Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trig formulas & PDE solutions
Uploaded by
Vasil GorgievOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig formulas & PDE solutions
Uploaded by
Vasil GorgievCopyright:
Available Formats
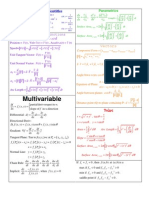
Formulas
Trigonometric formulas
sina sinb = 2 sin
1
2
(a b) cos
1
2
(a b)
cos a + cos b = 2 cos
1
2
(a + b) cos
1
2
(a b) cos a cos b = 2 sin
1
2
(a + b) sin
1
2
(b a)
sina cos b =
1
2
(sin(a b) + sin(a + b))
sina sinb =
1
2
(cos(a b) cos(a + b)) cos a cos b =
1
2
(cos(a b) + cos(a + b))
sin(a b) = sina cos b cos a sinb cos(a b) = cos a cos b sina sinb
Fourier series
Fourier series of f(x) dened on [L, L]:
1
2
a
0
+
n=1
(a
n
cos(nx/L) + b
n
sin(n/L))
where a
n
=
1
L
_
L
L
f(x) cos(nx/L)dx, b
n
=
1
L
_
L
L
f(x) sin(nx/L)dx.
Fourier cosine series (x [0, L]):
1
2
a
0
+
n=1
a
n
cos(nx/L) where a
n
=
2
L
_
L
0
f(x) cos(nx/L)dx.
Fourier sine series (x [0, L]):
n=1
b
n
sin(nx/L) where b
n
=
2
L
_
L
0
f(x) sin(nx/L)dx.
Dierentiation of a parameter in an integral
dI
dt
=
_
(t)
(t)
f
t
(x, t)dx + f((t), t)
(t) f((t), t)
(t).
Solution for wave equation with a source on R u
tt
c
2
u
xx
= f
u(x, t) =
1
2
[(x + ct) + (x ct)] +
1
2c
_
x+ct
xct
(s)ds +
1
2c
__
(x,t)
f
where (x) = u(x, 0), (x) = u
t
(x, 0), and
(x,t)
is the characteristic triangle for (x, t).
The Kirchho-Poisson solution for wave equation u
tt
c
2
u = 0
In 3D: u(x, t) =
1
4c
2
t
_
1
t
__
St
(
)d
_
+
1
4c
2
t
__
St
(
)d where S
t
is a sphere of radius ct.
In 2D: u(x, y, t) =
1
2c
t
_
__
Dt
(, )
_
(ct)
2
( x)
2
( y)
2
dd
_
+
1
2c
__
Dt
(, )
_
(ct)
2
( x)
2
( y)
2
dd where D
t
is a disk of radius ct.
Solution for the diusion equation with a source on R u
t
ku
xx
= f(x, t) (t > 0)
u(x, t) =
_
S(x y, t)(y)dy +
_
t
0
_
S(x y, t s)f(y, s)dyds (t > 0)
where S(x, t) =
1
4kt
e
x
2
/4kt
and (x) = u(x, 0).
The error function: Erf (x) =
2
_
x
0
e
p
2
dp; Erf () = 1.
1
in polar coordinates: =
2
r
2
+
1
r
r
+
1
r
2
2
in spherical coordinates: =
2
r
2
+
2
r
r
+
1
r
2
sin
sin
+
1
r
2
sin
2
2
Poissons formula for harmonic function in a disk: u(x) =
1
2a
_
|x
|=a
a
2
|x|
2
|x x
|
2
u(x
) ds
, or
u(r, ) =
1
2
_
2
0
a
2
r
2
a
2
2ar cos( ) + r
2
h()d where h() is the value of u on the circle r = a.
Greens rst identity:
__
D
v
u
n
dS =
___
D
v udV +
___
D
vudV
Greens second identity:
___
D
(uv vu)dV =
__
D
_
u
v
n
v
u
n
_
dS
Representation formula for a harmonic function u
u(x
0
) =
__
D
_
u(x)
n
K(x, x
0
) K(x, x
0
)
u
n
_
dS where K(x, x
0
) 1/(4|x x
0
|) for R
3
.
Solution of the Dirichlet problem for u = f using Greens function
u(x
0
) =
__
D
u(x)
G(x, x
0
)
n
dS +
___
D
f(x)G(x, x
0
) dV.
On the plane, dS and dV are replaced by dl (length element) and dA (area element), respectively.
Bessels dierential equation of order s:
d
2
dr
2
u +
1
r
d
dr
u + (1
s
2
r
2
)u = 0
Solutions of Bessels equation
For a non-integer s, the two independent solutions are
J
s
(r) =
j=0
(1)
j
(j + 1)(s + j + 1)
_
r
2
_
s+2j
where (s) =
_
0
e
t
t
s1
dt is the function.
For s = n, a non-negative integer, the solutions are
J
n
(r) =
j=0
(1)
j
j!(n + j)!
_
r
2
_
n+2j
Y
n
(r) =
2
_
+ ln
r
2
_
J
n
(r)
(1
n0
)
n1
j=0
(n j 1)!
j!
_
2
r
_
n2j
j=0
(1)
j
(H
j
+ H
n+j
)
j!(n + j)!
_
r
2
_
n+2j
Bessel functions of order s = 1/2: J
1/2
(r) =
_
2
r
sinr J
1/2
(r) =
_
2
r
cos r
For
sm
a,
sm
a being roots of the Bessel function J
s
_
a
0
J
s
(
sm
r)J
s
(
sm
r)rdr =
mm
1
2
a
2
[J
s
(
sm
a)]
2
=
mm
1
2
a
2
[J
s1
(
sm
a)]
2
Spherical harmonics: Y
m
l
(, ) = P
|m|
l
(cos ) e
im
_
2
0
_
0
Y
m
l
(, )Y
m
(, ) sindd =
ll
mm
4
2l + 1
(l + m)!
(l m)!
2
You might also like
- Solution Manual Elementary Classical Analysis Marsden Chap 1 To 4Document285 pagesSolution Manual Elementary Classical Analysis Marsden Chap 1 To 4queondax97% (59)
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Problem 3.52: Verify Stokes's Theorem For The Vector Field B Sin by EvaluatingDocument2 pagesProblem 3.52: Verify Stokes's Theorem For The Vector Field B Sin by EvaluatingEric KialNo ratings yet
- EXERCISES FOR INTRODUCTION FUNCTIONSDocument285 pagesEXERCISES FOR INTRODUCTION FUNCTIONSMun Su Park100% (1)
- Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0Document3 pagesUseful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0nh16888No ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Essential formulae for Number and AlgebraDocument16 pagesEssential formulae for Number and AlgebraMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Multivariable calculus practice problems and formulasDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus practice problems and formulaslieth-4No ratings yet
- Essential FormulasDocument7 pagesEssential FormulasShinigami01001No ratings yet
- MATH 103A Exercises 1: April 8, 2016Document7 pagesMATH 103A Exercises 1: April 8, 2016Anonymous HZfUNUGWzNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Formulas Math Midterm Test I DEDocument2 pagesFormulas Math Midterm Test I DEUmesh Rao H NNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Basic (1) MathDocument2 pagesBasic (1) MathIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Multivariable calculus exam with 7 problemsDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus exam with 7 problemslieth-4No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Final Exam Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Formula SheetYuhao ChenNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus Formulas GuideDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Formulas Guidevignes011No ratings yet
- N highest value wave parametersDocument31 pagesN highest value wave parametersGOWTHAMNo ratings yet
- Particle in a 3D Box Wave FunctionsDocument4 pagesParticle in a 3D Box Wave FunctionshuuutschNo ratings yet
- Formula For SOA MFEDocument4 pagesFormula For SOA MFEferferNo ratings yet
- Multivariable calculus practice problemsDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus practice problemslieth-4No ratings yet
- Wave Equation On The Unit DiskDocument5 pagesWave Equation On The Unit DiskColin EhrNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Solutions Chapter 7, Quantum Chemistry, 5 Ed., LevineDocument10 pagesProblem Set Solutions Chapter 7, Quantum Chemistry, 5 Ed., LevineSabellano Loven RalphNo ratings yet
- Example of The Use of Stokes TheoremDocument3 pagesExample of The Use of Stokes TheoremSam FraserNo ratings yet
- 3D Reaction-Diffusion EquationsDocument13 pages3D Reaction-Diffusion EquationsShalini JagtianiNo ratings yet
- List of exercises on series and sequencesDocument8 pagesList of exercises on series and sequencesp1tru1mariusNo ratings yet
- AP BC ReviewDocument7 pagesAP BC ReviewchowmeinnoodleNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For MathsDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For Mathsbobd123No ratings yet
- Math 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItDocument3 pagesMath 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 pagesX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039No ratings yet
- Physics Exam II Green's Identities Multipole MomentsDocument4 pagesPhysics Exam II Green's Identities Multipole Momentstms8c8No ratings yet
- Fourier Finite TransformsDocument8 pagesFourier Finite Transformserev_20No ratings yet
- The Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingDocument12 pagesThe Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingRaja Fathurrahim AkmaludinNo ratings yet
- Special Functions Supplement 2Document10 pagesSpecial Functions Supplement 2Lodo MetalicoNo ratings yet
- Shankar 10.2.3Document4 pagesShankar 10.2.3Arooj MukarramNo ratings yet
- Sol 9 Fall 04Document8 pagesSol 9 Fall 04Daniel Cervantes CabreraNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Large Deviations and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesSeminar in Large Deviations and ApplicationsDomenique SchwestermannNo ratings yet
- Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulaDocument11 pagesActual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formulanirakaru123No ratings yet
- AIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)Document7 pagesAIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)kishangopi123No ratings yet
- MATH 300 Fall 2004 Advanced Boundary Value Problems I Solutions To Sample Final Exam Friday December 3, 2004Document6 pagesMATH 300 Fall 2004 Advanced Boundary Value Problems I Solutions To Sample Final Exam Friday December 3, 2004tehepiconeNo ratings yet
- Notas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaDocument10 pagesNotas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaAndrés David Martínez MarteloNo ratings yet
- Exam Formulas For CALCULUSDocument3 pagesExam Formulas For CALCULUSWendy HuynhNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- Greens TheoremDocument9 pagesGreens TheoremAnonymous KIUgOYNo ratings yet
- Latihan Matematika Bab 6Document7 pagesLatihan Matematika Bab 6Risma fNo ratings yet
- Sol 4 Fall 04Document12 pagesSol 4 Fall 04Daniel Cervantes CabreraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 SolutionsAkshay NarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet