Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lapchole Inst
Uploaded by
Sugar Capule - ManuelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lapchole Inst
Uploaded by
Sugar Capule - ManuelCopyright:
Available Formats
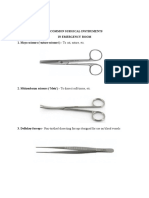
Needle holder - use to hold suturing needle for closing wounds during suturing and surgical procedure.
Dissection hook - use as probes for dissection and for raising blood vessels.
Cautery spatula - coagulating instrument to control of bleeding for hemostasis.
Clip applicator - use to clip or grasp tissues in place.
Hook scissor - Connected to diathermy this instrument is the main dissector used in laparoscopic surgery
Curved scissor - often cutting tools with blades that are bent to accommodate some specific cutting tasks
Sterilization ring applicator - use if sterilization procedure is needed. Toothed Grasper - Used for grasping tough tissue particularly if it is to be resected as the teeth may damage normal tissues.
Suction irrigation cannula - designed to provide clog-free suction, ensuring laparoscopic procedure progress smoothly.
Scissor - use to cut tough tissues
Atraumatic Grasper - Although more delicate than their toothed counterparts these dissectors may still damage normal tissue and care must
always be taken when handling delicate structures.
Suction Irrigator - A combination instrument that allows irrigation with fluid and suction to clear the area through the same instrument. Veress needle - a spring-loaded needle used to create pneumoperitoneum for laparoscopic surgery
Trocar & Cannula - is a medical instrument with a sharply pointed end, often three-sided, that is used inside a hollow cylinder (cannula) to introduce this into blood vessels or body cavities. Trocars are also used to introduce ports in the abdomen, such as during laparoscopic surgery
Olsen-Reddick - used to perform operative cholangiography. A catheter is passed down the centre of the instrument which also has a clamping mechanism to hold the catheter in position within the duct.
Stone Scoop - useful to pick up and retrieve small dropped items without crushing them such as gallstones during laparoscopic surgery.
Telescope - secondary effect of allowing others to view the surgical field either on color video monitors or by watching the video feed over the Internet at a remote location
Maryland Grasper - Slightly curved graspers that can be used to bluntly dissect as well as grasp tissue.
Cautery used to burn a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it
Mixters - Right angled instruments in either 5 or 10mm that are used to pass behind structures.
Disposable suture - Allows simple single handed placement of sutures and knot tying
Heavy toothed grasper - long shard teeth that cause significant trauma to tissues. They do provide a firm grasp on most tissues though and are used to retrieve resected specimens such as the gallbladder for removal from the abdomen
Ultrasonic dissector - Using mechanical energy the ultrasonic dissector coagulates and cuts tissue with excellent haemostatic properties and little dissemination of energy into surrounding tissues.
Laparoscopic ultrasound probe - Used primarily in the staging of upper gastrointestinal malignancies. The combination of exploratory laparoscopy and ultrasound examination of the liver, nodes and other solid organs allows improved patient selection for attempted curative resection
Disposable tacking device - spiral tack allows fixation of meshes during laparoscopic hernia repair.
Disposable bag - Allows containment of resected tissue to prevent soilage with infection or malignancy thereby preventing contamination and spread
Disposable stapler-cutter - particular device allows different sizes of staple to be fired by the same body of the stapler. Hinged mechanisms or "roticulating" devices improve access and positioning during laparoscopic surgery.
Disposable retractor - Passed through a 10mm port this instrument then fans out to provide broad retraction.
Laparoscopic tower - particular device allows different sizes of staple to be fired by the same body of the stapler. Hinged mechanisms or "roticulating" devices improve access and positioning during laparoscopic surgery.
You might also like
- Study The Following Instruments. Be Able To Identify and Know Its UsesDocument2 pagesStudy The Following Instruments. Be Able To Identify and Know Its UsesJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Cmca Rle L5 PrelimsDocument8 pagesCmca Rle L5 PrelimsJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Dissecting ForcepsDocument9 pagesDissecting ForcepsYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument41 pagesSurgical InstrumentsRen Mark CanlasNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument51 pagesAppendectomymoqtadirNo ratings yet
- Mayo Scissors CurvedDocument20 pagesMayo Scissors CurvedASHISH KUMAR YADAV100% (1)
- 20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErDocument8 pages20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErMelissa GoNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErDocument8 pages20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErMelissa GoNo ratings yet
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocument54 pagesBasic Surgical InstrumentsAlyssa CastroNo ratings yet
- Urinary InstrumentDocument3 pagesUrinary InstrumentHuey ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3a Surgical InstrumentsDocument47 pages3a Surgical Instrumentssoban moriwalaNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument50 pagesSurgical InstrumentsmUniKee_03873950% (2)
- Hysteroscopy MedscapeDocument23 pagesHysteroscopy MedscapeMaqsoodUlHassanChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Operating Room InstrumentsDocument59 pagesOperating Room InstrumentsMayolianne DumayNo ratings yet
- Or and DR Instruments PDFDocument59 pagesOr and DR Instruments PDFMayolianne Dumay100% (1)
- Surgical InstrumentDocument5 pagesSurgical Instrumentria_soriano_2100% (1)
- Normal Delivery Instrument SetsDocument14 pagesNormal Delivery Instrument SetsFrances Kaye Sta. CruzNo ratings yet
- NCMB312 RLE OR Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic Techniques PDFDocument70 pagesNCMB312 RLE OR Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic Techniques PDFwokorow100% (1)
- Common or InstrumentsDocument16 pagesCommon or InstrumentsCosmic PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nursing 3Document20 pagesAdvanced Nursing 3Justus NwakaNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Instruments Delivery Room InstrumentsDocument5 pagesOperating Room Instruments Delivery Room InstrumentsCharme Jean RaygonNo ratings yet
- OBG ARTICLES ANUM NooriDocument22 pagesOBG ARTICLES ANUM NooriVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Dilation and CurettageDocument4 pagesDilation and CurettageFernandez, Florence NicoleNo ratings yet
- Show and Tell InstrumentsDocument7 pagesShow and Tell InstrumentsAyako K. SUGIMOTONo ratings yet
- What Happens in The Operating RoomDocument137 pagesWhat Happens in The Operating RoomMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- An Assignment On: Submitted By-Submitted ToDocument19 pagesAn Assignment On: Submitted By-Submitted ToANUM NOORINo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Retrival DevicesDocument6 pagesEndoscopic Retrival Deviceschennai1stNo ratings yet
- Instruments PDFDocument26 pagesInstruments PDFTricia Andrei BonifacioNo ratings yet
- 13 Principles of Sterile TechniqueDocument3 pages13 Principles of Sterile TechniqueOlive Keithy Ascaño ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ot Instruments: Ms. Revathy. ADocument60 pagesOt Instruments: Ms. Revathy. AREVATHY.ANo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Tissue: Approxima TionDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic Tissue: Approxima TionDianNo ratings yet
- Portafolio de Instrumental QuirúrgicoDocument30 pagesPortafolio de Instrumental QuirúrgicoLeonardo Fabio Martinez VentoNo ratings yet
- Cutting and Dissecting Grasping and Clamping Retracting Probing and DilatingDocument77 pagesCutting and Dissecting Grasping and Clamping Retracting Probing and DilatingAndrea Pugh0% (1)
- DsaDocument235 pagesDsaLalaine De Jesus100% (1)
- Medical Supplies and InstrumentsDocument41 pagesMedical Supplies and Instrumentsriska silviaNo ratings yet
- Dilatation and Curettage InstrumentsDocument7 pagesDilatation and Curettage InstrumentsJamaica Leslie Noveno0% (1)
- Basic InstrumentationDocument55 pagesBasic Instrumentationmirai desu100% (1)
- Instrument of NormalDocument17 pagesInstrument of NormalEdraline Lumawig100% (2)
- Or Instruments SampleDocument9 pagesOr Instruments SampleSonia Letran SingsonNo ratings yet
- Uses of Surgical InstrumentsDocument10 pagesUses of Surgical InstrumentsjaidinjdNo ratings yet
- SialendosDocument18 pagesSialendosDr. T. Balasubramanian50% (2)
- NCMB312 RLE or Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic TechniquesDocument70 pagesNCMB312 RLE or Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic TechniquesNine SoleilNo ratings yet
- Basic SetDocument6 pagesBasic SetMelanie Moises JavierNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Surgical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Surgical InstrumentsKhawaja EshaNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Equipments and Machineries: By: RICACHO, Ma. Norilyn BSN4B - Group8Document38 pagesOperating Room Equipments and Machineries: By: RICACHO, Ma. Norilyn BSN4B - Group8Katrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Minor Oral Surgical Principles (NXPowerLite) / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument42 pagesMinor Oral Surgical Principles (NXPowerLite) / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- A Surgical InstrumentsDocument14 pagesA Surgical InstrumentsSanela DžanovićNo ratings yet
- Slides Surgical InstrumentsDocument43 pagesSlides Surgical InstrumentsHoney May Rollan Vicente100% (1)
- Types of Sutures and Their IndicationsDocument6 pagesTypes of Sutures and Their IndicationsAdina BurciuNo ratings yet
- OR InstrumentsDocument56 pagesOR Instrumentssellyna SaidinNo ratings yet
- Duties and Responsibilities of Scrub Nurse:: Before An OperationDocument7 pagesDuties and Responsibilities of Scrub Nurse:: Before An OperationMary Grace Relato BapialNo ratings yet
- Instruments For Basic Oral SurgeryDocument35 pagesInstruments For Basic Oral Surgeryahmed amerNo ratings yet
- Open Chole InstruDocument4 pagesOpen Chole InstruRI NANo ratings yet
- Equine Castration and CryptorchidismDocument14 pagesEquine Castration and CryptorchidismNatalie Howard100% (1)
- Cesarian Section Surgical Instrument SetDocument17 pagesCesarian Section Surgical Instrument SetHashmein Estrada Ramos100% (1)
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument53 pagesSurgical InstrumentsAbhishekNo ratings yet
- DrtfygbyuijDocument29 pagesDrtfygbyuijBibek RajNo ratings yet
- Richard PDFDocument2 pagesRichard PDFNidaNo ratings yet
- Imci 2Document39 pagesImci 2Sugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP TetanusDocument2 pagesNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- OsteoDocument3 pagesOsteoSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP Copd AirwaySugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyRespiDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyRespiSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- MMDSTDocument69 pagesMMDSTSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument1 pageMuscular SystemSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Glasgow Coma ScaleDocument3 pagesGlasgow Coma ScaleLanie Reyes de Guzman0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Document11 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Sugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Poc ScoliosisDocument20 pagesPoc ScoliosisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- PocDocument7 pagesPocSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans: Also Known AsDocument7 pagesThromboangiitis Obliterans: Also Known AsSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument8 pagesGliclazideSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Pott's DiseaseDocument8 pagesPott's DiseaseLorebell100% (2)
- Cancer NursingDocument208 pagesCancer NursingSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Particular CancersDocument8 pagesParticular CancersSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Femoral Neck FractureDocument21 pagesFemoral Neck FractureSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristDocument1 pageNursing TheoristSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument8 pagesGliclazideSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Mini Mental State ExaminationDocument4 pagesMini Mental State ExaminationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis HerpetiformisDocument11 pagesDermatitis HerpetiformisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- 3A Non Therapeutic CommDocument11 pages3A Non Therapeutic CommSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Background of The Study (Imci) Nora Paps REVISEDDocument2 pagesBackground of The Study (Imci) Nora Paps REVISEDSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument11 pagesCholelithiasisSugar Capule - Manuel100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- ESTAVILLO, Karen G. (FEVER UTI, CONSTI)Document4 pagesESTAVILLO, Karen G. (FEVER UTI, CONSTI)Karen EstavilloNo ratings yet
- Ecg PlacementDocument7 pagesEcg PlacementOliver Bagarinao100% (1)
- The Rolle of Surgery in Oncology: Surgery Departement Medical Faculty Ukrida UniversityDocument25 pagesThe Rolle of Surgery in Oncology: Surgery Departement Medical Faculty Ukrida UniversityGian Alodia RisamasuNo ratings yet
- Conrad Munashe Mashazhike: 58 Tembisa Section - +27 68 225 5504 - 25 May 2022Document3 pagesConrad Munashe Mashazhike: 58 Tembisa Section - +27 68 225 5504 - 25 May 2022Nathi MashazhikeNo ratings yet
- American Health National Security (HNS) Issue Omission Resolution Green Paper CD Fax Version 5-07-2010Document66 pagesAmerican Health National Security (HNS) Issue Omission Resolution Green Paper CD Fax Version 5-07-2010George SingletonNo ratings yet
- Medical TechnologistDocument2 pagesMedical Technologistapi-307429612No ratings yet
- Anti-HSV-2 IgG Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2Document2 pagesAnti-HSV-2 IgG Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2ElenaNo ratings yet
- Cook & Zumla - Manson's Tropical DiseasesDocument98 pagesCook & Zumla - Manson's Tropical DiseasessDamnNo ratings yet
- Medicinecomplete Clark Drug and PoisonDocument25 pagesMedicinecomplete Clark Drug and PoisonArménio SantosNo ratings yet
- Johnmar Abuan Health Activity 1: Ready To Go Situation 1Document10 pagesJohnmar Abuan Health Activity 1: Ready To Go Situation 1Katherine B. AbuanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) / Pengkajian: Paripurna Pasien Geriatri (P3G)Document55 pagesComprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) / Pengkajian: Paripurna Pasien Geriatri (P3G)SARAH AZIZAH 2015No ratings yet
- MenorrhagiaDocument44 pagesMenorrhagiaHugh Jacobs100% (1)
- Roleplay Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesRoleplay Discharge PlanningAnonymous KQKONmD9H100% (1)
- Treatment of Legionella Pneumonia: James YewDocument14 pagesTreatment of Legionella Pneumonia: James Yewyewha550No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlancnvfiguracionNo ratings yet
- Artikel Yang Telah Terakreditasi HONcodeDocument5 pagesArtikel Yang Telah Terakreditasi HONcoderidhola15No ratings yet
- Molecular Research in Human MicrobiomeDocument212 pagesMolecular Research in Human MicrobiomeLiceul Teoretic Mihail KogalniceanuNo ratings yet
- Telehealth Research and Evaluation Implications For Decision MakersDocument9 pagesTelehealth Research and Evaluation Implications For Decision Makerscharlsandroid01No ratings yet
- Date and Time Focus: D - Received Patient On BedDocument2 pagesDate and Time Focus: D - Received Patient On BedGraphaiene Neika WacasNo ratings yet
- FDA Inspection in India (2005 - 2012)Document11 pagesFDA Inspection in India (2005 - 2012)Asijit SenNo ratings yet
- Damage Control Orthopaedics DR Bambang SpOT (Salinan Berkonflik Enggar Yusrina 2015-10-14)Document37 pagesDamage Control Orthopaedics DR Bambang SpOT (Salinan Berkonflik Enggar Yusrina 2015-10-14)SemestaNo ratings yet
- Home Environmental AssessmentDocument2 pagesHome Environmental AssessmentSelvi Puspa SariNo ratings yet
- Determination of Risk Factors For Drug - Related Problems - A Multidisciplinary Triangulation ProcessDocument7 pagesDetermination of Risk Factors For Drug - Related Problems - A Multidisciplinary Triangulation Processzenita reizaNo ratings yet
- Karyotyping Activity Week 2 - Ian SibalDocument6 pagesKaryotyping Activity Week 2 - Ian SibalIan SibalNo ratings yet
- Actinomycosis: DR Maleeha Zia Mufti Lecturer Pathology Department AmcDocument21 pagesActinomycosis: DR Maleeha Zia Mufti Lecturer Pathology Department Amcmaleeha100% (1)
- Advancement in The Recently Development of Sublingual Tablet For Various Diseases A ReviewDocument7 pagesAdvancement in The Recently Development of Sublingual Tablet For Various Diseases A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Traditional Aboriginal Medicine PracticeDocument16 pagesTraditional Aboriginal Medicine PracticeAlike Camarillo Rabago100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis # 1 Acute Pain Related To Abdominal Incision.Document10 pagesNursing Diagnosis # 1 Acute Pain Related To Abdominal Incision.jhunanax100% (3)
- 1mg PrescriptionDocument2 pages1mg PrescriptionSankalp IN GamingNo ratings yet
- Factfile 1: Mental Health and EmploymentDocument4 pagesFactfile 1: Mental Health and Employmenttony_jameson-allenNo ratings yet