Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schedule Childhood
Uploaded by
Nevaeh AngeliseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schedule Childhood
Uploaded by
Nevaeh AngeliseCopyright:
Available Formats
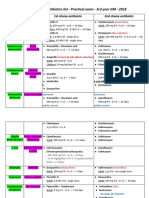
2013 Recommended Immunizations for Children from Birth Through 6 Years Old
1 2 4 6 12 15 18 1923
months
Birth
HepB
month
months
months
months
months
months
months
years
23
years
46
HepB RV DTaP Hib RV DTaP Hib PCV IPV RV DTaP Hib PCV
HepB DTaP Hib PCV IPV Influenza (Yearly)* MMR Varicella HepA
See back page for more information on vaccinepreventable diseases and the vaccines that prevent them.
DTaP
Is your family growing? To protect
your new baby and yourself against whooping cough, get a Tdap vaccine towards the end of each pregnancy. Talk to your doctor for more details.
PCV IPV
IPV MMR Varicella
Shaded boxes indicate the vaccine can be given during shown age range.
NOTE: If your child misses a shot,
you dont need to start over, just go back to your childs doctor for the next shot. Talk with your childs doctor if you have questions about vaccines.
FOOTNOTES: * Two doses given at least four weeks apart are recommended for children aged 6 months through 8 years of age who
are getting a flu vaccine for the first time and for some other children in this age group.
Two doses of HepA vaccine are needed for lasting protection. The first dose of HepA vaccine should be given between 12 months and 23 months of age. The second dose should be given 6 to 18 months later. HepA vaccination may be given to any child 12 months and older to protect against HepA. Children and adolescents who did not receive the HepA vaccine and are at high-risk, should be vaccinated against HepA. If your child has any medical conditions that put him at risk for infection or is traveling outside the United States, talk to your childs doctor about additional vaccines that he may need.
For more information, call toll free 1-800-CDC-INFO (1-800-232-4636) or visit http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines
Vaccine-Preventable Diseases and the Vaccines that Prevent Them Disease
Chickenpox Diphtheria Hib HepA HepB Flu Measles Mumps Pertussis Polio Pneumococcal Rotavirus Rubella Tetanus
Vaccine
DTaP* vaccine protects against diphtheria. Hib vaccine protects against Haemophilus influenzae type b.
Disease spread by Disease symptoms
Rash, tiredness, headache, fever Sore throat, mild fever, weakness, swollen glands in neck May be no symptoms unless bacteria enter the blood May be no symptoms, fever, stomach pain, loss of appetite, fatigue, vomiting, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), dark urine May be no symptoms, fever, headache, weakness, vomiting, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), joint pain Fever, muscle pain, sore throat, cough, extreme fatigue Rash, fever, cough, runny nose, pinkeye Air, direct contact
Disease complications
Infected blisters, bleeding disorders, encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Swelling of the heart muscle, heart failure, coma, paralysis, death Meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), intellectual disability, epiglottis (lifethreatening infection that can block the windpipe and lead to serious breathing problems), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Liver failure Chronic liver infection, liver failure, liver cancer Pneumonia (infection in the lungs)
Varicella vaccine protects against chickenpox. Air, direct contact
Air, direct contact
HepA vaccine protects against hepatitis A. HepB vaccine protects against hepatitis B. Flu vaccine protects against influenza. MMR** vaccine protects against measles. MMR**vaccine protects against mumps. DTaP* vaccine protects against pertussis (whooping cough). IPV vaccine protects against polio. PCV vaccine protects against pneumococcus. RV vaccine protects against rotavirus. MMR** vaccine protects against rubella. DTaP* vaccine protects against tetanus.
Personal contact, contaminated food or water Contact with blood or body fluids Air, direct contact Air, direct contact Air, direct contact Air, direct contact Air, direct contact, through the mouth Air, direct contact Through the mouth Air, direct contact Exposure through cuts in skin
Encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain Swollen salivary glands (under the jaw), fever, and spinal cord) , encephalitis (brain swelling), inflamheadache, tiredness, muscle pain mation of testicles or ovaries, deafness Severe cough, runny nose, apnea (a pause in Pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death breathing in infants) May be no symptoms, sore throat, fever, Paralysis, death nausea, headache May be no symptoms, pneumonia (infection Bacteremia (blood infection), meningitis (infection of in the lungs) the covering around the brain and spinal cord), death Diarrhea, fever, vomiting Severe diarrhea, dehydration Children infected with rubella virus sometimes Very serious in pregnant womencan lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, premature delivery, birth defects have a rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes Stiffness in neck and abdominal muscles, Broken bones, breathing difficulty, death difficulty swallowing, muscle spasms, fever
* DTaP combines protection against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. ** MMR combines protection against measles, mumps, and rubella.
Last updated on 01/28/2013 CS237423-A
You might also like
- Vaccines: Does herd immunity justify permanent impairment for a few?From EverandVaccines: Does herd immunity justify permanent impairment for a few?No ratings yet
- 1 Juliane Flores Bible FinalDocument170 pages1 Juliane Flores Bible FinalJuliane FloresNo ratings yet
- Asthma HandbookDocument157 pagesAsthma HandbookmsarwarNo ratings yet
- Big Question: What Happens When Immune System Overreacts?Document42 pagesBig Question: What Happens When Immune System Overreacts?Louloun MoussignacNo ratings yet
- Types of HypersensitivityDocument23 pagesTypes of HypersensitivityZaib ZaibNo ratings yet
- Anti-Microbial Therapy Final With AlarmsDocument245 pagesAnti-Microbial Therapy Final With AlarmsMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Anti Asthmatic DrugsDocument8 pagesAnti Asthmatic DrugsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- EDT007Document110 pagesEDT007mahchusNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument71 pagesThe Nervous SystemDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- Biofluidodinamica Lecture NotesDocument356 pagesBiofluidodinamica Lecture NotesverbicarNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Injection of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA Vaccine Can Induce Acute Myopericarditis in Mouse ModelDocument18 pagesIntravenous Injection of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA Vaccine Can Induce Acute Myopericarditis in Mouse ModelStacey KrellerNo ratings yet
- Excerpts From Dr. Plotkin Deposition - January 2018Document137 pagesExcerpts From Dr. Plotkin Deposition - January 2018Elena ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Michigan Nurses Association v. Huron Valley-Sinai HospitalDocument23 pagesMichigan Nurses Association v. Huron Valley-Sinai HospitalFindLawNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated Immune Responses8Document26 pagesCell-Mediated Immune Responses8Trifu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Asthma + COPDDocument60 pagesAsthma + COPDNur HasanahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac OutputDocument18 pagesCardiac OutputGauravSinghNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Chest Pain in Primary Care Patients-AAFPDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Chest Pain in Primary Care Patients-AAFPnouval_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Avandia - The Intimidation of Dr. John BuseDocument12 pagesAvandia - The Intimidation of Dr. John BuseVaccineInformation100% (1)
- ASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSDocument25 pagesASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSPrincess AñabezaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Full Notes NewDocument33 pagesInheritance Full Notes NewThasni Nazeer A2No ratings yet
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDocument75 pages5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)
- Evaluation of ConstipationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of ConstipationMark KovalNo ratings yet
- "Towards Eradicating Tuberculosis" - Aetiopathogenesis of TuberculosisDocument29 pages"Towards Eradicating Tuberculosis" - Aetiopathogenesis of Tuberculosisibnbasheer100% (7)
- Mechanical Properties of The Heart IDocument30 pagesMechanical Properties of The Heart ISeba W WolfNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology and Fluid BalanceDocument71 pagesRenal Physiology and Fluid BalanceparthNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Antibiotics Table FINALDocument3 pagesPharmacology Antibiotics Table FINALAndre AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics 1: AbsorptionDocument15 pagesPharmacokinetics 1: AbsorptionCecilia GrayebNo ratings yet
- Enuresis Aafp PDFDocument8 pagesEnuresis Aafp PDFyusditaoNo ratings yet
- 2 Cardiovascular System: Describe The Systemic Circulation in The Body and Give Its ImportanceDocument28 pages2 Cardiovascular System: Describe The Systemic Circulation in The Body and Give Its ImportanceBhavin ChangelaNo ratings yet
- Brain Damage/cognitive Skills disruption/Retardation/Neurochemical Changes in The Brain/behavioral and Mood Changes/ProblemsDocument11 pagesBrain Damage/cognitive Skills disruption/Retardation/Neurochemical Changes in The Brain/behavioral and Mood Changes/ProblemsUSNEWSGHOSTNo ratings yet
- Semaglutifes Sustaine ComparadoresDocument10 pagesSemaglutifes Sustaine ComparadoresIvan Dario Hernandez ErazoNo ratings yet
- EMS Infectious Disease PlaybookDocument86 pagesEMS Infectious Disease PlaybookAryttNo ratings yet
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Practical Assessment and ManagementDocument9 pagesGeneralized Anxiety Disorder: Practical Assessment and Managementc_mendozaaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Day 3 TemplateDocument24 pagesCardio Day 3 TemplateMikeNo ratings yet
- Dental Problems in Primary CareDocument7 pagesDental Problems in Primary Carehawraa tarhiniNo ratings yet
- Rapid Review Osteoartritis AafpDocument6 pagesRapid Review Osteoartritis AafpClaudio Miranda PayacánNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument79 pagesAsthmaraj patel100% (1)
- Adhd Deficit Atencion AafpDocument9 pagesAdhd Deficit Atencion AafpLisandro Marco del PontNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 SafetyDocument8 pagesCovid 19 SafetySargent GoodchildNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseDocument43 pages6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseAlacrity Xenoion SpadesNo ratings yet
- Overview of Immune SystemDocument49 pagesOverview of Immune SystemleeNo ratings yet
- Urschel - How To AnalyzeDocument4 pagesUrschel - How To Analyzek1988No ratings yet
- Summary of Pharmacology1 by 3alam El Teb DR - MahmoudDocument41 pagesSummary of Pharmacology1 by 3alam El Teb DR - MahmoudaamirNo ratings yet
- L9 PDFDocument22 pagesL9 PDFMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument8 pagesVaccinesKathryn CannNo ratings yet
- Acute and Preventive Pharmacologic Treatment of Cluster HeadacheDocument12 pagesAcute and Preventive Pharmacologic Treatment of Cluster Headachelusi jelitaNo ratings yet
- Audiometry Screening and Interpretation Aafp PDFDocument8 pagesAudiometry Screening and Interpretation Aafp PDFMaram AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Corporate ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDoctrine of Corporate ResponsibilityMar VicNo ratings yet
- Functional Human Physiology: For The Exercise and Sport Sciences The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac FunctionDocument186 pagesFunctional Human Physiology: For The Exercise and Sport Sciences The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac FunctionBery Agana F. PurbaNo ratings yet
- UAW Respiratory Antimicrobial Pharm Guide MedstuDocument19 pagesUAW Respiratory Antimicrobial Pharm Guide MedstuNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Twelve Reasons Why The Flu Shot Is DangerousDocument5 pagesTwelve Reasons Why The Flu Shot Is Dangerousjc200312127869No ratings yet
- Fungi Gram Positive Bacteria Viruses: Non-Tuberculous MycobacteriaDocument1 pageFungi Gram Positive Bacteria Viruses: Non-Tuberculous MycobacteriaImperium503No ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 HANDOUT Online ImmuneDocument28 pagesLECTURE 1 HANDOUT Online ImmuneFYMNo ratings yet
- American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) Funding Project Breakdown: Public Safety - $17,279,000Document8 pagesAmerican Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) Funding Project Breakdown: Public Safety - $17,279,000KTUL - Tulsa's Channel 8No ratings yet
- Perceptions About Childhood Vaccinations: Pam CooperDocument19 pagesPerceptions About Childhood Vaccinations: Pam CooperLancasterOnlineNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu Vaccine FactsheetDocument4 pagesSwine Flu Vaccine Factsheetmuzaffaruz5932No ratings yet
- Influenza (Flu) Description: It's Important To Note That Not Everyone With Flu Will Have A FeverDocument5 pagesInfluenza (Flu) Description: It's Important To Note That Not Everyone With Flu Will Have A FeverlynhareeNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Infections in HumansFrom EverandAnaerobic Infections in HumansSydney FinegoldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lab 3 - Modelling Time DelaysDocument30 pagesLab 3 - Modelling Time DelayslynNo ratings yet
- DR TB Treatment Guideline of Timor Leste - REVISED 3 March 2021Document13 pagesDR TB Treatment Guideline of Timor Leste - REVISED 3 March 2021Yoan Manuel Ruiz ArencibiaNo ratings yet
- Health Facts Covid 19 Fast Facts About CovidDocument2 pagesHealth Facts Covid 19 Fast Facts About Covidanastacia arceNo ratings yet
- Rife Healing FrequenciesDocument9 pagesRife Healing Frequenciessakins9429No ratings yet
- Natural History of DiseaseDocument31 pagesNatural History of Diseasegabo dasNo ratings yet
- Congenital and Perinatal Infections: Throwing New Light With An Old TORCHDocument27 pagesCongenital and Perinatal Infections: Throwing New Light With An Old TORCHdr_ashutosh756078No ratings yet
- DOH National Antibiotic Guidelines 2017Document264 pagesDOH National Antibiotic Guidelines 2017Degee O. Gonzales67% (3)
- Bordetella Pertussis (Pertussis) : Education GapsDocument13 pagesBordetella Pertussis (Pertussis) : Education GapsrhizkyNo ratings yet
- Lobar Pneumonia: Relative SparingDocument13 pagesLobar Pneumonia: Relative SparingTulus SihotangNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: 2696700 LAB/20N/45867 16/sep/2020 MR - Manish Vaish 13464912 StatusDocument2 pagesLab Report: 2696700 LAB/20N/45867 16/sep/2020 MR - Manish Vaish 13464912 StatusmanishNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - SepsisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - SepsisJoe Mark Salamero86% (21)
- Female CondomsDocument2 pagesFemale Condomsapi-507694117No ratings yet
- MMR NotesDocument2 pagesMMR NotesrotiNo ratings yet
- Acute Pharyngitis in Adolescents and AdultsDocument45 pagesAcute Pharyngitis in Adolescents and AdultsAlanGonzalezNo ratings yet
- MEHLMANMEDICAL Microbiology Assessment 1 1Document75 pagesMEHLMANMEDICAL Microbiology Assessment 1 1Feroz RaZa SoomrOoNo ratings yet
- American Family Physician PDFDocument8 pagesAmerican Family Physician PDFlionaNo ratings yet
- MCQs in para (With Answers)Document20 pagesMCQs in para (With Answers)janiceli020785% (26)
- Guidelines Ma School RequirementsDocument4 pagesGuidelines Ma School Requirementsomer naseer chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Candidate Copy: Admit Card For Computer Based Test Post: Certificate in Community Health For Nurses (GNM/B.SC - Nursing)Document6 pagesCandidate Copy: Admit Card For Computer Based Test Post: Certificate in Community Health For Nurses (GNM/B.SC - Nursing)gopi krishna ranjanNo ratings yet
- Don'T Forget Your Title: One Arm For All Get Your ShotDocument8 pagesDon'T Forget Your Title: One Arm For All Get Your ShotCatherine Joy PascualNo ratings yet
- Nelson's Pediatric Antimicrobial Therapy 28th Edition 2022Document382 pagesNelson's Pediatric Antimicrobial Therapy 28th Edition 2022Eduardo Rios DuboisNo ratings yet
- Essay On PandemicDocument1 pageEssay On PandemicROSE AMOR M. LACAYNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Specimen Collection and TransportDocument1 pageMicrobiology Specimen Collection and TransportUmesha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- SAGE Business Cases - The Challenge of Measuring The Economic Impact of Coronavirus 2020-1Document3 pagesSAGE Business Cases - The Challenge of Measuring The Economic Impact of Coronavirus 2020-1sebastianNo ratings yet
- Tetanus ProphylaxisDocument4 pagesTetanus ProphylaxisRifda LatifaNo ratings yet
- Vector Control Intro - Jan2019Document18 pagesVector Control Intro - Jan2019rosana_527421859No ratings yet
- Zona Zoster Variceliformå - Particularitate Clinicå Evolutivå (Prezentare de Caz)Document4 pagesZona Zoster Variceliformå - Particularitate Clinicå Evolutivå (Prezentare de Caz)ir1No ratings yet
- Imse Finals Reviewer - Pacate, Joyce C.Document9 pagesImse Finals Reviewer - Pacate, Joyce C.jcpacate1178qcNo ratings yet
- Pulse PolioDocument99 pagesPulse PolioChulbul Pandey100% (1)
- UntitledDocument460 pagesUntitledBrenda Cáceres MejíaNo ratings yet