Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Brylle CapiliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Brylle CapiliCopyright:
Available Formats
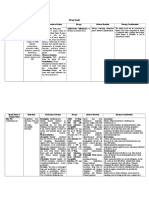
Drug Calcium Gluconate
Class: Mineral
Actions Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the body and is essential for maintenance of the functional integrity of nervous, muscular and skeletal systems and cell membrane an d capillary permeability. It is also an important activator in many enzymatic reactions and is essential to a number of physiologic processes including
Indications Calcium gluconate is used to treat conditions arising from calcium deficiencies such as hypocalcemic tetany, hypocalcemia related to hypoparathyroid ism and hypocalcemia due to rapid growth or pregnancy. It is also used in the treatment of black widow spider bites to relieve muscle cramping and as an adjunct in the treatment of rickets, osteomalacia, lead colic and
Contraindications Calcium salts are contraindicated in patients with ventricular fibrillation or hypercalcemia. Intrave nous administration of calcium is contraindicated when serum calcium levels are above normal. If neonates are required, or expected to require, treatment with calciumcontaining IV solutions, including continuous calcium-containing infusions such as parenteral nutrition, ceftriaxone sodium injection is contraindicated because of the risk of precipitation of ceftriaxone-calcium
Adverse Effects Bradycardia Hypotension Headache Constipation Diarrhea Flatulence Nausea Vomiting Hypomagnesemia Hypophosphatemia Extravasation necrosis
Interventions Assess for cutaneous burning sensations and peripheral vasodilation, with moderate fall in BP, during direct IV injection. Monitor ECG during IV administration to detect evidence of hypercalcemia: decreased QT interval associated with inverted T wave. Observe IV site closely. Extravasation may result in tissue irritation and necrosis. Monitor for hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia. Lab tests: Determine levels of calcium and phosphorus (tend to vary inversely) and magnesium frequently, during
transmission of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, smooth and skeletal muscles; renal function; respiration and blood coagulation. Calcium also plays regulatory roles in the release and storage of neurotransmi tters and hormones, in the uptake and binding of amino acids, and in cyanocobala min (vitamin B12) absorption and gastrin secretion
magnesium sulfate overdosage. Cal cium gluconate has also been employed to decrease capillary permeability in allergic conditions, nonthrombocyto penic purpura and exudative dermatoses such as dermatitis herpetiformis and for pruritus of eruptions caused by certain drugs. In hyperkalemia, calcium gluconate may aid in antagonizing the cardiac toxicity provided the patient is not receiving digitalis therapy
sustained therapy. Deficiencies in other ions, particularly magnesium, frequently coexist with calcium ion depletion
Drug Cefuroxime
Actions
Indications Susceptible bacterial septicemia, lower respiratory or urinary tract, skin and skin structure, meningitis and bone joint infection, gonorrhea. Surgical prophylaxis.
Contraindications
Adverse Effects
Interventions Before giving dug. Ask patient if she is allegic to penicillin or cephalosporin. Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity test giving first dose. Absorption of oral drug is induced.
Cefuroxime is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial Class: infections. Cephalosporin This Antibiotic medication is known as a cephalosporin antibiotic. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (e.g., commo n cold, flu). Unnecessary use or overuse of any antibiotic can lead to its decreased
Cefuroxime >10% (cefuroxime Diarrhea (4-11%; (cefuroxime injection) depends on injection) for Injection duration) USP and Dextrose Injection USP 1-10% is contraindicated in Decreased patients with hemoglobin or known allergy to the hematocrit (10%) cephalosporin group of Eosinophilia (7%) antibiotics. Solutions Nausea or vomiting containing dextrose (3-7%) may be Vaginitis (<5%) contraindicated in Transient rise in patients with hepatic hypersensitivity to corn transaminases (2products. 4%) Diaper rash (3%) Increase in alkaline phosphatase (2%) Thrombophlebitis (2%) Increase in lactate dehydrogenase (1%) <1% Anemia
effectiveness.
Cholestasis Colitis Dyspnea Epidermal necrolysis
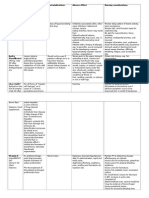
Drug Furosemide
Class: Loop diuretic
Indications For the Furosemide, a treatment of loop diuretic, edema inhibits water associated with reabsorption congestive heart in the failure, cirrhosis nephron by of the liver, and blocking the renal disease, sodiumincluding the potassiumnephrotic chloride syndrome. Also cotransporter for the (NKCC2) in treatment for the thick hypertension alo ascending ne or in limb of the combination loop of Henle. with other This is antihypertensive achieved agents. through competitive
Actions
Contraindications Documented hypersensitivity to furosemide or sulfonamides Anuria Concomitant ethacrynic acid therapy (increases risk of ototoxicity)
Adverse Effects Chest pain chills cough or hoarseness fever general feeling of tiredness or weakness headache lower back or side pain painful or difficult urination sore throat sores, ulcers, or
Interventions Furosemide is often given in conjunction with a potassium supplement or a potassium-sparing diuretic to counteract with potassium chloride.
The medication has a rapid onset of effect of about one hour when taken orally and five minutes by injection.
inhibition at the chloride binding site on the cotransporter , thus preventing the transport of sodium from the lumen of the loop of Henle into the basolateral interstitium. Consequently, the lumen becomes more hypertonic while the interstitium becomes less hypertonic, which in turn diminishes the osmotic gradient for water reabsorption throughout
white spots on the lips or in the mouth swollen or painful glands tightness in the chest unusual bleeding or bruising unusual tiredness or weakness wheezing
Duration of action is about six hours so it is possible to use a twice daily dose if necessary.
the nephron. Because the thick ascending limb is responsible for 25% of sodium reabsorption in the nephron, furosemide is a very potent diuretic..
Drug Lanoxin
Actions Increases force and velocity of myocardial contraction and prolongs refractory period of atrioventricul ar (AV) node by increasing calcium entry into myocardial cells. Slows conduction through sinoatrial and AV nodes and produces antiarrhythmi c effect.
Class: Cardiac glycoside
Indications LANOXIN is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate heart failure in adults. LANOXIN increases left ventricular ejection fraction and improves heart failure symptoms as evidenced by improved exercise capacity and decreased heart failurerelated hospitalizations and emergency care, while having no effect on mortality. Where possible, LANOXIN should be used in combination with a diuretic and an
Contraindications Digitalis glycosides are contraindicated in patients with ventricular fibrillation or in patients with a known hypersensitivity to digoxin. A hypersensitivity reaction to other digitalis preparations usually constitutes a contraindication to digoxin.
Adverse Effects Black, tarry stools blood in the urine or stools bloody vomit pinpoint red spots on the skin rash with flat lesions or small raised lesions on the skin severe stomach pain unusual bleeding or bruising
Interventions 1. Digoxin preparations must be stored in tightly covered, light resistant containers at room temp. 2. FOLLOW CLOSELY (especially in patients receiving diuretics or amphotericin) for decreased serum potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), or thyroxine (T4) along with increased calcium (Ca) will increase digoxin toxicity at a given level. Initial hyperkalemia results from release of intracellular K and indicates serious acute toxicity. 3. Follow HR and rhythm closely 4. Take apical-radial pulse before giving Digoxin; determine
angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.
whether bradycardia exists individualized to patient; if so, notify H.O., check last level result and hold medication 5. Monitor for dysrhythmias; respiratory congestion; peripheral edema 6. Monitor daily weights and perform accurate I & O 7. Order must be taken off by two RNs 8. Obtain periodic EKGs to assess both desired effects and signs of toxicity
Drug Mannitol Class: Diuretics, Osmotic Agents
Actions
Mannitol draws free water out of tissues (including the brain) and into the intravascular space, and can transiently decrease cerebral edema (until excreted by the kidney)
Indications Used for the promotion of diuresis before irreversible renal failure becomes established, the reduction of intracranial pressure, the treatment of cerebral edema, and the promotion of urinary excretion of toxic substances.
Contraindications Well established anuria due to severe renal disease. Severe pulmonary congestion or frank pulmonary edema. Active intracranial ble eding except during craniotomy. Severe dehydration. Progressive renal damage or dysfunction after institution of mannitol (mannitol (mannitol injection) injection) therapy, including increasing oliguria and azotemia. Progressive heart failure or pulmonary congestion after institution of mannitol (mannitol (mannitol injection) injection) therapy. Do not administer to patients with a
Adverse Effects Angina-like chest pains CHF Hypotension Phlebitis Convulsions Chills Dizziness Headache Acidosis Fluid/electrol yte imbalances Thirst Nausea Vomiting Blurred vision
Interventions History: Pulmonary congestion, active intracranial bleeding, dehydration, renal disease, CHF Physical: Skin color, lesions, edema, hydration; orientation, reflexes, muscle strength, pupils; pulses, BP, perfusion; R, pattern, adventitious sounds; urinary output patterns; CBC, serum electrolytes, urinalysis, renal function tests
known hypersensitivity to mannitol
Drug Paracetamol Class: Non-narcotic analgesic Antipyretic
Actions Decreases fever by a hypothalamic effect leading to sweating and vasodilation Inhibits pyrogen effect on the hypothalamicheat-regulating centers Inhibits CNS Prostglandin Synthesis with minimal effects on peripheral prostaglandin synthesis Does not cause ulceration of the GI tract and causes no anticoagulant action.
Indications Paracetamol is an analgesic and antipyretic drug.It is used for the relief of: Mild to moderate pain Fever Migraine Tension headaches
Contraindications Liver Failure Liver Problems Overdose of the Drug Acetaminoph en, Habit of Drinking Too Much Alcohol
Adverse Effects Minimal GI upset. Methemoglobine mia Hemolytic Anemia Neutropenia Thrombocytopeni a Pancytopenia Leukopenia Urticaria CNS stimulation Hypoglycemic coma Jaundice Glissitis Drowsiness Liver Damage
Interventions Do not exceed 4gm/24hr. in adults and 75mg/kg/day in children. Do not take for >5days for pain in children, 10 days for pain in adults, or more than 3 days for fever in adults. ExtendedRelease tablets are not to be chewed. Monitor CBC, liver and renal functions. Assess for fecal occult blood and nephritis. Avoid using OTC drugs with Acetaminophe n. Take with food or milk to minimize GI
upset. Report N&V. cyanosis, shortness of breath and abdominal pain as these are signs of toxicity. Report paleness, weakness and heart beat skips Report abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, itchiness or clay-colored stools. Phenmacetin may cause urine to become dark brown or winecolored. Report pain that persists for more than 3-5 days
Drug Phenobarbital
Class: Barbiturate (long acting), Sedative, Hypnotic, Anticonvulsan t, Antiepileptic agent
Actions General CNS depressant; barbiturates inhibit impulse conduction in the ascending RAS, depress the cerebral cortex, alter cerebellar function, depress motor output, and can produce excitation, sedation, hypnosis, anesthesia, and deep coma; at subhypnotic doses, has anticonvulsant activity, making it suitable for long-term use as an antiepileptic.
Indications Long-term management of tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures and partial seizures; status epilepticus, eclampsia, febrile convulsions in young children. Also used as a sedative in anxiety or tension states; in pediatrics as preoperative and postoperative sedation and to treat pylorospasm in infants
Contraindications Sensitivity to barbiturates; manifest hepatic or familial history of porphyria; severe respiratory or kidney disease; history of previous addiction to sedative hypnotics; uncontrolled pain; pregnancy (particularly early pregnancy) (category D), lactation; sustained release formulation for children < 12 y of age.
Adverse Effects
Interventions
Bradycardia, hypotension, syncope; drowsiness, lethargy, CNS excitation or depression, impaired judgment, hangover effect, confusion, somnolence, agitation, hyperkinesia, ataxia, nervousness, headache, insomnia, nightmares, hallucinations, anxiety, dizziness; rash, exfoliative dermatitis; nausea, vomiting, constipation; agranulocytosis, thrombocytopeni a, megaloblastic
History: Hypers ensitivity to barbiturates, manifest or latent porphyria; marked liver impairment; nephritis; severe respiratory distress; previous addiction to sedativehypnotic drugs; pregnancy; acute or chronic pain; seizure disorders; lactation, fever; hyperthyroidis m; diabetes mellitus; severe anemia; cardiac
anaemia; pain at inj site, thrombophlebitis (IV); oliguria: laryngospasm, respiratory depression, apnoea (especially with rapid IV admin), hypoventilation. Potentially Fatal: Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
disease; shock; uremia; impaired liver or renal function; debilitation Physical: Weig ht; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P, BP, orthostatic BP; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output, liver evaluation; LFTs, renal function tests, blood and urine glucose, BUN
Actions It relieves nasal Salbutamol congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth Class: Bronchodilato muscles of the bronchioles. The relief r (therapeutic); from nasal congestion and bronchospasm is adrenergics (pharmacologi made possible by the following mechanism c) that takes place when Salbutamol is administered. First, it binds to the beta2adrenergic receptors in the airway of the smooth muscle which then leads to the activation of the adenyl cyclase and increased levels of cyclic- 35adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). When cAMP
Drug
Indications Contraindications 1. Hypersensitivity to To control and adrenergic amines prevent reversible airway 2. Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstractive pulmonary disord er (COPD) Quick relief for bronchospasm For the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm Long-term control agent for patients with chronic or persistent bronchospasm
Adverse Effects
Interventions
1. Nervousness 1. Assess lung sounds, 2. Restlessness PR and BP before 3. Tremor drug 4. Headache administration and 5. Insomnia during peak of 6. Chest pain medication. 7. Palpitations 2. Observe fore 8. Angina paradoxical spasm 9. Arrhythmias and withhold 10. Hypertension medication and 11. Nausea and notify physician if vomiting condition occurs. 12. Hyperglycemi 3. Administer PO a medications with 13. Hypokalemia meals to minimize gastric irritation. 4. Extended-release tablet should be swallowed-whole. It should not be crushed or chewed. 5. If administering medication through inhalation, allow at least 1 minute between inhalation of aerosol medication. 6. Advise the patient
increases, kinases are activated. Kinases inhibit the phosphorylation of myosin and decrease intracellular calcium. Decreased in intracellular calcium will result to the relaxation of the smooth muscle airways
to rinse mouth with water after each inhalation to minimize dry mouth. 7. Inform the patient that Albuterol may cause an unusual or bad taste.
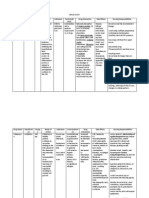
Drug kalium durule (KCl) Class: Electrolyte
Actions Principal intracellular cation of most body tissues, participates in a no. of physiologic processesmaintaining intracellular tonicity; transmission of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle; maint. of normal renal fxn; also plays a role in CHO metabolism & various enzymatic reactions
Indications Prevention and correction of potassium deficiency; when associated w/ alkalosis, use KCl; when associated w/ acidosis use potassium acetate, bicarbonate, citrate, or gluconate
Contraindications Allergy to tartrazine, aspirin; therapy w/ potassium-sparing diuretics / aldosteroneinhibiting agents; severe renal impairment w/ oliguria, anuria, azotemia; hyperkalemia; acute dehydration; heat cramps; GI disorders that delay passage in the GI tract; Use cautiously w/ cardiac disorders
Adverse Effects Dermatologic: Rash GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, GI obstruction-bleedingulceration/perforation Hematologic: Hyperkalemia inc. serum potassium, ECG changes Local: tissue sloughing, local necrosis, local phlebitis, and venospasm w/ injection
Interventions Administer liquid form to any patient w/ delayed GI emptying Administer oral drug after meals or with food and a full glass of water to decrease GI upset, have patient swallow tablet whole Agitate prepared IV solution to prevent layering of potassium, do not add potassium to an IV bag in the hanging position Caution patient not to use salt substitutes and that expended wax matrix capsules will be found in the stool
Drug co-amoxiclav
Actions
Indications Respiratory tract infections caused by strep. Pneumoniae, Group A beta hemolytic strep. Skin and skin structure infections caused by staph., strep. Otitis media, bone infections, GU infections
Contraindications Allergy to cephalosporin or penicillin; use cautiously with renal failure, lactation, pregnancy
Adverse Effects Headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal pain, flatulence, nephrotoxicity, bone marrow, depression, ranging from rash to fever
Interventions Arrange for culture and sensitivity tests of infection before and during therapy if infection does not resolve Give drug with meals, arrange for small frequent meals if GI complications occur
Bactericidal; inhibits synthesis Class: of bacterial cell Antibiotic, wall, causing cell Cephalosporin death (1st Gen)
You might also like
- Using Flowers For HealingDocument28 pagesUsing Flowers For HealingKarina Castilhos100% (1)
- Healthy Cooking Oil from RiceDocument7 pagesHealthy Cooking Oil from Ricehusainkabir63_113901No ratings yet
- Healing With Herbs and SpicesDocument23 pagesHealing With Herbs and Spicesnikanor1100% (2)
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument4 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPBrylle Capili100% (1)
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument4 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPBrylle Capili100% (1)
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument4 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPBrylle Capili100% (1)
- Neuropsychological Assessment in Children and AdolescentsDocument13 pagesNeuropsychological Assessment in Children and AdolescentsPradeep100% (1)
- Hyperparathyroidism and HypoparathyroidismDocument44 pagesHyperparathyroidism and Hypoparathyroidismshweta singhNo ratings yet
- Types of EnemaDocument6 pagesTypes of EnemaOmprakash Saini100% (2)
- Hand Therapy ProtocolsDocument19 pagesHand Therapy ProtocolsjonNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Press CatalogueDocument50 pagesPharmaceutical Press CataloguePharmaceuticalPress50% (2)
- SMLEQBank 15-12-15 PDFDocument294 pagesSMLEQBank 15-12-15 PDFIndrajit Barua0% (2)
- OB Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOB Drug StudyKismet Summons100% (8)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesDrug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsLovely Saad TubañaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- PharmaceuticsDocument76 pagesPharmaceuticsAbdul Manan67% (18)
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesBronchial AsthmaBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Final Case Presentation Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument41 pagesFinal Case Presentation Abnormal Uterine BleedingBrylle Capili67% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument8 pagesSodium BicarbonateRaf AylaniNo ratings yet
- Piroxicam Drug Study: NSAIDs Reduce InflammationTITLE Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Treats Bacterial Infections TITLE Salbutamol Nebulizer Relieves Asthma SymptomsDocument3 pagesPiroxicam Drug Study: NSAIDs Reduce InflammationTITLE Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Treats Bacterial Infections TITLE Salbutamol Nebulizer Relieves Asthma SymptomsBheiatriz de VeraNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- NCP For Bladder CaDocument4 pagesNCP For Bladder CaChris Tine CaccamNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument50 pagesHypercalcemia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentEvelyn EdgarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDocument6 pagesDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykymsh_kimNo ratings yet
- Archer Review Note 5Document11 pagesArcher Review Note 5karan SinghNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument34 pagesEndocrinologymiyuchix100% (2)
- Calcitriol, Calcium Carbonate and Zinc Capsules Calzem CompositionDocument5 pagesCalcitriol, Calcium Carbonate and Zinc Capsules Calzem CompositionAnjali MongaNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument6 pagesDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKuyesNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Complicati On Cause Symptom Management Prevention Patient Related Factors Patient End StrategyDocument12 pagesComplicati On Cause Symptom Management Prevention Patient Related Factors Patient End StrategyChiranjib ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia Pregnancy CaseDocument13 pagesEclampsia Pregnancy CaseJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- M3 - Lesson 1bDocument20 pagesM3 - Lesson 1bLhara MañoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument5 pagesKidneyAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Liver cirrhosis complications and managementDocument39 pagesLiver cirrhosis complications and managementДенис КовшNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritiscathycolNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsStacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid DisorderDocument196 pagesRheumatoid DisorderEndah Dwi AstutiNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Drugs used on urinary systemDocument46 pagesUnit VI Drugs used on urinary systemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- Treatment: Nephrotic SyndromeDocument19 pagesTreatment: Nephrotic Syndromedarwish6m.6elkassNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Drug Study Classification and Effects of Piperacillin Sodium and TazobactamDocument6 pagesDrug Study Classification and Effects of Piperacillin Sodium and TazobactamArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Approach ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesApproach ConsiderationsGunawan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On EpinephrineDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On EpinephrineMaesy Garcia LorenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Medications: LorsartanDocument3 pagesMedications: LorsartanJoy DunwanNo ratings yet
- Reading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Document15 pagesReading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Amlodipine BesylateDocument7 pagesAmlodipine BesylatebabuagoodboyNo ratings yet
- CKD Part 2Document26 pagesCKD Part 2subha95No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesAcute Kidney DiseaseJeff CorpuzNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument6 pagesHyperkalaemiaSSNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Cardiotronic MedicationsDocument13 pagesCardiotronic MedicationsTee WoodNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument4 pagesDiverticulitisBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Bryann Tuason CapiliDocument3 pagesBryann Tuason CapiliBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Chole Lithia SisDocument3 pagesChole Lithia SisBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Cherry Resume 13Document3 pagesCherry Resume 13Brylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesDiabetes MellitusBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- History and GenresDocument8 pagesHistory and GenresBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- COM11 QuestionsDocument1 pageCOM11 QuestionsBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- BSN 2y2-FloDocument1 pageBSN 2y2-FloBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Western XcuseDocument1 pageWestern XcuseBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- OLFU Valenzuela Nursing Fundraising for Sports FestDocument1 pageOLFU Valenzuela Nursing Fundraising for Sports FestBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Close Right Arm Fracture Nursing CareDocument12 pagesClose Right Arm Fracture Nursing CareBrylle Capili100% (1)
- Assessme NT Diagnosis Planning Interventi On Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessme NT Diagnosis Planning Interventi On Rationale EvaluationBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Western CuisineDocument28 pagesWestern CuisineBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Counter Strike CD KEYSDocument2 pagesCounter Strike CD KEYSBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Western XcuseDocument1 pageWestern XcuseBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Geria NCPDocument4 pagesGeria NCPBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- JenikaDocument4 pagesJenikaBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument2 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPMajj Majj100% (2)
- 1965 Cotton Pocket trolley accident police reportDocument2 pages1965 Cotton Pocket trolley accident police reportfireshadow10No ratings yet
- Hig RiskDocument1 pageHig RiskBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Student Handout PDFDocument8 pagesStudent Handout PDFBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- BlackBerry Desktop Software ReadmeDocument3 pagesBlackBerry Desktop Software ReadmeRirin Wahyuni PNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument3 pagesCHNBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument1 pageReferenceBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Health East Avenue Medical Centre East Avenue, Quezon CityDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Health East Avenue Medical Centre East Avenue, Quezon CityBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Bowel EliminationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Impaired Bowel EliminationMara Jon Ocden CasibenNo ratings yet
- Home-Based Care ManagementDocument56 pagesHome-Based Care ManagementJayvee FerandezNo ratings yet
- PCL S PDFDocument1 pagePCL S PDFspectre68No ratings yet
- Managing Diabetes During Ramadan FastingDocument7 pagesManaging Diabetes During Ramadan FastingEstmar ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE - A Review of CliDocument5 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE - A Review of CliJafrinta Irma R.A.No ratings yet
- Niosome Final...Document9 pagesNiosome Final...Ajma LineNo ratings yet
- Partial Versus Radical Nephrectomy: Balancing Nephrons and Perioperative RiskDocument3 pagesPartial Versus Radical Nephrectomy: Balancing Nephrons and Perioperative RiskmssfadNo ratings yet
- PATENT Annexure-A Domestic FilingDocument24 pagesPATENT Annexure-A Domestic FilingMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CA With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument62 pagesColorectal CA With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusJoan Rae TanNo ratings yet
- Sugar PolioDocument3 pagesSugar PolioHenrikas StaniuleviciusNo ratings yet
- Chloramphenicol: Ayen University - Al College of PharmacyDocument7 pagesChloramphenicol: Ayen University - Al College of Pharmacyمحمد حميد عطيةNo ratings yet
- Eular IatDocument7 pagesEular IatPaweł WawrzaszekNo ratings yet
- Chem 353 Pyruvate Dehydrogenase DeficiencyDocument24 pagesChem 353 Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Deficiencyapi-308400395No ratings yet
- Top 40 Eye Medication Names and PricesDocument27 pagesTop 40 Eye Medication Names and Pricesfasta pratamaNo ratings yet
- Brachytherapy: in The Treatment of Breast, Cervical, and Endometrial CancersDocument21 pagesBrachytherapy: in The Treatment of Breast, Cervical, and Endometrial CancerstnpawarNo ratings yet
- AripiprazolDocument12 pagesAripiprazolGabriel LemosNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Depression in Young PeopleDocument11 pagesAnxiety and Depression in Young PeopleKyle SaylonNo ratings yet
- 2006 Magnetom Flash 3 2Document44 pages2006 Magnetom Flash 3 2Herick SavioneNo ratings yet
- What Are Anxiety Disorders/depressions?Document2 pagesWhat Are Anxiety Disorders/depressions?Cams BlogNo ratings yet