Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transistors
Uploaded by
marina890416Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistors
Uploaded by
marina890416Copyright:
Available Formats
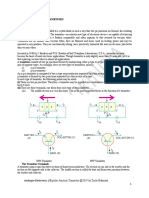
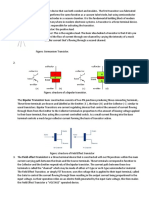
Bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
Main article: Bipolar junction transistor Bipolar transistors are so named because they conduct by using both majority and minority carriers. The bipolar junction transistor, the first type of transistor to be mass-produced, is a combination of two junction diodes, and is formed of either a thin layer of p-type semiconductor sandwiched between two n-type semiconductors (an npn transistor), or a thin layer of n-type semiconductor sandwiched between two p-type semiconductors (a pnp transistor). This construction produces two pn junctions: a baseemitter junction and a base collector junction, separated by a thin region of semiconductor known as the base region (two junction diodes wired together without sharing an intervening semiconducting region will not make a transistor). BJTs have three terminals, corresponding to the three layers of semiconductoran emitter, a base, and a collector. They are useful in amplifiers because the currents at the emitter and collector are controllable by a relatively small base current."[34] In an npn transistor operating in the active region, the emitterbase junction is forward biased (electrons and holes recombine at the junction), and electrons are injected into the base region. Because the base is narrow, most of these electrons will diffuse into the reverse-biased (electrons and holes are formed at, and move away from the junction) basecollector junction and be swept into the collector; perhaps one-hundredth of the electrons will recombine in the base, which is the dominant mechanism in the base current. By controlling the number of electrons that can leave the base, the number of electrons entering the collector can be controlled.[34] Collector current is approximately (common-emitter current gain) times the base current. It is typically greater than 100 for small-signal transistors but can be smaller in transistors designed for high-power applications. Unlike the field-effect transistor (see below), the BJT is a lowinput-impedance device. Also, as the baseemitter voltage (Vbe) is increased the baseemitter current and hence the collectoremitter current (Ice) increase exponentially according to the Shockley diode model and the Ebers-Moll model. Because of this exponential relationship, the BJT has a higher transconductance than the FET. Bipolar transistors can be made to conduct by exposure to light, because absorption of photons in the base region generates a photocurrent that acts as a base current; the collector current is approximately times the photocurrent. Devices designed for this purpose have a transparent window in the package and are called phototransistors.
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- BC547 TransistorDocument14 pagesBC547 TransistorErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerNo ratings yet
- IP 4 TransistorDocument3 pagesIP 4 TransistorRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- BE 3 UnitDocument19 pagesBE 3 Unit08sunnyjaganNo ratings yet
- NAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorDocument3 pagesNAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorChoiril AthoNo ratings yet
- Transistor: What Is A Transistor and How Does It WorkDocument7 pagesTransistor: What Is A Transistor and How Does It WorkmonalisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document78 pagesChapter 1-Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)junaid_usa2002No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor PDFDocument16 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor PDFVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 4 EEEDocument7 pagesModule 4 EEEchitraNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: Business Japanese Proficiency TestDocument24 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor: Business Japanese Proficiency TestVishal SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document78 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Dragana MladjenovicNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument4 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorHanun Fildzah MaheswariNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument27 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorShanti NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument15 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorpdekraaijNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document48 pagesChap 3belacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- EDCQNAUNITDocument16 pagesEDCQNAUNITashok94405251218258No ratings yet
- TRANSISTORDocument4 pagesTRANSISTORPappu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: Read A LetterDocument21 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor: Read A Letterivkreddy84381No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Module 1Document26 pagesElectronic Devices Module 1Nick WonkaNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument11 pagesBJTVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- Base (B) and Collector (C) .: Doped PNP NPN TransistorDocument1 pageBase (B) and Collector (C) .: Doped PNP NPN TransistorfatinamiraNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: BJT Redirects Here. For The Japanese Language Proficiency Test, SeeDocument11 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor: BJT Redirects Here. For The Japanese Language Proficiency Test, SeeGokulnath RaoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor - WikipediaDocument21 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor - WikipediaFABIAN NATANAEL MURRIETA RICONo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transistors and Their WorkingDocument22 pagesDifferent Types of Transistors and Their WorkingVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Transistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiDocument15 pagesTransistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiPRANGHI80% (10)
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Bab 3-bjtDocument80 pagesBab 3-bjtNoor Hanisah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Physics .Document33 pagesPhysics .Pappu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument14 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsIan MutugiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Bipolar Junction Transistor BJT JB STUDENTS PART 1Document68 pagesChapter 5-Bipolar Junction Transistor BJT JB STUDENTS PART 1eng4008No ratings yet
- Unit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument31 pagesUnit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorshivaniNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument44 pagesTransistorsramil.bocaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2Document30 pagesChapter - 2rkumaravelanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric CircuitDocument12 pagesFundamentals of Electric CircuitJun FermanoNo ratings yet
- 9 Transister PDFDocument17 pages9 Transister PDFpankaj jagadaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3AdsbymeNo ratings yet
- Bec (BJT Transistor)Document23 pagesBec (BJT Transistor)aditi pawarNo ratings yet
- BJT TransistorDocument10 pagesBJT TransistorShreepad Shivkar100% (1)
- Unit-Ii Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument39 pagesUnit-Ii Bipolar Junction Transistorpooja shutradharNo ratings yet
- STE Electronics10 Q2 Mod1 Lesson2-TRANSISTOR ANABELLE-BRONOLA v1Document12 pagesSTE Electronics10 Q2 Mod1 Lesson2-TRANSISTOR ANABELLE-BRONOLA v1April EspiñaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument33 pagesUntitledSahithi RNo ratings yet
- 3 0 bjt1Document32 pages3 0 bjt1nur_imani3112No ratings yet
- Lecture1 6Document21 pagesLecture1 6MjdNo ratings yet
- Ractice: Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument8 pagesRactice: Bipolar Junction TransistorFernando RuizNo ratings yet
- ECE 027 - Module 3 - Introduction of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Document58 pagesECE 027 - Module 3 - Introduction of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Miyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document8 pagesTransistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Fariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- TransisterDocument10 pagesTransisterart101988No ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Transistors As Amplifiers and SwitchesDocument22 pagesExperiment 6 Transistors As Amplifiers and SwitchesnormangNo ratings yet
- Transistors TutorialDocument92 pagesTransistors TutorialAmit Raj100% (18)
- Transistor Operating Conditions:: AnswerDocument7 pagesTransistor Operating Conditions:: Answersara khanNo ratings yet
- BJT SummaryDocument4 pagesBJT SummaryPatricia Rossellinni GuintoNo ratings yet
- Assessment 6 - ROBILLOSDocument2 pagesAssessment 6 - ROBILLOSRobillos, Alessandra Benedict S.No ratings yet
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- The Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesThe Bipolar TransistorMohammed MushfiqurNo ratings yet
- LM II TransistorDocument53 pagesLM II TransistorMa. Fe TabbuNo ratings yet
- B.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2022) SolutionsDocument18 pagesB.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2022) SolutionsShubham KeshriNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Thermodynamics Is A Branch of Physics Concerned With Heat and TemperatureDocument1 pageThermodynamics Is A Branch of Physics Concerned With Heat and Temperaturemarina890416No ratings yet
- XCVCCVCDocument1 pageXCVCCVCmarina890416No ratings yet
- This Article Is About Vehicles Powered by Rocket EnginesDocument2 pagesThis Article Is About Vehicles Powered by Rocket Enginesmarina890416No ratings yet
- A Categorization of These Constitutive Relations Allows Further Categorization ofDocument1 pageA Categorization of These Constitutive Relations Allows Further Categorization ofmarina890416No ratings yet
- On-Off Control: Bang-Bang Control Thermostat Negative FeedbackDocument1 pageOn-Off Control: Bang-Bang Control Thermostat Negative Feedbackmarina890416No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractmarina890416No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Joseph Black Carnot Napoleonic Wars Lord KelvinDocument1 pagePhysical Chemistry Chemical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Joseph Black Carnot Napoleonic Wars Lord Kelvinmarina890416No ratings yet
- MK 1Document1 pageMK 1marina890416No ratings yet
- Test Bank Ch.1Document4 pagesTest Bank Ch.1marina890416No ratings yet
- The Objective of This Report Is To Characterise A Plate With A Hole When It Is Subjected Under TensionDocument10 pagesThe Objective of This Report Is To Characterise A Plate With A Hole When It Is Subjected Under Tensionmarina890416No ratings yet
- GooddDocument1 pageGooddmarina890416No ratings yet
- Zeroth Law ofDocument1 pageZeroth Law ofmarina890416No ratings yet
- Vacuum Pump Shaft-Study 1-4Document11 pagesVacuum Pump Shaft-Study 1-4marina890416No ratings yet
- TigerDocument1 pageTigermarina890416No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is A Branch of Physics Concerned With Heat and TemperatureDocument1 pageThermodynamics Is A Branch of Physics Concerned With Heat and Temperaturemarina890416No ratings yet
- Finate ElementDocument6 pagesFinate Elementmarina890416No ratings yet
- Laws of ExponentsDocument2 pagesLaws of Exponentsmarina890416No ratings yet
- Space VelocityDocument1 pageSpace Velocitymarina890416No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument1 pageNewton's Laws of Motionmarina890416No ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageLaws of ThermodynamicsAndrey_gpNo ratings yet
- HohoDocument1 pageHohomarina890416No ratings yet
- Rigid-Body Dynamics Studies The Movement of Systems of Interconnected Bodies Under The ActionDocument1 pageRigid-Body Dynamics Studies The Movement of Systems of Interconnected Bodies Under The Actionmarina890416No ratings yet
- HohoDocument1 pageHohomarina890416No ratings yet
- PrincipleDocument1 pagePrinciplemarina890416No ratings yet
- Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesZeroth Law of Thermodynamicsmarina890416No ratings yet
- 2010 FSAE Front Bulkhead SupportDocument6 pages2010 FSAE Front Bulkhead Supportmarina890416No ratings yet
- Conceptual UnderstandingDocument4 pagesConceptual Understandingmarina890416No ratings yet
- Principles: Dynamics Is ADocument1 pagePrinciples: Dynamics Is Amarina890416No ratings yet
- Force and Torque Multiplication: Examples Two Hydraulic Cylinders InterconnectedDocument1 pageForce and Torque Multiplication: Examples Two Hydraulic Cylinders Interconnectedmarina890416No ratings yet
- 2009-10 Racing NewsDocument2 pages2009-10 Racing Newsmarina890416No ratings yet
- Touch SensorDocument17 pagesTouch SensorSanjana RathoreNo ratings yet
- Motors PDFDocument6 pagesMotors PDFMark Anthony Sabio LuceroNo ratings yet
- Drawing Lecture 1Document28 pagesDrawing Lecture 1Real NazihNo ratings yet
- Panel SpecificationDocument2 pagesPanel SpecificationsrkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers and Java: Walter Savitch Frank M. CarranoDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Computers and Java: Walter Savitch Frank M. CarranoBrandon KozakNo ratings yet
- UM1709 User Manual: STM32Cube Ethernet IAP ExampleDocument22 pagesUM1709 User Manual: STM32Cube Ethernet IAP ExampleTameClaudioNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Assistant System Engineer and Analyst SyllabusDocument10 pagesTNPSC Assistant System Engineer and Analyst SyllabussoundaryaNo ratings yet
- Citroen C4 B7 Edition BrochureDocument4 pagesCitroen C4 B7 Edition BrochureJéferson BischoffNo ratings yet
- Error Code Manual For ECORAY Generator XR7Document16 pagesError Code Manual For ECORAY Generator XR7Tekniah GlobalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1iris33% (3)
- BMI Kenya Telecommunications Report Q4 2014 - 04115036Document97 pagesBMI Kenya Telecommunications Report Q4 2014 - 04115036eugene123No ratings yet
- Cisco: Basic Switch and VLAN Configuration Guide With ExamplesDocument17 pagesCisco: Basic Switch and VLAN Configuration Guide With Examplessmuscat72No ratings yet
- Reactions of Metal ComplexesDocument25 pagesReactions of Metal ComplexesNuansak3No ratings yet
- 9500 MPR Product DescriptionDocument79 pages9500 MPR Product DescriptionRoger Juan Gomez Ramirez100% (1)
- Cebek TL 50 User ManualDocument4 pagesCebek TL 50 User Manualulton1237624No ratings yet
- T2800 Tacx Spare-Parts NEO-Smart 0217Document1 pageT2800 Tacx Spare-Parts NEO-Smart 0217Valentin BeatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: An Organization Study at Future Group CoDocument47 pagesChapter-1: An Organization Study at Future Group Cochethan kumar.sNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Mock Exam Topics 1 To 5, 9, 10Document6 pagesCIE IGCSE Mock Exam Topics 1 To 5, 9, 10Jenkins CK TsangNo ratings yet
- Sr. Solutions ArchitectDocument3 pagesSr. Solutions ArchitectAshok DwivediNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Converter For PH and Redox (ORP) Model PH402GDocument8 pagesGeneral Specifications: Converter For PH and Redox (ORP) Model PH402GHolicsNo ratings yet
- Bigfoot Brochure 15Document21 pagesBigfoot Brochure 15Muhammad Umar RiazNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Switched Reluctance Motor-LibreDocument9 pagesSpeed Control of Switched Reluctance Motor-LibreIndrajithSrNo ratings yet
- Modio AT Commands Set: Efficient PC CommunicationDocument36 pagesModio AT Commands Set: Efficient PC CommunicationmanejaisNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper For Industrial Automation and ControlDocument3 pagesSample Paper For Industrial Automation and ControlMatthew SibandaNo ratings yet
- Sico Service Catalogue CompressedDocument11 pagesSico Service Catalogue CompressedassurendranNo ratings yet
- Gpu Yamaha Edl20000te, Edl26000te - q9c 28197 E0Document38 pagesGpu Yamaha Edl20000te, Edl26000te - q9c 28197 E0Moni Gote del Ortus100% (1)
- License Control Item Lists (RAN15.0 - 01)Document42 pagesLicense Control Item Lists (RAN15.0 - 01)Firmansyah HermanaNo ratings yet
- Microwave ODUDocument5 pagesMicrowave ODUImranRafiqNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Electric PURY-P YLM-A1 PURY-EP YLM A Service Manual EngDocument434 pagesMitsubishi Electric PURY-P YLM-A1 PURY-EP YLM A Service Manual Engsantiago quinterosNo ratings yet
- 022501-164L - GeoXT 3000 Series - DS - 0712 - MGIS - HR - NCDocument2 pages022501-164L - GeoXT 3000 Series - DS - 0712 - MGIS - HR - NCArief Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet