Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior: The Brain
Uploaded by
Elena Nicoleta ManOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior: The Brain
Uploaded by
Elena Nicoleta ManCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
The Brain
Small; fits in your hands (under 3 pounds) About as solid as firm jello Main fuel source is sugar (glucose)
Brain vs. Mind
Mind: Not observable, our mental activities o Thinking, feeling, learning Brain: Observable, physical structure o Membranes, fluid, chemicals
What is the Brain made of?
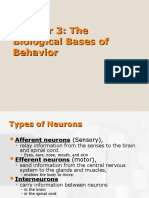
Neurons: Strings of long, thin cells o Messages to and from brain travel along neurons o May be fraction of an inch to 3 feet in length Glial Cells: Structure that supports neurons (myelin sheath) o The insulate the neurons; protect them o Help the neurons grow and function
Neuron Development
Begin developing at conception Mature human brain has about 100 billion neurons/glial cells Once developed, no more are produced Damage or disease is irreversible
Cell Body
Keeps neuron working; its fuel o Nucleus is in cell body with DNA instructions
Dendrites
Extensions from cell body o Receives info from environment/other neurons o Helps communicate through body
Axon
Single extension; gives signals to other neurons, organs, muscles o May be long or super-short
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
The Synapse
Synapse separates neurons o 20-30 billionths of a meter Information flows down axon into synapse Dendrite receptors take in information Synapse: gap between axon and dendrite Help send messages from neuron to neuron Released into synapse like water droplets being sprayed Type of info varies by neurotransmitter o Dopamine: Motor activity Less = Parkinsons More = schizophrenia o Serotonin: Emotions and sleep
Neurotransmitters
The Central Nervous System
Made up of the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord is as thick as your thumb and 16-18 inches long o Bundles of axons and dendrites
Peripheral Nervous System
All nerves outside brain and spinal cord Move muscles, sensations from body, etc. Two parts: somatic and autonomic Nerves connected to body parts you move voluntarily Our limbs, back, neck, chest, etc.
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, digestion, etc. Occurs automatically without thinking about it o Blinking, breathing (somewhat controlled)
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
Sympathetic
Set off by threatening, challenging physical or psychological things o Body is made ready for action A protection device o Fight or Flee from situations Sports, accidents, exams, etc. can trigger this response
Parasympathetic
Brings body back to a normal state Relaxed, peaceful feelings mean parasympathetic system is working
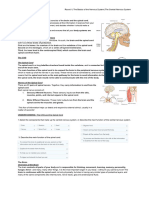
The Brain
3 Parts: Hindbrain, Midbrain, and forebrain 2 Halves: Right Hemisphere and Left Hemisphere
Hindbrain
Rear base of the skull; second largest division Unchanged over time Pons: Bridge connecting spinal cord with brain and its different parts o Balance, hearing, and even our amount of sleep
Medulla (Hindbrain)
Controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure o Excessive drinking may damage medulla o Results in death
Cerebellum (Hindbrain)
Controls coordination and posture o Helps make movement smooth o Loss of control with alcohol can damage cerebellum
Midbrain
Smallest division; above pons (middle of brain) Tells brain about incoming sensory information (reticular formation) Sends info into forebrain for processing
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
Midbrain Features
Without it, we would be in a coma o Forebrain would never be stimulated Unconsciousness: Anesthesia depresses reticular formation o Makes us unable to feel things Sleep: Reticular formation is blocked o Temporary unconsciousness Largest part; involved with many responses Sensory info, emotions, sleep, higher thinking skills, etc. Divided into layers and areas Relays sensory information to different parts of the brain Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, etc. o Problems lead to weird eating and drinking patterns
Forebrain
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Cerebral Cortex and Cerebrum
Cerebrum: Inner layer of forebrain Cortex: Outer layer of forebrain Spread out it would be 18 X 18 o Scrunched within the skull
Frontal Lobe
Located in front part of brain Social-emotional behaviors; allow us to act normal o Healthy personality, make decisions Motor Cortex: Works with voluntary body movements Located behind frontal lobe Somatosensory Cortex: Body sensations like touch, pain, temperature o Damage = Loss of feeling
Parietal Lobe
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
Temporal Lobe
Located below Parietal lobe Critical to hearing and speech Primary Auditory Cortex: Small area receiving info from the ears Located near the back of the brain Main area involved with vision Takes info from the eyes and makes it meaningful
Occipital Lobe
Hemispheres
Brain is divided into two equal halves Corpus Callosum connects the two o Corpus Callosum: Band of nerves Left brain controls right side of the body, right brain controls left side Studies show left side is language, right is more visual, size oriented
Recording
Wires (electrodes) in brain can record changes in neurons Can test what occurs with different stimulation EEG measures whole areas at once
You might also like
- Medical SurgicalDocument119 pagesMedical SurgicalTammy TamNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemTalha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous System: BrainDocument12 pagesThe Central Nervous System: BrainsheinelleNo ratings yet
- Sodium Borate: What Is Boron?Document2 pagesSodium Borate: What Is Boron?Gary WhiteNo ratings yet
- Body PartDocument100 pagesBody PartClarissa Muliawan100% (1)
- Unit-II Mechanisms of Mind: Training The BrainDocument23 pagesUnit-II Mechanisms of Mind: Training The BrainPallavi BhartiNo ratings yet
- WFRP - White Dwarf 99 - The Ritual (The Enemy Within)Document10 pagesWFRP - White Dwarf 99 - The Ritual (The Enemy Within)Luife Lopez100% (2)
- How Your Brain WorksDocument12 pagesHow Your Brain WorksPallavi BhartiNo ratings yet
- Druze ScriptureDocument15 pagesDruze ScriptureChristopher DeMott100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemKristie Becker100% (1)
- Focus Charting of FDocument12 pagesFocus Charting of FRobert Rivas0% (2)
- โท the BrainDocument39 pagesโท the BrainFadil Wanna-mart100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymhel03_chickmagnetNo ratings yet
- 1stQ Week5Document3 pages1stQ Week5Jesse QuingaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain and Spinal CordDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Brain and Spinal CordKate Nucum Fernandez100% (1)
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- Brain Structures and Their Function A-Level BiologyDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and Their Function A-Level BiologyUjjal Kumar Sarker100% (2)
- Accounting 110: Acc110Document19 pagesAccounting 110: Acc110ahoffm05100% (1)
- Brain and Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesBrain and Nervous SystemBrenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System868.CapalotNo ratings yet
- Trixie - Anatomy and Physiology (Brain Tumor)Document4 pagesTrixie - Anatomy and Physiology (Brain Tumor)Trixie Marie Sabile AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Control, Coordination and Human BrainDocument8 pagesControl, Coordination and Human BrainSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- L.4,2 - Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesL.4,2 - Nervous SystemJari JariNo ratings yet
- Interface Between Pituitary and BrainDocument4 pagesInterface Between Pituitary and BrainHuck KimNo ratings yet
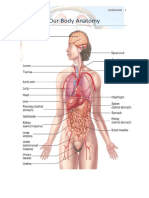
- OUR BODY Chapter - I (Science Class IV)Document4 pagesOUR BODY Chapter - I (Science Class IV)doultaniskNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument12 pagesHuman BrainJashwanthNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemshhhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument6 pagesLesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMNatoya RichardsNo ratings yet
- Nervous System FunctionsDocument10 pagesNervous System FunctionsJovi Leo PunoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemIhtisham Ul haqNo ratings yet
- Neurosciencie For KidsDocument10 pagesNeurosciencie For KidsAna Maria RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Cns Portfolio EditionDocument9 pagesThe Cns Portfolio Editionapi-438492450No ratings yet
- 4-The Nervous SystémDocument6 pages4-The Nervous SystémEma FröhlichováNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesThe Nervous SystemMegha DevanpalliNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument123 pagesNeurologic Assessmentdarkdark38No ratings yet
- Biopsyc Final NotesDocument33 pagesBiopsyc Final Notesapi-296712028No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument57 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorJAMES ALDRIN CALVEZ PAMPOSANo ratings yet
- Patients Profile I. Biographic DataDocument18 pagesPatients Profile I. Biographic DataEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The Nervous Systemlengers poworNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument35 pagesPhysiological Basis of BehaviorAnna Rhea BurerosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 3: Organization of The Nervous SystemTaz_devil91No ratings yet
- Brain Bee R1 P2Document9 pagesBrain Bee R1 P2sarahsyedazakiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyRachell SamsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Central Nervous SystemDocument102 pagesLecture 13 - Central Nervous Systemhamako02No ratings yet
- Class 5 - Science Chapter 4Document9 pagesClass 5 - Science Chapter 4aanya2706No ratings yet
- (16-17) Brain SummaryDocument57 pages(16-17) Brain SummarybartNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Michael Piccio, Collin Porter, Alex BaldwinDocument2 pagesNervous System Michael Piccio, Collin Porter, Alex BaldwinMichael PiccioNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy: Brain and Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesBrain Anatomy: Brain and Nervous SystemNader Smadi100% (2)
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASDocument16 pagesPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASJustin JoshNo ratings yet
- Function of The BrainDocument16 pagesFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyssairej06No ratings yet
- CHP 7 Class 10Document13 pagesCHP 7 Class 10sourabh nuwalNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- PYC 1501 Basic Psychology Structures Functions of HnsDocument11 pagesPYC 1501 Basic Psychology Structures Functions of Hnsektha_nankoomar91100% (5)
- Control and CoordinationDocument11 pagesControl and CoordinationADITYA MISHRANo ratings yet
- Neurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNeurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemItpixels OfficebackdoorNo ratings yet
- Control Coordination (Prashant Kirad)Document16 pagesControl Coordination (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal17No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviordewani mastaniNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemalanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument212 pagesNervous SystemJimvel PelayoNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesNeuroscienceZerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurologic SystemDocument127 pagesAssessment of Neurologic SystemAndrew WongNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemBarangay Onefourseven CaloocanNo ratings yet
- 04 RecursionDocument21 pages04 RecursionRazan AbabNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument10 pagesAdverbsKarina Ponce RiosNo ratings yet
- The Preparedness of The Data Center College of The Philippines To The Flexible Learning Amidst Covid-19 PandemicDocument16 pagesThe Preparedness of The Data Center College of The Philippines To The Flexible Learning Amidst Covid-19 PandemicInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Win Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsDocument11 pagesWin Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsadetriyunitaNo ratings yet
- Clinincal Decision Support SystemDocument10 pagesClinincal Decision Support Systemم. سهير عبد داؤد عسىNo ratings yet
- The Systems' Institute of Hindu ASTROLOGY, GURGAON (INDIA) (Registered)Document8 pagesThe Systems' Institute of Hindu ASTROLOGY, GURGAON (INDIA) (Registered)SiddharthSharmaNo ratings yet
- Fansubbers The Case of The Czech Republic and PolandDocument9 pagesFansubbers The Case of The Czech Republic and Polandmusafir24No ratings yet
- In The World of Nursing Education, The Nurs FPX 4900 Assessment Stands As A PivotalDocument3 pagesIn The World of Nursing Education, The Nurs FPX 4900 Assessment Stands As A Pivotalarthurella789No ratings yet
- In Mein KampfDocument3 pagesIn Mein KampfAnonymous t5XUqBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 INTRODUCTION TO PRESTRESSED CONCRETEDocument15 pagesChapter 4 INTRODUCTION TO PRESTRESSED CONCRETEyosef gemessaNo ratings yet
- Essay EnglishDocument4 pagesEssay Englishkiera.kassellNo ratings yet
- Technique Du Micro-Enseignement Une Approche PourDocument11 pagesTechnique Du Micro-Enseignement Une Approche PourMohamed NaciriNo ratings yet
- Kormos - Csizer Language Learning 2008Document29 pagesKormos - Csizer Language Learning 2008Anonymous rDHWR8eBNo ratings yet
- Sample Midterm ExamDocument6 pagesSample Midterm ExamRenel AluciljaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Social Structural Theories of CrimeDocument5 pagesChapter 12 Social Structural Theories of CrimeKaroline Thomas100% (1)
- Complete PDFDocument495 pagesComplete PDFMárcio MoscosoNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Digital Banking - New DelhiDocument4 pagesBrochure - Digital Banking - New Delhiankitgarg13No ratings yet
- Conversation Between God and LuciferDocument3 pagesConversation Between God and LuciferRiddhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletan Problems in Soccer PlayersDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletan Problems in Soccer PlayersAlexandru ChivaranNo ratings yet
- Lorraln - Corson, Solutions Manual For Electromagnetism - Principles and Applications PDFDocument93 pagesLorraln - Corson, Solutions Manual For Electromagnetism - Principles and Applications PDFc. sorasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Risk Assessment ProceduresDocument40 pagesChapter 4 - Risk Assessment ProceduresTeltel BillenaNo ratings yet
- 619Document3 pages619elektron2010No ratings yet
- Influencing Factors Behind The Criminal Attitude: A Study of Central Jail PeshawarDocument13 pagesInfluencing Factors Behind The Criminal Attitude: A Study of Central Jail PeshawarAmir Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Awareness and Usage of Internet Banking Facilities in Sri LankaDocument18 pagesAwareness and Usage of Internet Banking Facilities in Sri LankaTharindu Thathsarana RajapakshaNo ratings yet