Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 8 v2
Uploaded by
neptunaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 8 v2
Uploaded by
neptunaCopyright:
Available Formats
Atn zgr Ahmet Uur Birinci
12.12.2013
ME 482 ASSIGNMENT 8
INTRODUCTION
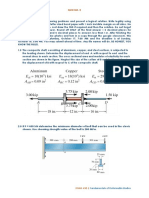
The main aim of the assignment is to investigate a uniformly loaded and simply supported beam. The beam is made of steel, it is 0.5m in length and the cross section is 50 mm deep by 10 mm wide. The uniform load is a pressure of 2 N/mm2. The main objectives are; to find out the effects of type of supports, namely pin-pin, pin-roller, to study the effect of placement of supports, namely neutral axis, bottom fibers and to compare structural and continuum elements.
ANALYSIS OF THE MODEL
Preliminary Analysis (Beam Theory):
Finite Element Analysis The material is steel with 210 MPa Youngs modulus and 0.3 Poissons ratio. For the pin supports, pinned boundary condition is applied; for the roller supports, displacement boundary condition in y-direction is applied. For continuum elements, 75 elements gave out 0.733 mm deflection, 250 elements gave out 0.776 mm deflection. The mesh was considered to be converged at 250 elements. For beam elements, 25 elements gave out 0.743 mm deflection, 50 elements gave out 0.744 mm deflection. The mesh was considered to be converged at 50 elements. Maximum bending stress, maximum deflection and the reaction at supports were investigated for CPS8R, B23 and B22 elements. The cases where pin-roller and pin-pin supports are applied at neutral axis and at the bottom were considered. The reaction force was scaled by multiplying by 10 to account for the 2D modeling of the beam. The results were compared with beam theory solutions.
Deflection for 75 elements
Deflection for 250 elements
Stress for CPS8R pin-pin supports at neutral axis
Stress for B23 pin-pin supports at the bottom
Stress for B23 pin-roller supports at the bottom
Table.1 Maximum Stress, Maximum Deflection and Reaction Force Values RF (N) Beam Theory 150 0.744 Pin-Roller CPS8R n.a 150 0,763 B23 n.a 150 0,744 B22 n.a 150 0,763 CPS8R Bottom 150 0,776 B23 Bottom 150 0,744 B22 Bottom 150 0,763 Pin-Pin CPS8R n.a 150 0,763 B23 n.a 150 0,744 B22 n.a 150 0,763 CPS8R Bottom 99 0,372 B23 Bottom 50 0,298 B22 Bottom 50 0,316 * The reaction forces in x and y-direction respectively. 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000 5000, 10750* 5000, 12500* 5000, 12500*
Table.2 Shear Stress Effect Pin-Roller Neutral Axis CPS8R 10 5 2 1 10 5 2 1 10 5 2 1 1 1,008 0,94 0,92 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1,02 1,13 5,45 47,1 1 1 1,2 1 1,02 1,11 1,94 3,55
B23
B22
CONCLUSIONS Pin-pin supporting can give the same results as pin-roller supporting if the pins are applied at the neutral axis. If the pins are applied at the bottom, stress concentration occurs at the pins, this results in less stress at the outer fibers. All the cases except for the pin-pin support at the bottom give out the same maximum bending stress with the beam theory. Maximum deflections are also accurate considering the beam theory solution to be true. For L/h = 10 and L/h = 5, all three elements give results consistent with the beam theory. For L/h < 5, beam theory fails to function. Beam elements give close results to the beam theory but the continuum elements give very different results for the maximum deflection. It is better to use continuum elements for L/h < 5.
You might also like
- Seminar Report (1)Document16 pagesSeminar Report (1)ashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- 5502-Article Text PDF-9260-1-10-20130718Document13 pages5502-Article Text PDF-9260-1-10-20130718Yadava JaffaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Engineering LTD.: Finite Element Analysis Report - VIII-2Document23 pagesPressure Vessel Engineering LTD.: Finite Element Analysis Report - VIII-2rahulNo ratings yet
- A Limiting Defect Study of An ElbowDocument7 pagesA Limiting Defect Study of An Elbowmaxeytm_839061685No ratings yet
- Issue No 11 - Elastic SpringbackDocument2 pagesIssue No 11 - Elastic SpringbackSani BuangNo ratings yet
- Modeling - Rigid End OffsetsDocument7 pagesModeling - Rigid End OffsetsAnonymous DNb6yWERfB100% (1)
- Issue No 11 - Elastic SpringbackDocument2 pagesIssue No 11 - Elastic Springbackrodrigo9bessim9rochaNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements (Fasteners)Document39 pagesDesign of Machine Elements (Fasteners)Nauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Springs TextDocument0 pagesSprings Texter_wenNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Finite Element Method of Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Deep BeamDocument7 pagesNon Linear Finite Element Method of Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Deep BeamIJMERNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Analysis of Structural Steel FramesDocument22 pagesNon-Linear Analysis of Structural Steel FramesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Strut-And-Tie Model Design Provisions: Robin G. Tuchscherer, David B. Birrcher, and Oguzhan BayrakDocument16 pagesStrut-And-Tie Model Design Provisions: Robin G. Tuchscherer, David B. Birrcher, and Oguzhan BayrakDavid Apaza QuispeNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Stress Concentration in Bolt Nut ConnectorsDocument6 pagesReduction of Stress Concentration in Bolt Nut ConnectorsjtorerocNo ratings yet
- Paper Iccst06 Staufik2Document11 pagesPaper Iccst06 Staufik2Syh TfkNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Flat Coil Configurations For Stepper MotorsDocument6 pagesManufacturing Flat Coil Configurations For Stepper MotorsJaswant Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Tension Members DesignDocument42 pagesTension Members DesignVermuch CasioNo ratings yet
- (18044824 - Transactions of The VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava, Civil Engineering Series.) NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF CASTELLATED BEAMDocument7 pages(18044824 - Transactions of The VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava, Civil Engineering Series.) NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF CASTELLATED BEAMShinichi KudoNo ratings yet
- Bolted Joints Analysis Methods and EvaluationDocument9 pagesBolted Joints Analysis Methods and EvaluationIJMERNo ratings yet
- Beam-To-Beam Joints With Bolted End-Plate Connections Concerning Steel Platforms Angra 2 NPPDocument10 pagesBeam-To-Beam Joints With Bolted End-Plate Connections Concerning Steel Platforms Angra 2 NPPihpeterNo ratings yet
- 5 - Threaded Fasteners PDFDocument41 pages5 - Threaded Fasteners PDFViven Sharma100% (1)
- Lee2008 Elbow LWTDocument5 pagesLee2008 Elbow LWTKurra SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Spring Back Effect Using Finite Element AnalysisDocument9 pagesSimulation of Spring Back Effect Using Finite Element AnalysisRahul DevNo ratings yet
- Astm A227Document5 pagesAstm A227Diganta KonerNo ratings yet
- Strut BucklingDocument9 pagesStrut BucklingEvonYong100% (1)
- Modal Analysis of Spindle Shaped Tensairity BeamsDocument7 pagesModal Analysis of Spindle Shaped Tensairity BeamsAkalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Bolt TorquingDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Bolt TorquingAlessandro Serafini100% (1)
- Failure Analysis of Motor Vehicle Coil Spring: Name: Shoaib Ishaq Qazi REG#: 787-FET/BSME/F18-BDocument13 pagesFailure Analysis of Motor Vehicle Coil Spring: Name: Shoaib Ishaq Qazi REG#: 787-FET/BSME/F18-BShoaib QaziNo ratings yet
- SU-8 Based Piezoresistive Mechanical Sensor: of 345 Kgs. 31BM CH-8803Document4 pagesSU-8 Based Piezoresistive Mechanical Sensor: of 345 Kgs. 31BM CH-8803Abhijit KakatiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Principal of Stress and Strain LAb 5Document6 pagesLab Manual For Principal of Stress and Strain LAb 5bmz00000No ratings yet
- Study of Rigid Bolt Joint in Beam-Column Connection of Gabled Portal FramesDocument6 pagesStudy of Rigid Bolt Joint in Beam-Column Connection of Gabled Portal FramesadilanwararNo ratings yet
- TALAT Lecture 2711: Design of A Helicopter DeckDocument11 pagesTALAT Lecture 2711: Design of A Helicopter DeckCORE MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Practical Advanced Analysis ForDocument16 pagesPractical Advanced Analysis ForAndre YPNo ratings yet
- Design of Single Plate Shear ConnectionsDocument12 pagesDesign of Single Plate Shear Connectionssecanet10No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Tension MembersDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Tension MembersGamtesa EjetaNo ratings yet
- FEA Coil Spring 2007Document15 pagesFEA Coil Spring 2007PrasannaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Mechanics of Solids-IIDocument3 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Mechanics of Solids-IIkohli kingNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Struts: Effects of Length and End ConditionsDocument12 pagesBuckling of Struts: Effects of Length and End ConditionsJoshua ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Paper Iccst06 Staufik1Document14 pagesPaper Iccst06 Staufik1Syh TfkNo ratings yet
- Air Vee BendingDocument4 pagesAir Vee BendingMohak Patel100% (1)
- ENGG 410 Quiz No 2Document3 pagesENGG 410 Quiz No 2Joana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- A More Generalized Approach For Analyzing Eccentrically Loaded ConnectionsDocument6 pagesA More Generalized Approach For Analyzing Eccentrically Loaded ConnectionsNacho ReyesNo ratings yet
- Determination of Pin-Bearing Strength for Bolted ConnectionsDocument9 pagesDetermination of Pin-Bearing Strength for Bolted ConnectionsEdwardGuangcoNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of An Octagonal Strain Ring Based Load Cell - 2Document16 pagesDesign and Development of An Octagonal Strain Ring Based Load Cell - 2Arunava ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Connecting RodDocument57 pagesConnecting RodNaveenprakashNo ratings yet
- Couchaux Et Al-2017-Ce/papersDocument10 pagesCouchaux Et Al-2017-Ce/papersCuneyt VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Design - Springs: D J D A D F D FDDocument3 pagesDesign - Springs: D J D A D F D FDIsa GomNo ratings yet
- Bolt Torque FormulaDocument24 pagesBolt Torque Formulaماهر زارعي100% (1)
- Mini Project 1Document17 pagesMini Project 1rgrNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Elliptical Pressure VesselsDocument7 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Elliptical Pressure VesselsAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Answer Key 3 - Prestressed Concrete DesignDocument2 pagesAnswer Key 3 - Prestressed Concrete DesignAndro RebuyasNo ratings yet
- Less DeflectionsDocument13 pagesLess DeflectionsRohitNo ratings yet
- Beam Column ConnectionDocument7 pagesBeam Column ConnectionSubzar Bhat0% (1)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- The Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsFrom EverandThe Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandEngineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsStephen A. HambricNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Strength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesFrom EverandStrength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- MakaleDocument3 pagesMakaleneptunaNo ratings yet
- Cotard Sendromu Ve Olgu RaporuDocument20 pagesCotard Sendromu Ve Olgu RaporuneptunaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine DesignDocument14 pagesSteam Turbine DesignFaiz de PorrasNo ratings yet
- Comparative Government Reading ListDocument13 pagesComparative Government Reading ListneptunaNo ratings yet
- Cotard Sendromu Ve Olgu RaporuDocument20 pagesCotard Sendromu Ve Olgu RaporuneptunaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractneptunaNo ratings yet
- Cotard Sendromu Ve Olgu RaporuDocument20 pagesCotard Sendromu Ve Olgu RaporuneptunaNo ratings yet
- 1895718371Document8 pages1895718371neptunaNo ratings yet
- User-Defined Motions 1: Create Motion: Walking MachineDocument1 pageUser-Defined Motions 1: Create Motion: Walking MachineneptunaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractneptunaNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Effects of Hot and Cold Rolling On The Mechanical Properties of A MaterialDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Effects of Hot and Cold Rolling On The Mechanical Properties of A MaterialneptunaNo ratings yet
- Questions Casting Extrusion Rolling-1Document2 pagesQuestions Casting Extrusion Rolling-1neptunaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractneptunaNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft Tut 009 E Gearsizing 1Document14 pagesKisssoft Tut 009 E Gearsizing 1neptunaNo ratings yet
- God and Man in The Quran (9839154389)Document308 pagesGod and Man in The Quran (9839154389)neptuna100% (2)
- Shoring and Reshore PDFDocument6 pagesShoring and Reshore PDFᜇᜒᜌᜓᜈᜎ᜔ᜇ᜔ ᜊᜒᜇᜓᜌ᜔No ratings yet
- Beams & LintelsDocument29 pagesBeams & LintelsPWQGroupNo ratings yet
- Graepel Gratings and More For Underfoot Safety: Technical Information Incl. Stock ListDocument86 pagesGraepel Gratings and More For Underfoot Safety: Technical Information Incl. Stock Listsorin_cNo ratings yet
- Formula Book For Structural Analysis-TC50312EDocument43 pagesFormula Book For Structural Analysis-TC50312EAbhiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Solved Structural Analysis ExamplesDocument16 pagesSolved Structural Analysis ExamplesMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1196-D1196M-12Document3 pagesAstm D 1196-D1196M-12Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Aa Spec 114001 PDFDocument24 pagesAa Spec 114001 PDFJakes100% (1)
- Precambering of Steel BeamsDocument10 pagesPrecambering of Steel BeamsVance KangNo ratings yet
- An Approximate Analysis of Combined System of Framed Tube, Shear Core and Belt Truss in High-Rise BuildingsDocument18 pagesAn Approximate Analysis of Combined System of Framed Tube, Shear Core and Belt Truss in High-Rise BuildingsToan PhamNo ratings yet
- Composite Beams With Formed Steel Deck: John A. Grant, JR., John W. Fisher, and Roger G. SlutterDocument20 pagesComposite Beams With Formed Steel Deck: John A. Grant, JR., John W. Fisher, and Roger G. SlutterConan EdogawaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular TankDocument38 pagesRectangular TankSam LowNo ratings yet
- Notes On Beam Deflection ExperimentDocument6 pagesNotes On Beam Deflection ExperimentViccknesh BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- g7 3j04 Lab - FinalDocument46 pagesg7 3j04 Lab - Finalyliu8877100% (1)
- Fully Deteriorated Cipp DesignDocument3 pagesFully Deteriorated Cipp DesignAnonymous YcAZv5qF67No ratings yet
- Australian Cross Laminated Timber Panel Structural Design GuideDocument26 pagesAustralian Cross Laminated Timber Panel Structural Design Guidesant1411No ratings yet
- Timoshenko Beam Theory Exact Solution For Bending, Second-Order Analysis, and StabilityDocument22 pagesTimoshenko Beam Theory Exact Solution For Bending, Second-Order Analysis, and StabilityTrươngVănMếnNo ratings yet
- The Unique High-Rise Structure of The MNC Tower 2 Building in JakartaDocument8 pagesThe Unique High-Rise Structure of The MNC Tower 2 Building in JakartaNityananda Permadi TjokrodimurtiNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Formulas and ConceptsDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials Formulas and ConceptsDeo WarrenNo ratings yet
- Planted ColumnDocument7 pagesPlanted Columnabdul khaderNo ratings yet
- Beam DeflectionDocument21 pagesBeam DeflectionTayyab Zafar100% (1)
- PROCEDURE: Please Refer Video of Deflection of Beam Experiment and Read Procedures inDocument3 pagesPROCEDURE: Please Refer Video of Deflection of Beam Experiment and Read Procedures infauzan1698No ratings yet
- Sypt 03 2021 22Document36 pagesSypt 03 2021 22Raihan MullaNo ratings yet
- Method of Virtual Work: Beams and Frames: CauseDocument8 pagesMethod of Virtual Work: Beams and Frames: Causeعبدالله عبدالحكيم عامرNo ratings yet
- Design CalculationsDocument50 pagesDesign CalculationsAmirthakadeshNo ratings yet
- 36 187 1 DR PDFDocument13 pages36 187 1 DR PDFDimas PutraNo ratings yet
- Large Deformation BeamDocument10 pagesLarge Deformation BeamAdimasu AyeleNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Cantilever Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318 14)Document34 pagesReinforced Concrete Cantilever Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318 14)Adnane OuNo ratings yet
- RC Beam Deflection Calculation ReviewDocument17 pagesRC Beam Deflection Calculation ReviewPRATEEK SHARMANo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Structures Vol. II Theory and AnalysisDocument3 pagesMechanics of Structures Vol. II Theory and Analysisvenkata369No ratings yet
- Mech Deform (CE) 20-21Document10 pagesMech Deform (CE) 20-21Kaye OleaNo ratings yet