Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Biology Form 4
Uploaded by
Hazwani KhairuzaimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4 Biology Form 4
Uploaded by
Hazwani KhairuzaimCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chemical Composition of the Cell
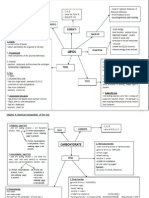
Concept Map 4.1 Chemical Composition of the Cell
1
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Concept Map
Chemical Composition of the Cells
Chemical compounds Inorganic compounds Carbohydrates Organic compounds Lipids Nucleic acids
Elements
Proteins Enzymes
2
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
Organic Compounds (contain carbon)
Living organisms
Inorganic Compounds (do not contain carbon)
Non-living organisms
� Lipids � Carbohydrates � Proteins � Vitamins � Nucleic acids
TRG Biology Form 4
� Water � Carbohydrates � Acids � Bases � Mineral salts
3
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
in the Chemical Compounds
compounds
� Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulphur � Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen � Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen � Hydrogen, oxygen � Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphorus, nitrogen
TRG Biology Form 4
� Proteins
� Carbohydrates � Lipids � Water � Nucleic acids
4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
of mineral ions (Elements)
compounds � Act as a cofactor for some enzymes � Mg2+ is required for the synthesis of chlorophyll � Formation of strong bones and teeth � Regulates osmotic pressure in cells � To maintain pH in the stomach � Helps in the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contractions
5
� Mg2+
� Ca2+ � Na2+ � CI � K+
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
of mineral ions
compounds � Synthesis of red blood cells � Synthesis of chlorophyll
� Fe2+
� NO 3 � SO4
2 3
� Components of macro molecules
� PO4
6
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
� Carbohydrates
� Primary source of energy � Starch is the main energy store of carbohydrates in plant cells � Glycogen is the main energy store of carbohydrates in animal tissues
� Proteins
� Build new cells and renew damaged tissues � Synthesis of enzymes, hormones, antibodies and haemoglobin � Synthesis of haemoglobin in red blood cells to transport oxygen � Structure: basic units are amino acids 7
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
� Lipids
� Fats and oil are important sources of energy � The layer of adipose tissue insulates the bodies of animals against cold temperatures � Solvent for vitamins A, D, E and K � Protect major organs of the body by lining with adipose tissue � Phospholipids are the main constituent of the plasma membrane � Forms complex molecule structure such as steroids � Wax prevents water loss in plants and infection by pathogens 8
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
� Nucleic acids
� Basic units are nucleotides, which store genetic information in codes � Two types of nucleic acids : � Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) � Ribonucleic acid (RNA) � DNA passes genetic information from one generation to another � Messenger RNA carries DNAs genetic code into the cytoplasm
9
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
H H O
Water molecule (two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom) 10
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of the Cell
Chapter 4.1
Chemical Composition of the Cell
Maintaining osmotic balance and turgidity Medium for biochemical reactions Lubricant Maintaining body temperature Solvent High surface tension and cohesion Support (structure of cells) Transport medium
TRG Biology Form 4
Copyright (c) Amazing Tunas Enterprise and its licensors. All rights reserved.
11
You might also like
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 4Document23 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 4Shephard Png80% (10)
- Enzymes: Biochemical Reactions Which Occur in Cells Are Called MetabolismDocument30 pagesEnzymes: Biochemical Reactions Which Occur in Cells Are Called MetabolismAZIANA YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition Oft He CellDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition Oft He CellAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Bio-Score Form 4 Chapter Answers SheetDocument23 pagesBio-Score Form 4 Chapter Answers SheetUmair Hisham100% (10)
- F4 Chapter 2&3 Essay QDocument4 pagesF4 Chapter 2&3 Essay QNoor Azlin JusohNo ratings yet
- General Biology: Transport Mechanism That Contributes To The Survival of The CellDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology: Transport Mechanism That Contributes To The Survival of The Cell할에이필No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneZue ZuerraNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Document14 pagesTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 50, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and DDocument7 pagesName: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 50, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and Dke2100% (2)
- Chemistry Form 4 Mid-Term ExamDocument7 pagesChemistry Form 4 Mid-Term ExamsanusiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 6Document50 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 6wenwen160499No ratings yet
- Form 4 Revision QuizDocument80 pagesForm 4 Revision QuizEnvira LeeNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 30, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and DDocument5 pagesName: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 30, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and Dke2No ratings yet
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Document12 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Firas Muhammad100% (2)
- Biology Form 4 RevisionDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 RevisionAyu YunusNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Chapter 2 (Exercise)Document11 pagesBiology F4 Chapter 2 (Exercise)Nadiah Murad60% (5)
- Chapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneRossliza Yaacob100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document9 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2klhuNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Introduction To BiologyDocument3 pagesExercise On Introduction To BiologyNorliyana Ali60% (5)
- Paper 1 Midyear Exam Biology Form 4 2010Document18 pagesPaper 1 Midyear Exam Biology Form 4 2010FidaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionDocument5 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionzaedmohdNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology NotesDocument32 pagesSPM Biology NotesAin Fza0% (1)
- Compilation of Experiments Form 4Document13 pagesCompilation of Experiments Form 4Marzila MohamedNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 6Document50 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 6Shephard Png91% (11)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid86% (22)
- SPM Biology 2006 k2Document15 pagesSPM Biology 2006 k2pss smk selandar100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneKeith ConneryNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseDocument3 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseAlan WangNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationDocument33 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationPau Siew LingNo ratings yet
- F4 SPM Biology Chapter 3 ObjectiveDocument7 pagesF4 SPM Biology Chapter 3 ObjectiveJanice NgNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 9Document32 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 9Shephard Png100% (14)
- Chemistry Quiz Chapter 5 Form 4 @Document4 pagesChemistry Quiz Chapter 5 Form 4 @Mohd NorihwanNo ratings yet
- Test Biology Form 4 Chapter 123Document4 pagesTest Biology Form 4 Chapter 123stanleyleeNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Test 1Document7 pagesForm 4 Biology Test 1Ventus TanNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 11Document7 pagesBiology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 11Nik HusnaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListDocument3 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListNursafika Bahira100% (1)
- Biologi Ting 4 Kertas 1 2013Document12 pagesBiologi Ting 4 Kertas 1 2013Nurwahidah ZolkifleeNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Document4 pagesSPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Felicia LingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biology Form 4: EnzymesDocument26 pagesChapter 4 Biology Form 4: EnzymesNurul Husna100% (1)
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Document22 pagesSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- Form 4 Chapter 3 EssayDocument8 pagesForm 4 Chapter 3 EssaykiongocNo ratings yet
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIINo ratings yet
- Topical Test 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Ujian Topikal 2: Struktur Sel Dan Organisasi SelDocument5 pagesTopical Test 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Ujian Topikal 2: Struktur Sel Dan Organisasi Selliyanaharuddin100% (1)
- Bio SPM 2003 P1Document13 pagesBio SPM 2003 P1SeanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 4Document65 pagesBIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 4Shephard Png88% (8)
- SPM Biology Nutrition Notes Cover Carbs, Proteins, FatsDocument12 pagesSPM Biology Nutrition Notes Cover Carbs, Proteins, FatsArthur IsaacNo ratings yet
- Biology Folio Form 4Document14 pagesBiology Folio Form 4adfizat100% (4)
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 2Document18 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 2Shephard Png100% (9)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1-10Document16 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1-10Nur Atiah Daud57% (7)
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 7Document32 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 7Shephard Png85% (13)
- Exercise Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument7 pagesExercise Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationNora Mn50% (2)
- What Organic Chemicals Are Important To LifeDocument5 pagesWhat Organic Chemicals Are Important To Liferocz dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4hmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of The CellDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition of The CellAeda NurynnaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 English AkuakulturDocument2 pagesTugas 2 English AkuakulturAndi AlbabNo ratings yet
- 2783 Ais - Database.model - file.PertemuanFileContent James Ralph Hanson Natural Products The Secondary Metabolites (Tutorial Chemistry Texts) 2003Document149 pages2783 Ais - Database.model - file.PertemuanFileContent James Ralph Hanson Natural Products The Secondary Metabolites (Tutorial Chemistry Texts) 2003Dyah Indah Rini100% (4)
- BT101 Complete Unit-I Part 2Document36 pagesBT101 Complete Unit-I Part 2srinivasu chintaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 4Document27 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 4Lee KaiYangNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes Part 2Document28 pagesZoology Notes Part 2Rochenick MagoNo ratings yet
- Marites PPT Demo Final....Document52 pagesMarites PPT Demo Final....Marites B. MartinNo ratings yet
- Kertas Model PT3 PDFDocument16 pagesKertas Model PT3 PDFAnonymous hSFsADEFK0% (1)
- Kertas Model PT3 PDFDocument16 pagesKertas Model PT3 PDFAnonymous hSFsADEFK0% (1)
- Endangered Ecosystem Biology Form 4Document18 pagesEndangered Ecosystem Biology Form 4Hazwani Khairuzaim100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To BiologyDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To BiologyHazwani Khairuzaim0% (1)
- Percubaan PMR 2011 Sains Kertas 2 PerakDocument19 pagesPercubaan PMR 2011 Sains Kertas 2 PerakHazwani KhairuzaimNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Coloring Worksheet - Name Organelles & Compare to Animal CellsDocument1 pagePlant Cell Coloring Worksheet - Name Organelles & Compare to Animal CellsHazwani KhairuzaimNo ratings yet
- Percubaan PMR 2011 Sains Kertas 2 PerakDocument19 pagesPercubaan PMR 2011 Sains Kertas 2 PerakHazwani KhairuzaimNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Paper PlateDocument2 pagesMitosis Paper PlateHazwani Khairuzaim0% (1)
- Science Form 1Document13 pagesScience Form 1Aziah Husain67% (3)
- 2008 Annual Debt StatementDocument12 pages2008 Annual Debt StatementEwing Township, NJNo ratings yet
- Welder Training in SMAW, GTAW & GMAW Welding Engineering & NDT Consultancy Welding Engineering Related TrainingDocument4 pagesWelder Training in SMAW, GTAW & GMAW Welding Engineering & NDT Consultancy Welding Engineering Related TrainingKavin PrakashNo ratings yet
- Butterfly Valve ConcentricDocument6 pagesButterfly Valve ConcentricpramodtryNo ratings yet
- TPB - Questionnaire Sample PDFDocument10 pagesTPB - Questionnaire Sample PDFhaneena kadeejaNo ratings yet
- List of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Document2 pagesList of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Aejaz MujawarNo ratings yet
- HVAC Report FINALDocument65 pagesHVAC Report FINALIanNo ratings yet
- Ate-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3Document13 pagesAte-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3MANJU R BNo ratings yet
- Brake System Troubleshooting GuideDocument98 pagesBrake System Troubleshooting Guideruben7mojicaNo ratings yet
- Electrical ManualDocument145 pagesElectrical ManualAbhishek KushwahaNo ratings yet
- t-47 Residential Real Property Affidavit - 50108 ts95421Document1 paget-47 Residential Real Property Affidavit - 50108 ts95421api-209878362No ratings yet
- O-Rings & SealsDocument10 pagesO-Rings & SealsPartsGopher.comNo ratings yet
- Effects of Climate Change and Global WarmingDocument14 pagesEffects of Climate Change and Global WarmingSwetal SosaNo ratings yet
- Vishal Seminar Report StrokeDocument40 pagesVishal Seminar Report StrokeVishal kaushikNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ResinDocument8 pagesJurnal ResinRizky Febrian SatrianiNo ratings yet
- Chad Yakobson ThesisDocument5 pagesChad Yakobson Thesiscrystaltorresworcester100% (2)
- Menu Selector - Hyatt Regency LucknowDocument11 pagesMenu Selector - Hyatt Regency LucknowShoubhik SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan The Food: TH THDocument8 pagesLesson Plan The Food: TH THFeraru FlorinNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Document168 pages2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Senam DzakpasuNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: in Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in Entrepreneurship 2 Semester, S.Y. 2019-2020Document48 pagesBusiness Plan: in Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in Entrepreneurship 2 Semester, S.Y. 2019-2020John Guden100% (1)
- B25 Pompe de Peinture PDFDocument98 pagesB25 Pompe de Peinture PDFchahineNo ratings yet
- Teardrop by Lauren KateDocument47 pagesTeardrop by Lauren KateRandom House Teens88% (16)
- Test Bank For Leadership and Management in Nursing 4th Edition Mary Ellen Grohar MurrayDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Leadership and Management in Nursing 4th Edition Mary Ellen Grohar Murraywitchingmazybs7k7100% (39)
- CX-5 BX-10 No. 1 & 1.5 Fluid Cylinder PartsDocument5 pagesCX-5 BX-10 No. 1 & 1.5 Fluid Cylinder PartsPierreNo ratings yet
- Trilead bis(carbonate) dihydroxide identified as SVHC due to reproductive toxicityDocument7 pagesTrilead bis(carbonate) dihydroxide identified as SVHC due to reproductive toxicityCekinNo ratings yet
- Genie Z45.25 J Internal Combustion - Service Manual - Part No. 219418Document331 pagesGenie Z45.25 J Internal Combustion - Service Manual - Part No. 219418marciogianottiNo ratings yet
- Here's Your Water Bill: LitresDocument4 pagesHere's Your Water Bill: Litrestvnm2ymmkdNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh National Building Code 2012 Part 07 - Construction Practices and SafetyDocument83 pagesBangladesh National Building Code 2012 Part 07 - Construction Practices and SafetyPranoy Barua100% (3)
- Ravi ProjectDocument92 pagesRavi ProjectAvinash Avii100% (1)
- PC 4. Emulsiones Tipo MayonesasDocument10 pagesPC 4. Emulsiones Tipo MayonesasmadarahuchihaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Psychopathological Aspects of Ehlers DanlosDocument5 pagesCognitive and Psychopathological Aspects of Ehlers DanlosKarel GuevaraNo ratings yet