Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercises: 4.1 Motion Is Relative
Uploaded by
amilcarsoaresOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercises: 4.1 Motion Is Relative
Uploaded by
amilcarsoaresCopyright:
Available Formats
Name ___________________________ Chapter 4 Linear Motion
Class __________________
Date ____________
Exercises
4.1 Motion Is Relative
(page 47)
1. Is the following sentence true or false? When we describe the motion of one object with respect to another, we say that the object is moving true relative to the other object. moving 2. An object is if its position relative to a fixed point changing is . 3. A driver is going 20 kilometers per hour down the street. What is the drivers speed relative to?
the pavement or the surface of Earth
4.2 Speed
4. 5. 6. 7.
(pages 4849)
Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved.
how fast an object is moving Define speed. time Complete the following equation: speed = distance/ . per How is the slash symbol read in km/h? Circle the letters of the sentences that are true of instantaneous speed. a. Instantaneous speed is the total distance covered divided by time. b. Instantaneous speed is the speed at any instant. c. The speedometer on a car shows the instantaneous speed. d. If you traveled 30 kilometers in 1 hour, your instantaneous speed would be 30 km/h. 8. How is average speed calculated? average speed = total distance covered divided by the time interval
9. If you traveled 80 kilometers in 2 hours, what was your average speed?
80 km = 40 km/h 2h
10. If your average speed is 30 kilometers per hour and your trip took 1 hour, what was the total distance covered?
30 km/h � 1h = 30 km
4.3 Velocity
(page 50)
Determine if each of the following statements is true or false. Write the correct word on the line provided.
false true true
11. Speed is velocity in a given direction. 12. The speed of a plane can be described as 300 mi/h. 13. The velocity of a car can be described as 60 km/h to the north. 14. Speed is a vector quantity. 15. Velocity is a vector quantity.
false true
Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook
Chapter 4
25
Name ___________________________ Chapter 4 Linear Motion
Class __________________
Date ____________
speed direction 16. If either the or the changing (or both are), then the velocity is changing.
is
4.4 Acceleration
(pages 5152)
17. What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity is changing.
18. How is acceleration calculated?
Acceleration is calculated by dividing the change of velocity by the time interval. increases 19. In physics, the term acceleration applies to both and decreases in speed. direction , 20. Acceleration is a change in speed, a change in or both. 21. Is the following sentence true or false? Acceleration is a vector quantity. true
22. If a car is traveling around a curve on a highway at a constant speed, is the car accelerating? Explain your answer.
Yes, the car is accelerating because it is constantly changing direction.
23. Circle the letter of the value and units that represent acceleration. a. 5 km b. 15 km/s c. 25 s/km d. 55 km/s2
4.5 Free Fall: How Fast
(pages 5355)
24. Is the following sentence true or false? In real life, air resistance has no false effect on the acceleration of a falling object. 25. An object moving under the influence of the gravitational force only is free fall said to be in . 26. Define elapsed time.
the time that has passed since the beginning of any motion
Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved.
Match each symbol or value with the correct phrase. Phrase
a b d c
Symbol or Value a. b. c. d. 10 m/s2 g v 9.8 m/s2
27. an approximate value of the acceleration of an object in free fall 28. used to represent acceleration due to gravity 29. an accurate value of acceleration of an object in free fall 30. used for both speed and velocity in the equation for instantaneous speed
26
Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook
Chapter 4
Name ___________________________ Chapter 4 Linear Motion
Class __________________
Date ____________
31. What is the instantaneous speed of an object that is at its highest point zero when it is thrown straight up in the air? 32. When an object is thrown straight up into the air, what is its acceleration 10 m/s2 or 9.8 m/s2 downward when it is moving upward? 33. What is the acceleration of the same object in the above question when it 10 m/s2 or 9.8 m/s2 downward is descending?
4.6 Free Fall: How Far
true
(page 56)
34. Is the following sentence true or false? For each second of free fall, an object falls a greater distance than it did in the previous second. 35. At the end of time t, an object in free fall has fallen a distance equal to
1 gt 2 2
36. What are the equations used to calculate velocity and distance for a freely falling object?
v = at d = 1 at2 2
4.7 Graphs of Motion
(pages 5758)
Use the graph below to answer Questions 3739.
Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved.
37. What is the relationship between time and speed on this graph?
Time and speed are directly proportional to each other on this graph.
38. What does the slope of the line on this graph represent?
speed per time or acceleration
39. What is the slope of the graph?
10
Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook
Chapter 4
27
Name ___________________________ Chapter 4 Linear Motion
Class __________________
Date ____________
Use the graph below to answer Questions 40 and 41.
40. The relationship between distance and time on this graph is parabolic quadratic and the curve is . 41. What does the slope of the line at each point represent?
speed at the point
4.8 Air Resistance and Falling Objects
(page 59)
42. Explain why a dropped coin reaches the ground before a feather.
Air resistance slows the movement of things with large surface areas, such as a feather.
43. Explain what would happen if a coin and a feather were dropped in a vacuum tube.
Without the presence of air, both would drop with the same acceleration.
Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved.
44. If air resistance is negligible, a falling object can be considered free falling or falling freely .
4.9 How Fast, How Far, How Quickly How Fast Changes (page 59)
Match each word or equation with the correct phrase. Phrase
d
Word or Equation a. b. c. d. e.
1 gt2 d= 2 v = gt acceleration speed distance
b e a c
45. the word for how fast something freely falls from rest after an elapsed time 46. the equation for speed and velocity 47. the word for how far an object has fallen 48. the equation for distance 49. the word for the rate at which velocity changes
28
Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook
Chapter 4
You might also like
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsFrom EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Potentialandkineticenergyworksheet PDFDocument2 pagesPotentialandkineticenergyworksheet PDFAndrew SorianoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics (2020)Document15 pagesGrade 10 Physics (2020)Mikail MoorajNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Self Test 2Document7 pagesUniform Circular Motion Self Test 2pauljkt1No ratings yet
- Nota Chapter 1 Physics Form 4Document23 pagesNota Chapter 1 Physics Form 4Haninii Suhaila HK100% (1)
- Ch. 5 Circular MotionDocument20 pagesCh. 5 Circular MotionTreeiciclesNo ratings yet
- Tensestable Mumbai IndiaDocument5 pagesTensestable Mumbai IndiaharishNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Corresponding Angles GCSE WorksheetDocument16 pagesThird Space Learning Corresponding Angles GCSE WorksheetGaurav MittalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanNo ratings yet
- Length & Time IGCSEDocument5 pagesLength & Time IGCSEsapini100% (2)
- Limits of Accuracy: This Chapter Will Show YouDocument12 pagesLimits of Accuracy: This Chapter Will Show Youqarree100% (1)
- Centripetal Force Worksheet1Document2 pagesCentripetal Force Worksheet1Mary Joy MaticNo ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter 5 QPDocument15 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter 5 QPputri aNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic EnergyDocument24 pagesPotential and Kinetic EnergyDare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Summary: Physics Grade 9Document23 pagesUnit 6 Summary: Physics Grade 9AhmedNo ratings yet
- Concept Summary: Batesville High School PhysicsDocument20 pagesConcept Summary: Batesville High School PhysicssbdmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 KinematicDocument11 pagesChapter 2 KinematicTutor_KLNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics WorksheetsDocument31 pages11 Physics WorksheetssbatrabatraNo ratings yet
- 2 Thermal Physics1Document18 pages2 Thermal Physics1Hakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya100% (1)
- Linear Motion ExerciseDocument5 pagesLinear Motion ExercisePei JingNo ratings yet
- 9702 Physics P2 QP Mock 2020 PDFDocument12 pages9702 Physics P2 QP Mock 2020 PDFTasneemNo ratings yet
- Sound PhysicsDocument4 pagesSound PhysicsMaha Letchumy BalakeristananNo ratings yet
- Convex Lenses Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesConvex Lenses Practice WorksheetRoyston EbenezerNo ratings yet
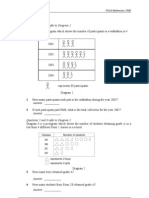
- Questions 1 and 2 Refer To Diagram 1.: PictogramDocument5 pagesQuestions 1 and 2 Refer To Diagram 1.: PictogramSiew CheanNo ratings yet
- Igcse 51 Density&PressureDocument40 pagesIgcse 51 Density&PressureHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- TEST (FORCE & Laws of Motion)Document2 pagesTEST (FORCE & Laws of Motion)Kumar Sushil100% (1)
- Force Problems With Answers PDFDocument2 pagesForce Problems With Answers PDFSoy Diego AlcantarNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics Practical Activity (Potential Divider)Document1 pageIgcse Physics Practical Activity (Potential Divider)Suta PinatihNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Markscheme (All in One)Document728 pagesChemistry Markscheme (All in One)AliMushtaq50% (2)
- Worksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Document9 pagesWorksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Joshua DellosaNo ratings yet
- Unit: Waves Name: - Lesson 5: Doppler Effect DateDocument6 pagesUnit: Waves Name: - Lesson 5: Doppler Effect DateBetty WangNo ratings yet
- 1 Worksheet (AS) KinematicsDocument3 pages1 Worksheet (AS) KinematicsMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To PhysicsDocument24 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To PhysicsyelbonifacioNo ratings yet
- Light & WaveDocument11 pagesLight & WaveDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Physics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument21 pagesPhysics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument60 pagesKinetic Particle Theoryapi-305909325100% (2)
- Doppler ExercisesDocument2 pagesDoppler ExercisesJulian AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pendulum ExpDocument4 pagesPendulum ExpRoyston EbenezerNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Student WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory System Student WorksheetfidANo ratings yet
- 5 Work, Energy and PowerDocument39 pages5 Work, Energy and PowerGeanelle BonilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Forces and Matter PDFDocument17 pagesChapter - Forces and Matter PDFasiyaNo ratings yet
- Space Quest Teachers Page Final-2Document10 pagesSpace Quest Teachers Page Final-2api-265230795No ratings yet
- Turning Effects of Forces PDFDocument6 pagesTurning Effects of Forces PDFMazharul SamiNo ratings yet
- CIE PhysicsDocument14 pagesCIE PhysicsengrroyNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument4 pagesKinematics WorksheetRobertYue100% (2)
- ICSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument5 pagesICSE Class 10 Physicssudhir_narang_3No ratings yet
- Electronic Control Questions FOR IGCSE PHYSICSDocument20 pagesElectronic Control Questions FOR IGCSE PHYSICSFahim Ahmed100% (1)
- Physics Book 5054 o Level PDFDocument1,015 pagesPhysics Book 5054 o Level PDFSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice 3 Circular MotionDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice 3 Circular MotionRazi's DarkzNo ratings yet
- Answers To IGCSE Physics Revision Q's 26-01-2013Document5 pagesAnswers To IGCSE Physics Revision Q's 26-01-2013Yaw Kean HuatNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy WorksheetDAJANEYNo ratings yet
- 75 Compound MeasuresDocument8 pages75 Compound MeasuresJoel GrayNo ratings yet
- Space PhysicsNotesDocument44 pagesSpace PhysicsNotesthethmusan.2007No ratings yet
- P2 Forces and Terminal Velocity FoundationDocument13 pagesP2 Forces and Terminal Velocity Foundationdownendscience100% (1)
- P2.1-2 Physics: ForcesDocument49 pagesP2.1-2 Physics: ForcesSteve Bishop100% (3)
- 85 Describing Motion OrganizerDocument10 pages85 Describing Motion OrganizerFernando Sorto50% (2)
- DPS Phy - SET - BDocument3 pagesDPS Phy - SET - BscNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionDocument29 pages2.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionnourNo ratings yet
- Graphical Analysis Ws 2Document3 pagesGraphical Analysis Ws 2blackwellbertNo ratings yet
- Books Doubtnut Question BankDocument45 pagesBooks Doubtnut Question BankAanchal mathsNo ratings yet
- Dubbing With DeepfakesDocument1 pageDubbing With DeepfakesamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Iso 4033 2012 12 PDFDocument14 pagesIso 4033 2012 12 PDFamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Ninja PDFDocument1 pageNinja PDFamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- PED DiagramDocument1 pagePED DiagramamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- The Perfect WayDocument1 pageThe Perfect WayamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Company Culture EvolutionDocument5 pagesCompany Culture EvolutionamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- LibrariesDocument2 pagesLibrariesamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Need A High FiveDocument8 pagesNeed A High FiveamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Dubbing With DeepfakesDocument1 pageDubbing With DeepfakesamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Five Lessons From History: Big Takeaways About How, and Why, People Do What They DoDocument14 pagesFive Lessons From History: Big Takeaways About How, and Why, People Do What They DoamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Need A High FiveDocument1 pageNeed A High FiveamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LeadershipDocument4 pages21st Century LeadershipamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Klingersil c-4430 Data PDFDocument2 pagesKlingersil c-4430 Data PDFDhim131267No ratings yet
- Estado de SuperficiesDocument33 pagesEstado de SuperficiesamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Plating Hot Dip GalvanizingDocument2 pagesMechanical Plating Hot Dip GalvanizingamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Reduce Friction With Metal Cover For BoltingDocument7 pagesReduce Friction With Metal Cover For BoltingamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Index: 3-A Sanitary Standards, 3-A Accepted Practices, & P3-A Sanitary StandardsDocument4 pagesIndex: 3-A Sanitary Standards, 3-A Accepted Practices, & P3-A Sanitary StandardsamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- O Ring BroDocument256 pagesO Ring BrohildanNo ratings yet
- Moment Inertia PDFDocument18 pagesMoment Inertia PDFSameOldHatNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LeadershipDocument4 pages21st Century LeadershipamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument8 pagesProblem SolvingamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- 5SymptomsYourMaintenanceStrategyNeedsOptimising US PDFDocument9 pages5SymptomsYourMaintenanceStrategyNeedsOptimising US PDFJesus Enrique Figueroa GilNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Ebook - Know EverythingDocument20 pagesCause and Effect Ebook - Know EverythingamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Strategy DynamicsDocument6 pagesStrategy DynamicsamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Outokumpu Steel Grades Properties Global StandardsDocument20 pagesOutokumpu Steel Grades Properties Global StandardsLance BlackstarNo ratings yet
- Moment of InertiaDocument44 pagesMoment of InertiaRaja DalalNo ratings yet
- The Billionaries Preparing For The ApocalipseDocument11 pagesThe Billionaries Preparing For The ApocalipseamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Colors and Our ActionsDocument2 pagesColors and Our ActionsamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- The Billionaries Preparing For The ApocalipseDocument11 pagesThe Billionaries Preparing For The ApocalipseamilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Why Am I Here?Document4 pagesWhy Am I Here?amilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- People Vs Felipe Santiago - FCDocument2 pagesPeople Vs Felipe Santiago - FCBryle DrioNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Before AdjectivesDocument2 pagesAdverbs Before AdjectivesJuan Sanchez PrietoNo ratings yet
- Wetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsDocument3 pagesWetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsManish thapaNo ratings yet
- Grammar For TOEFLDocument23 pagesGrammar For TOEFLClaudia Alejandra B0% (1)
- Lista Agentiilor de Turism Licentiate Actualizare 16.09.2022Document498 pagesLista Agentiilor de Turism Licentiate Actualizare 16.09.2022LucianNo ratings yet
- ITC Green Centre: Gurgaon, IndiaDocument19 pagesITC Green Centre: Gurgaon, IndiaAgastya Dasari100% (2)
- Gamboa Vs Chan 2012 Case DigestDocument2 pagesGamboa Vs Chan 2012 Case DigestKrissa Jennesca Tullo100% (2)
- W2-Prepares Feasible and Practical BudgetDocument15 pagesW2-Prepares Feasible and Practical Budgetalfredo pintoNo ratings yet
- PCI Bank V CA, G.R. No. 121413, January 29, 2001Document10 pagesPCI Bank V CA, G.R. No. 121413, January 29, 2001ademarNo ratings yet
- Maule M7 ChecklistDocument2 pagesMaule M7 ChecklistRameez33No ratings yet
- " Thou Hast Made Me, and Shall Thy Work Decay?Document2 pages" Thou Hast Made Me, and Shall Thy Work Decay?Sbgacc SojitraNo ratings yet
- KalamDocument8 pagesKalamRohitKumarSahuNo ratings yet
- Science Project FOLIO About Density KSSM Form 1Document22 pagesScience Project FOLIO About Density KSSM Form 1SarveesshNo ratings yet
- Nandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Document336 pagesNandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Digitaladda IndiaNo ratings yet
- Sarcini: Caiet de PracticaDocument3 pagesSarcini: Caiet de PracticaGeorgian CristinaNo ratings yet
- ED Tox PGS.2021Document4 pagesED Tox PGS.2021Jm uniteNo ratings yet
- BirdLife South Africa Checklist of Birds 2023 ExcelDocument96 pagesBirdLife South Africa Checklist of Birds 2023 ExcelAkash AnandrajNo ratings yet
- Torah Hebreo PaleoDocument306 pagesTorah Hebreo PaleocamiloNo ratings yet
- Recent Cases On Minority RightsDocument10 pagesRecent Cases On Minority RightsHarsh DixitNo ratings yet
- Assessment NCM 101Document1 pageAssessment NCM 101Lorainne Angel U. MolinaNo ratings yet
- SQ1 Mogas95Document1 pageSQ1 Mogas95Basant Kumar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Gastric Emptying PresentationDocument8 pagesGastric Emptying Presentationrahul2kNo ratings yet
- Field Assignment On Feacal Sludge ManagementDocument10 pagesField Assignment On Feacal Sludge ManagementSarah NamyaloNo ratings yet
- DMSCO Log Book Vol.25 1947Document49 pagesDMSCO Log Book Vol.25 1947Des Moines University Archives and Rare Book RoomNo ratings yet
- W 26728Document42 pagesW 26728Sebastián MoraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy of The Human Person: Presented By: Mr. Melvin J. Reyes, LPTDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy of The Human Person: Presented By: Mr. Melvin J. Reyes, LPTMelvin J. Reyes100% (2)
- Student Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDocument2 pagesStudent Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDANIELA SIMONELLINo ratings yet
- Aero - 2013q2 Apu On DemandDocument32 pagesAero - 2013q2 Apu On DemandIvan MilosevicNo ratings yet
- Conductivity MeterDocument59 pagesConductivity MeterMuhammad AzeemNo ratings yet
- Christianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONDocument64 pagesChristianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONWorld Religion NewsNo ratings yet