Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Demand Function For Product X Is Given by
Uploaded by
Anderson AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Demand Function For Product X Is Given by
Uploaded by
Anderson AliCopyright:
Available Formats
The demand function for Product X is given by: = 800- 2Px- 0.05Px -0.2Py + 4Pz + 0.
01I+ 2A
Where Px Price of good X Py Price of related good y Pz Price of related good z I A Income Advertising $7000.00 $250.00 $40.00 $100.00 $120.00
a. (i) Calculate the own Price elasticity of demand (PED) for Good X.
-2(120)-0.05(14400)-0.2(100)+4(40)+0.01(7000)+2(250)
=550 The quantity demanded is equal to 550 which was found using the demand function above. Now the function must be differentiated to find out how much quantity demanded would change with respect to the price of good X: Q/P * P/Q Lets find Q/P Q= 800- 2P-0.05 Q/P= -2 0.1 P If P = 120 then,
Q/P= -2 0.1 P = -2 -0.1 (120) = -14 All the elements of the formula is present so now the elasticity could be found: Q/P * P/Q -14* 120/550 The price elasticity for good X when price is $120 is equal to -3.05 Absolute value= 3.05 ( elastic)
(ii) Discuss whether revenue can be increased by increasing the price of Good X? The Percentage change in price is less than percentage change in quantity demanded. As price increases the revenue earned will decrease because the demand for the good will decrease. Buyers of that product will find a substitute for the product simply because the consumer does not want to spend to much of their income on a product that has been increased when they can get the same benefits of a similar product at a much cheaper price. Therefore the supplier who increases his price will get a decreased revenue. This is also influence by the buyers income and willingness to spend.
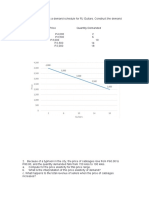
(iii) Illustrate on a well labelled demand graph for Product X, the Total Revenue earned when Price is equal to $120.00. Using the formula for total revenue= Price * Quantity Where Price = $120, and Quantity demanded as found in a(1) = 550 From the graph below it is seen that price=$120 and quantity demanded =550 therefore total revenue earned; Total revenue is therefore equal to 120* 550 = $66000
Demand Graph Showing Quantity plotted Against Price
Price
Price Elasticity of Demand = -3.05
120
Point; P= $120, Q=550
550
Quantity
b. (i) Determine the Cross-Price elasticity of demand (XED) between Good X and Good Y.
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand = % change in quantity demanded for one good/ % change in price of a related good
; Good Y increased from $100 to $140 Therefore the new demand function will read -2(120)-0.05(14400)-0.2(140)+4(40)+0.01(7000)+2(250)
Using the Cross Price Elasticity Formula above: (542-550/550*100) / (140- 100/100 *100) = -1.45/ 40 = -0.04
(ii) Using your answer for b. (i), explain the relationship between Good X and Good Y. (Substitute, Complement etc) From the answer above, it can be said that Goods X and Y are compliments of each other. They are compliments because the Cross price elasticity was a negative value i.e. -0.04
(iii) Determine the Cross-Price elasticity of demand (XED) between Good X and Good Z.
= 800- 2Px- 0.05Px -0.2Py + 4Pz + 0.01I+ 2A ; Pz= $40, , P= $120, Therefore when Pz = $50 -2(120)-0.05(14400)-0.2(140)+4(50)+0.01(7000)+2(250)
When Pz = $40 ,
and , when Pz = $50 ,
Therefore cross elasticity of demand = (590-550/550*100) /(50-40/40*100) =727/25 =0.29 Cross Elasticity of Demand between Goods X and Z = 0.29
(iv) Using your answer for b. (iii), explain the relationship between Good X and Good Z (Substitute, Complement etc)
From the above answer it can be said that goods X and Z are substitutes because the cross price elasticity was a positive figure i.e. 0.29
(v) Based on the solutions for parts b. (i) to (iv) above, suggest one example of an actual agricultural product that fits the description for each of the following: Product X, Product Y and Product Z.
Good X is Wheat and Good Y is Flour. These two are compliments to one another. Furthermore if there is an increase in price for Wheat, the price of flour will increase and the quantity demanded will decrease, therefor from the function it can be said that Good Z could be a substitute for good X and an example for this will be rice because both are staple foods.
c. Consider the following two situations:
Both situations highlighted above, will affect the Total Revenue earned by Producers of Good X. Explain which situation is more beneficial, to the producers of Good X, from a Total Revenue earned perspective.
Situation 1; A 15% increase; 0.29*(15/100)= 0.0435 = 0.0435*550 Quantity = 23.93
Therefore Total revenue= Price *Quantity =23.93 * 40 =$957.2 is the total revenue for good Z
Situation 2; A 60% decrease ; -0.04*-60%=0.024 Quantity =0.024*550= 13.2 Therefore Total Revenue= 13.2*100 =$1320 is the total revenue for good Y
Situation 2 will be more beneficial to the producers of good X because as we can see the total revenue earned for situation 2 which is Y was $1320 as opposed to situation 1 which the total revenue earned was $957.2. As there was a 60% decrease in the price of good Y, there was a greater quantity demanded so therefore a greater overall revenue compared to good Z. Simply put more buyers will be attracted to the cheaper good than the expensive.
d. (i) Calculate the Income elasticity of demand (YED) for Good X
= 800- 2Px- 0.05Px -0.2Py + 4Pz + 0.01I+ 2A -2(120)-0.05(14400)-0.2(140)+4(50)+0.01(8000)+2(250)
= % change in quantity demanded/ % change in income= (YED)
Therefore; (560-550/550*100)/(8000-7000/7000*100) =1.82/14.30 =0.13
(ii) Explain whether Good X is a normal good or an inferior good.
Income elasticity of demand for good X=0.13. Since this is a positive value, good Y is a normal good.
e. Assume that the own Price elasticity of demand (PED) for Good X is -2 and the Income elasticity of Demand (YED) for Good X is 3.
(i) Calculate the percentage change in consumption that will occur, when income declines by twenty percent (20%) .
Income Elasticity declines by 20% then YED= % change of demand/ -20% (a minus is used because it is a decline) = 3 YED= 3 Therefore % change in demand= -20%*3= -60% So when income declines by 20% the % change in consumption is decreased by 60%
(ii) Using the demand function presented for Good X above, determine the new quantity of Good X demanded when income declines by twenty percent (20%) , and the Income Elasticity of Demand (YED) for Good X is 3
Income =$7000 -2(120)-0.05(14400)-0.2(140)+4(50)+0.01(7000)+2(250) When income =$7000 the quantity demanded= 536 Therefore the quantity demanded of good X demanded when income declines by 20% is 536.
f. Suppose that the Cross-price elasticity of demand (XED) between Good X and Good Z is 4. (i) How much would the price of Good Z (Pz) have to change in order to increase the consumption of Good X by twenty five percent (25%)?
If n*2 (XED)= 4 and % change in X demanded=25% Then XED= 25%/ % change in price of good Z=4 Therefore price of good Z would have to change 25%/4= 6.25% Price of good Z would have to increase by 6.25% in order to increase the consumption of good X by 25%. (ii) Use a well-labeled illustration of the demand curve for Good X to show the effect on the demand for Good X, of the change in the Price of Good Z (Pz) as calculated in f. (i)above.
Demand Curve showing the effect on demand for good X, of the change in the price of good Z
Price of good X
Quantity of good X Demanded The graph illustrates rise in price of product X substitutes to shift the demand curve for product X to the right, hence more of product X will be purchased at each price, therefore the quantity demanded will increase.
You might also like
- Advanced Genetics Lecture 1: Chromosome Theory and CytogeneticsDocument39 pagesAdvanced Genetics Lecture 1: Chromosome Theory and CytogeneticsAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Answers to Questions and ProblemsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Answers to Questions and ProblemsAashima GroverNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument20 pagesElasticity of DemandManvendra Shahi100% (1)
- Elasticity of DemandDocument88 pagesElasticity of DemandAkshay ThaparNo ratings yet
- How demand changes based on price, income and cross-price elasticityDocument6 pagesHow demand changes based on price, income and cross-price elasticityHazleen Rostam100% (3)
- Ungraded Exercises Chapter 4-6Document20 pagesUngraded Exercises Chapter 4-6lana del reyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Complete SolutionsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Complete SolutionsVictor64% (14)
- Measurement of ElasticityDocument16 pagesMeasurement of ElasticityLeny MichaelNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Problems Sheet SolutionsDocument13 pagesDemand and Supply Problems Sheet SolutionsAli MehsenNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For AP Biology Practice Exam, Section IDocument13 pagesAnswer Key For AP Biology Practice Exam, Section Ibao'E yourfatherNo ratings yet
- Differentiation What Is Differentiation?Document7 pagesDifferentiation What Is Differentiation?Sohaib Anu100% (1)
- Managerial Economics and Business Strategy 8th Edition Baye Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesManagerial Economics and Business Strategy 8th Edition Baye Solutions ManualGeraldWalkerajqr100% (59)
- Managerial Economics and Business Strategy 9th Edition Baye Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesManagerial Economics and Business Strategy 9th Edition Baye Solutions ManualDrRubenMartinezMDspcg100% (56)
- Anna Kolos EO-107i - Coursework in MicroeconomicsDocument21 pagesAnna Kolos EO-107i - Coursework in MicroeconomicsRohan Nim0% (1)
- Microeconomics - Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesMicroeconomics - Midterm ExamChattip KorawiyothinNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - MergedDocument16 pagesProblem Set 1 - MergedSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Numericals - SS DD-Set IIDocument20 pagesNumericals - SS DD-Set IIudit singhNo ratings yet
- Numericals Solved - Demand Theory - Unit - 3Document6 pagesNumericals Solved - Demand Theory - Unit - 3shankar0% (2)
- Selected Solutions To Homework Problems Winter 2022Document10 pagesSelected Solutions To Homework Problems Winter 2022Amy KelnNo ratings yet
- Assignement - 2 Solution Masud RanaDocument16 pagesAssignement - 2 Solution Masud Ranaboom boomNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 With Answer-1Document7 pagesAssignment - 2 With Answer-1rawan ANo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Managerial Economics and Business Strategy 9th Edition Baye 1259290611 9781259290619Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Managerial Economics and Business Strategy 9th Edition Baye 1259290611 9781259290619daniellecolemizeadcokp100% (25)
- Solutions Final 2010hgdhDocument4 pagesSolutions Final 2010hgdhAnu AmruthNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 QuizDocument3 pagesLesson 2.3 QuizKristina NelsonNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Consumer Choice Concepts ExplainedDocument4 pagesElasticity and Consumer Choice Concepts Explainedm habiburrahman55No ratings yet
- Applied Economics Module 3Document13 pagesApplied Economics Module 3Jiell Renon VigiliaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kuliah Managerial Economic-Chapter 1 Dan 2-FinalDocument4 pagesTugas Kuliah Managerial Economic-Chapter 1 Dan 2-FinalIndria WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Answer Key 2Document4 pagesManagerial Economics - Answer Key 2Mo LashNo ratings yet
- Numericals With IllustrationsDocument19 pagesNumericals With IllustrationsGoutham AppuNo ratings yet
- Pricing ExamplesDocument15 pagesPricing ExamplesKunjal RambhiaNo ratings yet
- Business EcoDocument54 pagesBusiness EcoShi ManNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys (Problem Set-4)Document6 pagesAnswer Keys (Problem Set-4)srivastavavishistNo ratings yet
- How demand, revenue and elasticity relate for good ADocument6 pagesHow demand, revenue and elasticity relate for good AJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENTDocument3 pagesBUSINESS ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENTNguyễn Đức MinhNo ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument23 pagesEconomics AssignmentAqsa AnumNo ratings yet
- f5 Mock SolDocument16 pagesf5 Mock SolSalome farrenNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 3 2022 Income and Cross Price Elasticities Edited 2022 AnsDocument7 pagesPractice Set 3 2022 Income and Cross Price Elasticities Edited 2022 AnsRomit BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Econ Workings ReeditedDocument8 pagesEcon Workings ReeditedPatriqKaruriKimboNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document13 pagesTopic 3Darshilla Rive ChandramNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Practice Problems-Answer KeyDocument5 pagesSession 2-Practice Problems-Answer KeyMuskaan MusicidNo ratings yet
- ME Answer Keys (Problem Set-5) - 2020Document5 pagesME Answer Keys (Problem Set-5) - 2020aksNo ratings yet
- Solution 2Document9 pagesSolution 2Sara HussainNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy AssignmentDocument5 pagesEngineering Economy Assignmentعثمان محيب احمدNo ratings yet
- Mba50 Ex2 202223Document4 pagesMba50 Ex2 202223serepasfNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Derivatives Elasticity and Optimisation Solutions (AutoRecovered)Document8 pagesWorksheet On Derivatives Elasticity and Optimisation Solutions (AutoRecovered)medhaNo ratings yet
- 10 MEP PracticeNumericalsDocument18 pages10 MEP PracticeNumericalsDevansh JainNo ratings yet
- − π > 0, > π. −π < 0, since we stated that actual inflation isDocument3 pages− π > 0, > π. −π < 0, since we stated that actual inflation isMd. ShohagNo ratings yet
- Haiqa's and Saba's PartDocument9 pagesHaiqa's and Saba's Parthaiqa malikNo ratings yet
- Maneco Prelim TPDocument4 pagesManeco Prelim TPAgapito Jr LamelaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Demand CurvesDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Demand Curvesboom boomNo ratings yet
- EC370 Intermediate Microeconomics SolutionsDocument8 pagesEC370 Intermediate Microeconomics SolutionsHamed KhazaeeNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: X S X ZDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: X S X Zlana del reyNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques Assignment 1 Manish Chauhan (09-1128)Document8 pagesQuantitative Techniques Assignment 1 Manish Chauhan (09-1128)manishNo ratings yet
- Solutions to End-of-Chapter ProblemsDocument12 pagesSolutions to End-of-Chapter ProblemsHadia ZafarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design and Economics Homework 5Document10 pagesEngineering Design and Economics Homework 5Sofiane TighiltNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 (Solution)Document3 pagesProblem Set 2 (Solution)Akshit GaurNo ratings yet
- Consumer and Producer Surplus ExplainedDocument10 pagesConsumer and Producer Surplus ExplainedElíGomaraGilNo ratings yet
- (Document) Math Written Report Application of DerivatesDocument9 pages(Document) Math Written Report Application of DerivatespanganibanbeaNo ratings yet
- MBA Study Guide for Florida Orange Juice Market EquilibriumDocument6 pagesMBA Study Guide for Florida Orange Juice Market Equilibriumhimanshu shuklaNo ratings yet
- Luc Duy Khanh - EBBA 13.1 - ASSIGNMENT 2Document4 pagesLuc Duy Khanh - EBBA 13.1 - ASSIGNMENT 2Khánh Lục100% (1)
- AAEC 3301 - Lecture 5Document31 pagesAAEC 3301 - Lecture 5Fitrhiianii ExBrilliantNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Paper2Document7 pagesHurricane Paper2Anderson AliNo ratings yet
- Tropical ForestryDocument45 pagesTropical ForestryAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- Bio 1263 LabDocument8 pagesBio 1263 LabAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- References For Humans EssayDocument1 pageReferences For Humans EssayAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- BIOL2165 Tutorial 1 - Multigene FamilyDocument1 pageBIOL2165 Tutorial 1 - Multigene FamilyAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- BIOL2165 Tutorial 2 Translocation Inversion PolyploidyDocument1 pageBIOL2165 Tutorial 2 Translocation Inversion PolyploidyAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- LiteratureDocument1 pageLiteratureAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- Homework Demand and SupplyDocument4 pagesHomework Demand and SupplyLilia IstratiNo ratings yet
- Presentation Chapter 1 - 4Document95 pagesPresentation Chapter 1 - 4ElearnNo ratings yet
- Why consumption function is crucial for economic analysisDocument9 pagesWhy consumption function is crucial for economic analysisthejibNo ratings yet
- Diminishing Returns of ConsumptionDocument13 pagesDiminishing Returns of Consumptionanil_baroliaNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics Consumer EquilibriumDocument34 pagesMicro Economics Consumer EquilibriumSurajNo ratings yet
- 4 Application of Ss and DD TheoriesDocument60 pages4 Application of Ss and DD TheoriesMilon MirdhaNo ratings yet
- BAC 101 Course Module Week 2Document35 pagesBAC 101 Course Module Week 2Messy S. BegontesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Behavioral Foundation of MacroeconomicsDocument35 pagesChapter Six Behavioral Foundation of MacroeconomicsMERSHANo ratings yet
- DocDocument31 pagesDocolafedNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics (BCOM) - Modue II - 221018 - 165154Document9 pagesManagerial Economics (BCOM) - Modue II - 221018 - 165154ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument4 pagesTheory of Consumer BehaviorKhai VeChainNo ratings yet
- Law of Diminishing Marginal UtilityDocument4 pagesLaw of Diminishing Marginal UtilityVarun AlagNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three - Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument19 pagesChapter Three - Theory of Consumer BehaviorHana LeulsegedNo ratings yet
- Befa Unit 2Document20 pagesBefa Unit 2Manikanta100% (1)
- DemandDocument14 pagesDemand9xy42xfqgcNo ratings yet
- Exceptions To The Law of DemandDocument11 pagesExceptions To The Law of DemandJenson DonNo ratings yet
- ECON 201 - Problem Set 1Document5 pagesECON 201 - Problem Set 1KemalNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply FunctionsDocument35 pagesDemand and Supply FunctionsTimmy Clyde0% (1)
- Intermediate Micro With Calc. ProblemsDocument3 pagesIntermediate Micro With Calc. ProblemsDunbar AndersNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ElasticityDocument7 pagesTutorial ElasticityLena LeezNo ratings yet
- Essential MicroeconomicsDocument101 pagesEssential MicroeconomicsMorteza MehrabiNo ratings yet
- Price Theory Study questions consumer choice modelsDocument22 pagesPrice Theory Study questions consumer choice modelsRajeev ShahiNo ratings yet
- Ags 6Document28 pagesAgs 6hussein harbNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Course Outline for B.A. (Hons) EconomicsDocument2 pagesMicroeconomics Course Outline for B.A. (Hons) Economicsdheeraj sehgalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Equalibrium - Unit 3Document19 pagesConsumer Equalibrium - Unit 3JEHAN mNo ratings yet
- Unit5 (1) (Autosaved)Document36 pagesUnit5 (1) (Autosaved)conan QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Economics Direction: Choose and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer in Each Item BelowDocument4 pagesEconomics Direction: Choose and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer in Each Item BelowMariz Subong GandulinNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument32 pagesDemandKafonyi JohnNo ratings yet