Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aqs2143 - Economics Self Notes
Uploaded by
hanihusainiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aqs2143 - Economics Self Notes
Uploaded by
hanihusainiCopyright:
Available Formats
TYPE OF COMPANIES 1. 2. 3. A company is a business organization. Liability refers to something like responsibility.
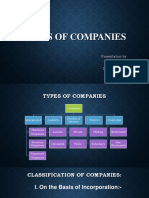
The Companies Act 1965 classifies companies based on: The liability of members The public status The relationship with other companies The place of incorporation Classification by the liability of members: Limited liability o Limited by shares o Limited by guarantee Unlimited company Private company Member limit is 50 Restrict right to transfer share Public company Does not necessarily a government company/body. People can have shares if the company is listed in the stock. Can seek listed status. Group refers to corporations/companies that are related (they have holding subsidiary relationship among themselves). Holding company is the main company Subsidiary company anak syarikat A company is deemed to be holding to a subsidiary company when: When it controls the composition of the board of directors. When it controls half of the voting power of the subsidiary. When it holds more than half of the issued capital. A foreign company is a company, corporation, society, association or other body incorporated outside Malaysia. A foreign company desiring to establish a place of business within Malaysia must become registered. There are three types of business firms namely proprietorship, partnership and corporation. Proprietorship Owned by an individual This individual possesses the ownership right to the firms profit. Is also personally liable for the firms debts. Partnership Unlimited company Owned by two or more individuals Possesses ownership right to the firms profit. Personally liable for the firms debts. Corporation Limited company Owned by shareholders Possesses ownership right to the firms profit. Liability is limited only to their amount of investment in the firm.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10. 11.
12.
13.
MONOPOLY (THEORY OF A FIRM MARKET STRUCTURE) 1. In monopoly, the firm is the industry. 2. They use the demand curve facing by the firm as the market demand curve. P {The usual demand curve is a reflection of monopolys demand curve.} D Q
3. Total quantity supplied in the market is what the firm decides to produce.
Total revenue
Units of output
4. An increase in output involves not just producing more and selling it, but also reducing the price of its output to sell it. 5. Its marginal revenue curve shows - the change in total revenue as a firm moves along the segment of the demand curve. 6. All firms practice increase output as long as marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost. 7. Marginal revenue (MR) minus marginal cost (MC) equals to marginal profit (if its positive). 8. Profit-maximising level of output for a monopolist is the one where MR=MC (intersection). 9. No supply curve in monopoly. They set price and quantity. 10. Amount of output supply depends on its marginal cost curve and its demand curve. 11. Price is determined based on the profit-max level curve and demand curve. 12. ATC price = Cost PML price = Revenue Profit = PML price ATC price
You might also like
- Joint Stock CompaniesDocument16 pagesJoint Stock CompaniesJoynul Abedin100% (8)
- Functions of Local Planning AuthorityDocument24 pagesFunctions of Local Planning Authorityhanihusaini50% (2)
- Estimating For Excavation WorksDocument27 pagesEstimating For Excavation Workshanihusaini100% (3)
- DraughtmanshipDocument39 pagesDraughtmanshiphanihusainiNo ratings yet
- Types of BusinessesDocument7 pagesTypes of BusinessesValiciaNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document25 pagesGroup 3Md Byzed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Company Law Types of CompanyDocument19 pagesCompany Law Types of CompanyAtulNo ratings yet
- Companies ActDocument129 pagesCompanies ActchangumanguNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes ReTypedDocument7 pagesRevision Notes ReTypedkvidiniotis99No ratings yet
- Classification of Companies (Part-Ii)Document16 pagesClassification of Companies (Part-Ii)Tania MajumderNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 3 Notes PDFDocument7 pagesEconomics Chapter 3 Notes PDFShAkeel AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Befa 1Document23 pagesBefa 121WH1A6634 NALLAMOTHU HIMA SRINo ratings yet
- LO3 Business Law (Organisations)Document7 pagesLO3 Business Law (Organisations)Pham Huyen MyNo ratings yet
- Joint Stock CompanyDocument40 pagesJoint Stock Companyarun447No ratings yet
- Joint Stock Company Gp1 by Professor & Lawyer Puttu Guru PrasadDocument32 pagesJoint Stock Company Gp1 by Professor & Lawyer Puttu Guru PrasadPUTTU GURU PRASAD SENGUNTHA MUDALIARNo ratings yet
- IEEDDocument6 pagesIEEDrupeshdahake8586No ratings yet
- 6.type and Basic Characterstics of Companies in Ethiopia Types of Business OrganizationsDocument14 pages6.type and Basic Characterstics of Companies in Ethiopia Types of Business OrganizationsTamene Tekile88% (8)
- ASSIGNMENT AnidaDocument14 pagesASSIGNMENT AnidaAnida BgdNo ratings yet
- Companies ActDocument47 pagesCompanies Actashmit.5217No ratings yet
- What Are The Types of Business Organization? Differentiate EachDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Types of Business Organization? Differentiate EachCarmelle BahadeNo ratings yet
- CHAP 6 - Raising Capital (Equity and Loans)Document13 pagesCHAP 6 - Raising Capital (Equity and Loans)aspiringwomandNo ratings yet
- Types of CompanyDocument3 pagesTypes of Companyshibashish PandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fin 2200Document7 pagesChapter 1 Fin 2200cheeseNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Economy Chapters 1-8Document48 pagesEnterprise Economy Chapters 1-8Martin Pelaez PerezNo ratings yet
- Corporate Accounting - NotesDocument52 pagesCorporate Accounting - NotesMalkeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document13 pagesAssignment 2ayesha iftikharNo ratings yet
- Legal EntitiesDocument3 pagesLegal Entitiesshaiknazma8639No ratings yet
- Be 313 - Week 4-5 - Unit Learning CDocument32 pagesBe 313 - Week 4-5 - Unit Learning Cmhel cabigonNo ratings yet
- BEHIND BIG BUSINESS (Reading)Document3 pagesBEHIND BIG BUSINESS (Reading)mario vega cartasNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OranizationsDocument6 pagesForms of Business Oranizationskremer.oscar2009No ratings yet
- Session 3-Chapter 5 - Starting A New BusinessDocument30 pagesSession 3-Chapter 5 - Starting A New BusinessLili GuloNo ratings yet
- BM1.2 DP0Document28 pagesBM1.2 DP0Elcan IbrahimliNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganizationDocument13 pagesForms of Business OrganizationPatricia PasilanNo ratings yet
- Accountant in Business: Types of OrganizationDocument24 pagesAccountant in Business: Types of OrganizationqmlcNo ratings yet
- ENTERPRISE, Forms of Business OwnershipDocument10 pagesENTERPRISE, Forms of Business OwnershipKristy JenacNo ratings yet
- Principles Tools ND TechniuesDocument3 pagesPrinciples Tools ND TechniuesMonica Bechayda RosalesNo ratings yet
- Joint Stock CompanyDocument10 pagesJoint Stock CompanyrohitNo ratings yet
- IB Business and Management Notes, SLDocument6 pagesIB Business and Management Notes, SLbush0234No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 2 AssignmentDocument7 pagesFinancial Accounting 2 AssignmentirmaNo ratings yet
- Classification of CompaniesDocument9 pagesClassification of CompaniesTania MajumderNo ratings yet
- HW PavithraKrishnamurthy Sub1BDocument2 pagesHW PavithraKrishnamurthy Sub1BArun VermaNo ratings yet
- Business OrganizationDocument60 pagesBusiness OrganizationbookwormdivaNo ratings yet
- Types of Companies Registered in SECPDocument4 pagesTypes of Companies Registered in SECPAXian TanveerNo ratings yet
- BL AssignmentDocument20 pagesBL AssignmentSheiryNo ratings yet
- Soc Sci 4A: Philippine Industrial EconomyDocument8 pagesSoc Sci 4A: Philippine Industrial EconomyCzarina Faye MolinaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business Studies RevisionDocument27 pagesIGCSE Business Studies Revisionvyaskush80% (5)
- Joint VentureDocument12 pagesJoint VentureAnzarNawazNo ratings yet
- Types of Companies - Classification and Different Kind of CompaniesDocument11 pagesTypes of Companies - Classification and Different Kind of CompaniesRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- BEHIND BIG BUSINESS (Reading)Document3 pagesBEHIND BIG BUSINESS (Reading)mario vega cartasNo ratings yet
- Quiz One Reviewer PDFDocument38 pagesQuiz One Reviewer PDFStephanie DizonNo ratings yet
- Joint Stock Companies 2Document12 pagesJoint Stock Companies 2Wamema joshuaNo ratings yet
- Types of CompaniesDocument3 pagesTypes of CompaniesHarshini AkilandanNo ratings yet
- Company Law - Assignment by Simon (BUBT)Document22 pagesCompany Law - Assignment by Simon (BUBT)Simon Haque67% (3)
- Joint Stock Company: Chapter - 4Document12 pagesJoint Stock Company: Chapter - 4Md. Sojib KhanNo ratings yet
- Business Organization & Financial Institutions PDFDocument8 pagesBusiness Organization & Financial Institutions PDFTAYYABA RAMZANNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Forms of CompaniesDocument12 pagesPresentation On Forms of CompaniesJappanJyot KalraNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is A Business OrganizationDocument18 pages1 What Is A Business Organizationpriyanka kulasooriyaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportKavindya DinaniNo ratings yet
- Befa Notes For Few TopicsDocument52 pagesBefa Notes For Few TopicsVangaveeti SnehaNo ratings yet
- FAR Chapter1 - FinalDocument14 pagesFAR Chapter1 - FinalDane Matthew PilapilNo ratings yet
- Types of Companies: Presentation by:-Rehaman.M MBA (Student)Document14 pagesTypes of Companies: Presentation by:-Rehaman.M MBA (Student)Sathyanaryanan RajappaNo ratings yet
- A Business Formation Deals With The Formalization And: Actual Implementation of Business Ideas Into PracticeDocument38 pagesA Business Formation Deals With The Formalization And: Actual Implementation of Business Ideas Into PracticeobishutolaniNo ratings yet
- Top Home-Based Business Ideas for 2020: 00 Proven Passive Income Ideas To Make Money with Your Home Based Business & Gain Financial FreedomFrom EverandTop Home-Based Business Ideas for 2020: 00 Proven Passive Income Ideas To Make Money with Your Home Based Business & Gain Financial FreedomNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law and Sustainable Development in Malaysia: DR Nor Asiah MohamadDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Law and Sustainable Development in Malaysia: DR Nor Asiah MohamadhanihusainiNo ratings yet
- Week13 Inputs DemandDocument29 pagesWeek13 Inputs DemandhanihusainiNo ratings yet
- AQS 1101 Understanding Working Drawing By: Prof. Dato' Ar. Dr. Asiah Abdul Rahim & Asst. Prof. Dr. Aliyah SanusiDocument2 pagesAQS 1101 Understanding Working Drawing By: Prof. Dato' Ar. Dr. Asiah Abdul Rahim & Asst. Prof. Dr. Aliyah SanusihanihusainiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Working DrawingDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Working DrawinghanihusainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 4Document76 pagesChapter 1 4Sean Suing100% (1)
- San Mateo Daily Journal 01-28-19 EditionDocument28 pagesSan Mateo Daily Journal 01-28-19 EditionSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi University: Priyadarshini Hills, Kottayam-686560Document136 pagesMahatma Gandhi University: Priyadarshini Hills, Kottayam-686560Rashmee DwivediNo ratings yet
- Dance Terms Common To Philippine Folk DancesDocument7 pagesDance Terms Common To Philippine Folk DancesSaeym SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Micro - Systemic Bacteriology Questions PDFDocument79 pagesMicro - Systemic Bacteriology Questions PDFShashipriya AgressNo ratings yet
- Jota - EtchDocument3 pagesJota - EtchRidwan BaharumNo ratings yet
- AAR Shell ProgrammingDocument13 pagesAAR Shell ProgrammingMarimuthu MuthaiyanNo ratings yet
- Controlador DanfossDocument2 pagesControlador Danfossfrank.marcondes2416No ratings yet
- Afzal ResumeDocument4 pagesAfzal ResumeASHIQ HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 2432 - Test Solutions - Tsol - 2432 - 21702Document5 pages2432 - Test Solutions - Tsol - 2432 - 21702Anmol PanchalNo ratings yet
- What Is Product Management?Document37 pagesWhat Is Product Management?Jeffrey De VeraNo ratings yet
- Slides - SARSDocument191 pagesSlides - SARSCedric PoolNo ratings yet
- Assignment-For-Final of-Supply-Chain - Management of Courses PSC 545 & 565 PDFDocument18 pagesAssignment-For-Final of-Supply-Chain - Management of Courses PSC 545 & 565 PDFRAKIB HOWLADERNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic-Progressions - MDDocument8 pagesArithmetic-Progressions - MDJay Jay GwizaNo ratings yet
- Check e Bae PDFDocument28 pagesCheck e Bae PDFjogoram219No ratings yet
- Dash 3000/4000 Patient Monitor: Service ManualDocument292 pagesDash 3000/4000 Patient Monitor: Service ManualYair CarreraNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Variability Threshold As An Alternative.25Document6 pagesHeart Rate Variability Threshold As An Alternative.25Wasly SilvaNo ratings yet
- D. Das and S. Doniach - Existence of A Bose Metal at T 0Document15 pagesD. Das and S. Doniach - Existence of A Bose Metal at T 0ImaxSWNo ratings yet
- JCIPDocument5 pagesJCIPdinesh.nayak.bbsrNo ratings yet
- USDA List of Active Licensees and RegistrantsDocument972 pagesUSDA List of Active Licensees and Registrantswamu885No ratings yet
- Strategic Capital Management: Group - 4 Jahnvi Jethanandini Shreyasi Halder Siddhartha Bayye Sweta SarojDocument5 pagesStrategic Capital Management: Group - 4 Jahnvi Jethanandini Shreyasi Halder Siddhartha Bayye Sweta SarojSwetaSarojNo ratings yet
- The Serious Student of HistoryDocument5 pagesThe Serious Student of HistoryCrisanto King CortezNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2karthik karti100% (1)
- University Fees Structure (Himalayan Garhwal University) - UttarakhandDocument1 pageUniversity Fees Structure (Himalayan Garhwal University) - UttarakhandabhaybaranwalNo ratings yet
- Marieb ch3dDocument20 pagesMarieb ch3dapi-229554503No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Plenipotentiary - 1Document6 pagesGuidelines For Plenipotentiary - 1Oladimeji Ibukun IjaodolaNo ratings yet
- 13507Document5 pages13507Abinash Kumar0% (1)
- Durability of Prestressed Concrete StructuresDocument12 pagesDurability of Prestressed Concrete StructuresMadura JobsNo ratings yet
- Stochastic ProcessesDocument264 pagesStochastic Processesmanosmill100% (1)
- SKF Shaft Alignment Tool TKSA 41Document2 pagesSKF Shaft Alignment Tool TKSA 41Dwiki RamadhaniNo ratings yet