Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves Misc
Uploaded by
zara_emmeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves Misc
Uploaded by
zara_emmeCopyright:
Available Formats
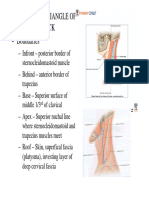
Triangle Submandibular
Submental
Borders Superior: body of mandible Anterior: anterior belly of digastric Posterior: posterior belly of digastric AND stylohyoid posteriorly Roof: skin, superficial fascia, platysma (phoenix wings), deep fascia Floor: mylohyoid muscle Superior: body of mandible Anterior: midline Posterior: anterior belly of digastric Roof: skin, superficial fascia, platysma, deep fascia Floor: mylohyoid muscle Superior: stylohyoid and posterior belly of digastric Inferior: superior belly of omohyoid Posterior: sternocleidomastoid Roof: skin, superficial fascia, platysma, deep fascia Floor: thyrohyoid, hyoglossus, constrictor pharyngeus medius/inferior
Neck Triangles (regional anatomy) ANTERIOR http://home.comcast.net/~wnor/lesson5.htm Arteries Veins Facial artery Facial vein Lingual artery
Nerves -Lingual nerve -branch of mandibular nerve (CNV3) -Submandibular ganglion -Hypoglossal nerve (CNXII)
Misc -Submandibular gland below all muscles -Hypoglossal nerve (CNXII) supplies all muscles of tongue except palatoglossus -The Submental lymph nodes -Superficial veins which form tributaries of the anterior jugular veins. -Mylohyoid muscle aids in swallowing and in depressing the mandible - Hypoglossal nerve continues to supply all muscles of the tongue except palatoglossus FLOOR Vagus nerve - contained within carotid sheath (with carotid and internal jugular vein) Internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve - supplies sensation to the epiglottis irritation causes coughing. External branch of superior laryngeal nerve- supplies cricothyroid muscle - Clinical note: Susceptible to damage during thyroidectomy as lies inferior and close to superior thyroid artery (which is ligated during thyroidectomy). Palsy results in loss of high pitch voice. MUSCLES Superficial layer sternohyoid (sh) superior belly of omohyoid (oh) Deep Layer
Carotid
After reflection of STERNOCoMtd, and internal jugular vein: -External carotid artery -Occipital artery -Facial artery -Lingual artery -Ascending pharyngeal artery -Superior thyroid artery -Internal carotid artery
SUPERFICIAL veins -common facial vein (cf) Other structures near by: -retromandibular vein (rm) -posterior auricular vein (pav) -facial vein (fv) -external jugular vein (ej) -anterior jugular vein (aj)
After reflection of STERNOCoMtd, and external jugular vein: -hypoglossal (XII) -C1 root of ansa cervicalis (C1) -C1 fibers running with hypoglossal nerve (nerve to thyrohyoid muscle (nth) -C2-C3 root of ansa cervicalis -ansa cervicalis (ac)
Muscular
Superior: superior belly of omohyoid Anterior: midline of neck Inferior: sternocleidomastoid Roof: skin, superficial fascia, platysma, deep fascia
thyroid (th) sternothyroid (st) -When the strap muscles are reflected, you are able to see the thyroid gland (tg) with its arteries (superior thyroid artery from the external carotid (sta) and the inferior thyroid artery from the thyrohyoid trunk from the subclavian (ita). POSTERIOR http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~rwillson/dentgross/headneck/Triangles/Posterior%20Triangle%20of%20the%20Neck.htm Borders Arteries Veins Nerves Posterior Boundary: trapezius m. Transverse cervical artery (tc) 1. Spinal Accessory nerve (XI) Anterior Boundary: sternocleidomastoid m. crosses the upper half of the Inferior Boundary: inferior belly of triangle diagonally and, omohyoid m. passing from the deep surface Floor: Splenius Capitus m, Levator of sternocleidomastoid Scapulae m, Scalenus Medius, and a inferiorly on levator scapulae portion of Scalenus Anterior. to reach the deep surface of Roof: superficial layer of Deep Investing trapezius, innervates Fascia sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. 2. Superficial cervical cutaneous branches of Cervical plexus - formed from ventral primary rami of spinal nerves C2-C4, which emerge from posterior border of sternocleidomastoid a. Lesser Occipital (C2) follows posterior border of SCM to innervate the scalp behind and above the ear. b. Great Auricular Nerve (C2,3) - crosses superficial to SCM and innervates the skin over the parotid gland, angle of the jaw and the posterior ear c. Transverse Cervical Cutaneous Nerve of the neck (C2,3) - crosses SCM superficially and, is cutaneous for the skin of the front and side of the neck (anterior triangle).
Triangle Occipital
Structures The lower four cervical nerves (C5,C6,C7,C8) are found in the scalene gap (space between scalenus anterior and scalenus medius muscles) and they, along with the first thoracic nerve (T1), make up the brachial plexus. Cervical nerves C5, C6, join to form the superior (upper) trunk of the brachial plexus, and these nerves as well as part of the superior trunk are found in the occipital triangle.
d. Supraclavicular Nerves (C3,4) - divides into medial, intermediate, and lateral branches, which supply sensation over the shoulder(from the sternoclavicular joint to the acromion process), lateral neck and anterior upper thoracic wall. Supraclavicular Inferior Boundary: clavicle Superior Boundary: inferior belly of Omohyoid m. Anterior Boundary: sternocleidomastoid m. Floor: Splenius Capitus m, Levator Scapulae m, Scalenus Medius m, and a small portion of the Scalenus Anterior m. Roof: superficial layer of Deep Investing Fascia Components Anterior scalene muscle Suprascapular artery Subclavian artery Subclavian vein External Jugular vein Suprascapular nerve Nerve to Subclavius Brachial plexus
Region Area Anterior to Supraclavicular Triangle
Neck (regional anatomy) Features
Notes
Joints
Description/Components
Ligaments/Tendons/Features
Clinical Correlate
DIAGRAMS
You might also like
- Diagnostic Radiology Lab Part 2 Answer SheetDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Radiology Lab Part 2 Answer SheetVictoria Sosa100% (1)
- Observational Patient Report Form PDFDocument1 pageObservational Patient Report Form PDFVictor PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Tort Final Pre WritesDocument5 pagesTort Final Pre WritesMartin Avanesian100% (1)
- Path CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Document37 pagesPath CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Coy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Flash Cards - Bone MarkingsDocument12 pagesFlash Cards - Bone Markingssimone dumbrellNo ratings yet
- Balanceador Coseng C 99 01 - ManualDocument10 pagesBalanceador Coseng C 99 01 - ManualMáximo Méndez100% (1)
- Kay's Final FRCA NotesDocument10 pagesKay's Final FRCA Notesmyat2567% (6)
- Gait Normalabnormal 120622041834 Phpapp02Document102 pagesGait Normalabnormal 120622041834 Phpapp02citaNo ratings yet
- 9 Anterior Triangle of The Neck E-LearningDocument22 pages9 Anterior Triangle of The Neck E-LearningHashim GhazoNo ratings yet
- 3d. Triangles of The NeckDocument82 pages3d. Triangles of The NeckBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Topographicanatomy Head TiskDocument61 pagesTopographicanatomy Head TiskRodicaPetrovaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 02 - Anatomic Topograhic Regions - HeadDocument94 pagesAnatomy Lecture 02 - Anatomic Topograhic Regions - HeadNikita Prasad100% (1)
- A Sole 16 12 14Document51 pagesA Sole 16 12 14Mariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Neck MusclesDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Neck MusclesMahnoor malikNo ratings yet
- Lymph Node Levels of NeckDocument4 pagesLymph Node Levels of NeckSaleh SaqerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Document23 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Radial and Median NervesDocument33 pagesRadial and Median NervesveegeerNo ratings yet
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck IIDocument49 pagesAnterior Triangle of The Neck IIvrajNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFDocument6 pagesIdoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFhieulee84No ratings yet
- Thoracic CageDocument66 pagesThoracic CageJohn KashNo ratings yet
- BIO 542 Lab PPT 01 - Neuroanatomy Review (Website)Document39 pagesBIO 542 Lab PPT 01 - Neuroanatomy Review (Website)NolanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy TopoDocument62 pagesAnatomy TopoDoina GoreanuNo ratings yet
- 16-Genital ProlapseDocument37 pages16-Genital Prolapseapi-3703352No ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDocument40 pagesPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Part 2 Thoracic CavityDocument56 pagesUnit 6 Part 2 Thoracic CavitySiraj ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (302) - 1Document82 pagesAnatomy (302) - 1Shehzad Noman SajidNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy 1Document12 pagesSurgical Anatomy 1Donya Gholami100% (1)
- 15 PharynxDocument9 pages15 Pharynxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Head and Neck AnswersDocument15 pagesHead and Neck AnswersANDRE MANo ratings yet
- Maternal AnatomyDocument27 pagesMaternal AnatomyGio BalisiNo ratings yet
- Study Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityDocument12 pagesStudy Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Anatomia TemporalDocument17 pagesAnatomia TemporalClaudia HeiderNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFRocio SandersNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lower LimbDocument4 pagesAnatomy Lower Limbch yaqoobNo ratings yet
- SCALP: (Keith L Moore)Document5 pagesSCALP: (Keith L Moore)rajtanniruNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 AnatomyDocument14 pagesLecture 3 AnatomyZA IDNo ratings yet
- Thorax AllDocument174 pagesThorax Allravindra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Obturator NerveDocument3 pagesObturator NerveDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Arteries of Upper Limb.Document16 pagesArteries of Upper Limb.Shimmering Moon100% (1)
- Posterior Triangle of Neck and Its AppliedDocument34 pagesPosterior Triangle of Neck and Its AppliedsnehalkmNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb 1Document14 pagesUpper Limb 1faraNo ratings yet
- C. Cardiac Notch: Evaluation Exam (Lungs Heart)Document4 pagesC. Cardiac Notch: Evaluation Exam (Lungs Heart)MARIA RADELINE LUNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb AnatomyDocument46 pagesUpper Limb AnatomyEduLessonNo ratings yet
- Thoracic CageDocument30 pagesThoracic CageLizz MarieNo ratings yet
- How I Evaluate The Neck Lymph NodesDocument29 pagesHow I Evaluate The Neck Lymph NodesMartín Avellaneda SantoméNo ratings yet
- I. History Taking A. Chief Complaint B. History of Present IllnessDocument4 pagesI. History Taking A. Chief Complaint B. History of Present IllnessKen MordenoNo ratings yet
- Triangles of NeckDocument6 pagesTriangles of NeckDr santoshNo ratings yet
- 4th Lecture HeadNeck and LympaticsDocument77 pages4th Lecture HeadNeck and LympaticsJeffrey Valdez Esteron100% (1)
- Anastomosis Around Elbow JTDocument14 pagesAnastomosis Around Elbow JTKinza100% (1)
- AIIMS November 2006 AnatomyDocument5 pagesAIIMS November 2006 Anatomyprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Erb's PointDocument14 pagesErb's PointRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Muscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionDocument37 pagesMuscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionMicky TsuiNo ratings yet
- Lungs 2014Document64 pagesLungs 2014atidNo ratings yet
- The Upper Extremity: Arm Muscles, Axilla, Brachial PlexusDocument37 pagesThe Upper Extremity: Arm Muscles, Axilla, Brachial Plexusdrkadiyala2No ratings yet
- Question 1 of 268: Vagus NerveDocument140 pagesQuestion 1 of 268: Vagus NerveFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 9, Abdominal WallDocument22 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 9, Abdominal WallAli Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- LARYNX and TRACHEADocument98 pagesLARYNX and TRACHEAPrincess Lorenzo MiguelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsDocument10 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsIssac LauNo ratings yet
- Nerves in Lower LimbDocument21 pagesNerves in Lower LimbTom WuNo ratings yet
- The Skull - Anatomy BonesDocument100 pagesThe Skull - Anatomy BonesFatima Kh SalahNo ratings yet
- The Lower Limb (Biomedic Unismuh 2012)Document65 pagesThe Lower Limb (Biomedic Unismuh 2012)Sadam_fasterNo ratings yet
- Neck TopographyDocument55 pagesNeck TopographyAnn AnaNo ratings yet
- Head & Neck-Posterior Triangle of NeckDocument7 pagesHead & Neck-Posterior Triangle of Neckkaurjasmine02203No ratings yet
- UW Psychiatry CorrectionsDocument52 pagesUW Psychiatry Correctionszara_emmeNo ratings yet
- UW Peds CorrectionsDocument40 pagesUW Peds Correctionszara_emmeNo ratings yet
- UW SurgeryDocument87 pagesUW Surgeryzara_emmeNo ratings yet
- UW OB CorrectionsDocument140 pagesUW OB Correctionszara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Pharm Ninja 1Document32 pagesPharm Ninja 1Haroon100% (1)
- Condition STRUCTURES INVOLVED (Definition) NotesDocument3 pagesCondition STRUCTURES INVOLVED (Definition) Noteszara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 54,55 - Triangles of NeckDocument14 pagesLecture 54,55 - Triangles of Neckzara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 54,55 - Triangles of NeckDocument14 pagesLecture 54,55 - Triangles of Neckzara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Shoulder AnatomyDocument5 pagesShoulder Anatomyzara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Dutton Chapter 11 Manual TherapiesDocument24 pagesDutton Chapter 11 Manual Therapiesmaria_dani100% (1)
- Review of Hydrogen Sulfide and Sour Gas Effects On The Eye - A Historical PerspectiveDocument22 pagesReview of Hydrogen Sulfide and Sour Gas Effects On The Eye - A Historical PerspectiveTaylorNo ratings yet
- Hernia FTDDocument71 pagesHernia FTDEmmanuel Papa AcquahNo ratings yet
- Tori Gwilt Service Learning Project Proposal Nurs320Document8 pagesTori Gwilt Service Learning Project Proposal Nurs320api-231010151No ratings yet
- Eppendorf Centrifugation Operating-Manual Centrifuge-5430-R PDFDocument92 pagesEppendorf Centrifugation Operating-Manual Centrifuge-5430-R PDFWinner Huarhua ChipaoNo ratings yet
- PYD Asanas V3 - 1Document33 pagesPYD Asanas V3 - 1aryakushalNo ratings yet
- SpringhDocument22 pagesSpringhMary Hiromi MizushimaNo ratings yet
- EXERCISESDocument14 pagesEXERCISESKasapharma y Kasanacorp Victor H. Zuñiga TapiaNo ratings yet
- Endodontic EmmergenciesDocument27 pagesEndodontic EmmergenciesJitender Reddy100% (1)
- HeadachesDocument42 pagesHeadachesAulia RahmiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background: It Is Commonly Found That TheDocument14 pages1.1 Background: It Is Commonly Found That ThetorkNo ratings yet
- Electric Chainsaw: Instruction ManualDocument10 pagesElectric Chainsaw: Instruction Manualshabab_14No ratings yet
- Robotrac ManualDocument202 pagesRobotrac ManualadasrafalskiNo ratings yet
- Death Roller RacingDocument7 pagesDeath Roller RacingVera MillerNo ratings yet
- Polaris 2002 Owners Manual (9917128) 03 PDFDocument146 pagesPolaris 2002 Owners Manual (9917128) 03 PDFCorey BarkerNo ratings yet
- Es fw105sg Washing Machine ManualDocument30 pagesEs fw105sg Washing Machine ManualM.M. AslamNo ratings yet
- Indikasi Torakotomi Chest TraumaDocument6 pagesIndikasi Torakotomi Chest TraumaanglingNo ratings yet
- Enjoy: Revisf OmDocument263 pagesEnjoy: Revisf OmEtinah ChevureNo ratings yet
- Mandibular MovementDocument56 pagesMandibular MovementSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- PZO900020EDocument12 pagesPZO900020Emartman1980100% (8)
- Introduction To Functional Electrical StimulationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Functional Electrical StimulationJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Law Unit 2 TortDocument10 pagesLaw Unit 2 Tortrima93No ratings yet
- Foot Cream Project: Name: - Namrata Pradhan (1215) SypgdpcmDocument8 pagesFoot Cream Project: Name: - Namrata Pradhan (1215) SypgdpcmVijay PradhanNo ratings yet