces a 3:1 phenotypic ratio 27. Which of the following is not true regarding mutations that occur in somatic cells? A. appear in a patch rather than throughout the body B. can be passed on to offspring C. the individual would have two different genotypes 28. Genes that are always being expressed and are not regulated are called _____ genes. A. gradient B. exergonic C. constitutive D. extranuclear E. conservative 29. Which of the following is not true regarding mutations? A. they are changes in the genetic material B. they are a source of variation C. they can be harmful D. only impact germ-lines E. changes can occur at the nucleotide or chromosome level 30. Which of the following is not true regarding pedigree diagrams? A. they depict a genetic trait in a family over multiple generations B. they are exclusively used for plant breeding C. they can help determine the inheritance pattern of dominant vs. recessive traits D. they can help determine the inheritance pattern of autosomal vs. sex-linked traits 31. Which of the following removes the lac repressor? A. CAP B. glucose C. allolactose D. antirepressor molecule
32. Garrod, working with metabolic diseases, and Beadle and Tatum, working with mutant bread mold discovered A. the presence of checkpoint proteins B. the stages of mitosis C. the laws of inheritance D. that genes code for proteins E. that tRNA codes for carbohydrates 33. The RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA strand when it reaches the ______. A. AUG B. UGA C. terminator D. repressor site E. repressor protein 34. mRNA is created during which process? A. translation B. transcription C. interphase D. mitosis E. meiosis 35. What is the function of a poly-A tail? A. allows mRNA to leave the nucleus B. indicates the 5 end for the ribosome C. extends the lifespan of an mRNA D. acts as the start codon E. acts as the stop codon 36. Which of the following is not true regarding regulatory transcription factors? A. bind to DNA B. travel from 3 to 5 creating mRNA C. prevent transcription from occurring D. promote transcription of a gene E. have two sites where binding occurs 37. Which of the following is not true regarding interphase? A. occurs prior to mitosis B. occurs prior to meiosis C. involves the division of the cytoplasm D. most of a cells life is spent in this stage E. has 2 checkpoints to regulate activities
38. Which of the following is not true regarding microtubules? A. dynamic and hollow B. astral microtubules help maintain the shape of the cell during mitosis C. polar microtubules push the spindles away from each other and towards the poles D. kinetochore microtubules help pull the chromosomes toward the poles 39. A dominant trait A. is only expressed in homozygous dominant individuals B. is only expressed in homozygous recessive individuals C. is only expressed in heterozygous individuals D. is expressed as along as one dominant allele is present E. is not expressed as long as one recessive allele is present 40. Which of the following is the term applied to an organism that has 3 or more copies of every chromosome? A. polyploidy B. monoploidy C. aneuploidy D. trisomic E. monosomic 41. Which of the following is not true regarding selfcrosses? A. a single individual acts as both the mother and father B. commonly performed with plants C. repeatedly performing self-crosses produces a single purely heterozygous strain 42. When a piece of chromosome 4 swaps places with a piece of chromosome 17, this type of mutation is referred to as a(n) A. insertion B. deletion C. inversion D. translocation
43. What do you call a single gene that controls multiple traits? A. incomplete dominance B. codominance C. sex-linked D. mutant allele E. pleiotropy 44. Proteins are created using an mRNA blueprint in a process called _____. (select the best answer) A. gene expression B. translation C. transcription D. interphase E. gene regulation 45. Transcription occurs in the ______ in prokaryotes and the ______ in eukaryotes. A. nucleolus; nucleus B. ribosome; mitochondria C. rough ER; cytoplasm D. cytoplasm; nucleus E. smooth ER; rough ER 46. Which of the following is not true regarding ribosomes? A. prokaryotes have a single type, eukaryotes have multiple types B. they can be found in the cytoplasm, attached to the rough ER, and in chloroplasts and mitochondria C. they are produced in the nucleolus D. they are formed from 6 protein subunits E. rRNA acts as a ribozyme 47. The hypothesis of one gene one enzyme had to be modified because A. enzymes can be created by modifying nucleotides B. many enzymes are coded for using rRNA C. not all proteins are enzymes D. not all enzymes are proteins E. genes code for all four categories of organic molecules
48. Which of the following is used by RNA polymerase to identify the starting point of a gene? A. AUG B. UGA C. promoter D. activator site E. activator protein 49. RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand from ______ creating an RNA copy from ______. A. 5 to 3; 5 to 3 B. 5 to 3; 3 to 5 C. 3 to 5; 5 to 3 D. 3 to 5; 3 to 5 50. What is the function of small effector molecules? A. bind with transcription regulatory factors B. transport amino acids C. transport nucleotides D. fold small proteins E. create RNA primers 51. Which of the following is true regarding transcription in prokaryotes? A. requires 4 transcriptional factors to activate the RNA polymerase B. they have multiple RNA polymerases which produce different types of RNA C. the RNA polymerase travels along the DNA strand from 5 to 3 D. the RNA polymerase requires a sigma factor to function and recognize the promoter 52. What do you call a strand of RNA that codes for multiple proteins? A. polypeptide tRNA B. polycistronic mRNA C. semiautonomous rRNA D. regulatory pRNA 53. cAMP bonds with which molecule to increase the expression of lac genes? A. CAP B. glucose C. allolactose D. antirepressor molecule
54. What happens if a cyclin fails to bind or detach from a cdk at a given checkpoint? A. the cell dies B. the cell becomes cancerous C. the cell undergoes cytokinesis D. interphase or mitosis stops until the mistake is corrected E. all transcription stops until the ribosomes catch up 55. The following is a list of things associated with meiosis, but not mitosis. Which of these statements needs to be removed from the list? A. form homologous chromosomes B. crossing over occurs C. happens throughout the body D. undergoes 2 rounds of division E. produces 4 unique haploid cells 56. Mendels work was groundbreaking because it A. was done with peas B. occurred in Austria C. involved controlled breedings D. acknowledged different alleles E. associated numbers with the different phenotypes 57. Which of the following is not true regarding proteins? A. they are made of monomers called amino acids B. they form polymers called polypeptides C. amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds D. they are formed via a process called translation E. they are formed by mitochondria 58. Which of the following is not a benefit of gene regulation? A. allows the cell to save energy B. allows the cell to save resources C. its important for development D. controls when, where, and for how long a protein will be produced E. its not influenced by external factors
59. If a gene codes for flower color, then alleles A. would be purple vs. white B. are generated using FOIL C. are all of the possible genotypes D. are all of the possible phenotypes E. are autosomal traits 60. What is the process where an RNA copy is created using a DNA template? A. gene expression B. translation C. transcription D. interphase E. gene regulation 61. The wild type allele is A. always the dominant allele B. the allele most common in wild populations C. the allele most common in mutant populations D. an allele that produces the most bizarre phenotype 62. Gene regulation in eukaryotes is different from prokaryotes because A. it allows genes to be turned on or off B. it targets various stages of gene expression C. it is used to control growth and development D. it utilizes activators and repressors
63. Which of the following is a phenotype? A. homozygous dominant B. PpRRTt C. pRT D. tall plant that produces red flowers with purple spots 64. Which of the following is not true regarding translation? A. initiation is assembly of the ribosome and the placement of the mRNA and first tRNA B. elongation involves the addition of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain C. termination occurs when a stop codon reaches the A site D. small effector molecules process the polypeptide chain forming a folded and functional protein 65. Which of the following is true regarding a dihybrid cross? A. used to determine the genotype of a dominant parent B. always occurs as a self-cross C. produces a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio D. produces a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio
Answer the following questions with the diagram to the right 66. What do you call this type of diagram? A. gel electrophoresis B. PCR C. Ames test D. karyotype E. pedigree 67. True (A) or False (B). The field of genetics that produces and studies these diagrams is called molecular genetics.
Answer the following questions with the diagram to the right 68. Which of the following is pointing to the A site? 69. Which of the following is pointing to the polypeptide chain? 70. Which of the following possesses an anticodon?
71. Which of the following is the template strand?
Answer the following questions with the diagrams below 72. Which phase is seen in this picture? A. interphase B. anaphase C. anaphase I D. telophase E. telophase II 73. Which phase is seen in this picture? A. interphase B. anaphase C. anaphase I D. telophase E. telophase II
74. Which phase is seen in this picture? A. prophase B. prophase I C. metaphase D. metaphase II E. cytokinesis
Answer the following questions with the diagram to the right 75. The arrow is pointing to the A. p arm B. q arm C. centromere D. centriole E. homologous chromosome 76. Which of the following best describes this form? A. acrocentric B. metacentric C. submetacentric D. telocentric
(77-85.) Located on the Y chromosome is something called the SRY, it is the sex determining gene on the Y chromosome and is responsible for physical maleness. 77. Even though its often referred to as a region, it is technically a gene which means it is A. a unit of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA B. a type of allele C. variable in terms of location D. a small chromosome 78. SRY lacks introns, what does this mean? A. it hates to waste time and is ruthlessly efficient B. after transcription it is a mature mRNA and doesnt require processing C. it still requires a cap and poly-A tail, but no splicing 79. What is the start codon for SRY? A. CGA B. AUG C. UGA D. UAA E. UAG 80. It is possible for an individual who is XXY to be physically and functionally female due to a mutation in the SRY. What kind of mutation would cause a gene to no longer produce a functional protein? A. silent B. missense C. nonsense D. Robertsonian
81. XXY is an example of A. polyploidy B. aneuploidy C. crossing over 82. What would happen if a severe mutation occurred in the promoter region associated with SRY? A. nothing, the gene itself remained untouched B. transcription would not occur because RNA polymerase cannot identify the promoter 83. If these mutations occurred due to an external factor, such as a chemical, they would be referred to as A. spontaneous mutations B. induced mutations C. point mutations D. deletions 84. What kind of test would you run to determine if a chemical could cause mutations to occur? A. gel electrophoresis B. PCR C. Ames test D. karyotype 85. The test mentioned above would indicate a mutation has occurred when bacteria being grown on a special medium A. all die B. survive C. appear pink in color D. form ring-like growth patterns
------------------------------------------------------------------- End of Scantron Portion ------------------------------------------------------------
In the space provided below answer the following questions. (86-94) You are tasked with breeding bloodhounds. After some research you discover that a large dewlap is dominant to a smooth neck, large floppy ears are dominant to short ears, and dark eyes are dominant to light colored eyes.
You produce the first litter by crossing a light eyed male that is heterozygous for his dewlap and ear length with a light eyed female that is homozygous dominant for her dewlap and ear length. Provide the following information for eye color, dewlap, and ear length. 86. What is the genotype for the dad?
87. What is the genotype for the mom?
88. List all of the gametes that can be produced by the dad:
89. List all of the gametes that can be produced by the mom:
90-91. Set up and solve a Punnett square. (2 points) (show your work)
92. What is the genotypic ratio for the offspring?
93. What is the phenotypic ratio for the offspring?
94. Would it be appropriate to apply a test cross to the puppies youve produced? Why or why not?
95. If you did perform a test cross, what would be the genotype of the other parent?
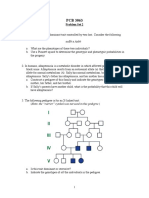
(96-100) Youre asked about coat patterns in bloodhounds, these dogs range from tan to liver to red, but some of them have dark markings and others do not. You search for information regarding the dark markings, but cant find any, so you construct a pedigree diagram to track this dark marking trait.
96. What does a black square indicate?
97. Is this trait autosomal or sex-linked?
98. Is this trait dominant or recessive?
99. What is the genotype for dog A? (remember to report both traits that can be determined from the chart)
100. What is the genotype for dog B?
Mock Exam 4 - Key
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 B A B B A A A B A B A D A C D B D C B A E B B A D 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 A B C D B C D C B C B C B D A C D E B D D C C C A 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 D B A D C E E E A C B C D D D D B AB C E A E B A C 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 A A C B C B B B C B
Mock Exam 4 - Key
In the space provided below answer the following questions. (86-94) You are tasked with breeding bloodhounds. After some research you discover that a large dewlap is dominant to a smooth neck, large floppy ears are dominant to short ears, and dark eyes are dominant to light colored eyes.
You produce the first litter by crossing a light eyed male that is heterozygous for his dewlap and ear length with a light eyed female that is homozygous dominant for her dewlap and ear length. Provide the following information for eye color, dewlap, and ear length. 86. What is the genotype for the dad? eeDdFf 87. What is the genotype for the mom? eeDDFF 88. List all of the gametes that can be produced by the dad: eDF, eDf, edF, edf 89. List all of the gametes that can be produced by the mom: eDF 90-91. Set up and solve a Punnett square. (2 points) (show your work) Eye color Dark = E; Light = e Dewlap Dewlap present = D; Smooth neck = d Ear length Floppy ears = F; Short ears = f
Mock Exam 4 - Key
92. What is the genotypic ratio for the offspring? 1 eeDDFF : 1 eeDDFf : 1 eeDdFF : 1 eeDdFf 93. What is the phenotypic ratio for the offspring? All have light eyes, a dewlap and floppy ears 94. Would it be appropriate to apply a test cross to the puppies youve produced? Why or why not? Yes, All offspring appear dominant. A test cross would determine if an individual is homozygous dominant or heterozygous for a trait. 95. If you did perform a test cross, what would be the genotype of the other parent? eeddff
(96-100) Youre asked about coat patterns in bloodhounds, these dogs range from tan to liver to red, but some of them have dark markings and others do not. You search for information regarding the dark markings, but cant find any, so you construct a pedigree diagram to track this dark marking trait. Dark markings Present = M; absent = m
96. What does a black square indicate? A male with dark markings (or a male expressing the trait in question) 97. Is this trait autosomal or sex-linked? Autosomal 98. Is this trait dominant or recessive? Recessive
99. What is the genotype for dog A? (remember to report both traits that can be determined from the chart) MmXY 100. What is the genotype for dog B?
MMXX MmXY MmXX MMXX mmXY MmXX MmXY MmXX M_XY M_XX mmXX M_XY mmXY
mmXX
mmXY
MmXX MmXX
MmXY
MmXY
MmXX
MmXY
M_XY
M_XX
M_XY
mmXX
Blue = not required for points, but very helpful
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- WhatDocument1 pageWhatalex_gaston_2No ratings yet
- ISYS Chapter 5 VocabDocument3 pagesISYS Chapter 5 Vocabalex_gaston_2No ratings yet
- Treatment MoodDis Student OutlineDocument26 pagesTreatment MoodDis Student Outlinealex_gaston_20% (1)
- KKLKLKDocument1 pageKKLKLKalex_gaston_2No ratings yet
- GGGDocument1 pageGGGalex_gaston_2No ratings yet
- GGGDocument1 pageGGGalex_gaston_2No ratings yet
- In Flight - RK LilleyDocument98 pagesIn Flight - RK LilleyJade Clarke-Mackintosh100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- GeneticsDocument104 pagesGeneticsAlbina AmangaliyevaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Q1 W4Document10 pages9 Science Q1 W4Jewel ParedesNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument11 pagesHeredity and EvolutionWeird DemonNo ratings yet
- Netics by Career Point PDFDocument61 pagesNetics by Career Point PDFmuzamil shabirNo ratings yet
- Incomplete-and-Codominance-Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesIncomplete-and-Codominance-Worksheet Answersreielleceana0779% (19)
- Biological Psychology Kalat 11th Edition Test BankDocument39 pagesBiological Psychology Kalat 11th Edition Test BankJessie Ramirez100% (25)
- CHAPTER 3 Heredity and VariationDocument63 pagesCHAPTER 3 Heredity and VariationLopak TikeNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss - Could It Be Usher Syndrome - PPTX 1.14.13for Posting To WebDocument41 pagesHearing Loss - Could It Be Usher Syndrome - PPTX 1.14.13for Posting To WebrajaalfatihNo ratings yet
- Class X PreBoard QP ScienceDocument10 pagesClass X PreBoard QP ScienceanantshuklaphysicsNo ratings yet
- Sanders C04Document38 pagesSanders C04Vo UyNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical TestDocument9 pages1st Periodical TestJezzaMay TambauanNo ratings yet
- Heterosis: Molecular BasisDocument1 pageHeterosis: Molecular BasisShree Krishna AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Allen Rank Booster Self Evaluation Test-9Document20 pagesAllen Rank Booster Self Evaluation Test-915 Gaurav Jha X-ANo ratings yet
- Bsczo 103 PDFDocument241 pagesBsczo 103 PDFNeeraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Minion Lesson Plan RevisedDocument4 pagesMinion Lesson Plan Revisedapi-257802265No ratings yet
- Grade 8Document2 pagesGrade 8Neptune LopezNo ratings yet
- MIT7 01SCF11 3.3prob1Document4 pagesMIT7 01SCF11 3.3prob1Maureen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressDocument31 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressGlory Mae ProllesNo ratings yet
- Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument10 pagesNon Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceErl denber M. AbordajeNo ratings yet
- Gamsat Practice QuestionsDocument28 pagesGamsat Practice QuestionsDr Peter Griffiths100% (6)
- Aipotu IDocument12 pagesAipotu IsirtrooskawkaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument4 pagesMendelian Genetics423003157No ratings yet
- Mendelian & Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument37 pagesMendelian & Non-Mendelian GeneticsJubair Al-rashid100% (2)
- Genetics Ninestiles TMIDDocument14 pagesGenetics Ninestiles TMIDPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Genetics Problem Set 2Document5 pagesGenetics Problem Set 2kristalNo ratings yet
- SexLinked InheritancePPT2Document45 pagesSexLinked InheritancePPT2ahmedkamalkarar2007No ratings yet
- Biology 9648/01: Temasek Junior College Preliminary Examinations 2015 Higher 2Document18 pagesBiology 9648/01: Temasek Junior College Preliminary Examinations 2015 Higher 2Sun WeilingNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionDocument12 pagesGen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionLeonard CubeloNo ratings yet
- Create A Baby LabDocument4 pagesCreate A Baby Labapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XIDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XINaomeNo ratings yet