Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Planets Core - MP 4 Project
Uploaded by
api-246424279Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Planets Core - MP 4 Project
Uploaded by
api-246424279Copyright:
Available Formats
Science
Honors Project MP 4: New Planets Core DUE: June 4, 2013
Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered!
It revolved around a nearby star, just outside our solar system. An unmanned space probe was sent to bring back rock core samples* from the new planet. You, as a geologist, have the special assignment of examining the rock core sample and developing a geological timeline that tells the history of your newly discovered planet. Considerations: 1. The honors project extends what we are learning in class by exploring beyond Sedimentary rocks to learn about and understand how Metamorphic and Igneous rocks are formed. Also you will be recreating a geological timeline based on your observations, just as we do in class with the Grand Canyon using Principles of Geology. 2. The honors project is completely independent of school (there will be little to no time given in class to complete it). 3. Dont procrastinate! It takes time and effort to submit a project that is worthy of honors distinction. 4. Complete all work on your own. It is permissible to ask questions, but not to have someone do your work for you.
New Planets Core
A new planet has just been discovered! It revolved around a nearby star, just outside our solar system. An unmanned space probe was sent to bring back rock core samples* from the new planet. You, as a geologist, have the special assignment of examining the rock core sample and developing a geological timeline that tells the history of your newly discovered planet. You are expected to apply the geological principles you have learned to identify the rocks and fossils and draw conclusions. Consider the Law of Superposition and Principle of Horizontality when observing the core sample. Be prepared to defend your interpretation of the geological history of your planet.
*Geologists can drill deep down into the surface of a planet and pull up a tube containing
all the rock layers beneath the crust. The sample inside the tube is called a core sample and it shows the order of the rock layers below. Geologists use these rock layers to infer how the planet evolved over time and what environmental changes might have occurred.
An Actual Core Sample
Drilling for a CORE SAMPLE
To be turned in:
Print out of WebQuest Test Your Skills Results Identification of Rock Layers Worksheet Geological Timeline Planets Factual History: Story or Geological Report
**Make sure your name and period are on your project**
Part One: WebQuest
Before you can identify the rock layers found in the core sample, you must first learn about the three types of rocks. Go to the following WebQuest: http://www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/index.html Follow the WebQuest through every page and interact with all of the activities. Be sure to use the attached worksheet when reading to help organize your thoughts and take notes. At the end of the WebQuest there is a fifteen question, multiple choice, test. Complete the test and print out the Rock Cycle Assessment Test Results page when you must score at least a 73% (11 out of 15 questions). That means you may need to take the test several times before printing the results of a passing grade! Next, you will use the information you learned in the WebQuest and infer what types of rocks each layer contains in the core sample.
Part Two: Identifying Rock Layers in the Core Sample
Look at the core sample. Using the observations and evidence, identify which type of rock each layer is made of: Metamorphic, Igneous, or Sedimentary. For the Sedimentary rocks, go a step further and identify the rock name: Sandstone, Limestone, or Shale. Fill in the rock type and environment information on the Identification of Rock Layers worksheet. Examples of the environments are: Beach, Desert, Swamp, Ocean, Volcano, Heat and Pressure towards the center of the Earth, etc. In addition to turning in the worksheet, you will use it to guide your geological timeline.
Part Three: Geological Timeline of the New Planet
Once geologists know what types of rocks are in the core sample, they can use the geological principles such as the Law of Superposition and Principle of Horizontality to create a timeline of the planets history. You will create a timeline, by hand or electronically, showing the history of your new planet. Your timeline should show the rock layers in the order that they were deposited and what type of rock existed during each time period. Consider the following: - Which rock layers came first? Which rock layers are most recent? - What does the width of the layer tell you? - Are the rock layers horizontal or did something happen to cause a shift in that layer? Visit these websites to create a timeline online: http://timerime.com/ http://www.timetoast.com/ http://www.preceden.com/
Part Four: Planets Factual History
Use the timeline to create a document describing the geological history of the new planet. You can either write the history as a story OR a factual, geological report (pick one). You are describing your timeline in narrative form, including how the environment has changed over time and the evidence that led to your interpretation of the core sample (rock types). Your history must include: - What type of rock is in each layer (in order that it was deposited) - Describe what environment formed each type of rock and how long it took (relative to other layers) - What evidence led you to the identification of the rock (support your claim) Be sure to look at the rubric before turning it in to ensure that all the parts (4) are completed correctly. **Make sure your name and period are on your project**
**All four parts must be turned together to be graded**
Grading Rubric: 0
Test Your Skills WebQuest Assessment Identification of Rock Layers
Student did not turn in the assessment results. Student completed Identification of Rock Layers worksheet and there are 4 or more errors. Timeline was not in the order that the rocks were deposited OR did not include the rock types OR was not turned in. Factual history of planet included only ONE of the three criteria OR was not turned in. Criteria: (1) how the environments changed over time in the order that the rocks were deposited, (2) evidence used to ID rock layers, and (3) environments are accurate. There are more than two errors in the capitalization of sentences AND/OR ending punctuation AND/OR spelling.
1
Assessment was printed out and turned in, but students did not pass test (score at least 11 out of 15 points). Student completed Identification of Rock Layers worksheet and there are 2-3 errors. Timeline was in the order that the rocks were deposited, included the rock types but did not differentiate the amount of time for each layer. Factual history of planet described how the environments changed over time in the order that the rocks were deposited but may not have included the evidence used to identify the rock layers OR the environments of the rock layers contained errors. There are 1-2 errors in the capitalization of sentences AND/OR ending punctuation AND/OR spelling.
2
Assessment was printed out and turned in. Student scored at least 11 out of 15 on the test (73%). Student completed Identification of Rock Layers worksheet and there are 1 or less errors. Timeline was in the order that the rocks were deposited, included the rock types, and differentiated the amount of time for each layer. Factual history of planet (1) described how the environments changed over time in the order that the rocks were deposited AND (2) included the evidence used to identify the rock layers. (3) The environments are accurate to the type of each rock. All sentences are capitalized and have ending punctuations. There are NO spelling errors.
Timeline
Factual History of Planet
Factual History of Planet: Spelling and Grammar
Total Score: ____________ out of 10 points Extra Credit Points Possible: Total Rubric Score 10 9-7 6-4 3-0 Extra Credit Points
(added to Final MP 4 Average)
3 2 1 0
Rock Cycle WebQuest Guide Go to http://www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/index.html. Read and answer the following questions (or fill in the blanks). Be sure to watch all animations. There is a TEST at the end of the WebQuest (you MUST score at least 11 out of 15 points to pass). Type of Rocks Rock characteristics include: crystals, ribbon-like layers, glassy surface, gas bubbles, sand or pebbles, and fossils. 1. What are some characteristics of sedimentary rocks?
2. What are some characteristics of metamorphic rocks?
3. What are some characteristics of igneous rocks?
4. Name 2 examples of each type of rock (names of rocks in your collection): Sedimentary: ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________
Metamorphic: ______________________ Igneous: ______________________
WebQuest Guide continued How Rocks Change 5. Heat and pressure result in this kind of rock ____________________________. 6. Melting of rocks forms (the stuff in the Mantle of the Earth) _____________________. 7. Rocks melt at what temperature range? __________________________________ 8. When a volcano erupts, magma comes out and hardens is an example of this process: _______________________. 9. The slow cooling of magma under the Earths surface forms (intrusive or extrusive) igneous rocks? _______________________ 10. Weathering and erosion breaks and moves pieces of rocks called _________________. 11. Compaction and cementation result in this kind of rock _________________________.
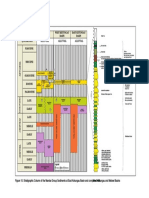
Core Sample from New Planet
Observations/Evidence
Layer 1: Layer is tan in color. Surface of rock is
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1
gritty and individual sand grains are visible.
Layer 2: Layer is dark grey/black in color. Surface
is smooth and composed of clay and silt particles. Imprints of fern leaves are visible.
Layer 3: Layer is orange/red in color. Surface of
rock is gritty and individual sand grains are visible. Sand grains are uniformly small and well rounded. Fossils of reptile or insect tracks are noted.
Layer 4:
Layers smooth surface is shiny, like
glass, and black in color.
Layer 5: Layer is tan in color. Surface of rock is
gritty and individual sand grains are visible.
Layer 6: Layer is white in color and is made of
sand and clay. Imprints of fossilized shells are evident. Rock fizzes when in contact with HCL acid.
Layer 7: Layer contains wavy stripes of white and
black color. Small, flat surfaces that are shiny or sparkly are evident.
Identification of Rock Layers
*Turn this Worksheet in* Core Sample from New Planet
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ____________________________ Period: _____________
Rock Type and Environment
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1
Layer 1: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
Layer 2: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
Layer 3: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
Layer 4: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
Layer 5: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
Layer 6: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
Layer 6: Type of Rock is ____________________ Environment:
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Orogenic Gold Review: By: Ghaneswari Yugamaris Muhammad Arba Azzaman Ni'matul Azizah Raharjanti Sam ReachDocument17 pagesOrogenic Gold Review: By: Ghaneswari Yugamaris Muhammad Arba Azzaman Ni'matul Azizah Raharjanti Sam ReachArba AzzamanNo ratings yet
- Pyroxenes 5Document27 pagesPyroxenes 5AkshiNo ratings yet
- O Vulcanismo Serra Geral em Torres, Rio Grande Do Sul, Brasil: Empilhamento Estratigráfico Local e Feições de Interação Vulcano-SedimentarDocument1 pageO Vulcanismo Serra Geral em Torres, Rio Grande Do Sul, Brasil: Empilhamento Estratigráfico Local e Feições de Interação Vulcano-SedimentarlixhellNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sedimentology Fonnesu Et Al PDFDocument40 pages2017 Sedimentology Fonnesu Et Al PDFDenny Anugerah SaputraNo ratings yet
- Brechas EpitermalesDocument61 pagesBrechas EpitermalesLuis Llanllaya100% (1)
- Banded Iron Formations BIFDocument2 pagesBanded Iron Formations BIFAlexandru StefanNo ratings yet
- A Palaeoproterozoic Dolomite (Vempalle Formation, Cuddapah Basin, India) Showing Phanerozoic-Type DolomitisationDocument50 pagesA Palaeoproterozoic Dolomite (Vempalle Formation, Cuddapah Basin, India) Showing Phanerozoic-Type DolomitisationFARHA NAAZNo ratings yet
- Kaolin Brochure Precious Stone RangeDocument179 pagesKaolin Brochure Precious Stone Rangekmae dizonNo ratings yet
- Vanadium DepositsDocument10 pagesVanadium DepositsAnonymous bcHKSCr100% (1)
- Rock Mechanics & Tunnel EngineeringDocument35 pagesRock Mechanics & Tunnel EngineeringAbdul Ahad Ghifar EnteNo ratings yet
- 9 - CNI Month End Nachingwea Report September 2011 - FinalDocument11 pages9 - CNI Month End Nachingwea Report September 2011 - FinalRozalia PengoNo ratings yet
- SutartoDocument7 pagesSutartoDevi LestianingrumNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Rocks)Document8 pagesModule 2 (Rocks)JamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- GN Api RajabasaDocument15 pagesGN Api RajabasaAlmiftahurrizqiNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answers: © Teaching Siriusly 2018Document8 pagesThe Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answers: © Teaching Siriusly 2018HelenNo ratings yet
- Resource Geology Review SheetDocument33 pagesResource Geology Review SheetKelvin FajardoNo ratings yet
- 160 Million Years Old Plant Fossils Has Been Discovered in The Honduras 'Central America.Document6 pages160 Million Years Old Plant Fossils Has Been Discovered in The Honduras 'Central America.g.ponmudiNo ratings yet
- Depositional Environment and Gross Lithologies InterpretationDocument120 pagesDepositional Environment and Gross Lithologies Interpretationwahyutrisutrisno91No ratings yet
- Ree Note - For Gsi PortalDocument3 pagesRee Note - For Gsi PortalPrashantDhoteNo ratings yet
- AGE Melawi Basin West Ketungau Basin East Ketungau Basin Quaternary Alluvial Alluvial Alluvial PlioceneDocument1 pageAGE Melawi Basin West Ketungau Basin East Ketungau Basin Quaternary Alluvial Alluvial Alluvial PlioceneMuhammad AbianNo ratings yet
- Pat Soil Final Lab 1Document11 pagesPat Soil Final Lab 1Patrick Anthony Calica JeminezNo ratings yet
- Geology ReportDocument14 pagesGeology ReportBernard GichiaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Week 4 DLLDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Week 4 DLLReyes CzarinaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5-Soil, Sedimentary Rocks, Structures, and Environments Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab 5-Soil, Sedimentary Rocks, Structures, and Environments Lab ReportGil GameshNo ratings yet
- Salt RangeDocument35 pagesSalt RangeMuhammad Waqas89% (18)
- Topic 11 Rocks Minerals NotesDocument51 pagesTopic 11 Rocks Minerals Notescrammy riveraNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Rock Characterization and Identification - LECTUREDocument1 pageMetamorphic Rock Characterization and Identification - LECTUREomeaveNo ratings yet
- Geology Hydrocarbon Habitat Southern Gulf of Seuz, EgyptDocument20 pagesGeology Hydrocarbon Habitat Southern Gulf of Seuz, EgyptRoy CoxNo ratings yet
- Carbonate Hand SamplesDocument7 pagesCarbonate Hand SamplescherNo ratings yet