Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITIL Service Operation in Policy
Uploaded by
ilayavplOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ITIL Service Operation in Policy
Uploaded by
ilayavplCopyright:
Available Formats
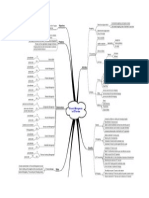
ITIL Information Technology Infrastructure Library An Introduction to IT Service Operation What is ITIL
ITIL is not a standard, it is guidance on IT best practices. Co-Operative Systems uses ITIL principles and practices to deliver quality managed IT services. It is a lifecycle model for continuous improvement - Vendor neutral, none prescriptive, adopts best practices. ITIL defines the following The Purpose of Service Operation? : To Maintain Business satisfaction and confidence in IT, Minimise service outages and their impact, & Provide IT service appropriately. The Scope of Service Operation? : What Services are to be provided, what Processes will be followed, what Technology is used, what People aspects are there? The Resulting Value to the Business? - Reduction in unplanned costs, Reduction in duration and frequency of outages, Provide data on performance, Meet security needs, Provide access to Services, Facilitate automation of routine work Context There is an ITIL for each context: Service Strategy understanding organisational objectives & customer needs , with service management as an asset Service Design turns service strategy into a plan for delivering objectives Service Transition how an organisation will move from one set up to another Service Operation best practices for managing services, even in a fluid set up (this document) Continual Service Improvement best practices on achieving incremental improvement
Service Management & Operation as Practice
Key concepts and definitionsService: A means of delivering value to the customer by facilitating outcomes for them without them owning risks and costs IT Service - A combination of IT , people and processes , to support customer business processes to a service level target. In addition Supporting IT Services are used by the IT provider to deliver customer facing services. Outcome - The result of carrying out an activity Service Management : Customers want set outcomes at appropriate levels of cost/price/reliability , these expectations shift over time . Customers want IT services to behave like utilities such as water or power. The IT provider transforms capabilities and resources into valuable services in the way that hotels, airlines and banks do IT Service Management: The IT organisation acts as a service provider to deliver the service outcomes customers need. A Service Level Agreement (SLA) describes the service to be provided , the targets to be met and the responsibilities of service provider and customer.
Service providers maybe be internal to the business unit or external usual providing services to many customers. Stakeholders in Service Management Customers those who buy services, these may be internal or external Users Those who use the service day to day Suppliers Deliverers of the service Utility and Warranty define Services Utility - What the service does Warranty Availability , capacity, reliability Best Practice Organisation should benchmark themselves against their peer, adopting best practices. ITIL is a widely recognised source of best practice guidance Concepts: Assets and Process Asset a resource (a direct input eg Finances, #people , infrastructure )capability (ability too coordinate, control or deploy eg management, knowledge processes, skills, experience) , These maybe Customers or Service providers assets Process - Transforms an input into an output, characteristics include - process customers, measurability, responsiveness to triggers Function - Organising for Service Management A group of people and tools that carry out process(es) - Service Desk user contact point, manages incidents and service requests - Technical Management manages IT infrastructure thru service lifecycle - IT Operations Management - carries out the daily operational activities needed to manage IT services and infrastructure - Application Management - managing applications through lifecycle (but not apps development) Roles A set of responsibilities, activities, authorities of a team or person. People may have several roles Service Portfolio Set of services managed by a service provider: Service pipeline services under consideration but not yet in operation Service catalogue- Live IT services, a list published to customers + any supporting services Retired services services no longer in use Governance and Management Systems -Consistent policies and rules for conducting business Governance -Ensures that strategy and policy are implemented, that procedures are followed. Achieved by defining roles and responsibilities and measuring outcomes. Management Systems -Provide standards and quality control & continuos improvement eg ISO9001 (plan, do, act check) The Service Lifecycle Service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation The organisation functions as a team, with different specialisations, maturing and becoming agile
Technology can be used to assist in automating the process itself Processes and functions may have roles across different elements of the lifecycle eg - Performance testing may be defined at transition but continue in operation Continual assessment and feedback drives forward service improvements
Service Operation Principles
Executing processes to optimise cost and quality of service Enabling business to meet objectives Executing control activities to manage services Delivering service within agreed SLA Effective functioning of components that support services Maintaining user satisfaction with services Achieving balance in service operations inevitable conflicts Internal focus vs. External focus eg- too much IF can lead to none affordable services, too much EF can lead to promises that can be met Stability vs. Responsiveness - too much stability can lead to rigidity at times of crises, too much Responsiveness leads to poor overall service levels Quality vs. Cost of Service - If these arent in balance you have a service people cant afford or a service that runs at a loss Reactive vs.Pro-active - being too reactive leads to poor service, being too pro-active pushes up costs
Service Operation Processes
Managing Events, Incidents, Problems, Requests, Access Event Management Managing events thru their lifecycle Being able to detect changes in states Being able to determine appropriate control actions Being able to able to measure outcome of event handling vs. SLA Scope may include Configuration Items (CI), Software Licensing (eg monitoring usage) , Environmental Conditions (eg Fire ) , Security (eg Intrusion detection), Normal Actvitiy (usage with safe parameters) Business Value -Event Managements value to the business is that Events are usally controlled before significant costs are incurred Principles Notifications only go to those responsible for actions, centralise the process, use common standards eg logging,. Classify events. Automate as much as possible Types of events (many) eg Informational eg Back up complete, Warning eg- Disk reaching out of space, Exceptional eg- Software not being used Key considerations Which CI & services should be monitored, what events should be logged, who should be told, what tools should be used , how will events be actioned <event management flow chart > Critical Success Factor (CSF) - eg capturing all events Key Performance indicators (KPI) - eg % of incidents resolved without impact on the business
Risks identifying risks - eg Adequate funds to capture appropriate events, avoiding being flooded with insignificant events -Incident Management The purpose of incident management is to restore normal service asap and minimise the adverse impact. Incidents may be reported by user or monitoring processes or be anticipatory eg unless action is taken now a problem will occur Incident management process : Standardised methods and procedures to ensure efficient incident handling and reporting Communicate incidents to other stakeholders with aim of actions to reduce likelihood of a further similar Enhance business perception of IT by professional handling of incidents Maintain user satisfaction with IT Effective incident management lowers the costs of outages both in overall downtime and by reducing the number of future incidents Principles : Incidents to be resolved within agreed time frames Customer satisfaction to be maintained Incidents to be recorded, prioritised and categorised, and incidents to be tracked over lifespan eg Open, In progress, Wait, Resolved, Closed It is possible to use template for standard incidents A separate procedure for priority1 incindents is required Key components should be monitored so that failures are detected early Incidents should receive initial diagnosis/triage immediately after logging Incident escalation processes should be in place functional and hierarchical Ownership of the incident remains with service desk at all times The service desk must keep all relevant parties up to date on the incident resolution progress Once a resolution has been put in place the solution should be tested The end user should evidence that they are satisfied eg by accepting closure email CSF are defined and KPIs measured Challenges and risks include logging all incidents, availability of information and solutions to resolve incidents, peaks in incident loads <incident process flow> <incident matching procedure >
-Request Fulfilment Provide info to users and customers on availability of services and the procedure to obtain them Maintain user and customer satisfaction through efficient and professional handling of service requests The resulting value is quick turn around and request actioning, leading to cost reductions
A request fulfilment process is defined for the business -Problem Management A Problem is the underlying cause of one or more incidents The objective of problem management is to: Prevent problems and resulting incidents happening Eliminate recurring incidents Minimise the impact of incidents that can not be prevented Problem management can be reactive (responding to a problem that has occurred) or better ProActive anticipating possible problems and removing/reduce ng the likelihood The resulting value is higher availability of services , higher productivity and reduced spend on fixes
A problem management process is defined for the business A Problem review should be carried out after major incidents what was done correctly/wrongly /what could be done better in future to prevent recurrence/any third party actions needed
-Access Management Providing users with the ability to access services (ie the execution of policies and actions defined in Information Security Management The objectives of Access Management are: Manage access to services based on agreed policies Efficiently respond to requests for service access/denial Oversee access to services to make sure access is appropriate -the resulting value is maintaining effective confidentiality, ensuring people have access to the resources they need, providing the ability to audit services usage, ensuring regulatory compliance eg SORP An Access management process is defined for the business
Organising for Service Operation
There is no single prescriptive best way to organise, and best practice needs to be tailored for in each situation taking into account needs of the business and customers plus constraints of resources Functions and Roles need to be defined, put into practice and managed :Service desk function - logging and resolving service incidents Technical management function providing staff with the appropriate skills and access to resources to do their jobs well IT operation function The execution and monitoring of operational activities and events in IT Infrastructure inc Backup/Restore, Print management, Internet management , Facilities management eg IT room Application management function - Developing, supporting, managing and enhancing the applications that support the business A RACI model can be used to define peoples roles and responsibilities R- Responsible A-Accountable (only 1 person should be accountable for each process) C-Consulted I -Informed A service owner is to be defined for each service to be delivered, plus service practioners to carry out the tasks within each role eg - Incident Process manager, 1st, 2nd and 3rd line Analysts, Request Fulfillment process manager & so on for each Service Operation Process that the business carries out
Implementing Service Operation
When making changes consideration needs to be made to continuing to provide service at least to existing level It is useful to use standard project management techniques to manage costs and resources when implementing new operations It is imperative to consider risks to maintaining stable operation eg problems caused by changes in work flows, effect on 3rd parties, Security risks Before going live it is useful to have walked through the service design and transition prior to going live, to ensure planned services will be fit for purpose Consideration needs to be made of the IT tools that will be used Apps+licences and infrastructure
Challenges Risks and Critical Success Factors
Challenges include Getting engagement, getting funding, appropriate service design, getting an appropriately skilled team Risks include Loss of momentum, loss of key staff, loss of funding, lack of management support, poor system design, management distrust Critical Success Factors these usually include Management Support, Staff Champions who are positive, training staff with a service management culture, Appropriate tools to assist in good service delivery, Result measurement
Key Messages and lessons
Success depends on getting the correct balance amongst the conflicting priorities of quality,costs, being reactive vs proactive, and differing views Staff need to be engaged with the processes for optimum outcomes Understanding the difference between events, incidents, service request and access requests etc so that they handled correctly but also how these items overlap Roles and responsibilities must be clearly defined and understood Operational goals must be clearly stated Services must be defined so that they are able to meet operational goals IT can not function in isolation without overall good governance within the organisation as a whole
For more information -see ITIL foundations on the web or ITIL handbook available online
Co-Operative Systems PA 2013
You might also like
- WI WP ITSM ImplemetationWhite PaperDocument9 pagesWI WP ITSM ImplemetationWhite PaperalexandruNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service DeliveryDocument1 pageITIL Service DeliverygringoricanNo ratings yet
- IT Service Management: OwnershipDocument22 pagesIT Service Management: OwnershipchandrukanthNo ratings yet
- Itil (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) - Systematic Approach To High QualityDocument32 pagesItil (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) - Systematic Approach To High QualityXtine Ramos100% (1)
- IT Service Continuity Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandIT Service Continuity Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- FIN Mindmap v4Document1 pageFIN Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Itil and The CMDBDocument5 pagesItil and The CMDBPaul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- It Services and ManagementDocument18 pagesIt Services and ManagementAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- CAP Mindmap v4Document1 pageCAP Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Incident Management Policy DraftDocument4 pagesIncident Management Policy DraftDerick Burton (Ben Sisco)No ratings yet
- Iso20000 2Document4 pagesIso20000 2Karloz PsyNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enDocument18 pagesChecklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enFeleke AfeworkNo ratings yet
- Service Catalogue TemplateDocument3 pagesService Catalogue TemplateJerod King100% (1)
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDocument17 pagesITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloNo ratings yet
- Capacity Management DeckDocument29 pagesCapacity Management DeckMelissa Miller100% (1)
- Sample Metrics For ITIL ProcessesDocument3 pagesSample Metrics For ITIL ProcessessantuchetuNo ratings yet
- Huit Major Incident Process v2.2Document17 pagesHuit Major Incident Process v2.2Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- It Service Management: Improvement Plan: BY Uday Mishra, Global It Service Operation ManagerDocument31 pagesIt Service Management: Improvement Plan: BY Uday Mishra, Global It Service Operation Managerrajesh.j162763No ratings yet
- AVM Mindmap v4Document1 pageAVM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Security Policy: PurposeDocument4 pagesCloud Computing Security Policy: PurposeSimone GiorgiNo ratings yet
- Service asset and configuration management Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandService asset and configuration management Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Foundation - Summary of Key PointsDocument16 pagesITIL V3 Foundation - Summary of Key Pointsst_marianoNo ratings yet
- BMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperDocument10 pagesBMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperRoss ManningNo ratings yet
- 03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue JourneyDocument28 pages03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue Journeyarsman1100% (1)
- PinkSCAN Change MGMTDocument8 pagesPinkSCAN Change MGMTMartin LeckNo ratings yet
- FNAL OLA TemplateDocument23 pagesFNAL OLA Templatehallarmemon0% (1)
- ITIL - Foundation NewDocument155 pagesITIL - Foundation NewAnonymous zWUrYoc2VNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Support and Service DeliveryDocument2 pagesITIL Service Support and Service DeliveryhyrtksnNo ratings yet
- ITIL+Service Operation 1203Document49 pagesITIL+Service Operation 1203Андрей ИвановNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Design MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Design MindmapIgor100% (3)
- ISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsDocument1 pageISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsAditya YerunkarNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapAllanNo ratings yet
- ITIL Problem Management ProcessDocument10 pagesITIL Problem Management ProcessSandhiyan RaviNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Catalogue TemplateDocument14 pagesTechnical Service Catalogue TemplateManav Patel100% (1)
- ITSM Assessment Artifacts-1Document1 pageITSM Assessment Artifacts-1Murali PvNo ratings yet
- Ola TemplateDocument8 pagesOla Templatetoto_falaNo ratings yet
- Service catalogue management Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandService catalogue management Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- Summary ITSMDocument24 pagesSummary ITSMAnonymous wovReoA100% (2)
- The CMDB As The Brain of ITDocument4 pagesThe CMDB As The Brain of ITmojo_92No ratings yet
- Major Incident ReportDocument5 pagesMajor Incident ReportKarthikeyan GurusamyNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps To Defining IT Services - A Hands On WorkbookDocument13 pages5 Steps To Defining IT Services - A Hands On WorkbookEdho ArmandoNo ratings yet
- ITIL ConceptDocument57 pagesITIL Conceptsumanpk133100% (1)
- Introduction To ITIL V3Document62 pagesIntroduction To ITIL V3asheeshNo ratings yet
- Incident Management for Procurement A Clear and Concise ReferenceFrom EverandIncident Management for Procurement A Clear and Concise ReferenceNo ratings yet
- ITIL-Service StrategyDocument11 pagesITIL-Service StrategyTùng Phạm100% (1)
- An It Il RoadmapDocument19 pagesAn It Il RoadmapIslam WayNo ratings yet
- Iso - Iec 20000Document22 pagesIso - Iec 20000Vincenzo OstoniNo ratings yet
- Change Management Policies FinalDocument24 pagesChange Management Policies FinalBPG ServiceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To It Service Management: Slide 1Document10 pagesIntroduction To It Service Management: Slide 1Chandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Enterprise LAN Network ArchitectureDocument4 pagesEnterprise LAN Network ArchitectureilayavplNo ratings yet
- ITILV3 and Information Security White Paper May09Document40 pagesITILV3 and Information Security White Paper May09Fabiano Rodrigues Martins CostaNo ratings yet
- IT Security Audit PolicyDocument90 pagesIT Security Audit Policychiragi100% (2)
- Introduction To Tcp/IpDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Tcp/IpilayavplNo ratings yet
- RRM TestDocument5 pagesRRM TestismoilNo ratings yet
- 02 OSI ReferenceDocument57 pages02 OSI ReferenceilayavplNo ratings yet
- C IntroductionDocument22 pagesC IntroductionMonnappa B GaneshNo ratings yet
- C LanguageDocument39 pagesC LanguageilayavplNo ratings yet
- MPLS VPNPS MPLSVPN007 160508Document2 pagesMPLS VPNPS MPLSVPN007 160508ilayavplNo ratings yet
- ZXWM m900 DWDM EquipmentDocument11 pagesZXWM m900 DWDM EquipmentilayavplNo ratings yet
- Fh84fr6ht GBR EngDocument6 pagesFh84fr6ht GBR EngEsmir ŠkreboNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Operations of PolynomialsDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Operations of Polynomialsapi-287816312No ratings yet
- Beer Lambert'S Law: Dr. Swastika Das Professor of ChemistryDocument19 pagesBeer Lambert'S Law: Dr. Swastika Das Professor of ChemistryShabanaNo ratings yet
- STRUNK V THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA Etal. NYND 16-cv-1496 (BKS / DJS) OSC WITH TRO Filed 12-15-2016 For 3 Judge Court Electoral College ChallengeDocument1,683 pagesSTRUNK V THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA Etal. NYND 16-cv-1496 (BKS / DJS) OSC WITH TRO Filed 12-15-2016 For 3 Judge Court Electoral College ChallengeChristopher Earl Strunk100% (1)
- Resolution: Owner/Operator, DocketedDocument4 pagesResolution: Owner/Operator, DocketedDonna Grace Guyo100% (1)
- EPSS 627: DescriptionDocument2 pagesEPSS 627: DescriptionudayakumartNo ratings yet
- Npad PGP2017-19Document3 pagesNpad PGP2017-19Nikhil BhattNo ratings yet
- SCC5-4000F Single ShaftDocument15 pagesSCC5-4000F Single ShaftudelmarkNo ratings yet
- Cash Budget Sharpe Corporation S Projected Sales First 8 Month oDocument1 pageCash Budget Sharpe Corporation S Projected Sales First 8 Month oAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Caddy Arc 251i Service ManualDocument52 pagesCaddy Arc 251i Service Manualrikycien100% (8)
- Wire Rope TesterDocument4 pagesWire Rope TesterclzagaNo ratings yet
- NIFT GAT Sample Test Paper 1Document13 pagesNIFT GAT Sample Test Paper 1goelNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Marketing PlanDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Marketing Planfvhacvjd100% (1)
- APRStt Implementation Notes PDFDocument36 pagesAPRStt Implementation Notes PDFCT2IWWNo ratings yet
- Corregidor Title DefenseDocument16 pagesCorregidor Title DefenseJaydee ColadillaNo ratings yet
- Game ApiDocument16 pagesGame ApiIsidora Núñez PavezNo ratings yet
- Caldon Lefm 240ci Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Integral Manifold DesignDocument6 pagesCaldon Lefm 240ci Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Integral Manifold DesignJim LimNo ratings yet
- D15 Hybrid P1 QPDocument6 pagesD15 Hybrid P1 QPShaameswary AnnadoraiNo ratings yet
- Alem Ketema Proposal NewDocument25 pagesAlem Ketema Proposal NewLeulNo ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument2 pagesGeography NotesMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Hansen Aise Im Ch12Document66 pagesHansen Aise Im Ch12Rizki19maretNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI PowerCube 500Document41 pagesHUAWEI PowerCube 500soumen95No ratings yet
- A Project Report On "A Comparative Study Between Hero Honda Splendor+ and Its Competitors To Increase The Market Share in MUDHOL RegionDocument70 pagesA Project Report On "A Comparative Study Between Hero Honda Splendor+ and Its Competitors To Increase The Market Share in MUDHOL RegionBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Gifted Black Females Attending Predominantly White Schools Compressed 1 CompressedDocument488 pagesGifted Black Females Attending Predominantly White Schools Compressed 1 Compressedapi-718408484No ratings yet
- Intergard 475HS - Part B - EVA046 - GBR - ENG PDFDocument10 pagesIntergard 475HS - Part B - EVA046 - GBR - ENG PDFMohamed NouzerNo ratings yet
- When I Was A ChildDocument2 pagesWhen I Was A Childapi-636173534No ratings yet
- 120 Câu Tìm Từ Đồng Nghĩa-Trái Nghĩa-Dap AnDocument9 pages120 Câu Tìm Từ Đồng Nghĩa-Trái Nghĩa-Dap AnAlex TranNo ratings yet
- POLYTHEOREMSDocument32 pagesPOLYTHEOREMSYen LeeNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Laboratory Products - Heraeus KulzerDocument288 pagesCatalogue Laboratory Products - Heraeus KulzerDentaDentNo ratings yet
- Retail Visibility Project of AircelDocument89 pagesRetail Visibility Project of Aircelabhishekkraj100% (1)