Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PP Blues Onset 1-10 Days After Birth
Uploaded by
Bianca CamilleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PP Blues Onset 1-10 Days After Birth
Uploaded by
Bianca CamilleCopyright:
Available Formats
PP Blues PP Depression PP Psychosis
onset 1-10 days after birth 1-12 months after birth Within first month after birth
symptoms Sadness, tears Anxiety,feeling of loss,sadness Delusions or hallucinations
incidence 70% of all births 10% of all births 1% to 2% of all births
Etiology Probable hormonal Hx of previous depression,hormonalPossible activation of previous mental
(possible) changes,stress of life response,lack of social support illness family hx of bipolar d/o
changes
therapy Support, empathy Counseling,drug therapy Psychotherapy,drug therapy
Nursing Offering compassion & Referring to counseling Referring to counseling,safeguarding
Role understanding mother from injury to self or to newborn
Maternal Concerns & Feelings during Postpartum:
ABANDONMENT - Only hours before, they were the center of attention, with everyone asking about their
health and well-being. Now suddenly, the baby is the chief interest. The woman may feel confused by a
sensation very close to jealousy. Father may have much same feelings Shared responsibility for infant care
can help to make both partners feel equally involved in the baby’s care and can help alleviate these
feelings.
DISAPPOINTMENT - It can be difficult for parents to feel positive immediately about a child who does
not meet their expectations. Handle the child warmly. Comment on the child good points.
POSTPARTUM BLUES (Baby blues)- 50% of women experience some feelings of overwhelming sadness.
The mother burst into tears easily or may feel let down or be irritable. Maybe due to hormonal changes
(decrease estrogen & progesterone). It maybe a response to dependence and low self-esteem caused by
exhaustion, being away from home, physical discomfort, and the tension endangered by assuming a new
role. A woman needs aasurance that sudden crying episodes are normal. Allow to Verbalize feelings
POSTPARTUM BLUES
· “baby blues”; normal part of postpartum experience but only for a few days
· Tearfulness, irritability, sometimes insomnia
· Causes: hormonal fluctuations, physical exhaustion, maternal role adjustment
o Reassure that this is normal
o Anticipatory guidance and individualized support from health care personnel are important to help
the parents understand
o Keeping lines of communication open
o Allow her to make as many decision as possible can help give her sense of control over her life
o Allow her to verbalize her feelings and concerns
POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION
· A serious & debilitating depression, occurring within first 9 months after delivery, often within the initial
weeks or months
· Sadness, crying, insomnia, decreased appetite, withdrawal and sometimes suicidal ideation or the desire
to harm the infant
· Somatic symptoms: headaches, diarrhea, constipation, severe anxiety, feeling as though they are jumping
out of their skinm and/or just not feeling like themselves
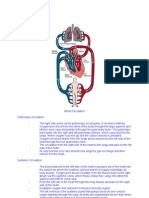
Physiologic Changes of Postpartal Period
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM – 1st or 2nd week postpartum, the blood volume has returned to its
normal pre-pregnancy level.
Blood Volume
Hemorrhage – bleeding of > 500cc
CS – 600 – 800 cc normal NSD 500 cc
Early postpartum hemorrhage– bleeding within 1st 24 hrs. Baggy or relaxed uterus & profuse bleeding –
uterine atony. Complications: hypovolemic shock.
Mgt:
1.) massage uterus until contracted
2.) cold compress
3.) modified trendelenberg
4.) IV fast drip/ oxytocin IV drip
The 40% increase in blood volume during pregnancy enters the maternal circulation within 5 to 10
minutes after placental delivery making this period very critical to gravidocardiacs because their
damaged heart may not be able to handle this sudden increase in cardiac workload.
Blood volume returns to nonpregnant levels 1-2 weeks after delivery resulting in a decline in cardiac
output by 30%.
Blood Components
Hct rises in the first 3 to 7 days due to hemoconcentration caused by excretion of large amounts of
fluids in the urine (diuresis during the first few days after delivery). Hct level returns to normal on the
fourth to fifth postpartum week.
Leukocytosis of 20,000 to 30,000 (normal is 5000 to 10000) during the first 12 days characterized by
increased neutrophils and easinophils and decreased lymphocytes.
Fibrinogen and thromboplastin remains elevated until the 3rd postpartum week.
Increased leukocyte sedimentation rate.
1. Cardiovascular system
· 30-50% increase in total cardiac volume during pregnancy will be reabsorbed into the general
circulation within 5-10 minutes after placental delivery
· Blood loss: vaginal birth- 300-500 ml; cesarean birth- 500-1000ml
· Blood volume decrease to non pregnant levels by fourth week after delivery
· Hematocrit rises by the 3rd-7th postpartum day
· WBC increases to 20000-30000/mm3
o Cannot be used as an indicator or signs of postpartum infection
o Part of body’s defense system against infection
o Aid to healing
· Extensive activation of the clotting factors which encourages thromboembolization:
o Ambulation is done early 4-8hours after normal vaginal delivery
When ambulating the newly-delivered patient for the first time, the nurse
should hold on to the patient’s arm.
o Massage is contraindicated.
· All blood values are back to prenatal levels by the 3rd-4th week postpartum
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 2006 - PES - Normal Physiological Characteristics of Elite SwimmersDocument23 pages2006 - PES - Normal Physiological Characteristics of Elite SwimmersJennifer AbateNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Reviewer - 2Document6 pagesActivity 1 Reviewer - 2Francis Zaccheau ValdezNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia UpToDateDocument60 pagesPreeclampsia UpToDateMauricio Marin MontoyaNo ratings yet
- FasciaDocument2 pagesFasciaBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Fournier GangreneDocument1 pageFournier GangreneBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- What Is The Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Oral Glucose Tolerance TestBianca Camille100% (1)
- FasciaDocument2 pagesFasciaBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Fournier Gangrene 1Document16 pagesFournier Gangrene 1Bianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Name: Bianca Camille N. AliñoDocument2 pagesName: Bianca Camille N. AliñoBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PostpartumDocument1 pageCardiovascular System PostpartumBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- NAME of DRUG Generic Name: Salmeterol Xinafoate Classification: Beta2-SelectiveDocument2 pagesNAME of DRUG Generic Name: Salmeterol Xinafoate Classification: Beta2-SelectiveBianca Camille100% (2)
- Postpartum CareDocument13 pagesPostpartum CareChristian100% (11)
- Name of DrugDocument1 pageName of DrugBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Phagocytosis - The Ingestion of A Particulate Matter Involving TheDocument1 pagePhagocytosis - The Ingestion of A Particulate Matter Involving TheBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument3 pagesImmediate Care of The NewbornBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument29 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyBianca CamilleNo ratings yet
- Ok - Effect of Melatonin On Broiler ChicksDocument12 pagesOk - Effect of Melatonin On Broiler ChicksOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part6Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part6Jose EscobarNo ratings yet
- PCV and EsrDocument40 pagesPCV and EsrArslan Arshad100% (2)
- Physiology Laboratory MidtermsDocument114 pagesPhysiology Laboratory MidtermsJessamineNo ratings yet
- BC-2800 Service Training: Hematology Global Technical Support Department Version V2.0 NO.:MXQ-12028-BC-2800Document157 pagesBC-2800 Service Training: Hematology Global Technical Support Department Version V2.0 NO.:MXQ-12028-BC-2800Edgar Mendoza GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Hematology and Blood Biochemistry ProfileDocument11 pagesHematology and Blood Biochemistry ProfileBiomédica Fabiane IngrideNo ratings yet
- The Effect of High Temperature On The Hematological Parameters of Bakery WorkersDocument4 pagesThe Effect of High Temperature On The Hematological Parameters of Bakery WorkersYaser MNo ratings yet
- Fecamds Alt To Practical PhysioDocument7 pagesFecamds Alt To Practical PhysioNwaoha Chibuzor AnthonyNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Hematology L5Document22 pagesHematology L5Haibat Sultan StationeryNo ratings yet
- Manual Centrifuga M24Document4 pagesManual Centrifuga M24BiomedicaNo ratings yet
- Review in Causes of Viscosity in FluidsDocument7 pagesReview in Causes of Viscosity in FluidsSaryth Darianna Cardenas FNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Manual Procedure and Automated For Determinant of Wbcs and PCV in Maternity and Labor Hospital in Karbala CityDocument3 pagesComparison Between Manual Procedure and Automated For Determinant of Wbcs and PCV in Maternity and Labor Hospital in Karbala Cityyousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- Hemo Control PresentationDocument31 pagesHemo Control PresentationAnthony CasasNo ratings yet
- Manual de Usuario - Centrifuga NF 048Document12 pagesManual de Usuario - Centrifuga NF 048Brevas CuchoNo ratings yet
- System M Insevice Overview 11.8.11Document26 pagesSystem M Insevice Overview 11.8.11Travis DayNo ratings yet
- MLSP Lecture Finals ReviewerDocument22 pagesMLSP Lecture Finals ReviewerAkira Anne KreyceNo ratings yet
- A01a00053nen Abx DifftrolDocument4 pagesA01a00053nen Abx DifftrolNAMPEWO ELIZABETHNo ratings yet
- Dengue Management Guideline 2020, Training Materials Top SheetDocument257 pagesDengue Management Guideline 2020, Training Materials Top Sheetdeepak das100% (1)
- WWW Ncbi NLM Nih Gov PMC Articles PMC4997795 Report ClassicDocument15 pagesWWW Ncbi NLM Nih Gov PMC Articles PMC4997795 Report ClassicStephany Mendez MendozaNo ratings yet
- CBC Reviewer Anaphy LabDocument9 pagesCBC Reviewer Anaphy LabARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Haematological Parameters and Factors Affecting TH PDFDocument12 pagesHaematological Parameters and Factors Affecting TH PDFZainab HasanNo ratings yet
- Nigella Sativa (Black Seed) Safety: An Overview: Open Access ReviewDocument11 pagesNigella Sativa (Black Seed) Safety: An Overview: Open Access ReviewShinta DamayantiNo ratings yet
- BioBuild Desert CrossingDocument8 pagesBioBuild Desert CrossingSubbaraju GvNo ratings yet
- Surgery: Cholecystectomy: Mariano Marcos State UniversityDocument23 pagesSurgery: Cholecystectomy: Mariano Marcos State UniversityFrancine JoseNo ratings yet
- J World Aquaculture Soc - 2016 - Phulia - Replacement of Soybean Meal With Fermented Jatropha Curcas Kernel Meal in TheDocument8 pagesJ World Aquaculture Soc - 2016 - Phulia - Replacement of Soybean Meal With Fermented Jatropha Curcas Kernel Meal in TheShigufta AliNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Iron-Enriched Baker's Yeast and Its Efficiency in Recovery of Rats From Dietary Iron DeficiencyDocument11 pagesPreparation of Iron-Enriched Baker's Yeast and Its Efficiency in Recovery of Rats From Dietary Iron DeficiencyAsdfNo ratings yet