Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Three Cell Model
Uploaded by
Junats LboneteOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Three Cell Model
Uploaded by
Junats LboneteCopyright:
Available Formats
PREPARED BY: LABONETE, JONATHAN M. SANCHEZ, DANIEL JOSEPH N.
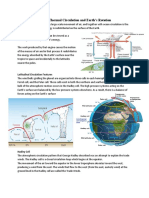
Three Cell Model This model represents the average circulation of the atmosphere and is used to describe the atmospheric transport of energy. The three-cell model divides the circulation of each hemisphere into three distinct cells: the heat driven Hadley cells that circulates air in the tropics, a Ferrel cell in the middle latitude, and a polar cell.
Hadley Cell The intense incoming solar radiation in the equatorial region creates rising air. The rising air cools condenses and forms a region of intense clouds and heavy precipitation. This area is called the InterTropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) and corresponds regions over which the tropical rain forests are found. The ITCZ moves north and south following the sun during the year. Because the stratosphere is stable, rising air that reaches the tropopause moves poleward. By the time the air moving northward reached about 30 N it has become a westerly wind (it is moving to the east) due to the Coriolis force. Because of conservation of angular momentum, the poleward moving air increases speed. The increased speed and the Coriolis force are responsible for the subtropical jet. This poleward moving air piles up (notice on a globe how lines of constant longitude converge) forming an area of high pressure at the surface-- the subtropical highs. Some of the air sinks toward the surface. Subsidence inhibits cloud formation and this is the reason many large deserts are found near 30N and 30S. Once the sinking air reaches the ground, some flows to the equator, turning west (in the northern hemisphere) as it goes due to the Coriolis force. This surface air forms the trade winds that blow steadily from the northeast in the northern hemisphere and southeast in the southern hemisphere. Ferrel Cell Some of the diverging air at the surface near 30N moves poleward and is deflected to the east by the Coriolis force resulting in the prevailing westerly winds at the surface. At about 60N the air rises cools and condenses and forms clouds and precipitation. This is the general region of the polar front. Some of this rising air returns equatorward. Polar Cell Sinking air at the poles warms and results in a high pressure over the poles. At the surface, the poleward moving air gets pulled to the right by the Coriolis force (in the northern hemisphere) forming the polar easterly winds. The cold polar air meets with the warm subtropical air moving poleward and forms the boundary between these two air masses known as the polar front. The warm air from the subtropics pushes up over the cold equatorward moving polar air. This polar front is the source of much of the changing weather in the US, particularly in fall, winter and spring. The large temperature contrast results in the polar front jet stream in the vicinity of the polar front.
You might also like
- Lesson 7 (MET-O)Document13 pagesLesson 7 (MET-O)Elevado Elegene L.No ratings yet
- Pauline - 2011 - Volunteer Satisfaction and Intent To Remain An Analysis of Contributing Factors Among Professional Golf Event VolunteerDocument24 pagesPauline - 2011 - Volunteer Satisfaction and Intent To Remain An Analysis of Contributing Factors Among Professional Golf Event VolunteerAmirah RashidiNo ratings yet
- Structural Adjustment Essay - LSEDocument6 pagesStructural Adjustment Essay - LSEWilliam ClareNo ratings yet
- Valuing and Managing The Philippines' Marine Resources Toward A Prosperous Ocean-Based Blue EconomyDocument26 pagesValuing and Managing The Philippines' Marine Resources Toward A Prosperous Ocean-Based Blue EconomyAna TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Natural and Man Made DisastersDocument23 pagesNatural and Man Made Disasterssureshgraphics100% (1)
- Week 7 - The Wind and Pressure Systems Over The Oceans-1Document112 pagesWeek 7 - The Wind and Pressure Systems Over The Oceans-1Paulo GeneraloNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Household Preparedness On Flood Management in Riverside: A Focus On Apete Community in Ibadan, NigeriaDocument26 pagesAnalyzing Household Preparedness On Flood Management in Riverside: A Focus On Apete Community in Ibadan, NigeriaIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards and Disasters PDFDocument25 pagesNatural Hazards and Disasters PDFtrilion_2000No ratings yet
- Battle Review of PEFTOK in KoreaDocument3 pagesBattle Review of PEFTOK in KoreaJonathanAndroTan100% (1)
- Corbett in Orbit - A Maritime Model For Strategic Space TheoryDocument16 pagesCorbett in Orbit - A Maritime Model For Strategic Space TheoryCarlos Serrano FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Art of War Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesArt of War Reaction PaperJoannaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Research Methods: (Pick The Date)Document15 pagesOrganizational Research Methods: (Pick The Date)rinnimaruNo ratings yet
- DabbawalaDocument18 pagesDabbawalaRatish NairNo ratings yet
- Harvard Citation Style Examples For UWADocument6 pagesHarvard Citation Style Examples For UWAMasiur HossainNo ratings yet
- The Expanded Role of Air Power in The Defence and Security of SingaporeDocument11 pagesThe Expanded Role of Air Power in The Defence and Security of Singaporefake7083No ratings yet
- Handout On Reporting Science & TechnologyDocument23 pagesHandout On Reporting Science & TechnologySOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Benham RiseDocument24 pagesBenham RiseRhea CelzoNo ratings yet
- Academic Achievement and LET Performance of The Bachelor of Elementary Education Graduates, University of Northern PhilippinesDocument7 pagesAcademic Achievement and LET Performance of The Bachelor of Elementary Education Graduates, University of Northern PhilippinesJASH MATHEWNo ratings yet
- CorregidorDocument11 pagesCorregidorMadz RoñoNo ratings yet
- 18-19 Module 4 PDFDocument14 pages18-19 Module 4 PDFrow rowNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Advocacy ExploDocument24 pagesClimate Change Advocacy ExploPrincess Joy Cassandra TiconNo ratings yet
- Rebuttal Argument Essay War On Global Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesRebuttal Argument Essay War On Global Climate Changeapi-254356307No ratings yet
- Heneral Luna: A Reaction Paper: Requirement in English For Academic & Professional PurposesDocument2 pagesHeneral Luna: A Reaction Paper: Requirement in English For Academic & Professional PurposesAnonymous jCWDlGANo ratings yet
- DM Plan Ramu Upazila Coxsbazar District - English Version-2014Document128 pagesDM Plan Ramu Upazila Coxsbazar District - English Version-2014CDMP BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Laudato SiDocument165 pagesLaudato SiChurch MilitantNo ratings yet
- The National TerritoryDocument18 pagesThe National TerritoryAgnes CastilloNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument26 pagesThesisJohnray RocheNo ratings yet
- Size and The Structure of Authority in Canal Irrigation Systems PDFDocument22 pagesSize and The Structure of Authority in Canal Irrigation Systems PDFEnrique BellidoNo ratings yet
- Four Ethical Issues of The Information AgeDocument7 pagesFour Ethical Issues of The Information AgeMithinga NarzaryNo ratings yet
- Buku Sea Power and Strategy in The Indian Ocean HALAMAN 25-28Document23 pagesBuku Sea Power and Strategy in The Indian Ocean HALAMAN 25-28Ari NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Traffic CongestionDocument45 pagesDealing With Traffic Congestion蔡育新No ratings yet
- Exploring Indigenous Approaches To Peacebuilding: The Case of Ubuntu in South AfricaDocument14 pagesExploring Indigenous Approaches To Peacebuilding: The Case of Ubuntu in South AfricaAbdul Karim Issifu100% (2)
- Disaster Preparedness in Manila PDFDocument117 pagesDisaster Preparedness in Manila PDFDondon DondonNo ratings yet
- Singapores Defense Policy Essential or Excessive PDFDocument114 pagesSingapores Defense Policy Essential or Excessive PDFCeleryBallNo ratings yet
- Question 1: Describe Difference Between Strategy and Tactics? AnsDocument5 pagesQuestion 1: Describe Difference Between Strategy and Tactics? AnsMishelNo ratings yet
- Critiques of Modernization Theory: Modernization: Factors, Pre-Requisites and Conceptual FormulationsDocument2 pagesCritiques of Modernization Theory: Modernization: Factors, Pre-Requisites and Conceptual Formulationsyounus shaikhNo ratings yet
- Application of RS and GIS in Flood Management - IndiaDocument9 pagesApplication of RS and GIS in Flood Management - IndiaAbi HoodNo ratings yet
- Awareness Final PDFDocument10 pagesAwareness Final PDFCrissa ReyesNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTS of WEATHER and CLIMATEDocument71 pagesELEMENTS of WEATHER and CLIMATEMel DridNo ratings yet
- Physical GeographyDocument83 pagesPhysical GeographySangeen AliNo ratings yet
- Media Times - Media's Responsibility: Disaster-Prone PhilippinesDocument6 pagesMedia Times - Media's Responsibility: Disaster-Prone PhilippinesCenter for Media Freedom & ResponsibilityNo ratings yet
- Camp Management ToolkitDocument598 pagesCamp Management Toolkittaha_basit2441No ratings yet
- Environmental Science Is An Interdisciplinary Academic Field That Integrates PhysicalDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Science Is An Interdisciplinary Academic Field That Integrates PhysicaldhritimanNo ratings yet
- Esrf FdiDocument26 pagesEsrf FdiJoel ChikomaNo ratings yet
- Expository Essay West Philippine Sea DisputesDocument2 pagesExpository Essay West Philippine Sea DisputesJoann Hipolito SabateNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three 3 0 Research Methodology 3 1 IntroductionDocument11 pagesChapter Three 3 0 Research Methodology 3 1 IntroductionRussell Monroe100% (1)
- RTU Research 1 Thesis Outline For Qualitative Research PDFDocument2 pagesRTU Research 1 Thesis Outline For Qualitative Research PDFRenelle HabacNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theories of Popular Culture Part I-Ppt-13Document13 pagesIntroduction To Theories of Popular Culture Part I-Ppt-13Keith KnightNo ratings yet
- What Are Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument3 pagesWhat Are Hydrometeorological Hazardsangelic dailyNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction Education in Indonesia Challenges and Recommendations For Scaling UpDocument28 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction Education in Indonesia Challenges and Recommendations For Scaling UpKatherine JonesNo ratings yet
- Geostrategy - WikiDocument13 pagesGeostrategy - WikiJohnnutz IonutzNo ratings yet
- South China Sea Study GuideDocument8 pagesSouth China Sea Study Guideapi-297586186No ratings yet
- Inchoen Landing - Military Review Must ReadDocument7 pagesInchoen Landing - Military Review Must ReadNiubility100% (1)
- Community Planning For Disaster ManagementDocument5 pagesCommunity Planning For Disaster ManagementDharmaTuals: Dharma And RitualsNo ratings yet
- The DroughtDocument11 pagesThe DroughtEngineer 1122100% (1)
- Philippine EconomyDocument26 pagesPhilippine EconomyA.P. MadarangNo ratings yet
- Global Circulation of AtmosphereDocument7 pagesGlobal Circulation of AtmosphereSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hydrosphere PPTDocument27 pagesHydrosphere PPTsopanrayNo ratings yet
- An Essay 2Document5 pagesAn Essay 2Oren AppleNo ratings yet
- General Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth's RotationDocument3 pagesGeneral Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth's RotationGie AndalNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument1 pageMethodologyJunats LboneteNo ratings yet
- Understanding of SpeechDocument2 pagesUnderstanding of SpeechJunats LboneteNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document58 pagesPresentation 1Junats LboneteNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Management StudyDocument7 pagesManagement StudyJunats LboneteNo ratings yet
- Trusses PDFDocument58 pagesTrusses PDFManzur Maruf RahmanNo ratings yet
- Death ClaimDocument3 pagesDeath ClaimJunats LboneteNo ratings yet
- Symmetries and Conservation Laws-Consequences of Noether TheoremDocument8 pagesSymmetries and Conservation Laws-Consequences of Noether TheoremmastinaropuruNo ratings yet
- Atmel 2565 Using The Twi Module As I2c Slave - Applicationnote - Avr311Document14 pagesAtmel 2565 Using The Twi Module As I2c Slave - Applicationnote - Avr311m3y54mNo ratings yet
- Urban Road Types 25.01.2022Document5 pagesUrban Road Types 25.01.2022Balogun IbrahimNo ratings yet
- T 096Document3 pagesT 096abelNo ratings yet
- PythagorasDocument109 pagesPythagorasaditya00012No ratings yet
- Body Deassembly 9 Interior TrimDocument7 pagesBody Deassembly 9 Interior TrimCarlos TecnicNo ratings yet
- EConsole1 Quick Start Guide ENGDocument21 pagesEConsole1 Quick Start Guide ENGManuel Casais TajesNo ratings yet
- OK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFDocument2 pagesOK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFborovniskiNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document12 pagesLab 6Sujan HeujuNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1, Grade 10Document2 pagesWEEK 1, Grade 10Sheela BatterywalaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and AtomsDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table and AtomsShoroff AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Solids 1Document16 pagesTypes of Solids 1Fern BaldonazaNo ratings yet
- Practice Question ElectricityDocument3 pagesPractice Question ElectricityIvan SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One PDFDocument74 pagesChapter One PDFAdelu BelleteNo ratings yet
- 1995 S320 S420 S500 Owner's Manual Edition C PDFDocument153 pages1995 S320 S420 S500 Owner's Manual Edition C PDFnpachecorecabarrenNo ratings yet
- User's Manual HEIDENHAIN Conversational Format ITNC 530Document747 pagesUser's Manual HEIDENHAIN Conversational Format ITNC 530Mohamed Essam Mohamed100% (2)
- Java Lab Assignment.Document2 pagesJava Lab Assignment.KAYNo ratings yet
- 003pcu3001 Baja California - JMH - v4 PDFDocument15 pages003pcu3001 Baja California - JMH - v4 PDFEmir RubliovNo ratings yet
- HANA OverviewDocument69 pagesHANA OverviewSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 DB RDMDocument49 pages3 DB RDMfaisal shahzadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sensor Air PST Datasheet 51 en 2780071435Document3 pagesPressure Sensor Air PST Datasheet 51 en 2780071435Luis GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Analysis of Stress and StrainDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Analysis of Stress and StrainLong Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- GTG - TFA Belt DrivenDocument2 pagesGTG - TFA Belt Drivensuan170No ratings yet
- Bootloader3 PDFDocument18 pagesBootloader3 PDFsaravananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Process Capability AnalysisDocument21 pagesChapter 6 - Process Capability AnalysisKaya Eralp AsanNo ratings yet
- Ex450-5 Technical DrawingDocument12 pagesEx450-5 Technical DrawingTuan Pham AnhNo ratings yet
- 3700 RES 5.5.1 Install GuideDocument38 pages3700 RES 5.5.1 Install Guidejlappi100% (1)
- Index Terms LinksDocument31 pagesIndex Terms Linksdeeptiwagle5649No ratings yet
- P 130881757895329843Document44 pagesP 130881757895329843Vijay MohanNo ratings yet
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (593)