Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Guide To Popular Bible Translations
Uploaded by
A. HeraldOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Guide To Popular Bible Translations
Uploaded by
A. HeraldCopyright:
Available Formats
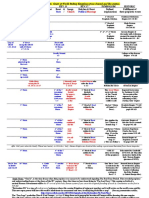
A Guide to Popular Bible Translations
Translation (Abbreviation)
Amplified Bible
Date
1965; updated 1987
Reading Level
NA
Translation Method
Verbal equivalence; amplification of word meanings Hybrid: Verbal equivalence with dynamic balance and common language
Translators
Frances Siewert and Lockman Foundation Editorial Board Common English Bible Committee, an alliance of five denominational publishers (117 translators from 22 faith traditions and 5 countries; 77 field testing groups with 400 participants in 13 denominations) American Bible Society; over 100 translators and reviewers Crossway American Bible Society; Robert Bratcher, NT Bratcher and 6 others, OT 90 scholars, primarily Southern Baptist 54 English scholars
Manuscripts and/or Texts Used
Greek text of Westcott and Hort; various translations
Common English Bible (CEB)
2010, 2011
Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia (4th edition), Biblia Hebraica Quinta (5th edition); Nestle Aland 27th Edition (1993), Gottingen Septuagint (in progress), Ralf's Septuagint (2005) Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia (4th edition), UBS Greek NT (3rd edition, corrected)
Conservative revision of 30-35 passages in the RSV
The Contemporary English Version (CEV) English Standard Version (ESV)
1995
Dynamic equivalence
1951, 2002
11 6
Verbal equivalence Dynamic equivalence
Good News Bible; The Bible in Today's English Version (TEV)
Holman Christian Standard Bible (HCSB) King James Version (KJV)
1976
Biblia Hebraica (3rd edition), UBS Greek NT (3rd edition)
Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia (4th edition), Nestle Aland 27th Edition (1993)
Masoretic (OT), Textus Receptus (NT); The Bishop's Bible, 1568 Paraphrase of American Standard Version (1901) Paraphrase from original languages Masoretic (OT), Nestle-Aland Greek NT
2003
Hybrid: Verbal equivalence with dynamic balance Verbal equivalence
1611
12
The Living Bible (LB) The Message
The New American Bible (NAB) New American Standard Bible (NASB) New Century Version (NCV) New International Version (NIV) New International Reader's Version (NIrV) New Jerusalem Bible New King James Version 1982 (NKJV) New Living Translation (NLT)
1971 The Message 1993; 2001 1970 NT revised, 1986
8 6 7
Paraphrase Paraphrase Dynamic equivalence, 1970; verbal equivalence, 1986
Kenneth Taylor Eugene Peterson 55 scholars, including some Protestants 61 evangelical scholars (original and update), sponsored by Lockman Foundation A team composed of the World Bible Translation Center and 50 scholars and translators
Biblica: 2011 update by 10 person committee ( 2%4% change from 1978 edition) based on some TNIV changes
1971; update 1995
11
Verbal equivalence
Biblia Hebraica, Nestle's Greek Text, 23rd edition (1971); Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia, Nestle-Aland/UBS, 26th edition (1995) Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia; UBS Greek NT Biblia Hebraica; eclectic mix of original texts for NT
1991
Dynamic equivalence Hybrid: Verbal equivalence with dynamic balance Verbal equivalence, with dynamic balance and some simplification Verbal equivalence, with dynamic tendencies Verbal equivalence
1978, 2011
1996
40, including stylists
Simplification of NIV Original Languages; La Bible de Jrusalem (French) Revision of KJV Biblia Hebraica Textus Receptus (NT)
1985 1982
8 11
Approximately 30 Approximately 60 scholars and church leaders 90 scholars, primarily from Trinity Evangelical Divinity School and Asbury Seminary National Council of Churches; 30 scholars 27 scholars and 52 retellers; from the emergent movement
1996; 2007
Dynamic equivalence
Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia; UBS Greek NT (1993), Nestle-Aland Novum Testamentum Graece (1993) Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia (3rd edition); UBS Greek NT (3rd edition, corrected) revision of RSV (1952) not disclosed
*Definitions provided on second page
New Revised Standard Version (NRSV) The Voice
1990
11
Verbal equivalence
2011
Paraphrase
Definitions
Dynamic equivalence:
Emphasis on reproducing the functional meaning of the ancient words with freedom to rearrange the order of the words (syntax) in the target language. The most widely used Hebrew text of the Old Testament. Emphasis is on expressing the meaning in contemporary language, with numerous additional words. "Received Text"; 1550 edition of the Greek NT used by most translators before 1900. Emphasis is on reproducing the modern English equivalent of the ancient words, with tendency to use same word order as the ancient language.
Masoretic: Paraphrase:
Textus Receptus: Verbal equivalence:
You might also like
- Bible Translations ChartDocument3 pagesBible Translations ChartRuth50% (2)
- Old Testament CommentariesDocument27 pagesOld Testament Commentariesffphil100% (1)
- Bible TranslationsDocument195 pagesBible Translationsotorressr100% (4)
- Rose Bible ECharts JudgesDocument2 pagesRose Bible ECharts Judgesganmoses100% (1)
- Bible Translation Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesBible Translation Comparison Charttroconeitor100% (19)
- How We Get Bible PDFDocument18 pagesHow We Get Bible PDFLTTuang100% (5)
- Rose Bible E-Charts Names PDFDocument4 pagesRose Bible E-Charts Names PDFDrum Code100% (2)
- Bible Reading HelpsDocument6 pagesBible Reading Helpslisandersen100% (1)
- Zondervan Essential Companion To Christian History by Stephen BackhouseDocument18 pagesZondervan Essential Companion To Christian History by Stephen BackhouseZondervan100% (3)
- Forever Infallible in Errant (Jeffrey Khoo)Document825 pagesForever Infallible in Errant (Jeffrey Khoo)LarryB100% (1)
- NT Student Guide FinalDocument302 pagesNT Student Guide FinalAbidan GM100% (2)
- Inductive Study OverviewDocument2 pagesInductive Study Overviewlejulie100% (8)
- Rose Bible ECharts FeastsDocument3 pagesRose Bible ECharts FeastsLuisNo ratings yet
- Bible AtlasDocument199 pagesBible AtlasSamuel Maclean Arthur100% (5)
- Rose Bible ECharts Twelve Disciples JamesDocument2 pagesRose Bible ECharts Twelve Disciples JamesEarl OpinionNo ratings yet
- Rose Bible Echarts Mormonism PDFDocument2 pagesRose Bible Echarts Mormonism PDFBalakumar Sh100% (1)
- A General Introduction To The BIBLEDocument501 pagesA General Introduction To The BIBLERuben Beniamin Ghidanac88% (42)
- Catholic Church Methodist Churches Baptist Churches: Denominations Comparison Chart ISBN: 9781890947347, Which AlsoDocument2 pagesCatholic Church Methodist Churches Baptist Churches: Denominations Comparison Chart ISBN: 9781890947347, Which AlsoDhominick Abana Pagulayan100% (1)
- Rose Bible E-Charts Denom PDFDocument2 pagesRose Bible E-Charts Denom PDFkoinoniabcnNo ratings yet
- Bible Study Handbook (PDFDrive) PDFDocument305 pagesBible Study Handbook (PDFDrive) PDFPaskahlita Ruauw100% (4)
- Bible Translation DifferencesDocument30 pagesBible Translation DifferencesA. Herald100% (1)
- Prophetic Chart Daniel RevelationDocument3 pagesProphetic Chart Daniel RevelationFrank Nic. Bazsika100% (1)
- The Bible Old Testament TimelineDocument6 pagesThe Bible Old Testament Timelinebresail4No ratings yet
- The Cycle of Israel's Religious ExperienceDocument59 pagesThe Cycle of Israel's Religious ExperienceHarpak h.khani100% (2)
- Noah's Flood ChiasmDocument3 pagesNoah's Flood ChiasmComprachosNo ratings yet
- Rose Bible E-Charts NamesDocument4 pagesRose Bible E-Charts NamesRa-SoCabAri100% (2)
- Book of Acts SummaryDocument2 pagesBook of Acts SummaryIsrael FortoNo ratings yet
- Jesus Crucifixion Events Rose EchartDocument2 pagesJesus Crucifixion Events Rose Echartgreg_993096093No ratings yet
- Leviticus, Volume III of Commentaries On The PentateuchDocument464 pagesLeviticus, Volume III of Commentaries On The PentateuchChalcedon Foundation100% (8)
- How To Study The BibleDocument2 pagesHow To Study The Biblevolmink100% (15)
- HE LD Estament: UR EW Nderstanding OFDocument1 pageHE LD Estament: UR EW Nderstanding OFKristine Dahang Mabalos100% (1)
- The Passing of Time: The Home Bible Study LibraryDocument13 pagesThe Passing of Time: The Home Bible Study LibraryDr.Terry W. PreslarNo ratings yet
- Basic Bible Survey OT Chapter 5Document5 pagesBasic Bible Survey OT Chapter 5Kim JohnNo ratings yet
- The CSB Baker Illustrated Study Bible SamplerDocument32 pagesThe CSB Baker Illustrated Study Bible SamplerBible Gateway85% (13)
- New Testament SurveyDocument66 pagesNew Testament SurveyAdam89% (9)
- The Bible's Difficult Scriptures EXPLAINED!Document131 pagesThe Bible's Difficult Scriptures EXPLAINED!MustardSeedNews92% (51)
- How To Study The BibleDocument2 pagesHow To Study The Bibleapi-104705434No ratings yet
- CSB Verse Comparison ChartDocument6 pagesCSB Verse Comparison ChartBible Gateway100% (4)
- Facts of The BibleDocument19 pagesFacts of The Biblesmithyjohn13100% (2)
- Dispensation A Theology HeidemanDocument11 pagesDispensation A Theology HeidemanreybeezNo ratings yet
- The TrinityDocument7 pagesThe TrinityDwordwasGod100% (3)
- Nazarene EssentialsDocument59 pagesNazarene EssentialsJames_FogalNo ratings yet
- Ot OutlineDocument1 pageOt OutlineDominic Venuso100% (1)
- Forever SettledDocument168 pagesForever Settledhighmail8877No ratings yet
- Bible Commentary, (1871), 1879 EditionDocument1,668 pagesBible Commentary, (1871), 1879 Editioncoxfn100% (3)
- The 66 Books of The BibleDocument0 pagesThe 66 Books of The BibleA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Study of RomansDocument20 pagesStudy of RomansbubbleNo ratings yet
- How We Got The BibleDocument7 pagesHow We Got The BibleDwordwasGod100% (3)
- Bible Commentary ADocument650 pagesBible Commentary AManuelBentoFalcón100% (1)
- Commentary on Leviticus: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryFrom EverandCommentary on Leviticus: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Commentary on Proverbs: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryFrom EverandCommentary on Proverbs: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryNo ratings yet
- Theological Themes of Psalms: The Theology of the Book of PsalmsFrom EverandTheological Themes of Psalms: The Theology of the Book of PsalmsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bible Translations Comparison: Compare 20 Popular Versions of the BibleFrom EverandBible Translations Comparison: Compare 20 Popular Versions of the BibleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Commentary on 1-2 Timothy and Titus: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryFrom EverandCommentary on 1-2 Timothy and Titus: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryNo ratings yet
- Commentary on Colossians and Philemon: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryFrom EverandCommentary on Colossians and Philemon: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryNo ratings yet
- Commentary on Genesis: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryFrom EverandCommentary on Genesis: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryNo ratings yet
- HCSB - Bible Translation: Navigating the Horizons in Bible TranslationsFrom EverandHCSB - Bible Translation: Navigating the Horizons in Bible TranslationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Commentary on Romans: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryFrom EverandCommentary on Romans: From The Baker Illustrated Bible CommentaryNo ratings yet
- Ecclesiastes in English and HebrewDocument34 pagesEcclesiastes in English and HebrewA. Herald100% (1)
- Original Aramaic Proves Beyond Any Doubt That Jesus Is GodDocument5 pagesOriginal Aramaic Proves Beyond Any Doubt That Jesus Is GodA. Herald100% (2)
- The Two WitnessesDocument3 pagesThe Two WitnessesA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- 14 Reasons To Baptize in Jesus NameDocument2 pages14 Reasons To Baptize in Jesus NameA. Herald100% (2)
- The Ancient Hebrew Lexicon of The BibleDocument616 pagesThe Ancient Hebrew Lexicon of The BibleA. Herald100% (4)
- The Holy Bible Webster's BibleDocument1,311 pagesThe Holy Bible Webster's BibleA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Worshipping GodDocument52 pagesWorshipping GodA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Grief Therapy BookDocument35 pagesGrief Therapy BookA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of The Holy SpiritDocument28 pagesThe Gifts of The Holy SpiritA. Herald100% (4)
- The Lords Prayer GuideDocument1 pageThe Lords Prayer GuideA. Herald100% (1)
- Sent Bib: Ayisyen TradiksyonDocument1,710 pagesSent Bib: Ayisyen TradiksyonA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- How To Pray With PowerDocument2 pagesHow To Pray With PowerA. Herald100% (4)
- The Holy Bible: Websters BibleDocument1,832 pagesThe Holy Bible: Websters BibleA. Herald100% (1)
- Spying Into The Spirit WorldDocument5 pagesSpying Into The Spirit WorldA. Herald100% (1)
- The New Birth BookDocument12 pagesThe New Birth BookA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- I Am A SoldierDocument1 pageI Am A SoldierA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Locked Up: Expanded StudyDocument1 pageLocked Up: Expanded StudyA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Exploring God's Word Online Bible StudyDocument174 pagesExploring God's Word Online Bible StudyA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Exploring God's Word Online Bible StudyDocument174 pagesExploring God's Word Online Bible StudyA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- The Future of The English LanguageDocument0 pagesThe Future of The English LanguageA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- The Three DivisonsDocument1 pageThe Three DivisonsA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- What Does The Holy Ghost Do?Document1 pageWhat Does The Holy Ghost Do?A. Herald100% (1)
- Graddol - English NextDocument132 pagesGraddol - English NextMauro MedenNo ratings yet
- The Holy Bible in Latvian NTDocument388 pagesThe Holy Bible in Latvian NTblainerNo ratings yet
- Success at Bible TeachingDocument0 pagesSuccess at Bible TeachingA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Ask Jesus Into Our HeartDocument7 pagesAsk Jesus Into Our HeartA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- How To Identify Your Spiritual GiftsDocument27 pagesHow To Identify Your Spiritual GiftsA. Herald100% (6)
- The Secret of Spiritual PowerDocument6 pagesThe Secret of Spiritual PowerA. Herald100% (1)
- The Book of RevelationsDocument102 pagesThe Book of RevelationsA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- The Church of Jesus Christ Latter Day SaintsDocument0 pagesThe Church of Jesus Christ Latter Day SaintsA. HeraldNo ratings yet
- Narada Bhakti SutraDocument2 pagesNarada Bhakti SutraPhalgun Balaaji0% (1)
- MRJ Tamil - Satyarth Prakash Part 7 of 7Document103 pagesMRJ Tamil - Satyarth Prakash Part 7 of 7Virendra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sri Vishnu Sahasranamam - Skanda Puranam - TAMDocument12 pagesSri Vishnu Sahasranamam - Skanda Puranam - TAMkaumaaramNo ratings yet
- Vedanta DharaDocument1 pageVedanta DhararraaNo ratings yet
- Iśopanisad: Commentary byDocument115 pagesIśopanisad: Commentary bynitai10885% (13)
- Four Vedas in TamilDocument2 pagesFour Vedas in TamilRazfar33% (3)
- Mandukya UpanishadDocument2 pagesMandukya Upanishadapi-383510067% (3)
- Purashcharanam VidhiDocument1 pagePurashcharanam VidhiVarun Srivatsan100% (2)
- Narayana Upanishad UpdateDocument2 pagesNarayana Upanishad UpdateNityaNiranjan PedroNo ratings yet
- Shiva Sahasranama Linga Purana Tel v1Document21 pagesShiva Sahasranama Linga Purana Tel v1lambatiNo ratings yet
- Vedanga: See AlsoDocument3 pagesVedanga: See AlsocrppypolNo ratings yet
- Yajur Veda-Chapter-40Document13 pagesYajur Veda-Chapter-40ManurbhavNo ratings yet
- How Old Is Vedic Astrology - Vandana RichDocument3 pagesHow Old Is Vedic Astrology - Vandana RichNick KolevNo ratings yet
- NesupamapebariliDocument4 pagesNesupamapebariliBhabani Shankar PadhyNo ratings yet
- Durga Saptashati in HindiDocument160 pagesDurga Saptashati in HindiAnimeshAshuNo ratings yet
- Taittiriya Upanishad KannadaDocument139 pagesTaittiriya Upanishad KannadaRavikiran SuryanarayanamurthyNo ratings yet
- Divine 108 Names of Vishnu The Power of JoyDocument3 pagesDivine 108 Names of Vishnu The Power of JoyGodsutra SutraNo ratings yet
- Gayatri MantraDocument2 pagesGayatri MantraAnandh ShankarNo ratings yet
- Panniru ThirumuraiDocument22 pagesPanniru ThirumuraiRokeshwar Hari Dass100% (4)
- The Text of The NTestament - Critical Editions and Modern Textual CriticismDocument401 pagesThe Text of The NTestament - Critical Editions and Modern Textual Criticismemima7197% (33)
- Sources of Hindu LawDocument14 pagesSources of Hindu LawGauri MittalNo ratings yet
- Shanti Mantra - SiddhartaDocument5 pagesShanti Mantra - SiddhartaVaisnava100% (1)
- Brahmasutra Madhva EnglishDocument367 pagesBrahmasutra Madhva Englishvishal100% (1)
- Bashkala Upanishad (English) PDFDocument8 pagesBashkala Upanishad (English) PDFChristian IrigarayNo ratings yet
- Vishnu Sahasranama Stotram: Class 01 - 27 Feb 2020 Rajesh AnandaramuDocument21 pagesVishnu Sahasranama Stotram: Class 01 - 27 Feb 2020 Rajesh AnandaramuBibekNo ratings yet
- Roga Nashana Vaishnava Kavacham - Garuda Puranam - TAMDocument4 pagesRoga Nashana Vaishnava Kavacham - Garuda Puranam - TAMkaumaaram100% (2)
- Bajrang BaanbbDocument2 pagesBajrang BaanbbsunilNo ratings yet
- 21st Century King James VersionDocument3 pages21st Century King James VersionCyntheilleNo ratings yet
- Gayatri MantraDocument9 pagesGayatri MantraStephane CholletNo ratings yet
- Sreerama's Birth Date - ArticleDocument5 pagesSreerama's Birth Date - Articlejayan65No ratings yet