Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mankiw Chapter 18 Reading Notes
Uploaded by
ptbarnabicCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mankiw Chapter 18 Reading Notes
Uploaded by
ptbarnabicCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 5 THE MARKETS FOR FACTORS OF PRODUCTION The supply and demand for labor, land, and capital
ital determine the prices paid to workers, landowners, and capital owners Factors of Production- the inputs used to produce goods and services The demand for a factor of production is a derived demand Derived Demand- a firms demand for a factor of production is derived from its decision to supply a good in another market
The Demand For Labor Labor markets are governed by supply and demand
The Competitive Profit- Maximizing Firm It is assumed that the firm is competitive in the market meaning the firm is a price taker It is assumed that the firm is profit maximizing Profit Maximizing- the firms primary goal is to maximize its profit
The Production Function and the Marginal Product of Labor A firm must determine how the size of its labor force impacts its output of goods Production Function- the relationship between the quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output of that good Marginal Product of Labor- the increase in the amount of output from an additional unit of labor Diminishing Marginal Product- the property whereby the marginal product of an input declines the quantity of the input increases
The Value of the Marginal Product and the Demand for Labor Profit Worker = Revenue Worker Wage Value of the Marginal Product- the marginal product of an input times the price of the output Value of the Marginal Product decreases with the increase in labor Marginal Revenue Product- the extra revenue the firm gets from hiring an additional unit of a factor of production A competitive, profit-maximizing firm hires workers up to the point where the value of the marginal product of labor equals the wage o vMPL = Wage
The Value of Marginal Product curve is the labor-demand curve for a competitive profit-maximizing-firm A competitive firm hires labor up to the point at which the value of the marginal product equals wage. A competitive firm hires labor up to the point at which price equals marginal cost
What Causes the Labor- Demand Curve to Shift Factors that may cause the labor- demand curve to shift o Output Price o Technological Change o Supply of Other Factors Output price changes the value of marginal product of labor Technological Advances may increase or reduce the need for laborers Labor Augmenting- technological advance that raises employment Labor Saving- technological advance that reduces employment
The Supply of Labor The Trade-Off Between Work and Leisure People face trade offs Cost of something is what you give up to get it Labor Supply curve may not be upward sloping
What Causes the Labor- Supply Curve to Shift Factors that may shift the Labor- Supply Curve o Changes in Preferences o Changes in Alternative Opportunities o Immigration
Equilibrium in the Labor Market Two facts about how wages determined in competitive labor markets 1. The wage adjusts to balance the supply and demand for labor 2. The Wage equals the value of the marginal product of labor Any event that changes the supply or demand for labor must change the equilibrium wage and the value of the marginal product by the same amount because these must always be equal
Economics of Immigration
Makes more sense to describe immigrants in terms of skill levels than in terms of citizenship Wage effects are ameliorated by immigration
Productivity and Wages Highly productive workers are highly paid Less Productive workers are less highly paid
The Other Factors of Production: Land and Capital Capital- the equipment and structures used to produce goods and services
Equilibrium in The Markets for Land and Capital Purchase Price- the price a person pays to own that factor of production indefinitely Rental Price- the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time Labor, Land, and Capital each earn the value of their marginal contribution to the production process The equilibrium purchase price of a piece of land or capital depends on both the current value of the marginal product and the value of the marginal product expected to prevail in the future.
Linkages Among the Factors of Production When the supply of a factor falls, its equilibrium factor price rises An event that changes the supply of any factor of production can alter the earnings of all the factors
The Economics of the Black Death Wages increased and rents decreased as a result of the Black Plague
You might also like
- Cfin4 Integrative Problem Ch04Document3 pagesCfin4 Integrative Problem Ch04Jagatjeet Mohapatra0% (1)
- Microeconomics Chapter 4 Market Forces Supply DemandDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 4 Market Forces Supply DemandptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet, Class-8 Economics: Chapter 5: Microeconomics and MacroeconomicsDocument2 pagesInformation Sheet, Class-8 Economics: Chapter 5: Microeconomics and MacroeconomicsSami Sumon100% (1)
- Case Study of Costs ConceptDocument21 pagesCase Study of Costs ConceptHosanna AleyeNo ratings yet
- Uhu081 PDFDocument2 pagesUhu081 PDFsahibjotNo ratings yet
- CryptoDocument57 pagesCryptoafs100% (1)
- Carlinsoskice Solutions ch02Document10 pagesCarlinsoskice Solutions ch02Clara Lustosa100% (1)
- Panjab University, Chandigarh-160014 (India) : Faculty of Business Management and CommerceDocument79 pagesPanjab University, Chandigarh-160014 (India) : Faculty of Business Management and CommerceVidhu Vasav GillNo ratings yet
- Consumer Choice Theory ExplainedDocument24 pagesConsumer Choice Theory ExplainedSurendra Singh100% (1)
- Session 3-Summary PDFDocument4 pagesSession 3-Summary PDFRajAt D Everaj EverajNo ratings yet
- Recrdian Theory of RentDocument1 pageRecrdian Theory of Rentkumarrohit007No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Notes Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument1 pageChapter 6 Notes Principles of MicroeconomicsDerek Ng100% (1)
- Foreign Aid and Foreign InvestmentDocument16 pagesForeign Aid and Foreign InvestmentKumkum SultanaNo ratings yet
- Consumers EquilibriumDocument52 pagesConsumers EquilibriumabdanNo ratings yet
- Cost of ProductionDocument46 pagesCost of ProductionYavin VencatapillayNo ratings yet
- National Colloquium On Rural Management: Referred From The Profile of MR SinghDocument5 pagesNational Colloquium On Rural Management: Referred From The Profile of MR SinghApoorv SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Managerial AssignmentDocument5 pagesManagerial AssignmentHajra ANo ratings yet
- Notes Economics Mankiw CH 1Document2 pagesNotes Economics Mankiw CH 1Jeegar BhattNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics AssignmentDocument17 pagesManagerial Economics AssignmentDeepshikha Gupta50% (2)
- Principles of Economics - The Classical Long Run ModelDocument53 pagesPrinciples of Economics - The Classical Long Run ModelMIchael Jay GuintoNo ratings yet
- Moving Average Forecast for Period 6Document13 pagesMoving Average Forecast for Period 6Star Dimasaca BenturadoNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Merit, Public and Private GoodsDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Merit, Public and Private GoodsMehak KaushikkNo ratings yet
- International Economic EnvironmentDocument24 pagesInternational Economic EnvironmentRocKstar AbhiNo ratings yet
- Role of Government in Market EconomiesDocument24 pagesRole of Government in Market EconomiesManjunath ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Sde173 PDFDocument68 pagesSde173 PDFMuhammad Rifki0% (1)
- CH 29Document36 pagesCH 29Robelen CallantaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 - Law of Demand in A City of GujaratDocument1 pageCase Study 1 - Law of Demand in A City of GujaratSatyam VidyarthiNo ratings yet
- Cost Benefit AnalysisDocument4 pagesCost Benefit Analysisamara_amzNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics AssignmentDocument2 pagesManagerial Economics Assignmentharshit2010pmbNo ratings yet
- The duel between Mercedes and TeslaDocument17 pagesThe duel between Mercedes and TeslaAyan DasNo ratings yet
- Role of Green Economy in The Context of Indian EconomyDocument5 pagesRole of Green Economy in The Context of Indian EconomyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument3 pagesDemand and SupplyShalu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Social and Environmental Acc.Document15 pagesSocial and Environmental Acc.Ňïł Chowdhury JoyNo ratings yet
- Exchange RateDocument10 pagesExchange RateSteeeeeeeephNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Concept of National Income AccountingDocument37 pagesUnderstanding the Concept of National Income Accountingshivanshu123No ratings yet
- Ricardo Theory of Land Rent ModelDocument4 pagesRicardo Theory of Land Rent ModelnyapnyapokeNo ratings yet
- Indifference Analysis ExplainedDocument91 pagesIndifference Analysis ExplainedShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate RiskDocument30 pagesExchange Rate RiskPallabi DowarahNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow ModelDocument12 pagesCircular Flow ModelpodderNo ratings yet
- Bovee Bia 2ce ch03 Stu-1Document19 pagesBovee Bia 2ce ch03 Stu-1Mwongera MwaraniaNo ratings yet
- ch02 - EFFICIENT MARKETS AND GOVERNMENTDocument18 pagesch02 - EFFICIENT MARKETS AND GOVERNMENTwatts183% (6)
- MBS I Sem Ch-1Document55 pagesMBS I Sem Ch-1bijay adhikari100% (2)
- Methodology of Calculating CPI in Bangladesh PDFDocument7 pagesMethodology of Calculating CPI in Bangladesh PDFShahriar Azad100% (1)
- Intercultural EncountersDocument38 pagesIntercultural EncountersAngelyn LingatongNo ratings yet
- EAB Numerical Elasticity of DemandDocument10 pagesEAB Numerical Elasticity of DemandReeha NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Law of Demand - Elasticity of Demand PDFDocument134 pagesLaw of Demand - Elasticity of Demand PDFNitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CONTRADICTIONS OF FREE TRADEDocument25 pagesCONTRADICTIONS OF FREE TRADEramkumar100% (1)
- Various Forces of Change in Business EnviromentDocument5 pagesVarious Forces of Change in Business Enviromentabhijitbiswas25No ratings yet
- Prepared by Iordanis Petsas To Accompany by Paul R. Krugman and Maurice ObstfeldDocument39 pagesPrepared by Iordanis Petsas To Accompany by Paul R. Krugman and Maurice ObstfeldNazish GulzarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: Neha AggarwalDocument82 pagesEnvironmental Science: Neha AggarwalPayel Dutta100% (1)
- Microeconomics Chapter 2 - The Economic Problem Scarcity and ChoiceDocument46 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 2 - The Economic Problem Scarcity and ChoicecristalNo ratings yet
- Shri. K.M. Savjani & Smt. K.K. Savjani B.B.A./B.C.A College, VeravalDocument26 pagesShri. K.M. Savjani & Smt. K.K. Savjani B.B.A./B.C.A College, VeravalKaran DalkiNo ratings yet
- Body - Shop - An Exploration of Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument5 pagesBody - Shop - An Exploration of Corporate Social ResponsibilitykarellteNo ratings yet
- Innovative and Sustainable Business ModelDocument12 pagesInnovative and Sustainable Business ModelYossy RyanantaNo ratings yet
- IS-LM Curve Model ExplainedDocument28 pagesIS-LM Curve Model ExplainedabhishekNo ratings yet
- NegotiationsDocument5 pagesNegotiationsAre EbaNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth & Economic DevelopmentDocument20 pagesEconomic Growth & Economic DevelopmentMayank JhaNo ratings yet
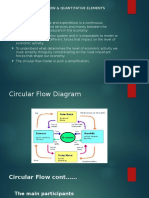
- Week5-6: Circular Flow & Quantitative ElementsDocument4 pagesWeek5-6: Circular Flow & Quantitative ElementsMmapontsho TshabalalaNo ratings yet
- Daniels - IBT - 16e - Final - PPT - 07 Economic Integration and CooperationDocument42 pagesDaniels - IBT - 16e - Final - PPT - 07 Economic Integration and Cooperationrola mohammadNo ratings yet
- Instruments of International Trade PoliciesDocument11 pagesInstruments of International Trade PoliciesDinesh GannerllaNo ratings yet
- Theory of DemandDocument10 pagesTheory of DemandSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Demand ElasticityDocument12 pagesChapter 04 Demand Elasticity1234assNo ratings yet
- Factor Markets and The Income DistributionDocument17 pagesFactor Markets and The Income Distributionshabbirmia570No ratings yet
- French Revolution Reign of Terror executions describedDocument2 pagesFrench Revolution Reign of Terror executions describedptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Pyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsDocument2 pagesPyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution DBQDocument2 pagesThe Industrial Revolution DBQptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Napoleon's Proclamation to Strengthen His PowerDocument1 pageNapoleon's Proclamation to Strengthen His PowerptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Therapy ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter 15 Therapy ReviewptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Pyromania Project PicturesDocument1 pagePyromania Project PicturesptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- ZIonism and Theodore HerzlDocument2 pagesZIonism and Theodore HerzlptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Martin Luther King Is Mistakenly OverDocument1 pageMartin Luther King Is Mistakenly OverptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Psychology DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPsychology DefinitionsptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- MIddle Sexes Psychology MovieDocument3 pagesMIddle Sexes Psychology MovieptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Inception ProjectDocument3 pagesInception ProjectptbarnabicNo ratings yet
- Micro Real Final S2022 Solns PDFDocument9 pagesMicro Real Final S2022 Solns PDFjay WuNo ratings yet
- Pretest NCFDocument4 pagesPretest NCFShane BellenNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Notes 14Document23 pagesManagerial Economics Notes 14bevinj100% (2)
- Aqa Econ1 QP Jun12Document16 pagesAqa Econ1 QP Jun12sexysexy21No ratings yet
- Principles of Economics: Twelfth EditionDocument39 pagesPrinciples of Economics: Twelfth EditionYara BallanNo ratings yet
- The Economic Implications of Learning by Doing - ArrowDocument20 pagesThe Economic Implications of Learning by Doing - ArrowjosecaceresNo ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument3 pagesMarket EquilibriumAudrey NahuriraNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Invisible Hand and How Markets WorkDocument23 pagesUnderstanding the Invisible Hand and How Markets WorkEthelyn Cailly R. ChenNo ratings yet
- Classical Theory of Income & Employment Lecture 5Document10 pagesClassical Theory of Income & Employment Lecture 5Salman HaiderNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Syllabus GuideDocument5 pagesIGCSE Economics Syllabus Guideครูพิเศษ EFLNo ratings yet
- LECG Bid For CIRM Economic StudyDocument37 pagesLECG Bid For CIRM Economic StudyCalifornia Stem Cell ReportNo ratings yet
- Macro CH 17 Monetary Growth & InflationDocument10 pagesMacro CH 17 Monetary Growth & InflationAshkan TorkamanNo ratings yet
- Tokenomics Dynamic Adoption and ValuationDocument38 pagesTokenomics Dynamic Adoption and Valuationm_vamshikrishna22No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Is & LM AnalysisDocument16 pagesUnit 5 Is & LM AnalysisAnshumaan PatroNo ratings yet
- Economics 1501 1: What Economics Is All About: Product Possibility Curve (PPC Curve)Document51 pagesEconomics 1501 1: What Economics Is All About: Product Possibility Curve (PPC Curve)Zahied MukaddamNo ratings yet
- Lectures On WalrasDocument13 pagesLectures On WalrasMiah Maye PormonNo ratings yet
- ECON3007 Tutorial 2 2017Document3 pagesECON3007 Tutorial 2 2017Sta KerNo ratings yet
- Monetary Economics and Global Economy: Macroeconomics (7ed)Document77 pagesMonetary Economics and Global Economy: Macroeconomics (7ed)(K12HN) Nguyen Thuy LinhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Theory of MarketsDocument24 pagesLecture Notes: Theory of MarketsAdruffNo ratings yet
- Econ 04Document23 pagesEcon 04Whiterose TranNo ratings yet
- Shy Chapter 7Document18 pagesShy Chapter 7Prinny ThomasNo ratings yet
- Final 2020 SolutionDocument12 pagesFinal 2020 SolutionShokhrud SafarovNo ratings yet
- Ebook College Algebra With Applications For Business and Life Sciences 2Nd Edition Larson Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesEbook College Algebra With Applications For Business and Life Sciences 2Nd Edition Larson Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsorrancemaneuverpmvll100% (10)
- Unit 4 Supply - Demand NotesDocument40 pagesUnit 4 Supply - Demand NotesKaidontlivehereNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solutions To Assignment 2 (OPTIONAL)Document10 pagesSuggested Solutions To Assignment 2 (OPTIONAL)famin87No ratings yet
- Review Exercises: X y # F FDocument5 pagesReview Exercises: X y # F Ffjavier.hernandezNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Emotional Intelligence On Work Life Balance An EmpiricalDocument309 pagesThe Impacts of Emotional Intelligence On Work Life Balance An EmpiricalRajlaxmi GargNo ratings yet